42.5 Advanced Topics in Sensitivity Analysis
42.5.1 Sensitivity to Outliers and Influential Observations
Outliers can drive results, so it’s important to assess robustness to their inclusion:
# Identify influential observations
model = lm(mpg ~ wt + hp + qsec, data = mtcars)
# Calculate influence measures
influence_measures = influence.measures(model)
# Cook's Distance
cooks_d = cooks.distance(model)
influential = cooks_d > 4 / nrow(mtcars) # Common threshold
# DFBETAS (change in coefficient when observation removed)
dfbetas_vals = dfbetas(model)
# Compare models with/without influential observations
model_full = lm(mpg ~ wt + hp + qsec, data = mtcars)
model_no_influential = lm(
mpg ~ wt + hp + qsec,
data = mtcars[!influential, ]
)
# Compare coefficients
compare_df = data.frame(
Variable = names(coef(model_full)),
Full_Sample = coef(model_full),
Excl_Influential = c(
coef(model_no_influential),
rep(NA, length(coef(model_full)) - length(coef(model_no_influential)))
)
)
# Winsorization approach
library(DescTools)
mtcars_winsor = mtcars
mtcars_winsor$wt = DescTools::Winsorize(mtcars$wt, val = c(0.01, 0.99))
mtcars_winsor$hp = DescTools::Winsorize(mtcars$hp, val = c(0.01, 0.99))
model_winsor = lm(mpg ~ wt + hp + qsec, data = mtcars_winsor)
# Compare original vs. winsorized42.5.2 Sensitivity to Measurement Error
If key variables are measured with error, results may be biased:
# Simulate measurement error
# This helps understand potential attenuation bias
library(simex)
# SIMEX (Simulation-Extrapolation) for measurement error correction
# Assumes classical measurement error in covariates
# Fit model with x = TRUE
naive_model <- lm(mpg ~ wt + hp, data = mtcars, x = TRUE)
# Apply SIMEX
# lambda is the factor by which measurement error variance increases
simex_model <- simex(
naive_model,
SIMEXvariable = "wt", # Variable with measurement error
measurement.error = 0.1, # Assumed ME variance (proportion of var)
lambda = seq(0.1, 2, 0.1), # Extrapolation sequence
B = 100 # Number of simulations
)
# View results
summary(simex_model)
#> Call:
#> simex(model = naive_model, SIMEXvariable = "wt", measurement.error = 0.1,
#> lambda = seq(0.1, 2, 0.1), B = 100)
#>
#> Naive model:
#> lm(formula = mpg ~ wt + hp, data = mtcars, x = TRUE)
#>
#> Simex variable :
#> wt
#> Measurement error : 0.1
#>
#>
#> Number of iterations: 100
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> -3.931701 -1.603200 -0.225173 -0.007991 1.066691 5.806683
#>
#> Coefficients:
#>
#> Asymptotic variance:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 37.376807 1.987465 18.806 < 2e-16 ***
#> wt -3.974826 0.644667 -6.166 1.01e-06 ***
#> hp -0.030611 0.006577 -4.654 6.63e-05 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Jackknife variance:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 37.376807 1.583219 23.608 < 2e-16 ***
#> wt -3.974826 0.636895 -6.241 8.24e-07 ***
#> hp -0.030611 0.009077 -3.372 0.00213 **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
# Compare naive vs corrected coefficients
data.frame(
Coefficient = names(coef(naive_model)),
Naive = coef(naive_model),
SIMEX_Corrected = coef(simex_model)
)
#> Coefficient Naive SIMEX_Corrected
#> (Intercept) (Intercept) 37.22727012 37.37680699
#> wt wt -3.87783074 -3.97482594
#> hp hp -0.03177295 -0.03061053
# SIMEX extrapolates back to zero ME, giving corrected estimateFigure 42.11 plots SIMEX extrapolation.
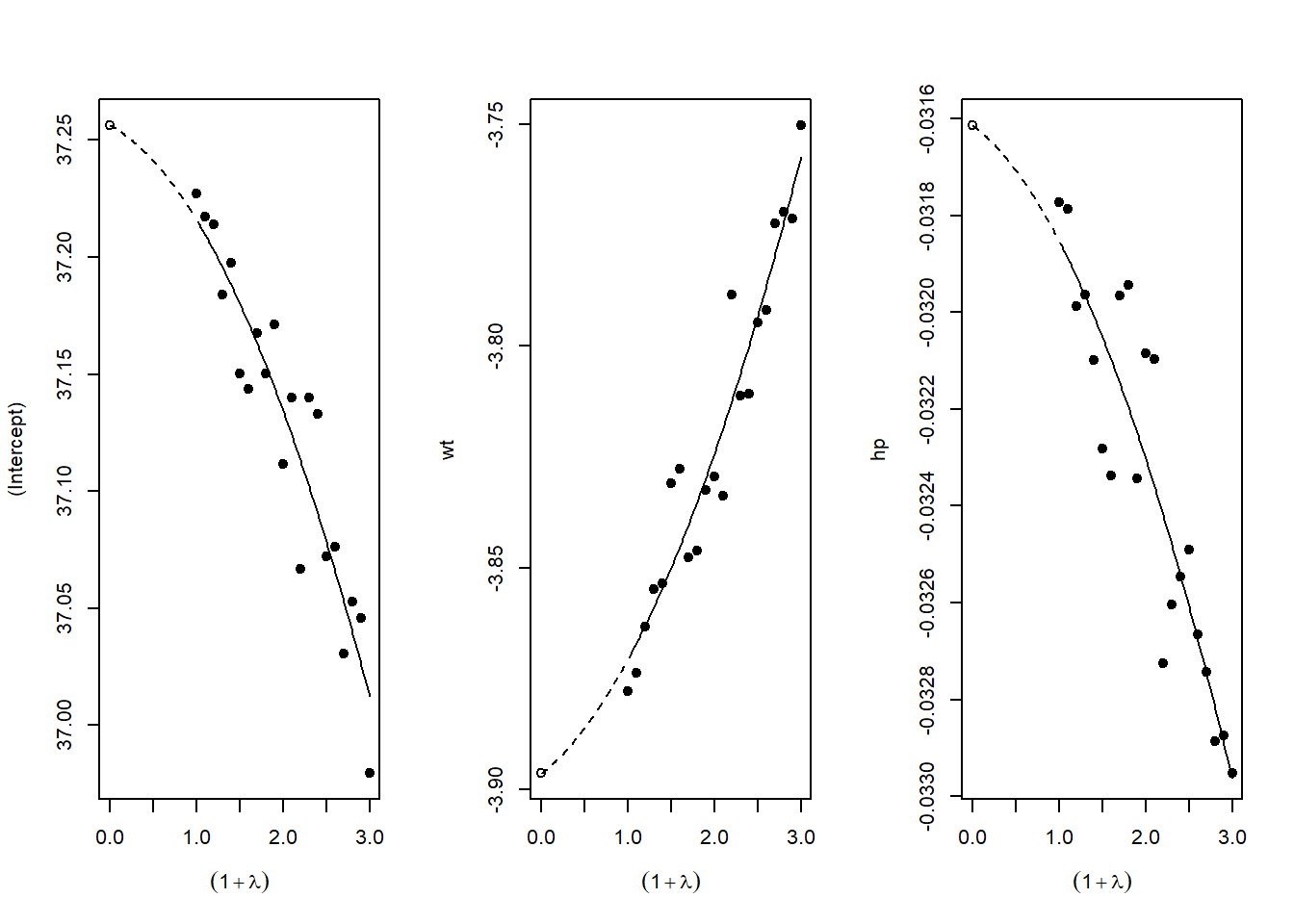
Figure 42.11: SIMEX extrapolation plots for measurement error correction