41.3 Application
The easiest way to create synthetic data is to use the synthpop package. Alternatively, you can do it manually
library(synthpop)
library(tidyverse)
library(performance)
# library(effectsize)
# library(see)
# library(patchwork)
# library(knitr)
# library(kableExtra)
head(iris)
#> Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
#> 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
#> 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
#> 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
#> 4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
#> 5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
#> 6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
synthpop::codebook.syn(iris)
#> $tab
#> variable class nmiss perctmiss ndistinct
#> 1 Sepal.Length numeric 0 0 35
#> 2 Sepal.Width numeric 0 0 23
#> 3 Petal.Length numeric 0 0 43
#> 4 Petal.Width numeric 0 0 22
#> 5 Species factor 0 0 3
#> details
#> 1 Range: 4.3 - 7.9
#> 2 Range: 2 - 4.4
#> 3 Range: 1 - 6.9
#> 4 Range: 0.1 - 2.5
#> 5 'setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica'
#>
#> $labs
#> NULL
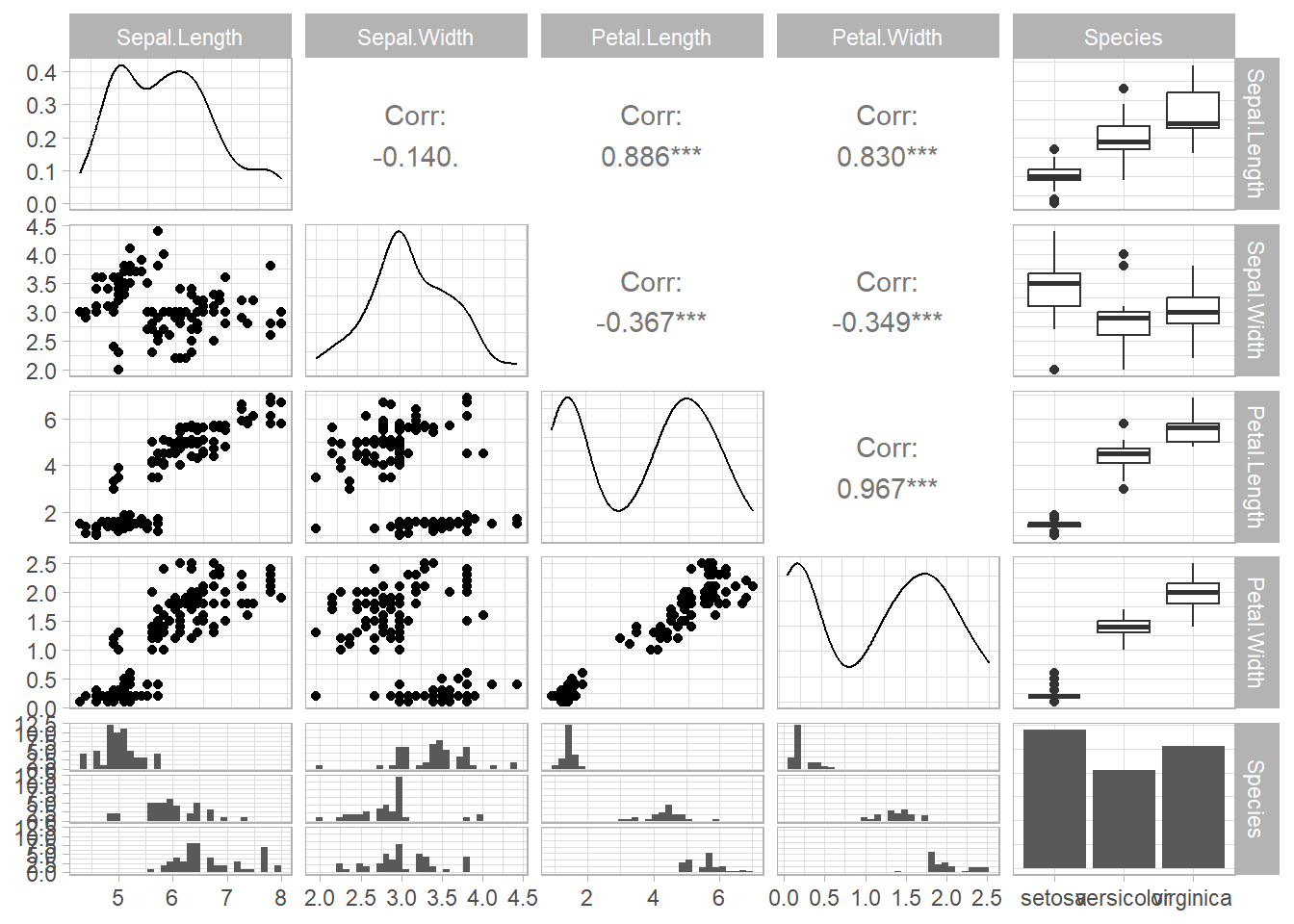
syn_df <- syn(iris, seed = 3)
#>
#> Synthesis
#> -----------
#> Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
# check for replciated uniques
replicated.uniques(syn_df, iris)
#> $replications
#> [1] TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE
#> [13] TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE
#> [25] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [37] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [49] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [61] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE
#> [73] FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE
#> [85] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE
#> [97] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE
#> [109] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [121] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [133] FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [145] FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#>
#> $no.uniques
#> [1] 148
#>
#> $no.replications
#> [1] 17
#>
#> $per.replications
#> [1] 11.33333
# remove replicated uniques and adds a FAKE_DATA label
# (in case a person can see his or own data in
# the replicated data by chance)
syn_df_sdc <- sdc(syn_df, iris,
label = "FAKE_DATA",
rm.replicated.uniques = T)
#> no. of replicated uniques: 17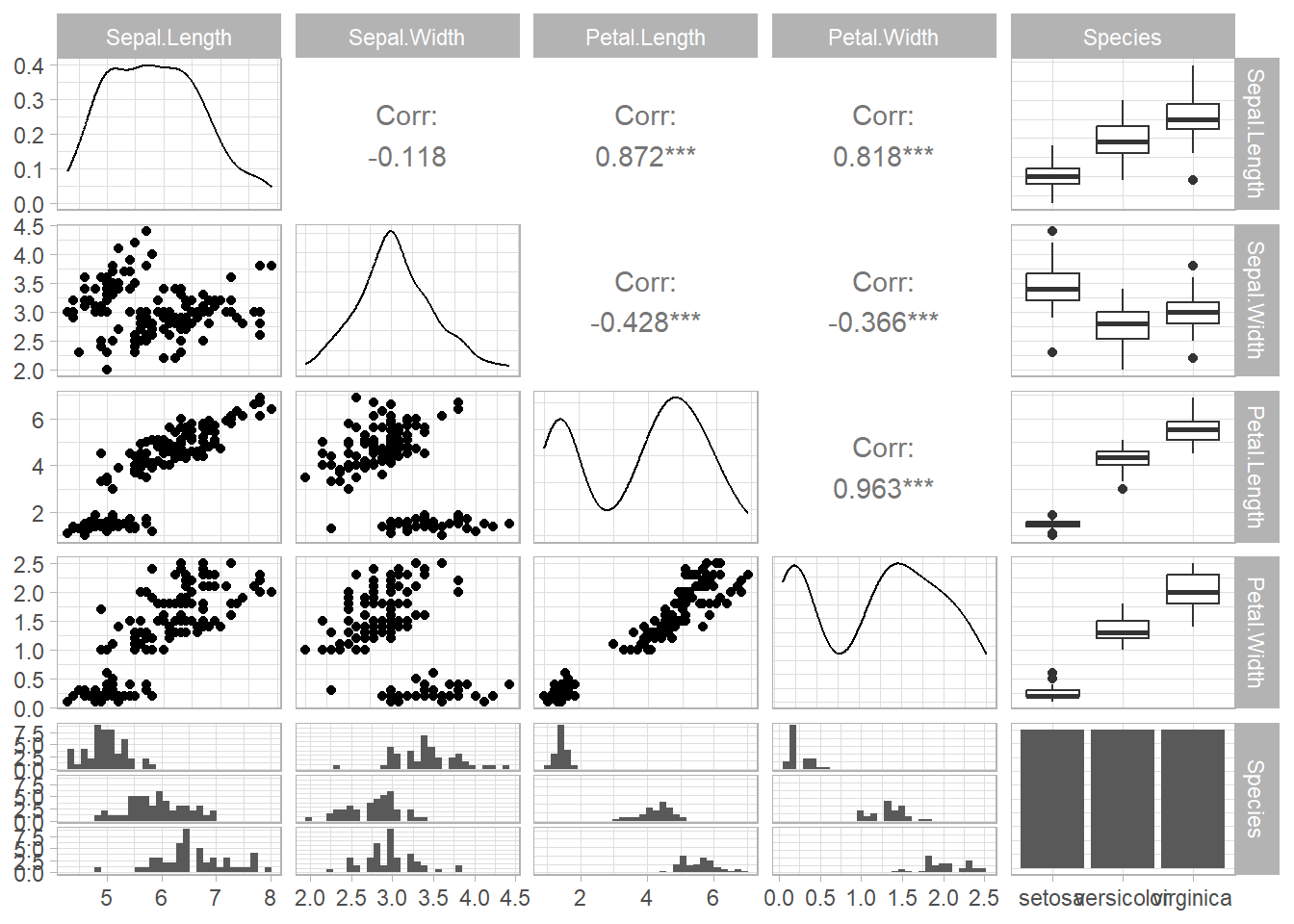
lm_ori <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width + Petal.Length , data = iris)
# performance::check_model(lm_ori)
summary(lm_ori)
#>
#> Call:
#> lm(formula = Sepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width + Petal.Length, data = iris)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.96159 -0.23489 0.00077 0.21453 0.78557
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 2.24914 0.24797 9.07 7.04e-16 ***
#> Sepal.Width 0.59552 0.06933 8.59 1.16e-14 ***
#> Petal.Length 0.47192 0.01712 27.57 < 2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 0.3333 on 147 degrees of freedom
#> Multiple R-squared: 0.8402, Adjusted R-squared: 0.838
#> F-statistic: 386.4 on 2 and 147 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
lm_syn <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width + Petal.Length , data = syn_df$syn)
# performance::check_model(lm_syn)
summary(lm_syn)
#>
#> Call:
#> lm(formula = Sepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width + Petal.Length, data = syn_df$syn)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -0.79165 -0.22790 -0.01448 0.15893 1.13360
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 2.96449 0.24538 12.081 < 2e-16 ***
#> Sepal.Width 0.39214 0.06816 5.754 4.9e-08 ***
#> Petal.Length 0.45267 0.01743 25.974 < 2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 0.3658 on 147 degrees of freedom
#> Multiple R-squared: 0.8246, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8222
#> F-statistic: 345.6 on 2 and 147 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16Open data can be assessed for its utility in two distinct ways:
General Utility: This refers to the broad resemblances within the dataset, allowing for preliminary data exploration.
Specific Utility: This focuses on the comparability of models derived from synthetic and original datasets, emphasizing analytical reproducibility.
For General utility
Specific utility
# just like regular lm, but for synthetic data
lm_syn <- lm.synds(Sepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width + Petal.Length , data = syn_df)
compare(lm_syn, iris)
#>
#> Call used to fit models to the data:
#> lm.synds(formula = Sepal.Length ~ Sepal.Width + Petal.Length,
#> data = syn_df)
#>
#> Differences between results based on synthetic and observed data:
#> Synthetic Observed Diff Std. coef diff CI overlap
#> (Intercept) 2.9644900 2.2491402 0.71534988 2.884829 0.2640608
#> Sepal.Width 0.3921429 0.5955247 -0.20338187 -2.933611 0.2516161
#> Petal.Length 0.4526695 0.4719200 -0.01925058 -1.124602 0.7131064
#>
#> Measures for one synthesis and 3 coefficients
#> Mean confidence interval overlap: 0.4095944
#> Mean absolute std. coef diff: 2.314347
#>
#> Mahalanobis distance ratio for lack-of-fit (target 1.0): 3.08
#> Lack-of-fit test: 9.23442; p-value 0.0263 for test that synthesis model is
#> compatible with a chi-squared test with 3 degrees of freedom.
#>
#> Confidence interval plot: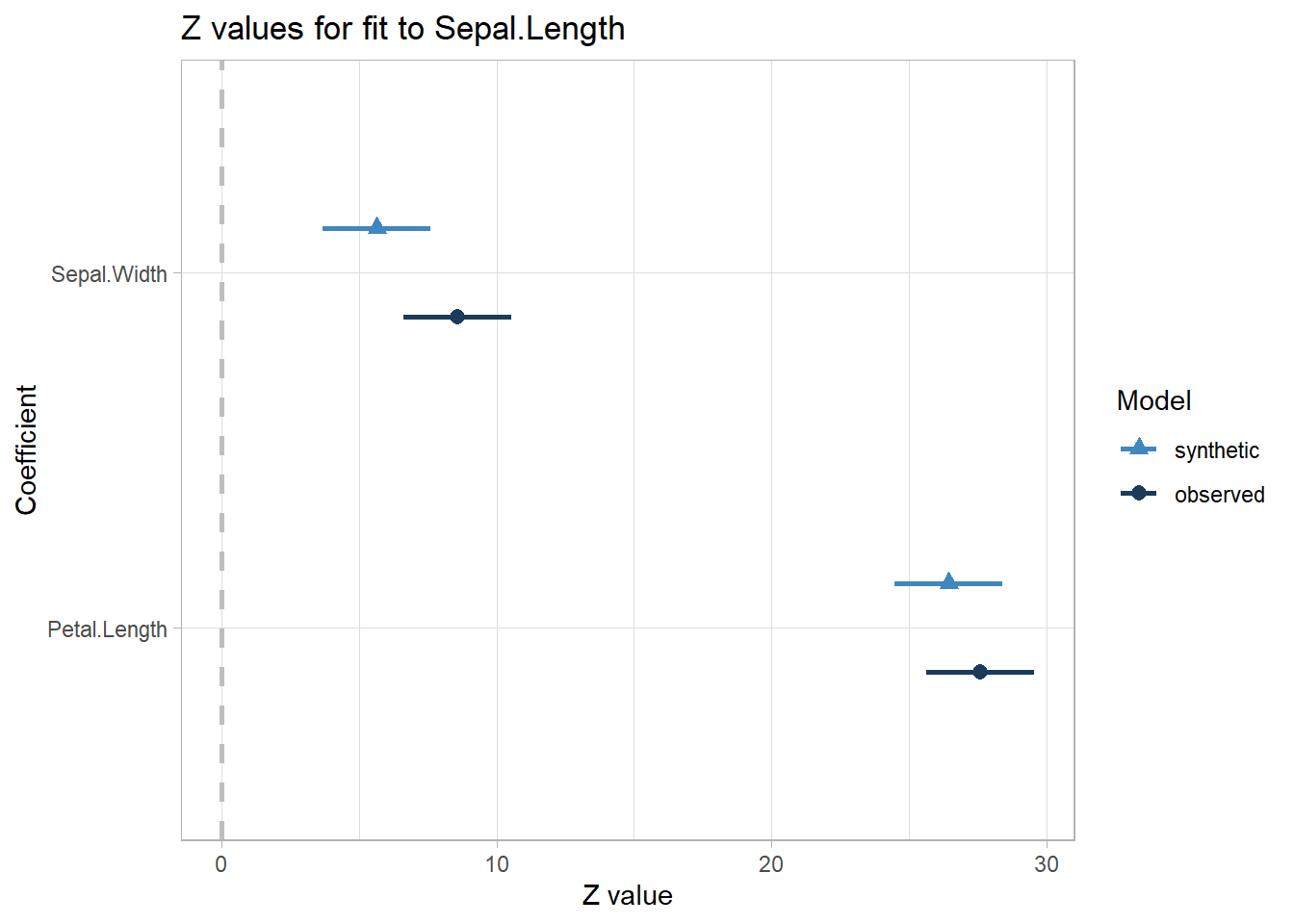
You basically want your lack-of-fit test to be non-significant.