第 34 章 ggplot2中传递函数作为参数值
本章汇总ggplot2中常见的参数值是一个函数的情形。
library(tidyverse)
library(palmerpenguins)
penguins <- penguins %>% drop_na()
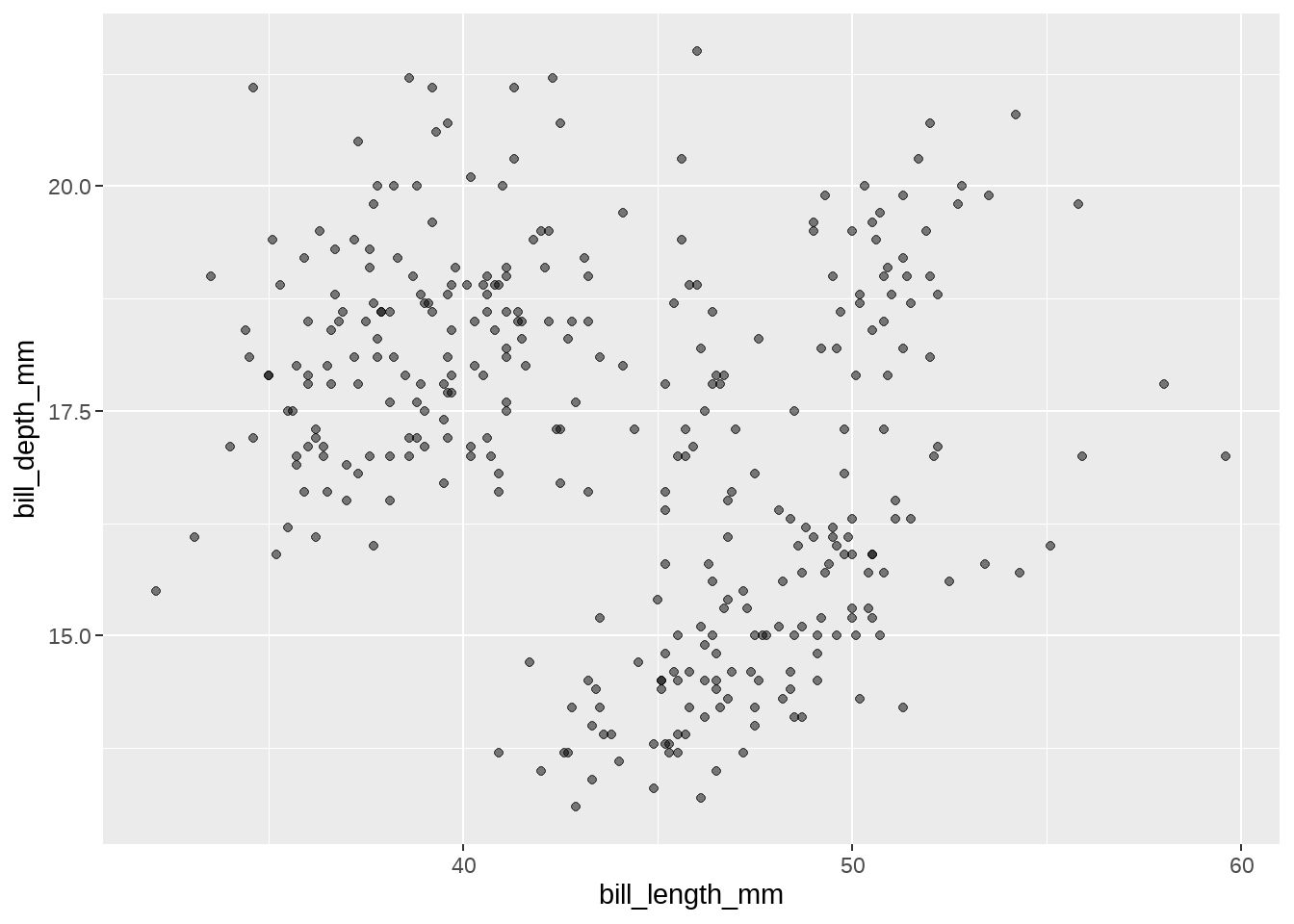
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point()
34.1 data可以是一个函数
图层中的data可以是一个函数,它继承全局声明中的data作为函数的参数
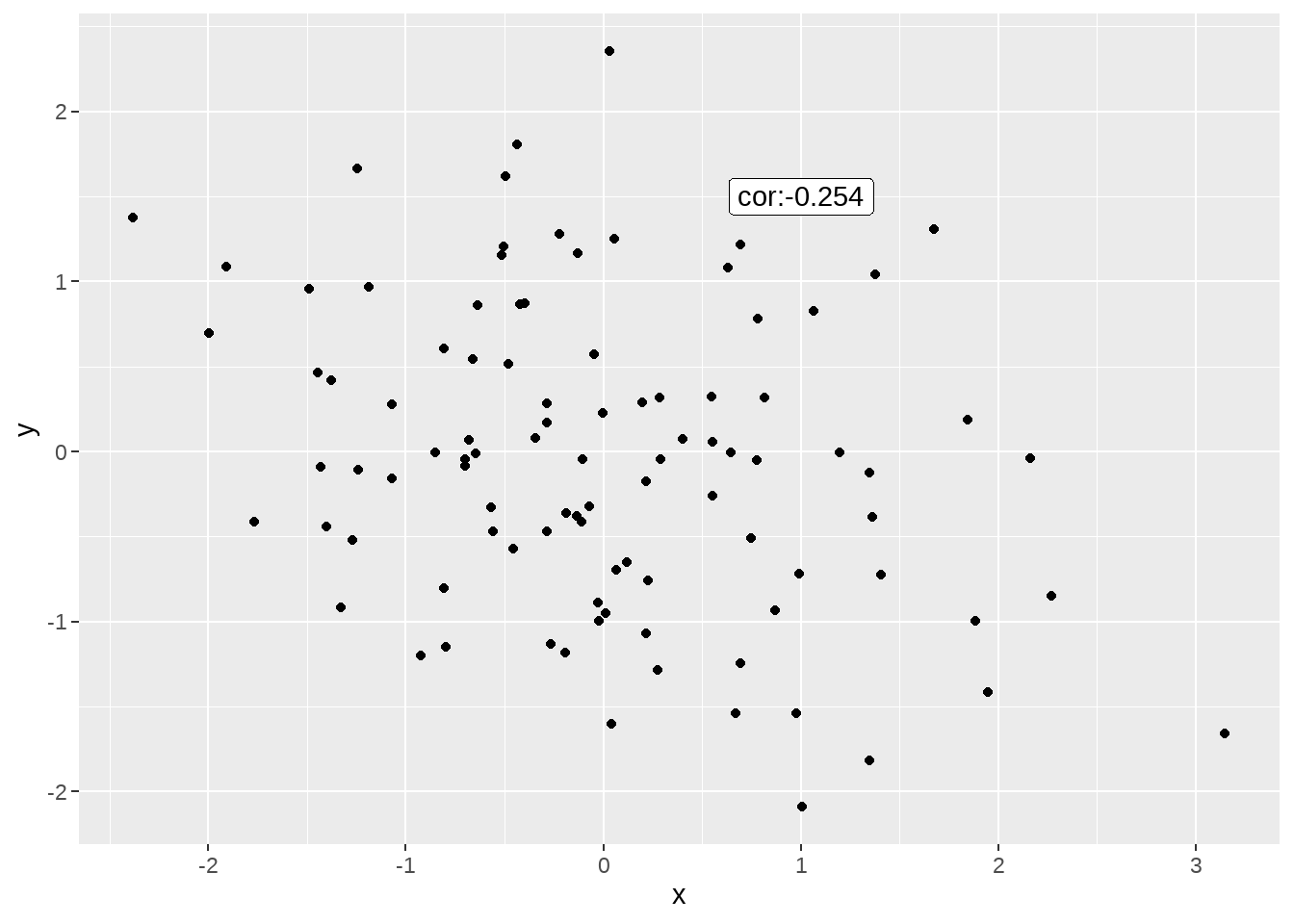
data.frame(
x = rnorm(100),
y = rnorm(100)
) %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
geom_label(
data = function(d) d %>% summarise(cor = cor(x, y)),
aes(x = 1, y = 1.5, label = paste0("cor:", signif(cor, 3)))
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(data = ~ select(., -species), color = "gray80") +
geom_point(aes(color = species)) +
facet_wrap(vars(species))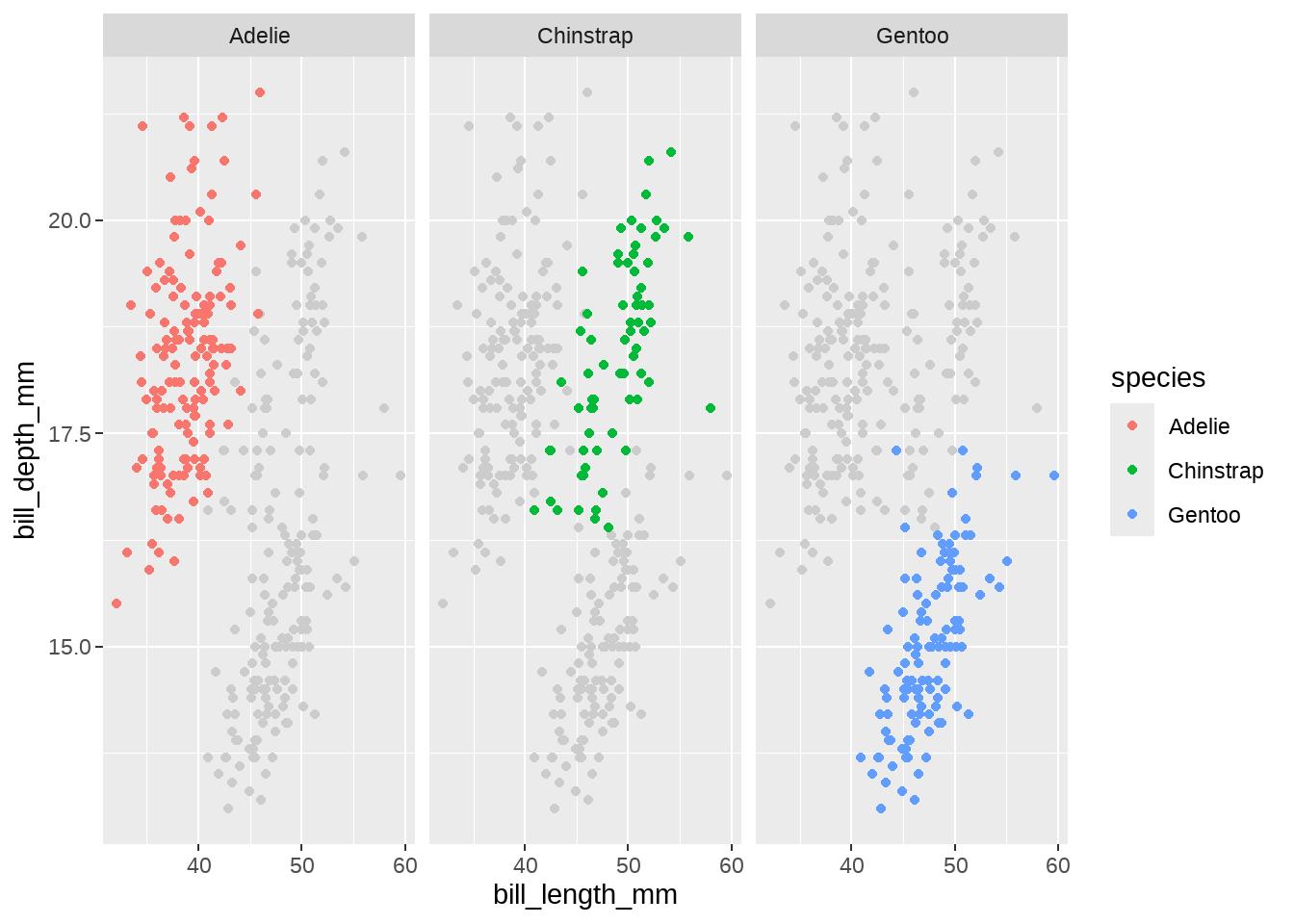
summary_df <- function(df) {
df %>%
group_by(sex) %>%
summarise(
mean = mean(body_mass_g)
)
}
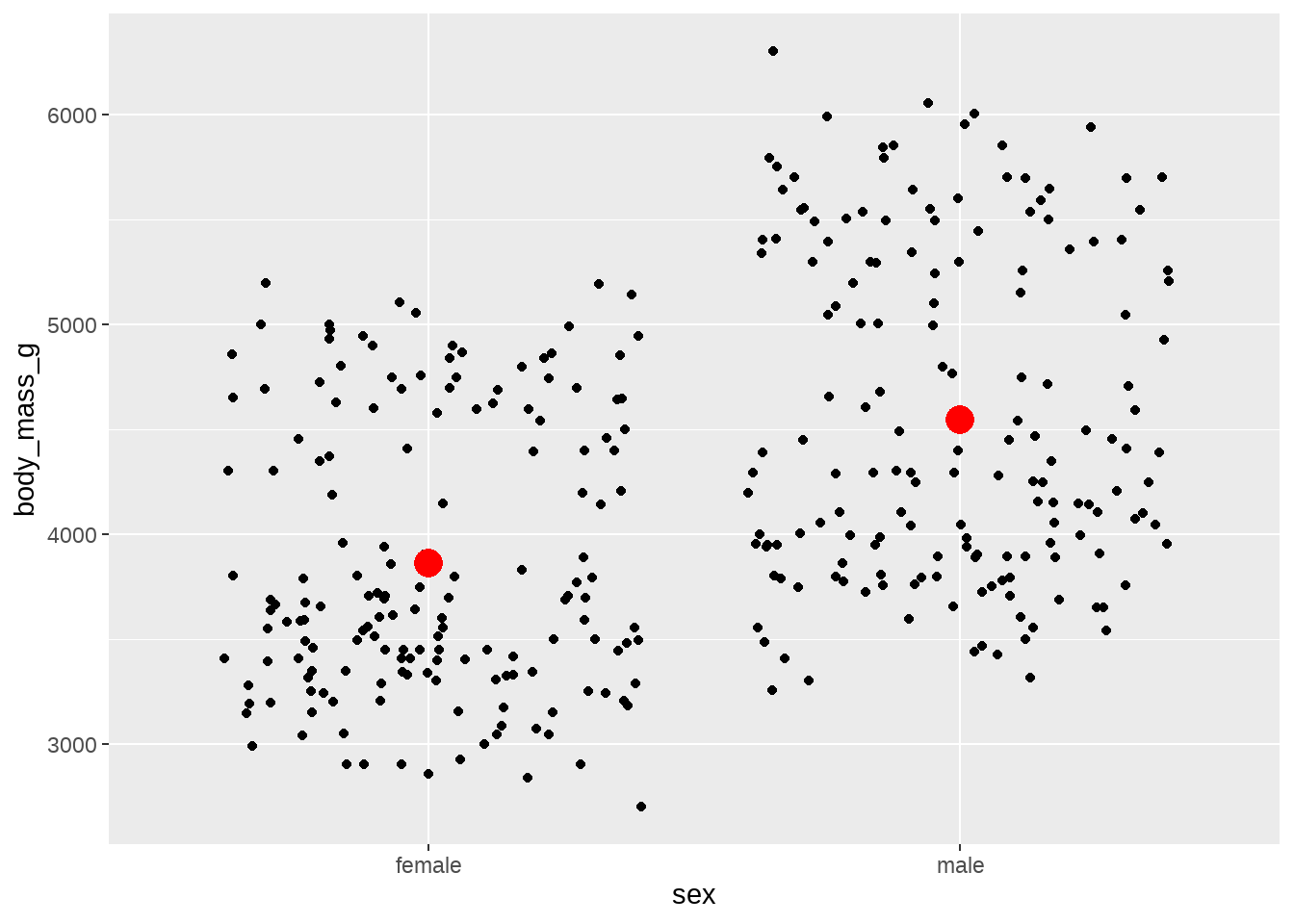
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = sex, y = body_mass_g)) +
geom_jitter() +
geom_point(
data = summary_df,
aes(y = mean), color = "red", size = 5
)
34.2 标度 scale_**() 中的参数可以接受函数作为参数值
34.2.1 limits
one of:
limits = NULL使用默认的范围limits = c(a, b)可以是一个长度为2 的数值型向量。如果是NA,比如c(a, NA),表示设定下限为a,但是上限不做调整,维持当前值。可以是一个函数,函数将坐标轴的界限(长度为2 的数值型向量)作为参数,返回一个新的2元向量,作为界限。函数可以写成lambda函数形式。但注意的是,给位置标度设置新的界限,界限之外的数据会被删除。
如果我们的目的是想局部放大,不应该使用
scale_x_continuous(limits = c(a, b))里用,而是应该在坐标系统coord_cartersian()函数里面使用limit参数。
coord_cartersian(limit = c(4, 9))下面看一些案例
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(limits = range(penguins$bill_length_mm))
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
limits = function(x) c( x[1] - 10, x[2] + 10 )
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
limits = ~ c(min(.) - 10, max(.) + 10)
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(limits = ~ range(.x))
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(limits = function(x) {
if (x[1] < 20) {
x
} else {
x[1] <- 20
return(x)
}
})
make_scale_expander <- function(...) {
function(x) {
range(c(x, ...))
}
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(limits = make_scale_expander(80))
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(limits = ~ range(c(.x, 80)))
34.2.2 breaks
breaks 表示坐标轴或者图例中刻度位置(take a break,一条连线的坐标轴被打断了地方)
一般情况下,内置函数会自动完成
breaks = NULL,就是去掉刻度用户可提供一个数值类型的向量,代表刻度显示的位置
也可以是函数,该函数接受坐标范围(包含最小值和最大值的长度为2的向量)作为参数,返回一个数值类型的向量。比如常用的
scales::extended_breaks()函数,函数也可以写成 lambda 函数的形式。
下面看具体案例
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
breaks = function(y) seq(floor(y[1]), ceiling(y[2]), by = 2)
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
breaks = function(y) seq(floor(min(y)), ceiling(max(y)), by = 2)
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
breaks = function(y) seq(floor(min(y)), ceiling(max(y)), by = 5)
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
expand = expansion(mult = 0, add = 0),
breaks = function(x) seq(min(x), max(x), 5)
)
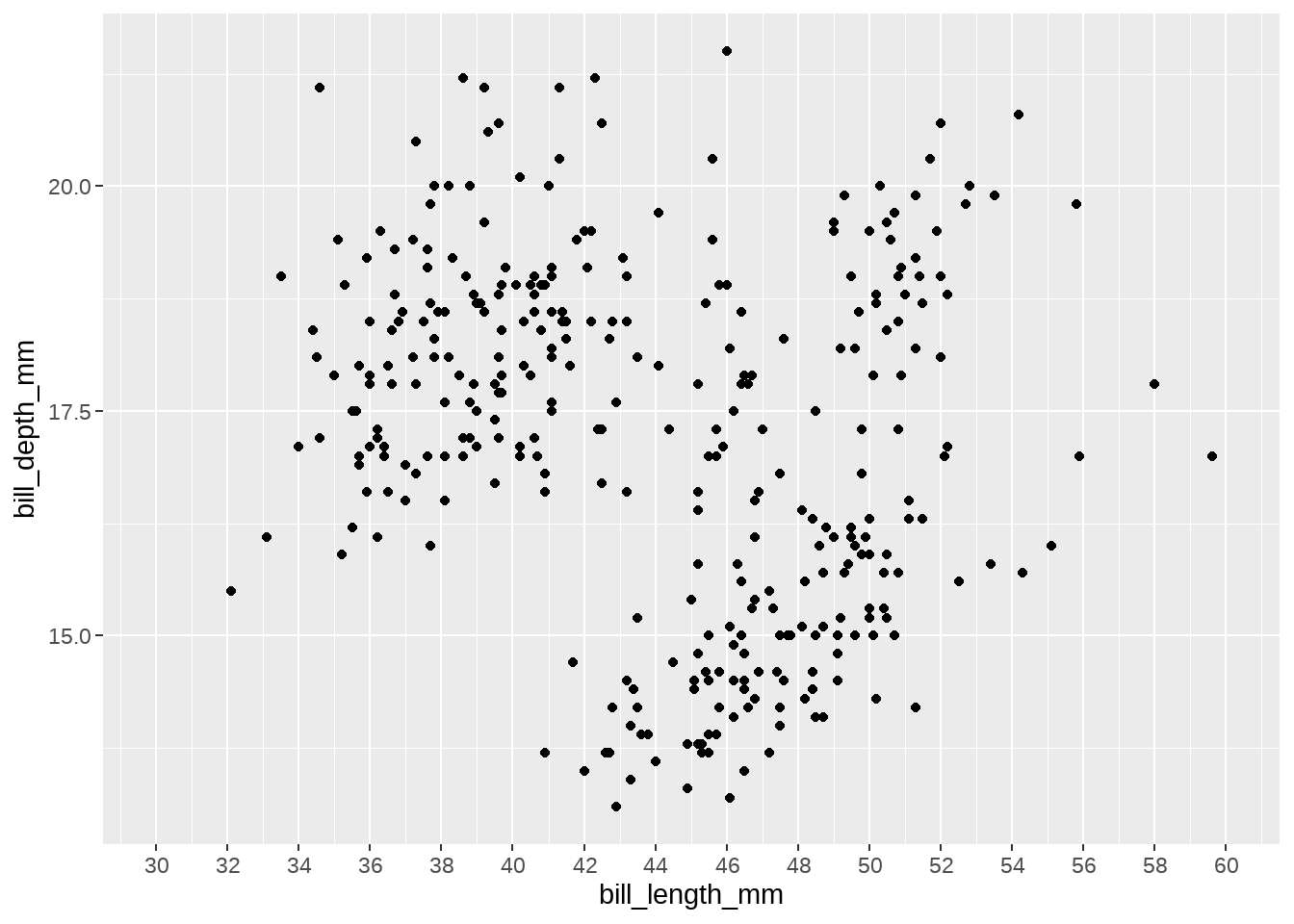
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
limits = c(30, 60),
breaks = scales::breaks_pretty(12)
)
34.2.3 labels
参数labels, 坐标和图例的间隔标签
- 一般情况下,内置函数会自动完成
- 也可人工指定一个字符型向量,与
breaks提供的字符型向量一一对应 - 也可以是函数,把
breaks提供的字符型向量当做函数的输入参数 -
labels = NULL,就是去掉标签
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = species, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_jitter() +
scale_x_discrete(labels = function(x) str_sub(x, 1, 1)) 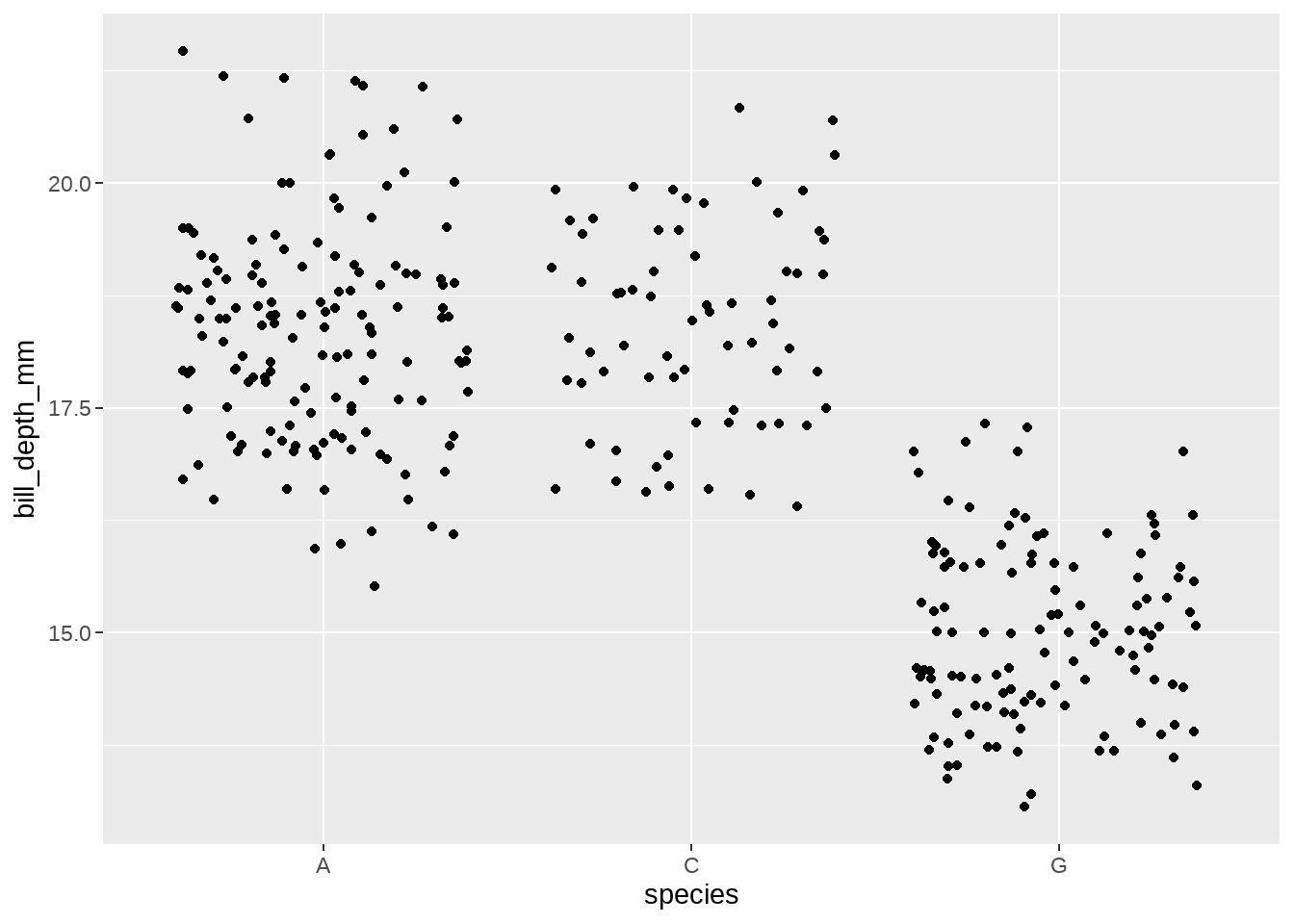
pairs56 <- tibble::tribble(
~species, ~new_name,
"Adelie", "A",
"Chinstrap", "C",
"Gentoo", "G"
) %>%
tibble::deframe()
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = species, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_discrete(labels = function(x) str_replace_all(x, pattern = pairs56)) 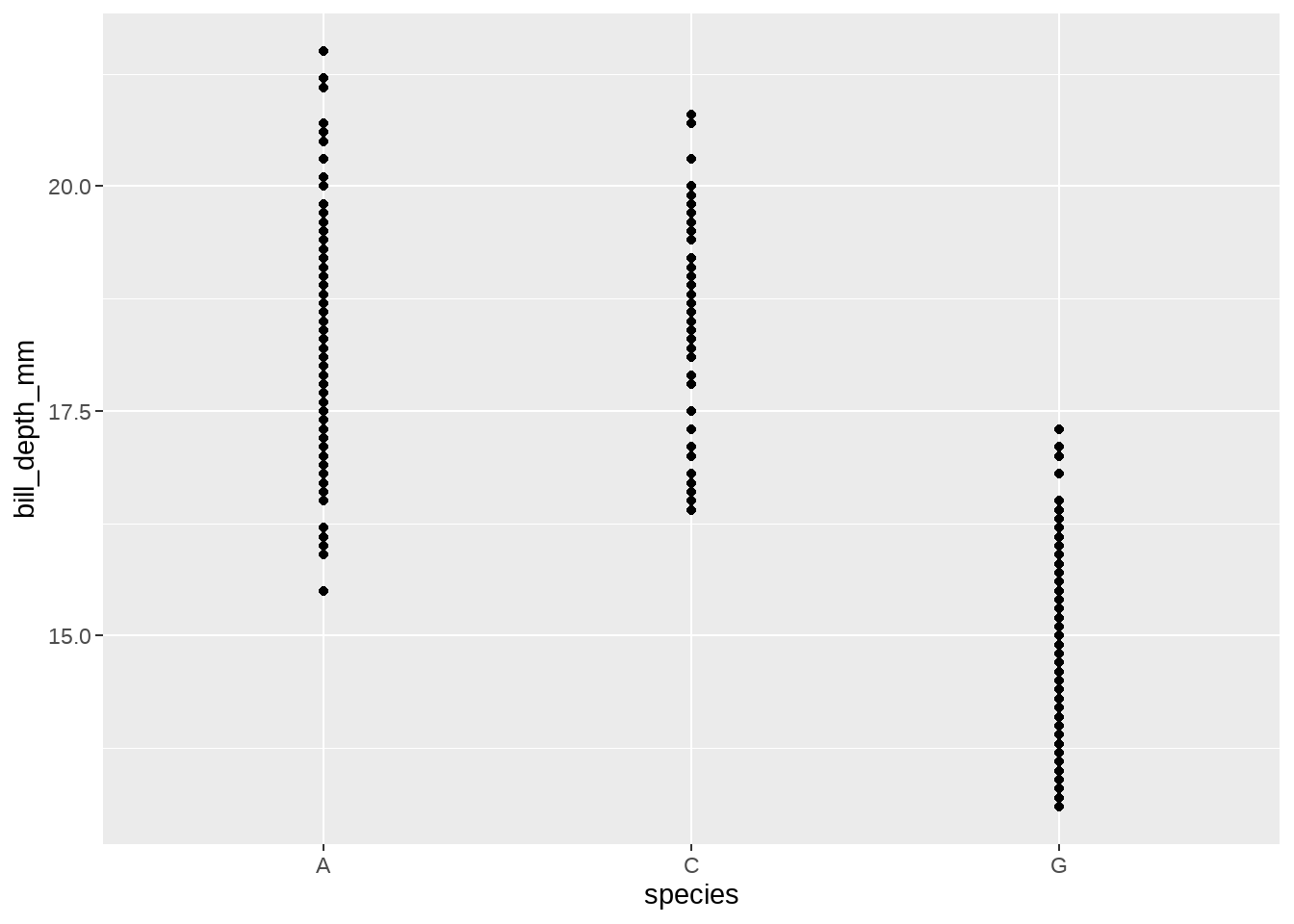
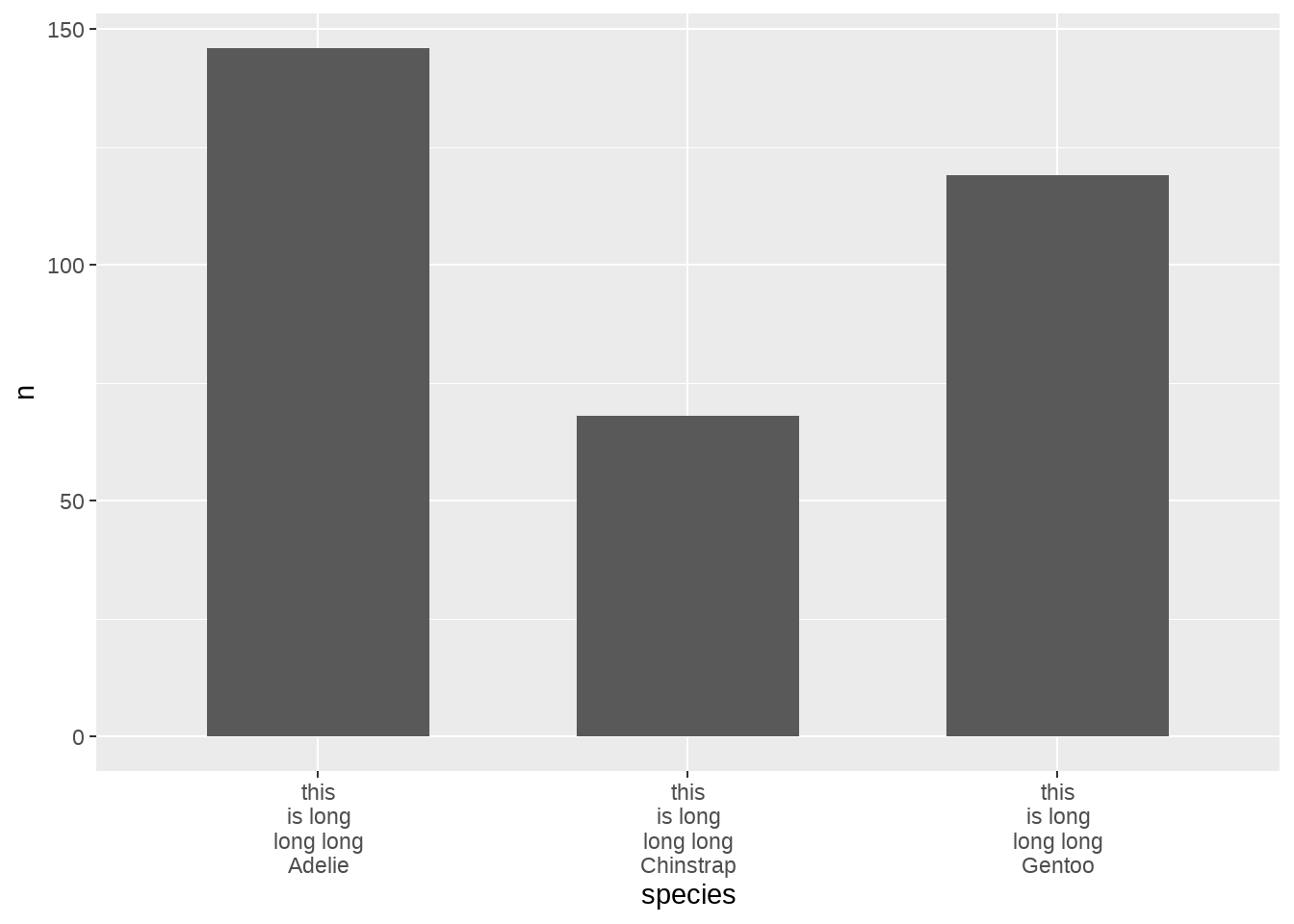
penguins %>%
count(species) %>%
mutate(species = paste0("this is long long long ", species)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = species, y = n)) +
geom_col(width = 0.6) +
scale_x_discrete(
labels = function(x) stringr::str_wrap(x, width = 10)
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
labels = function(x) paste0(x, "_mm")
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
labels = ~ paste0(.x, "_mm")
)
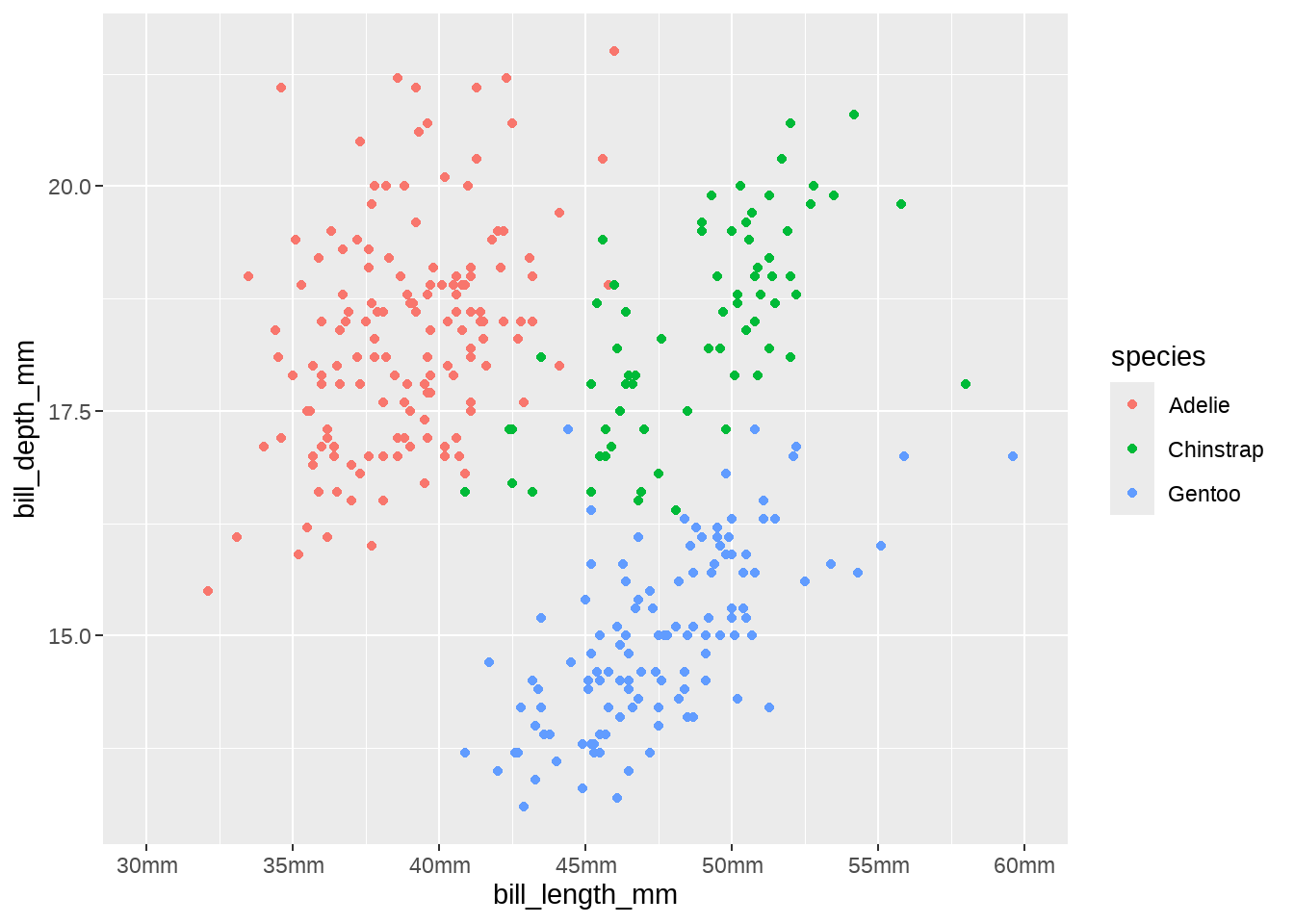
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = species)) +
scale_x_continuous(
limits = c(30, 60),
breaks = scales::breaks_width(width = 5),
labels = scales::unit_format(unit = "mm", sep = "")
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_continuous(
labels = scales::dollar
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = species)) +
scale_x_continuous(
limits = c(30, 60),
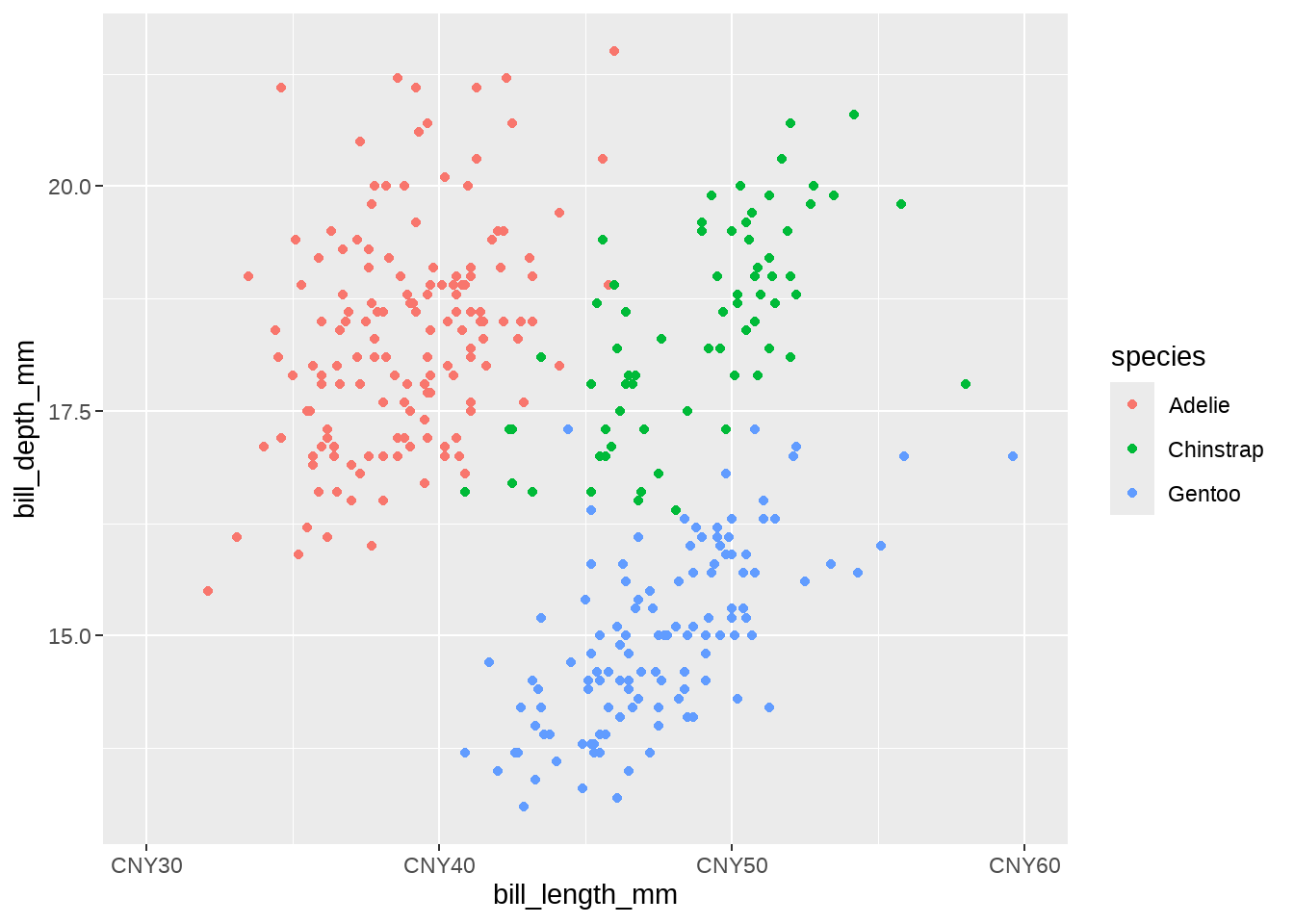
labels = scales::label_number(prefix = "CNY", sep = "")
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(colour = species)) +
scale_x_continuous(
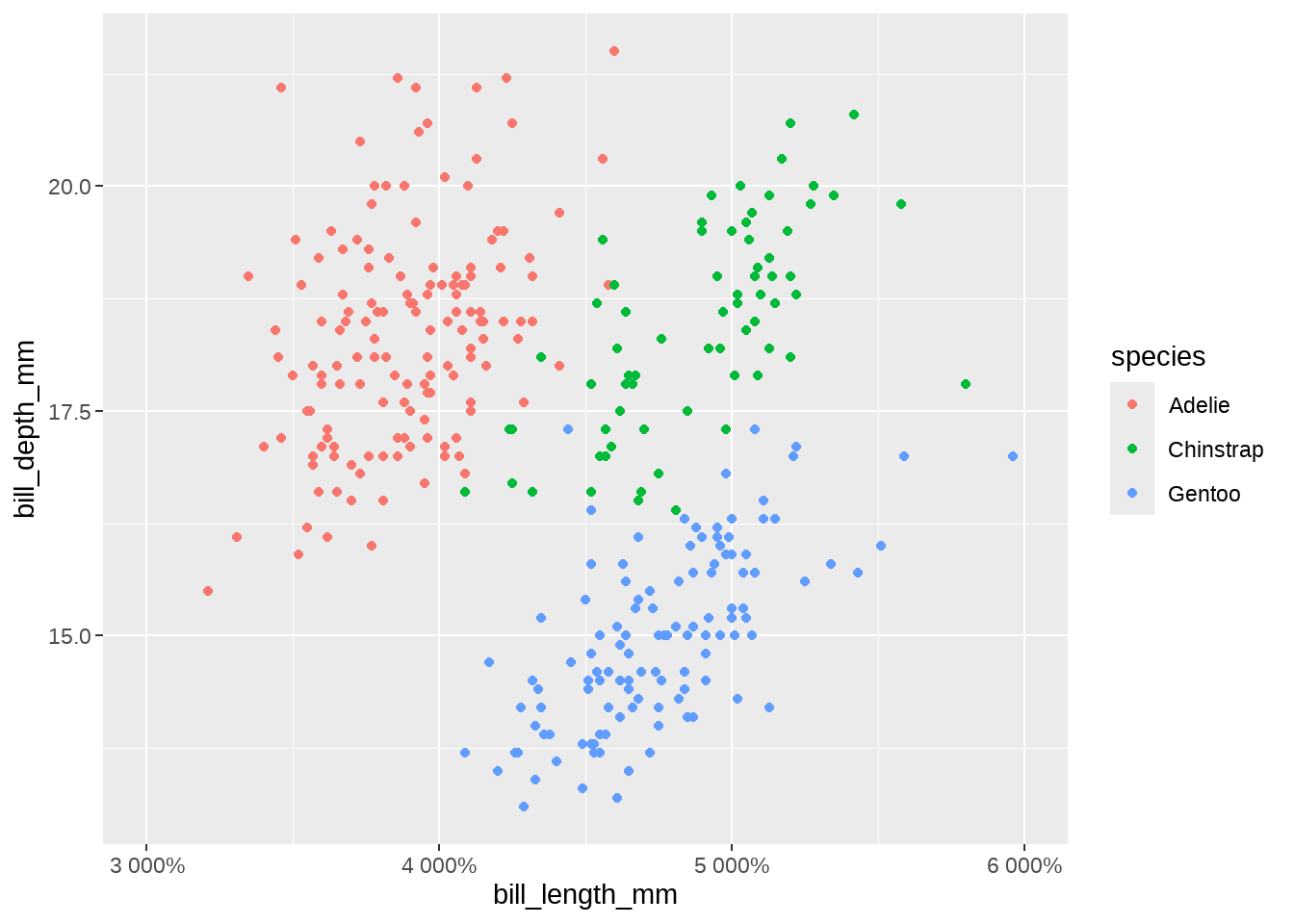
limits = c(30, 60),
labels = scales::label_percent()
) 
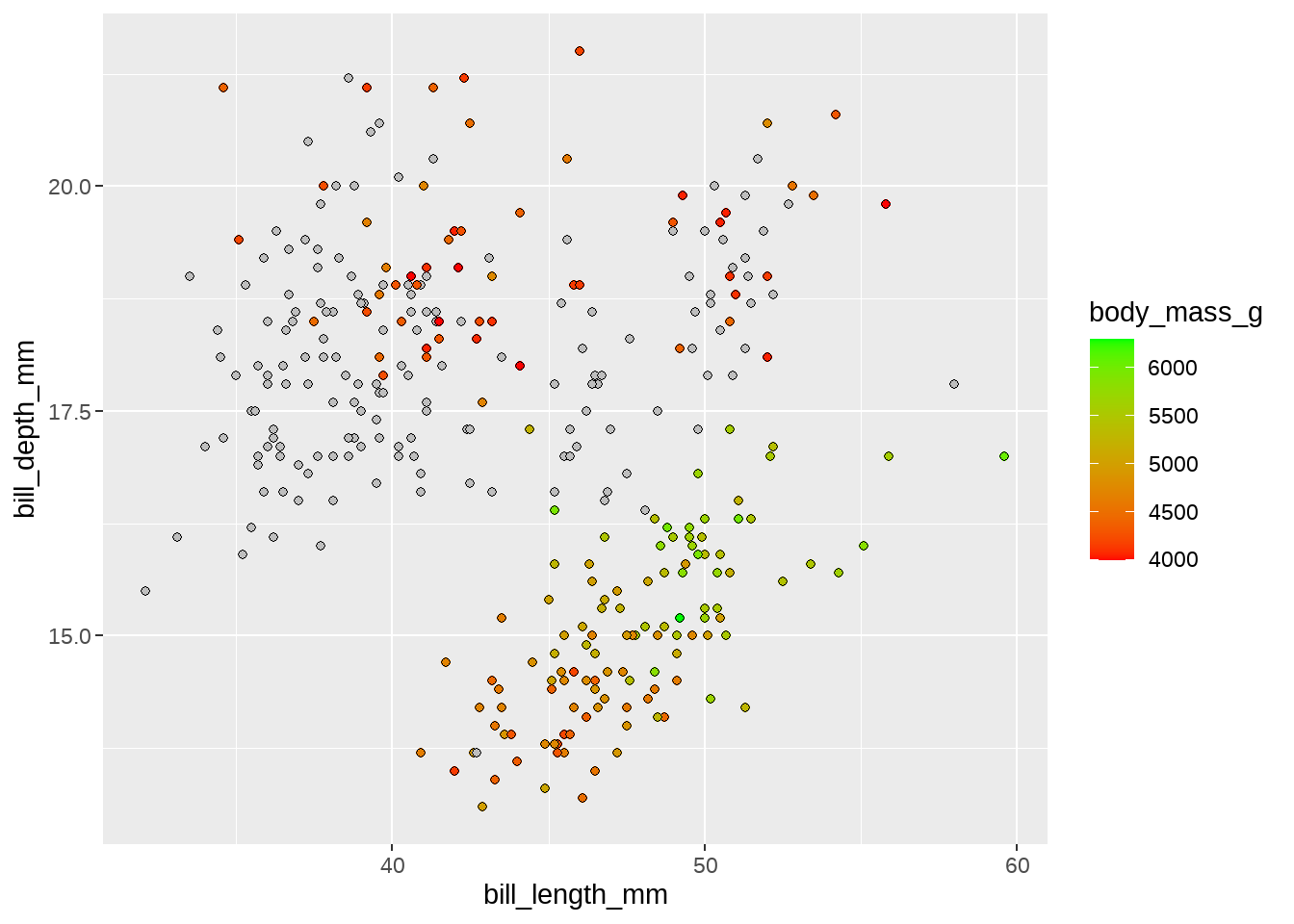
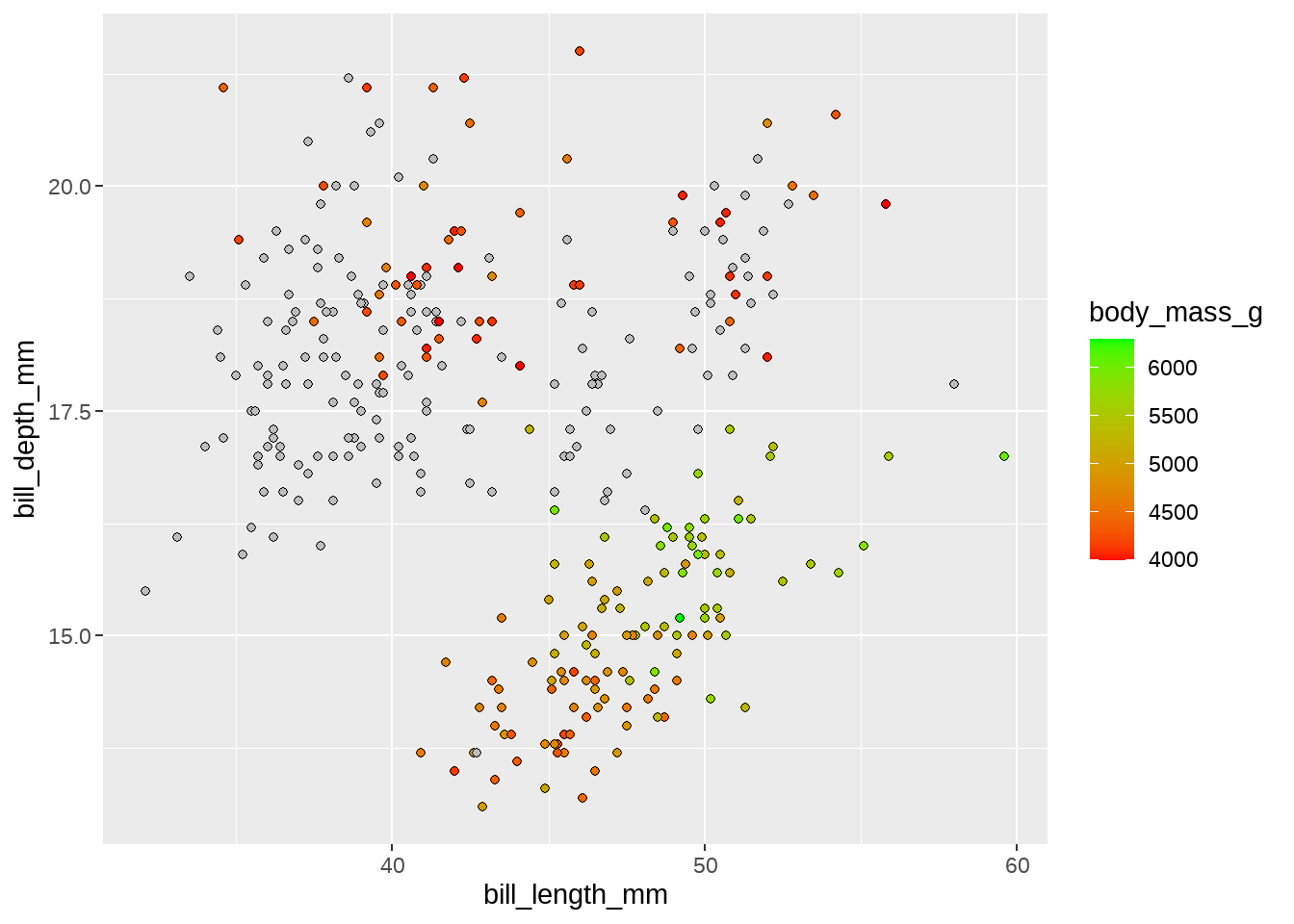
34.2.4 oob
oob函数用于处理超出范围的数据,scales宏包可以满足用户需求,当然用户也可以自己定义
- 默认(
scales::censor()) 把超出界限的值替换成NA -
scales::squish()用于将越界值挤压到范围内。 -
scales::squish_infinite()用于将无限值挤压到范围内。 - 用户自定义函数,该函数接受limits和映射数据作为参数,返回修改后的映射数据
下面看具体案例
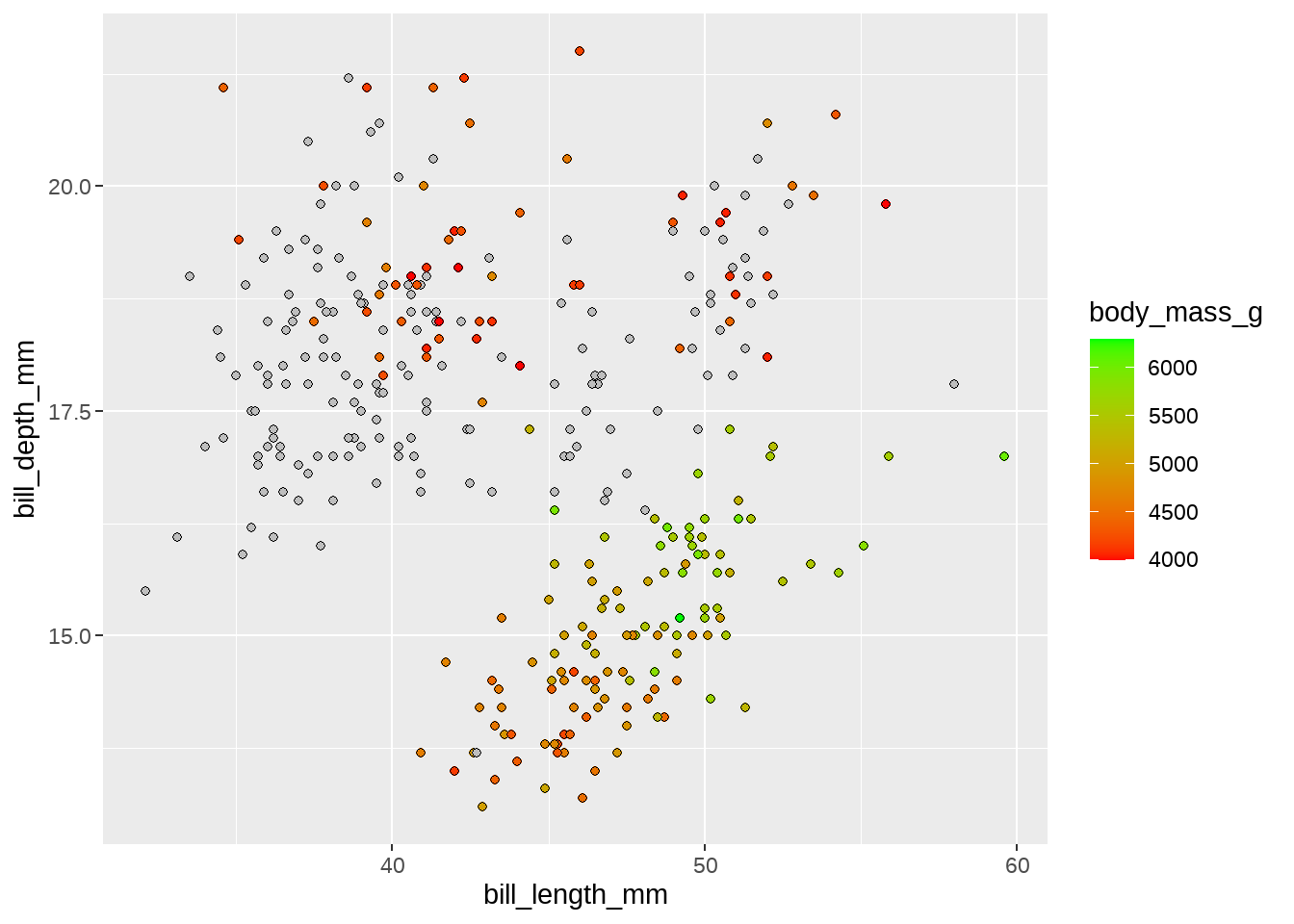
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(fill = body_mass_g), shape = 21) +
scale_fill_gradient(
low = "red", high = "green", na.value = "grey",
limits = c(4000, NA),
oob = scales::censor
)
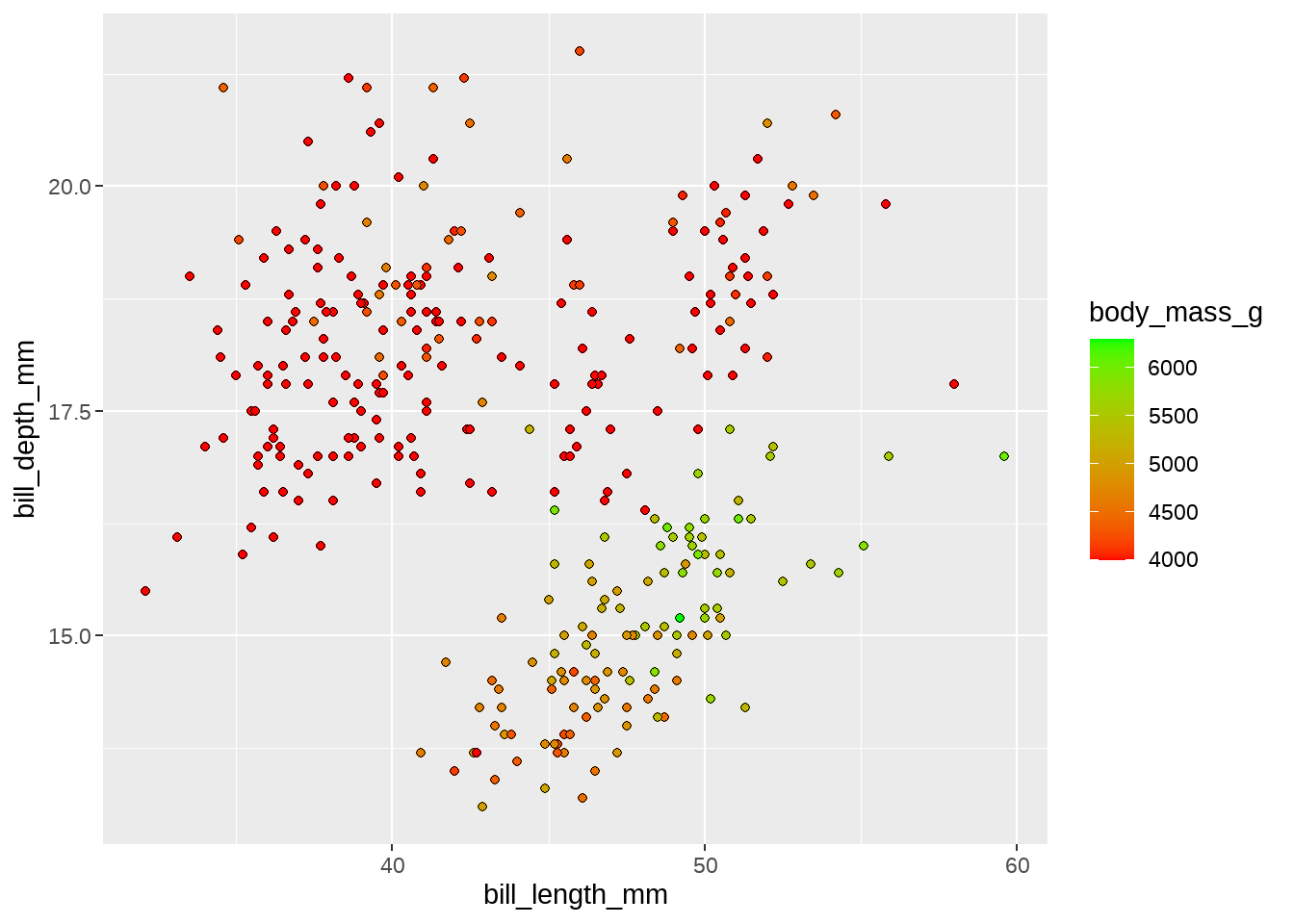
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(fill = body_mass_g), shape = 21) +
scale_fill_gradient(
low = "red", high = "green", na.value = "grey",
limits = c(4000, NA),
oob = scales::squish
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(fill = body_mass_g), shape = 21) +
scale_fill_gradient(
low = "red", high = "green", na.value = "grey",
limits = c(4000, NA),
oob = function(x, ...) x # do nothing
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(fill = body_mass_g), shape = 21) +
scale_fill_gradient(
low = "red", high = "green", na.value = "grey",
limits = c(4000, NA),
oob = scales::rescale_none # do nothing
)
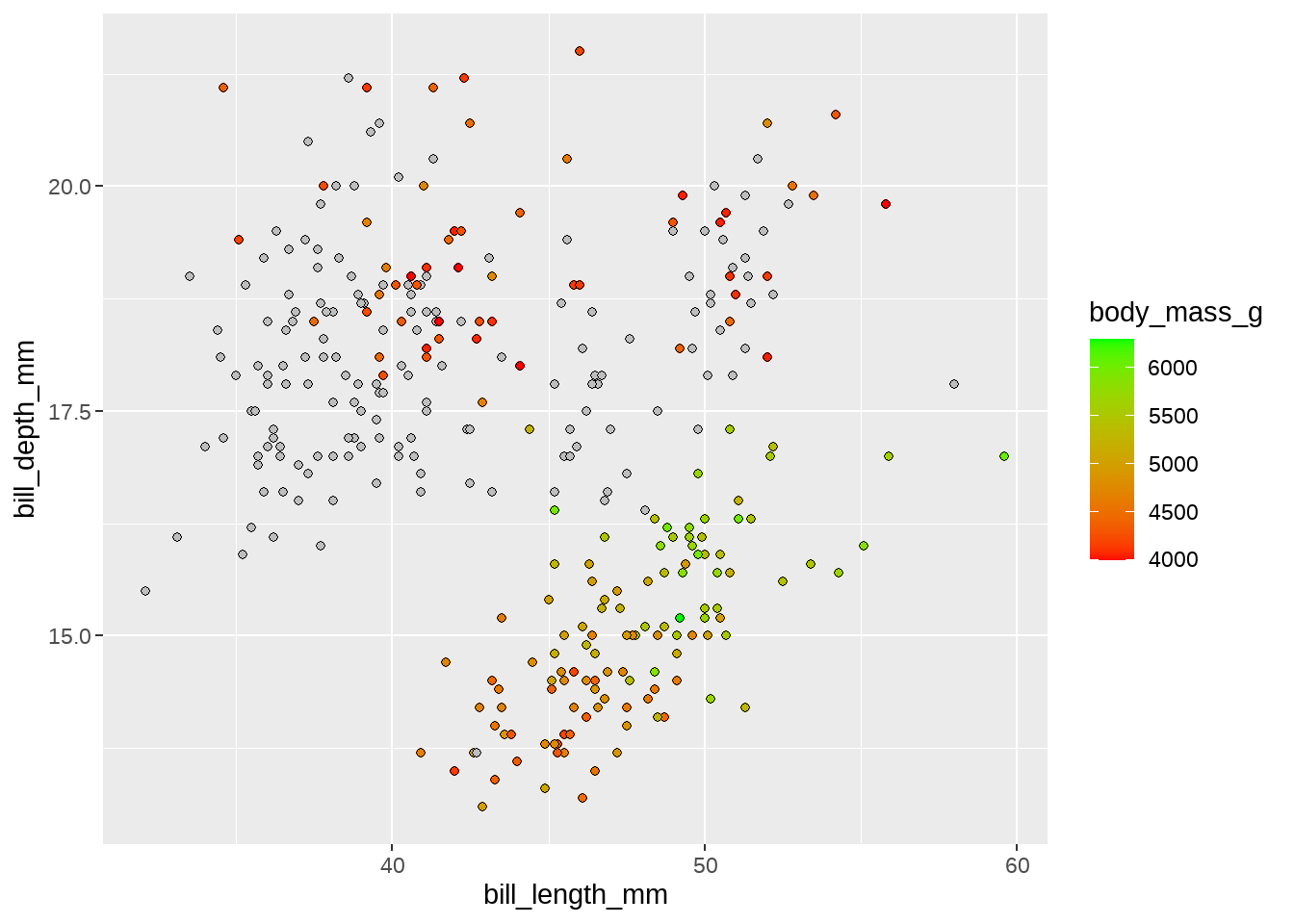
# modify data values outside a given range
#
my_oob_fun <- function(x, range) {
x[x < min(range)] <- NA
x[x > max(range)] <- NA
return(x)
}
my_oob_fun(1:10, c(2, 6))## [1] NA 2 3 4 5 6 NA NA NA NA
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(fill = body_mass_g), shape = 21) +
scale_fill_gradient(
low = "red", high = "green", na.value = "grey",
limits = c(4000, NA),
oob = my_oob_fun # using limits and fill-aes as argument
)
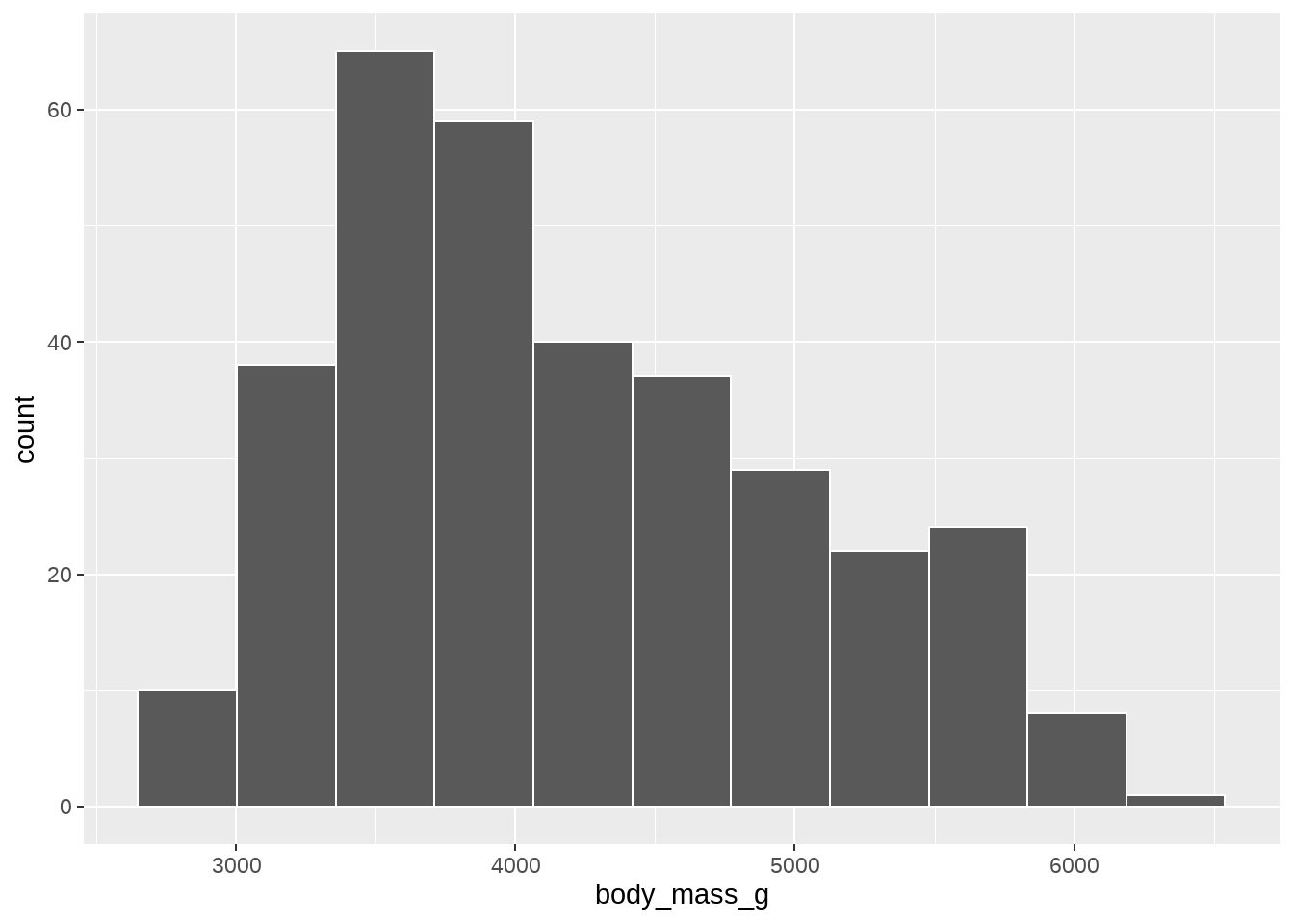
34.3 geom_histogram()中的binwidth
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = body_mass_g)) +
geom_histogram(color = "white")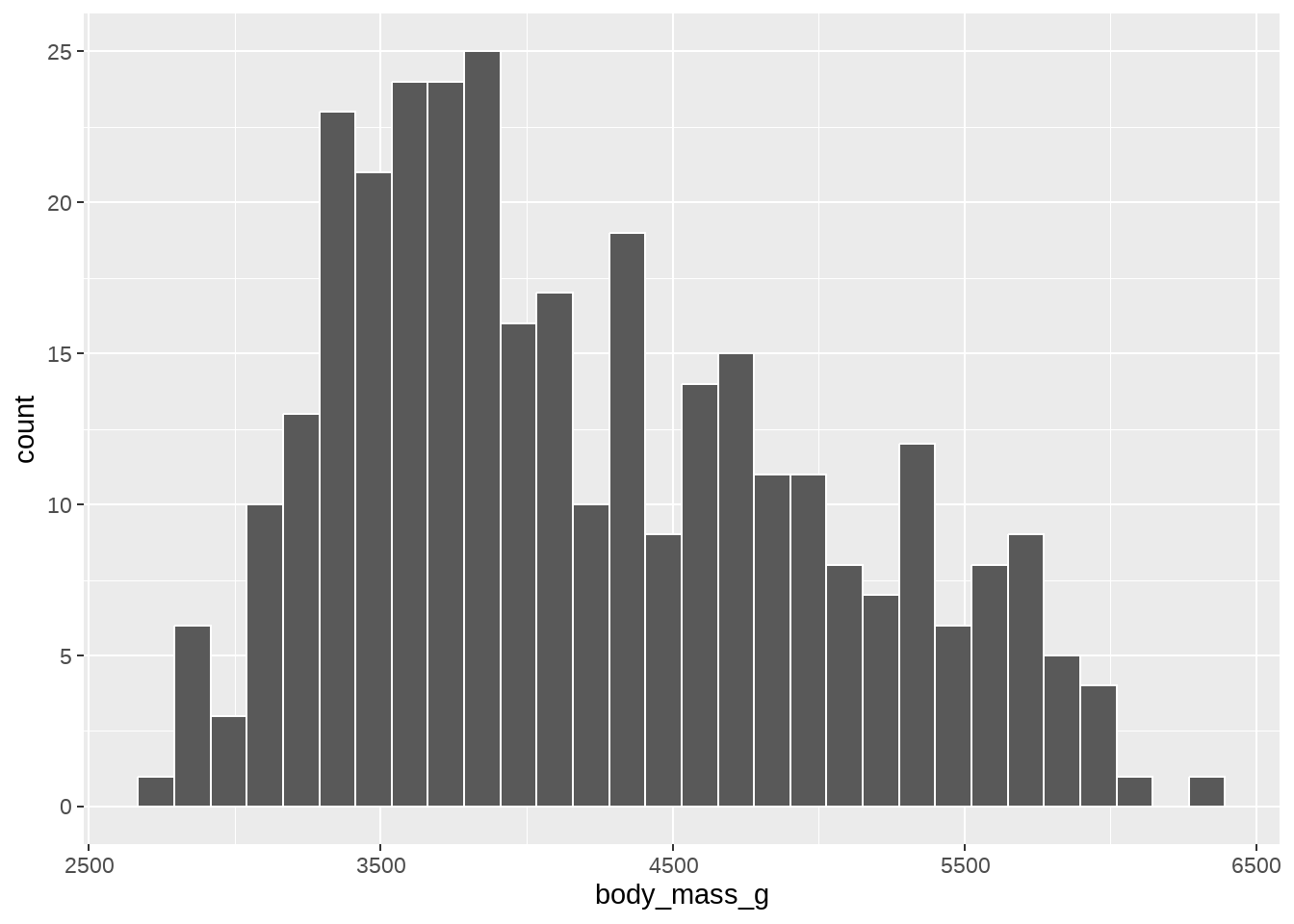
myfun <- function(x) {
n <- length(x)
r <- IQR(x, na.rm = TRUE)
2*r/n^(1/3)
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = body_mass_g)) +
geom_histogram(
binwidth = myfun,
color = "white"
)
34.4 geom_text()中的 hjust
图中柱子上的字体没有显示完整
d <- tibble::tribble(
~name, ~value,
"Alice", 2.12,
"Bob", 68.45,
"Carlie", 15.84,
"Dave", 7.38,
"Eve", 0.56
)
d %>%
ggplot(aes(x = value, y = fct_reorder(name, value)) ) +
geom_col(width = 0.6, fill = "gray60") +
geom_text(aes(label = value, hjust = 1)) +
theme_classic() +
scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL)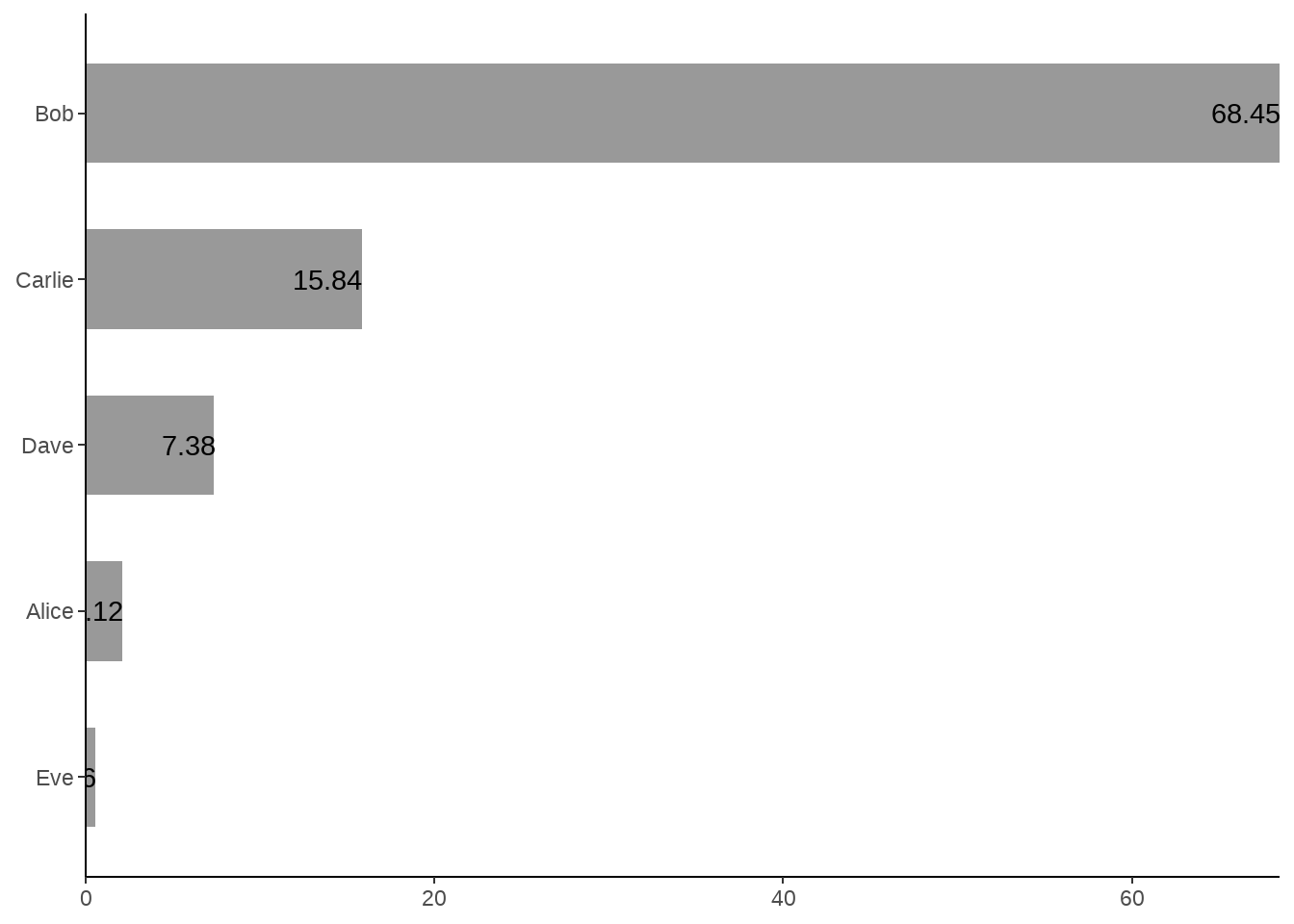
d %>%
ggplot(aes(x = value, y = fct_reorder(name, value)) ) +
geom_col(width = 0.6, fill = "gray60") +
geom_text(aes(label = value, hjust = ifelse(value > 50, 1, -.1)) ) +
theme_classic() +
scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL)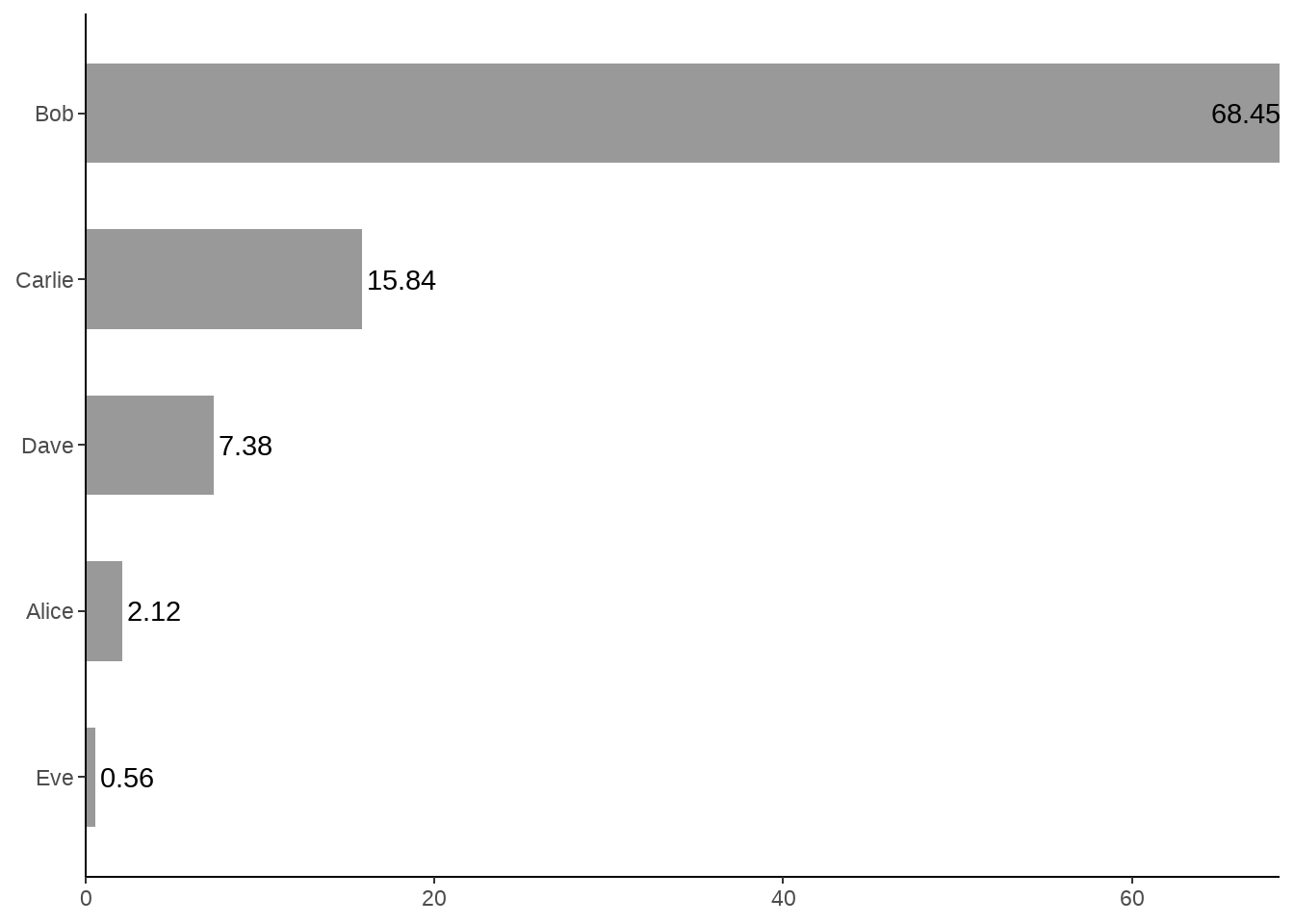
d %>%
ggplot(aes(x = value, y = fct_reorder(name, value)) ) +
geom_col(width = 0.6, fill = "darkorange") +
geom_text(
aes(
label = if_else(value < 1, "<1%", paste0(round(value, digits = 1), "%")),
hjust = if_else(value > 50, 1, -.1)
)) +
theme_classic() +
scale_x_continuous(expand = c(0, 1)) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL)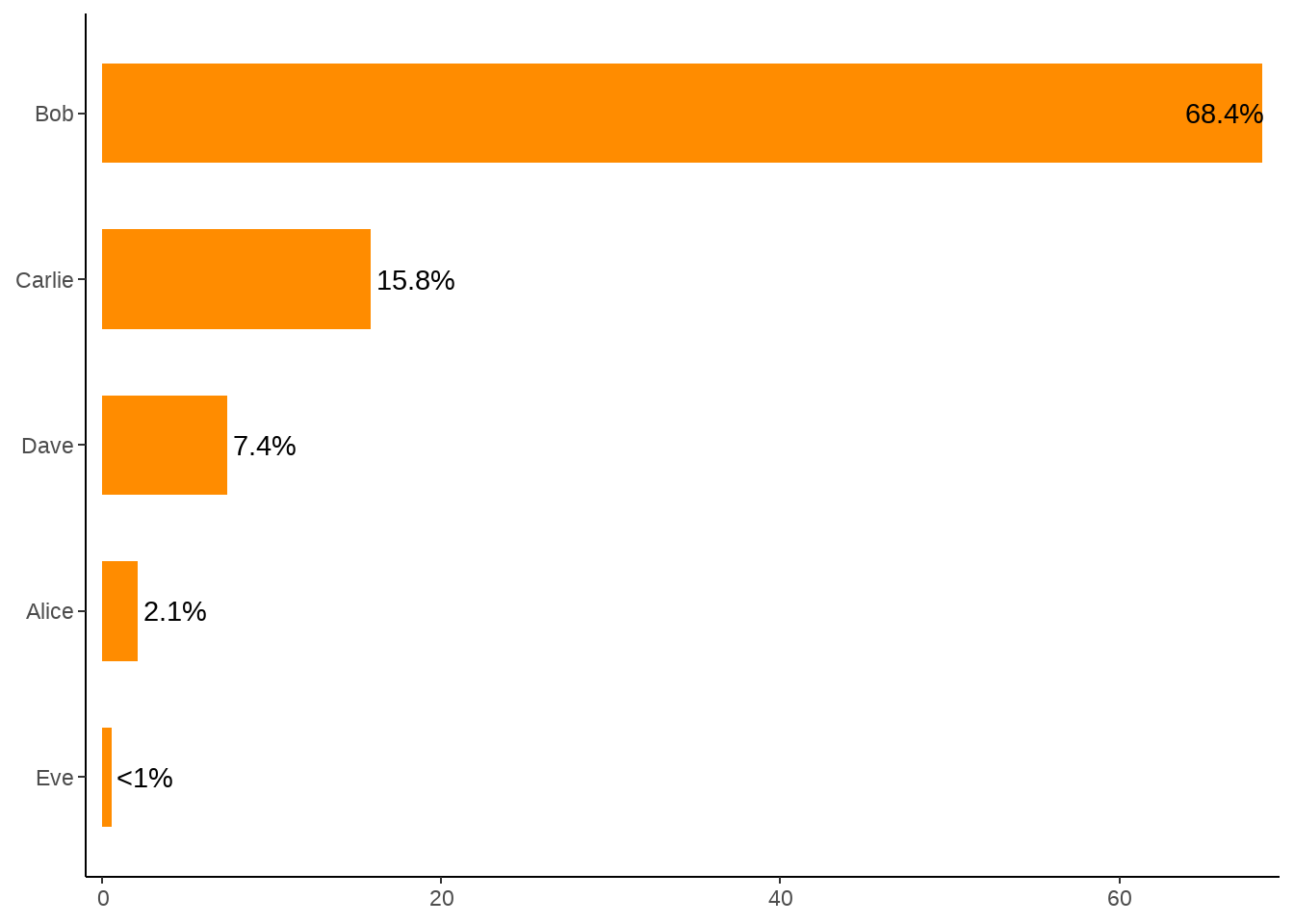
34.5 stat_summary()中的fun和fun.data
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = species, y = bill_length_mm)) +
geom_point() +
stat_summary(fun = mean,
geom = "point", colour = "red", size = 5 )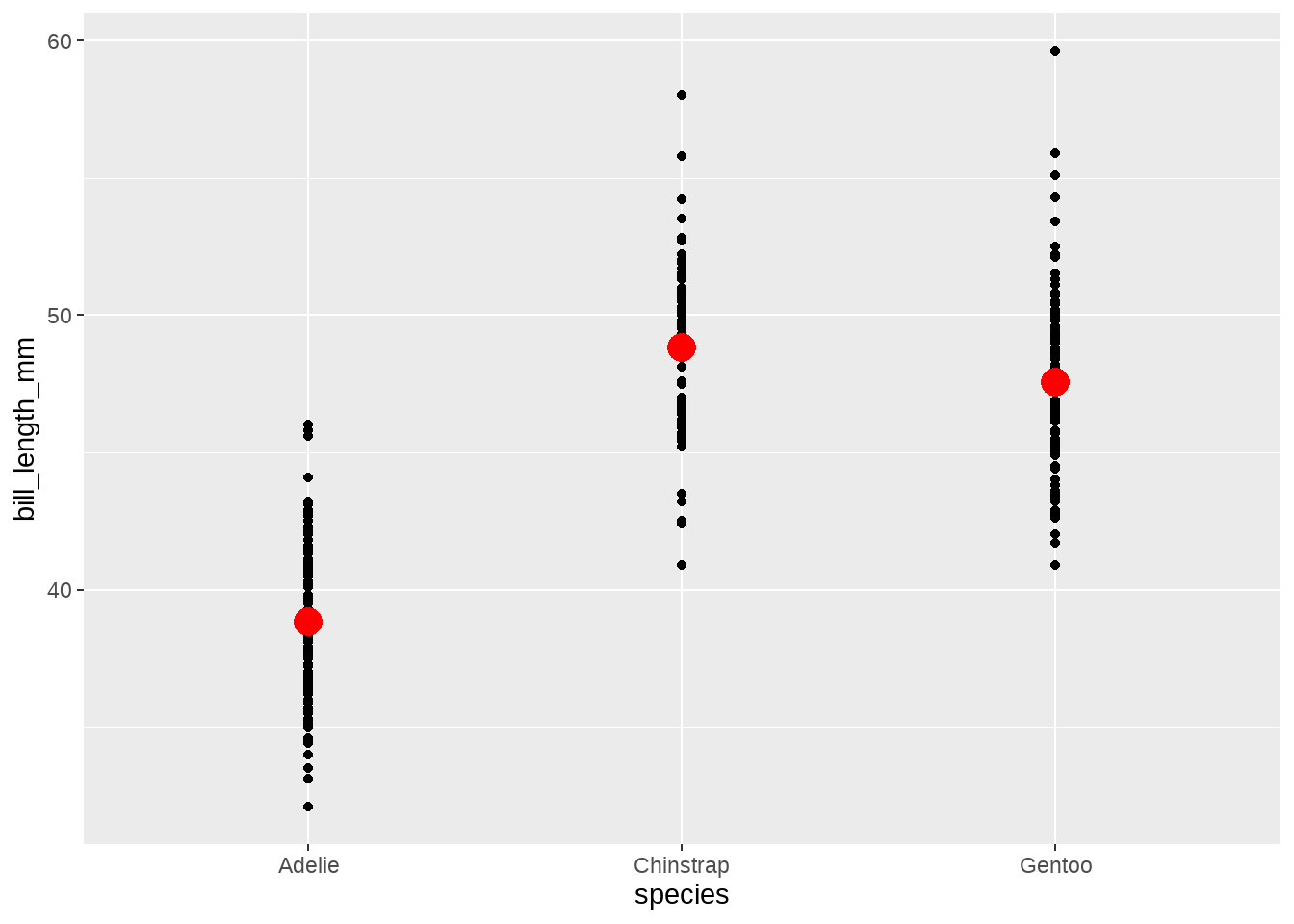
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = species, y = bill_length_mm)) +
geom_point() +
stat_summary(fun = function(x) max(x) - min(x),
geom = "point", colour = "red", size = 5 )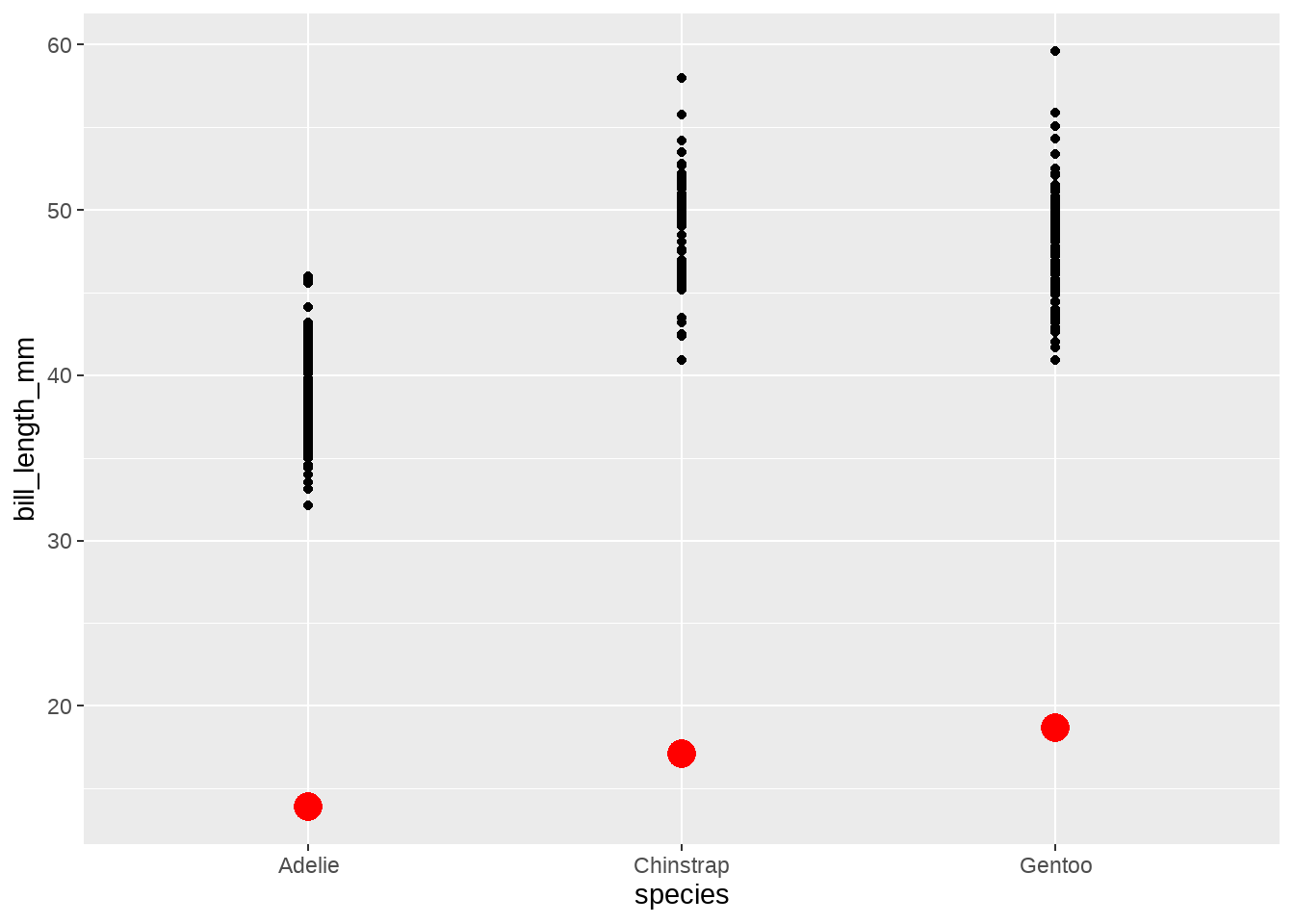
myfun <- function(x) {
tibble(
y = sum(x > mean(x))
)
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(species, body_mass_g)) +
stat_summary(
fun.data = myfun,
geom = "bar",
)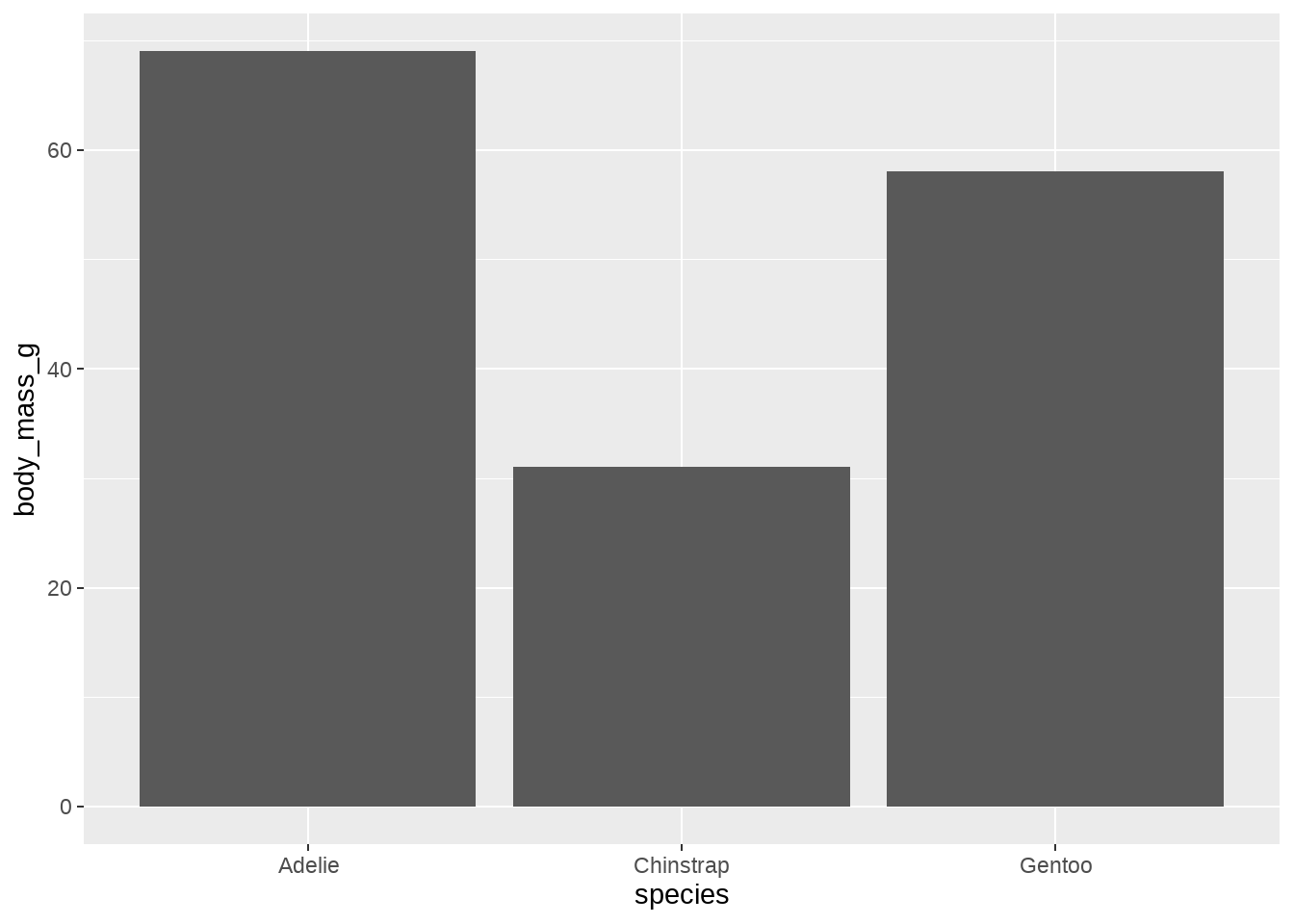
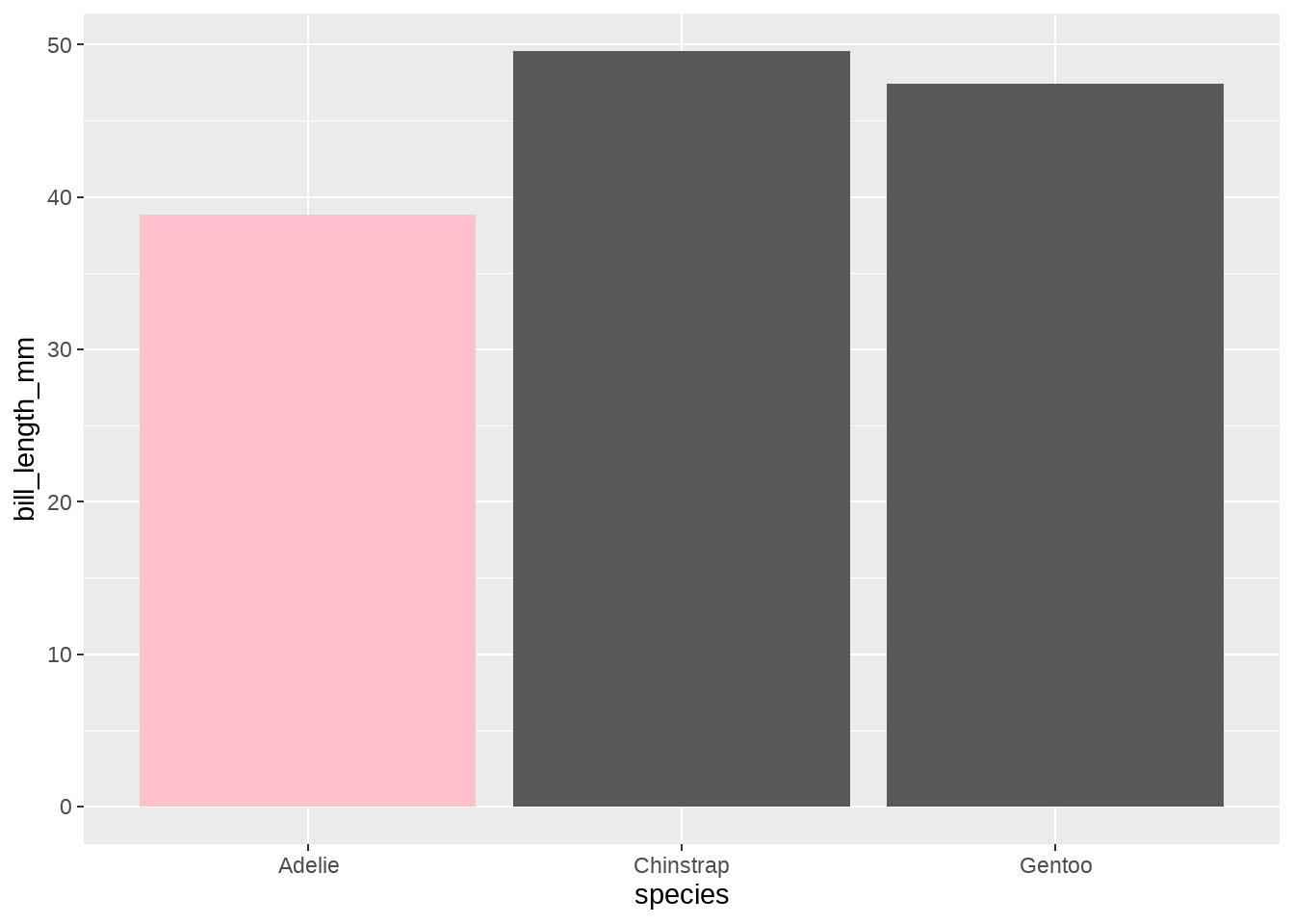
calc_median_and_color <- function(x, threshold = 40) {
tibble(y = median(x)) %>%
mutate(fill = ifelse(y < threshold, "pink", "grey35"))
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(species, bill_length_mm)) +
stat_summary(
fun.data = calc_median_and_color,
geom = "bar"
)
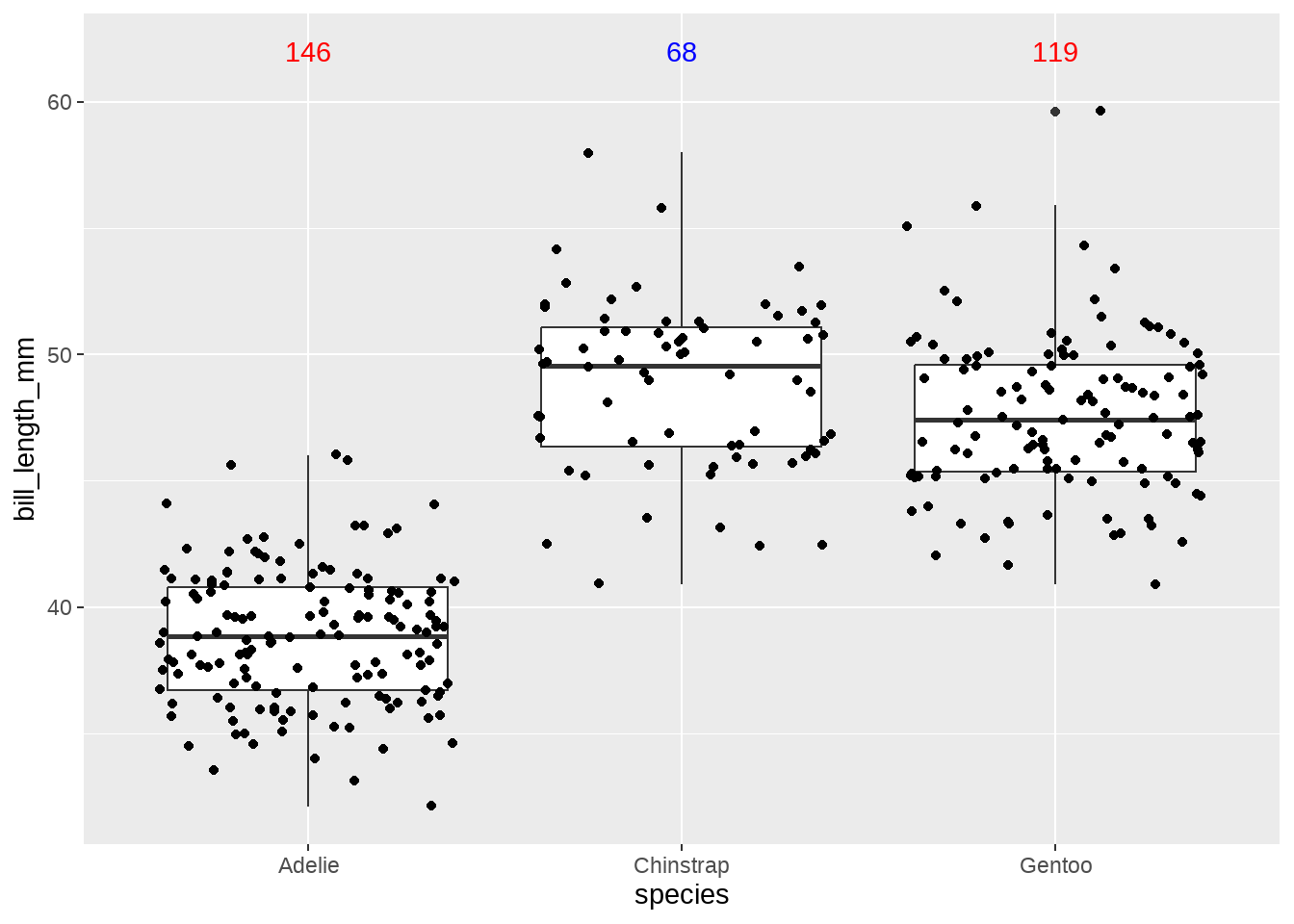
n_fun <- function(x) {
data.frame(y = 62,
label = length(x),
color = ifelse(length(x) > 100, "red", "blue")
)
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = species, y = bill_length_mm)) +
geom_boxplot() +
geom_jitter() +
stat_summary(
fun.data = n_fun,
geom = "text"
)
34.6 theme()中element_text()
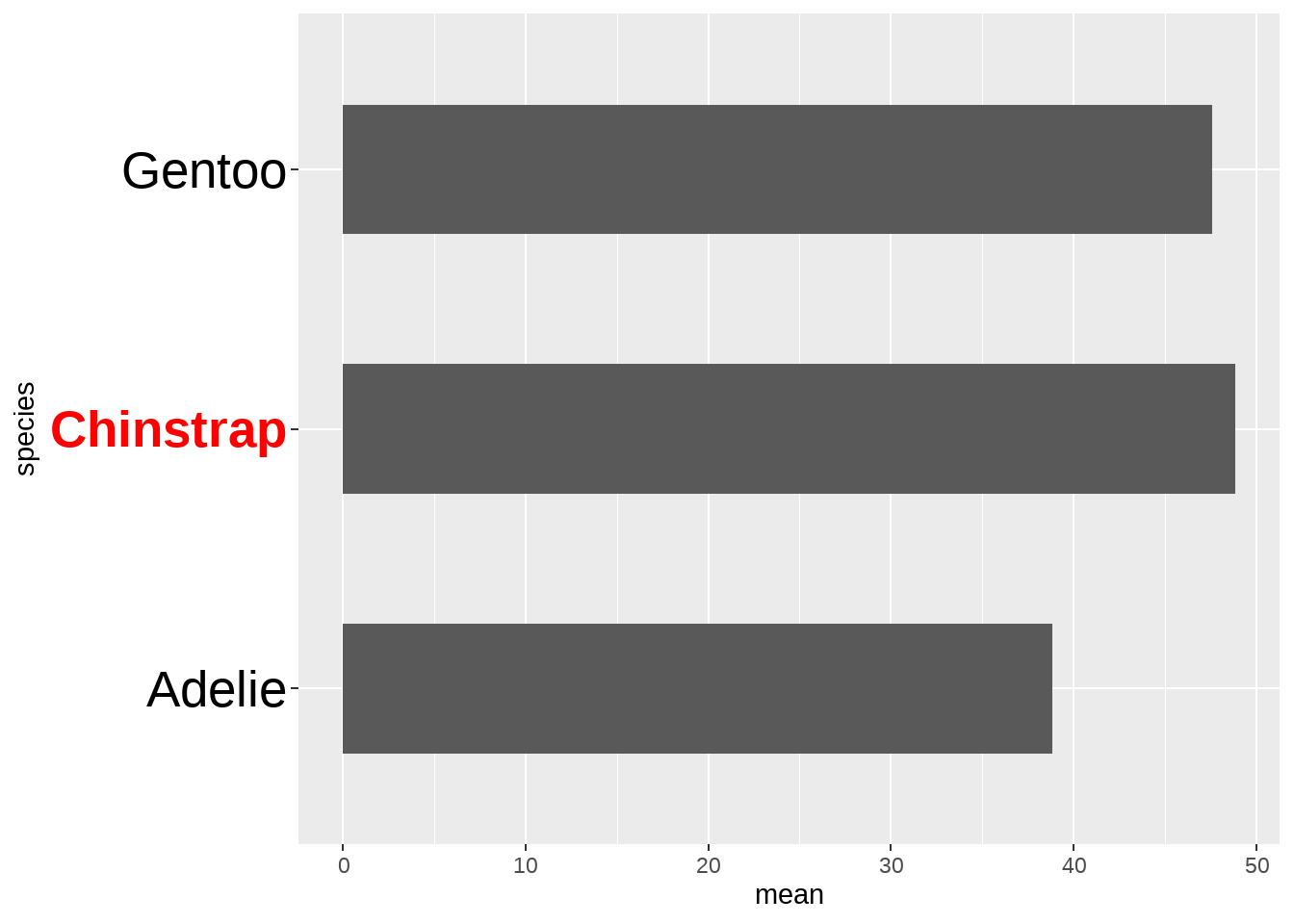
penguins_df <- penguins %>%
group_by(species) %>%
summarize(mean = mean(bill_length_mm))
penguins_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = mean, y = species)) +
geom_col(width = 0.5) +
theme(
axis.text.y = element_text(
color = c("black", "red", "black"),
face = c("plain", "bold", "plain"),
size = 20
)
)
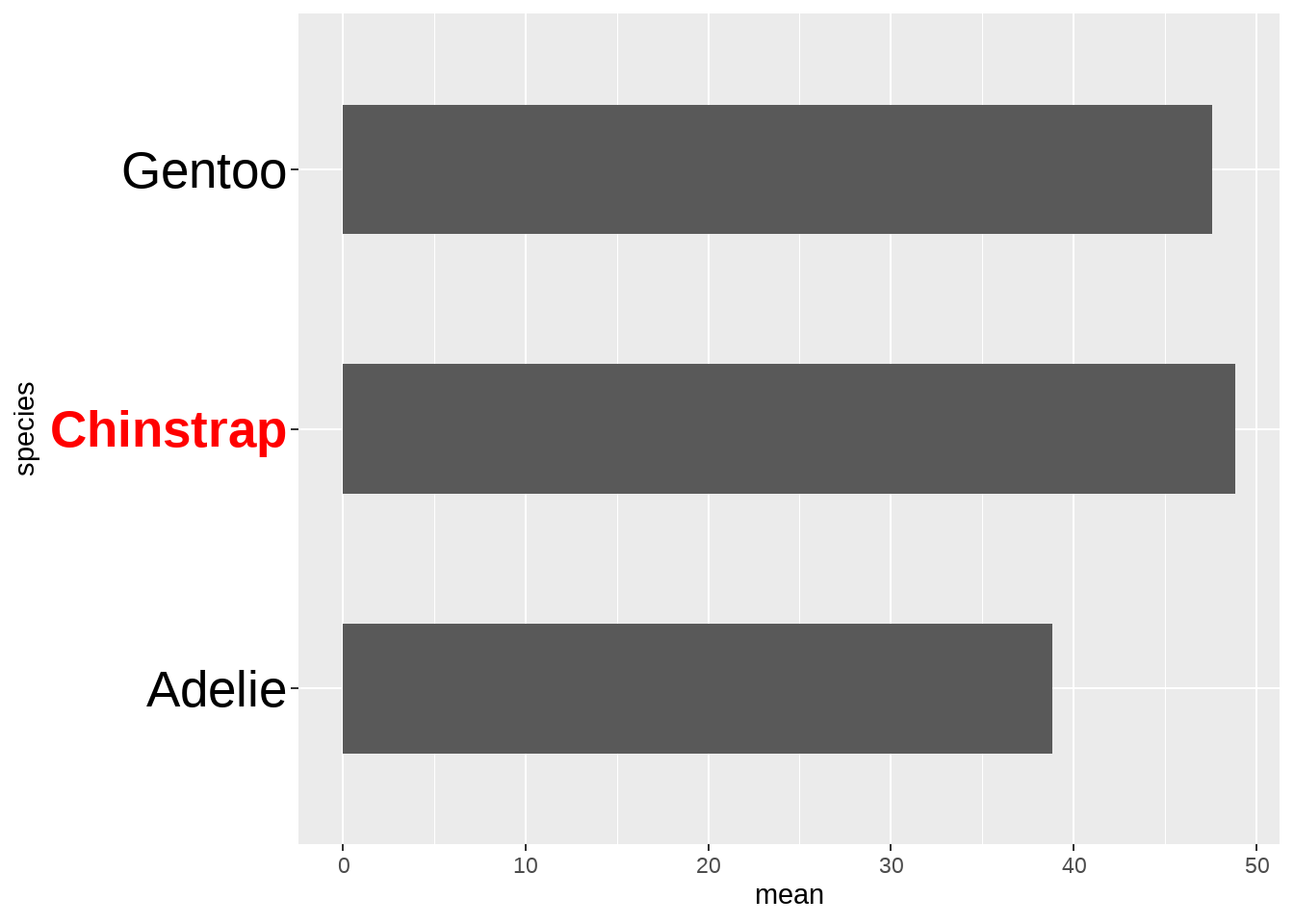
penguins_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = mean, y = species)) +
geom_col(width = 0.5) +
theme(
axis.text.y = element_text(
color = if_else(penguins_df$mean > 48, "red", "black"),
face = if_else(penguins_df$mean > 48, "bold", "plain"),
size = 20
)
)
34.7 facet_wrap()中的labeller
labeller =可以是函数。函数的参数是一个数据框,分组变量的若干层级是数据框的一列(多个分组就对应数据框的多列)。函数返回列表或者字符串类型的数据框。
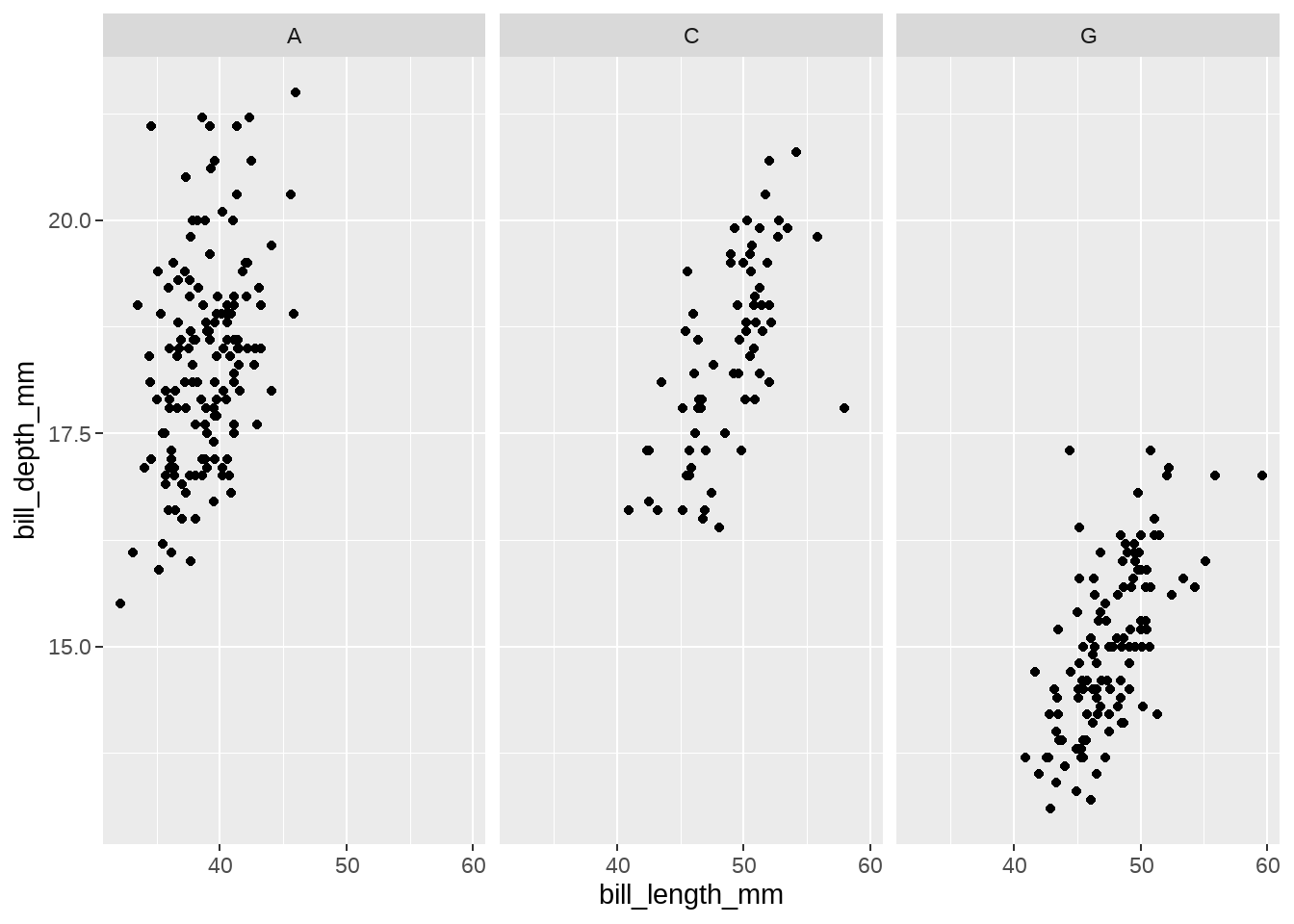
penguins %>%
distinct(species) %>%
as.data.frame()## species
## 1 Adelie
## 2 Gentoo
## 3 Chinstrap
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), # dataframe of the names are passed to labeller
labeller = function(df) {
ls <- str_sub(df[, 1], 1, 1) # df[, 1] is character vector
list(ls) # return list
}
)
相当于
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species),
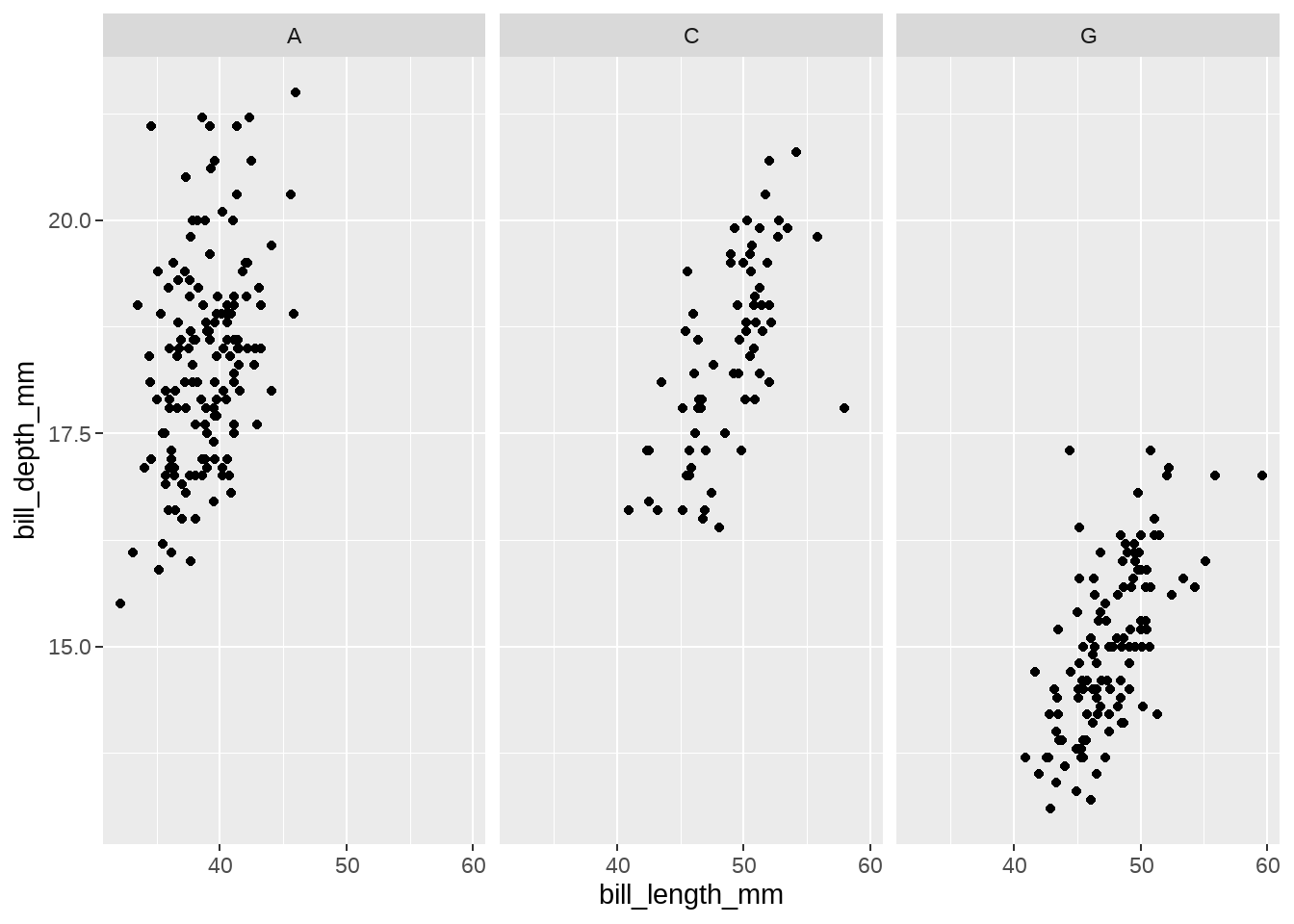
labeller = function(df) {
list(c(
Adelie = "A",
Chinstrap = "C",
Gentoo = "G"
))
}
)
species_names <- list(
"Adelie" = "Adelie, n = 146",
"Chinstrap" = "Chinstrap, n = 68",
"Gentoo" = "Gentoo, n = 119"
)
plot_labeller <- function(variable, value) { # does not use dataframe of labels
return(species_names[value]) # just return list
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), labeller = plot_labeller)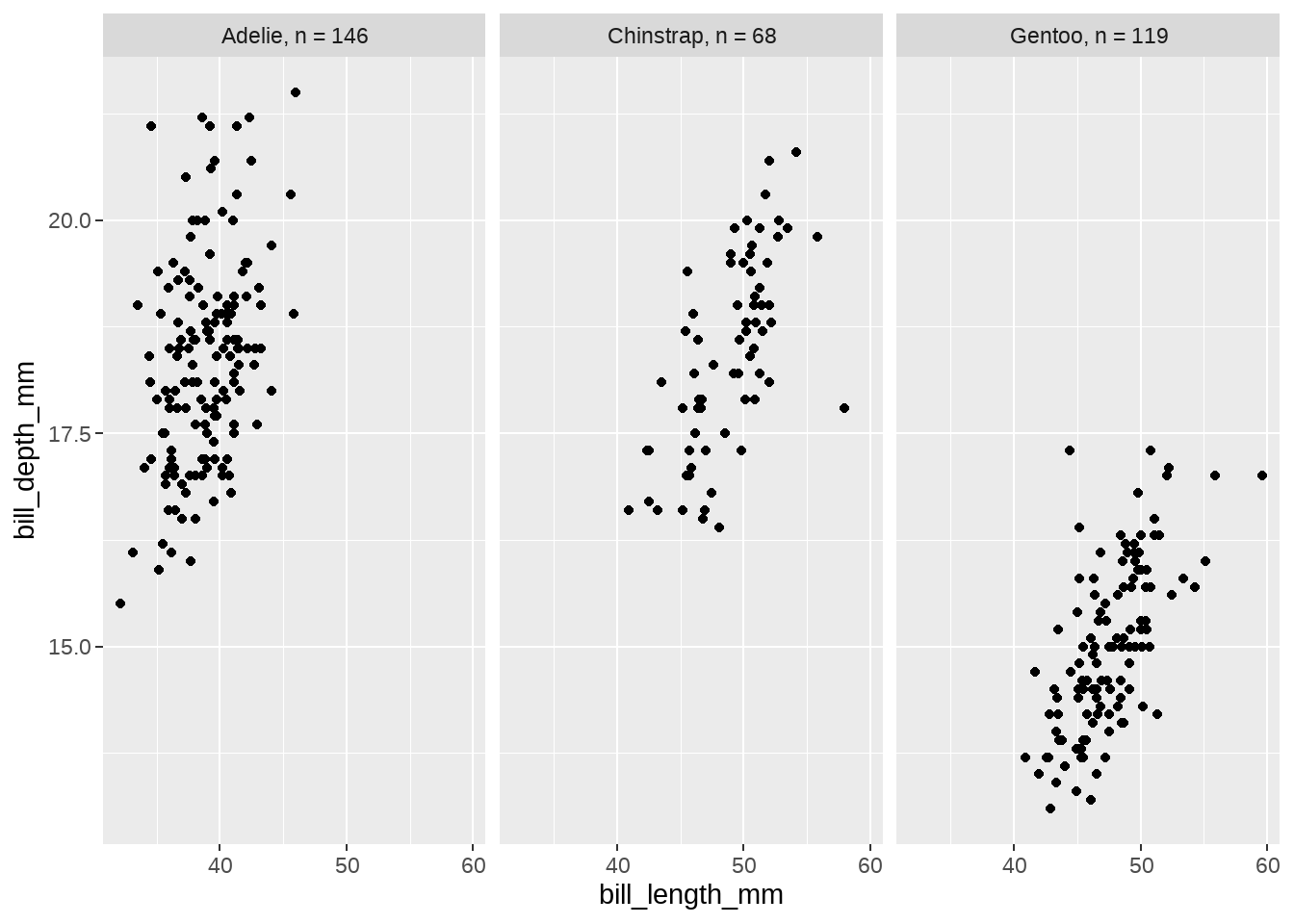
mylabel <- function(value) {
return(lapply(value, function(x) species_names[x]))
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), labeller = mylabel)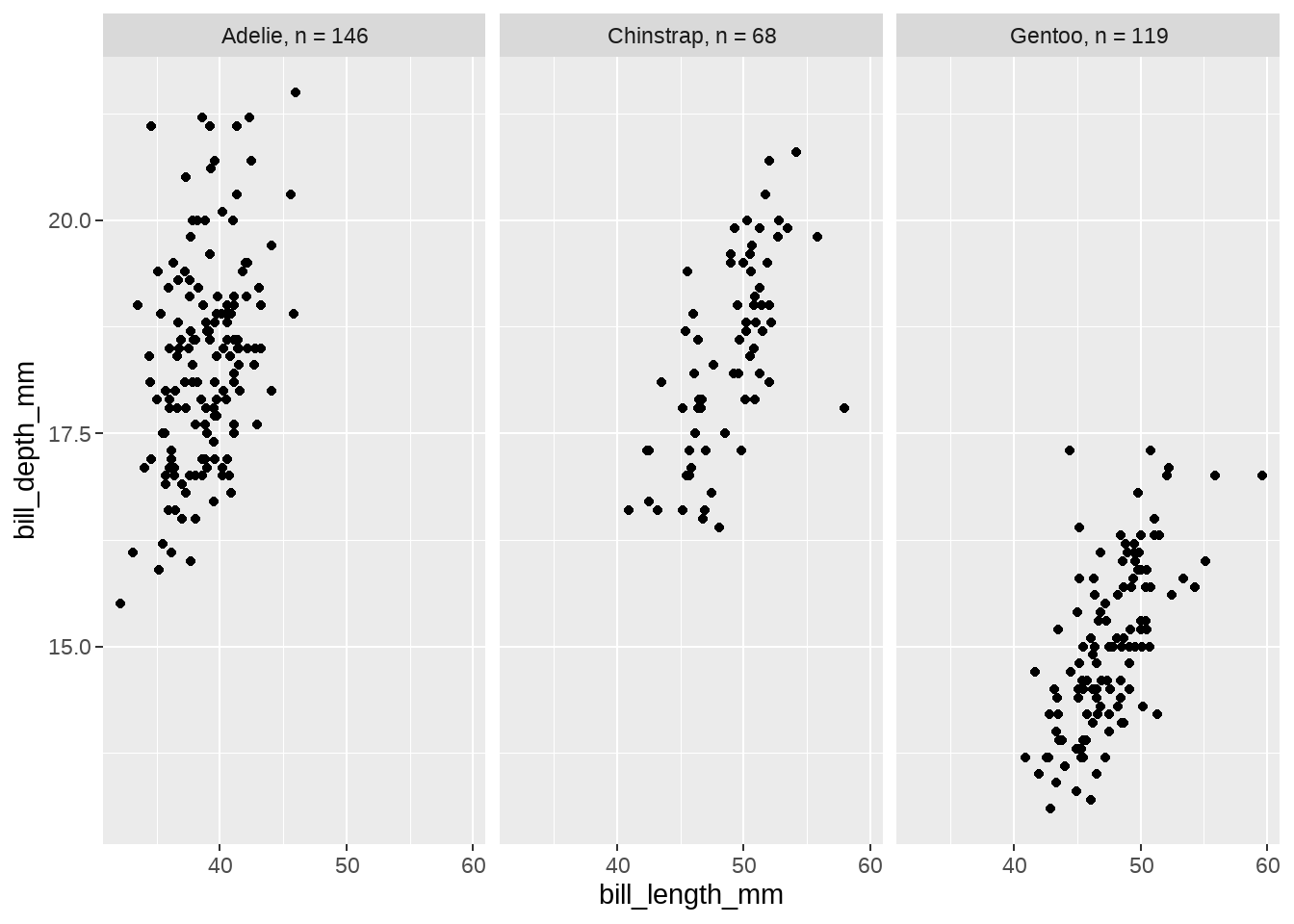
34.7.1 使用as_labeller()
使用配套的as_labeller(),更加简单清晰。因为只需要把命名向量传给as_labeller(),as_labeller()将其视为查询表一样,一一对应完成替换即可。如果传给as_labeller()不是向量,而是函数,就让这个函数作用到原来的标签上,返回新的字符串向量。
把处理列表的问题,变成了我们熟悉的向量的问题
species_names <- c(
"Adelie" = "Adelie, n =146",
"Chinstrap" = "Chinstrap, n =68",
"Gentoo" = "Gentoo, n =119"
)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), labeller = as_labeller(species_names))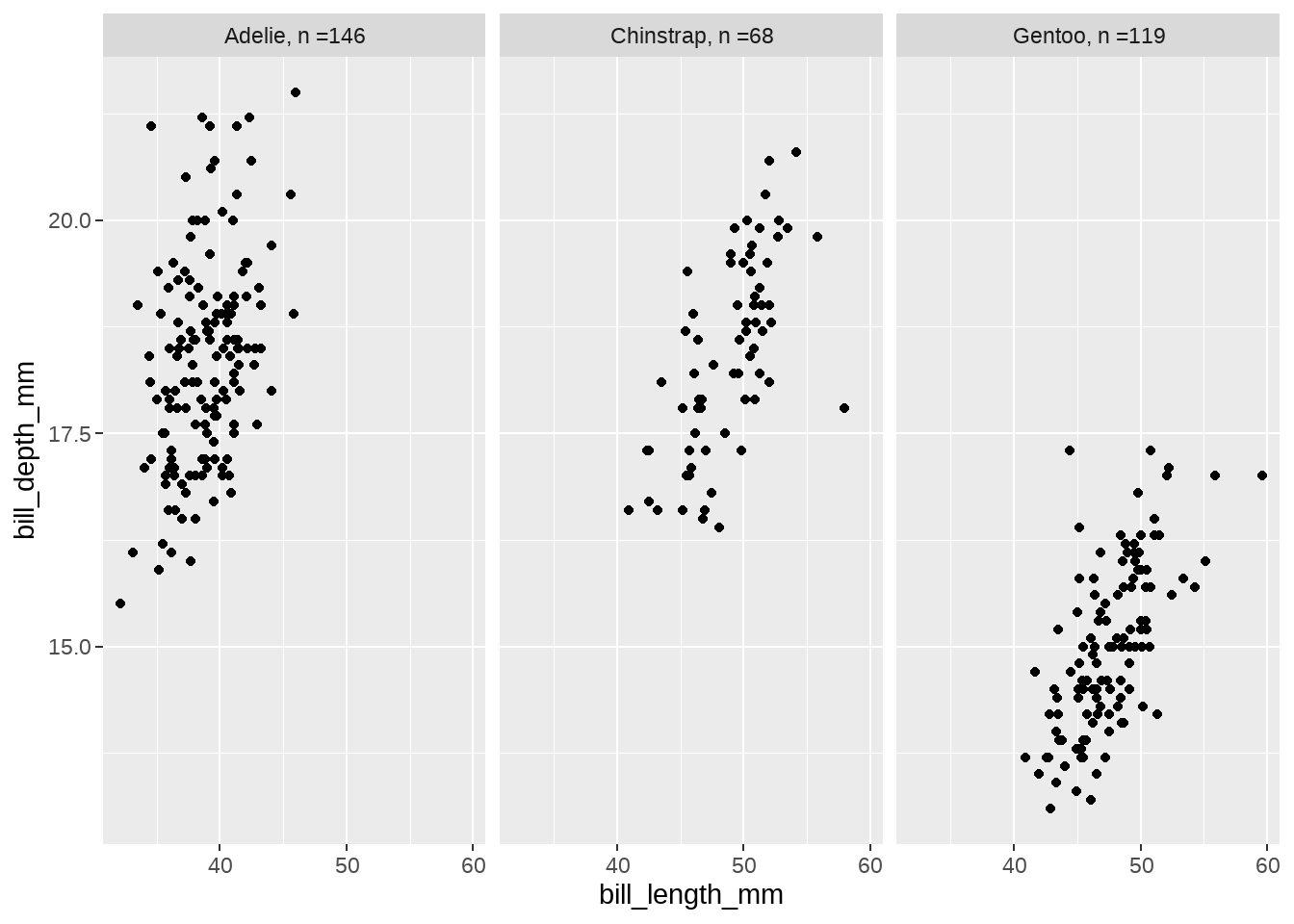
new_label <- penguins %>%
count(species) %>%
mutate(n = paste0(species, ", n =", n)) %>%
tibble::deframe()
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), labeller = as_labeller(new_label))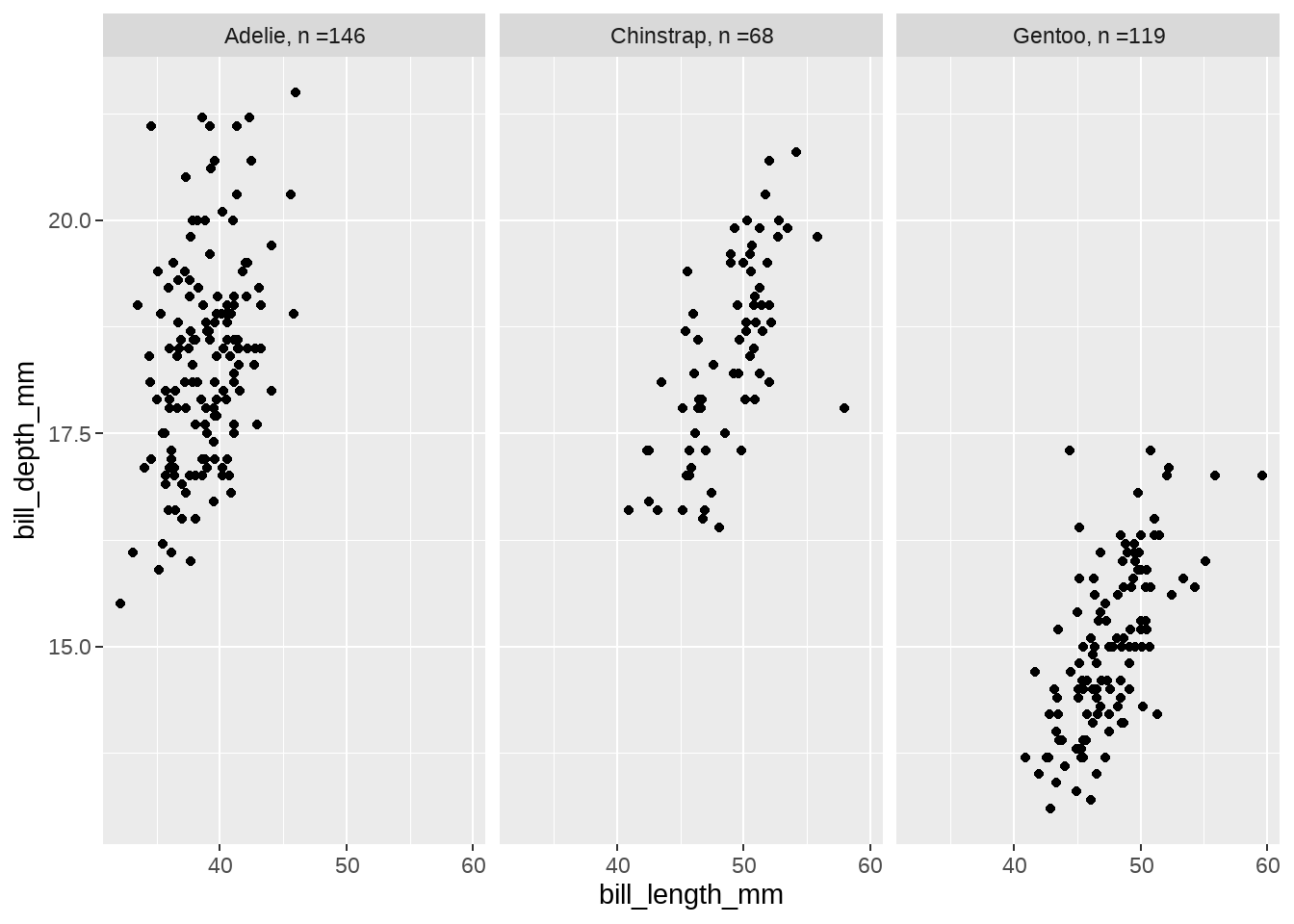
appender <- function(string, suffix = "-foo") paste0(string, suffix)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), labeller = as_labeller(appender))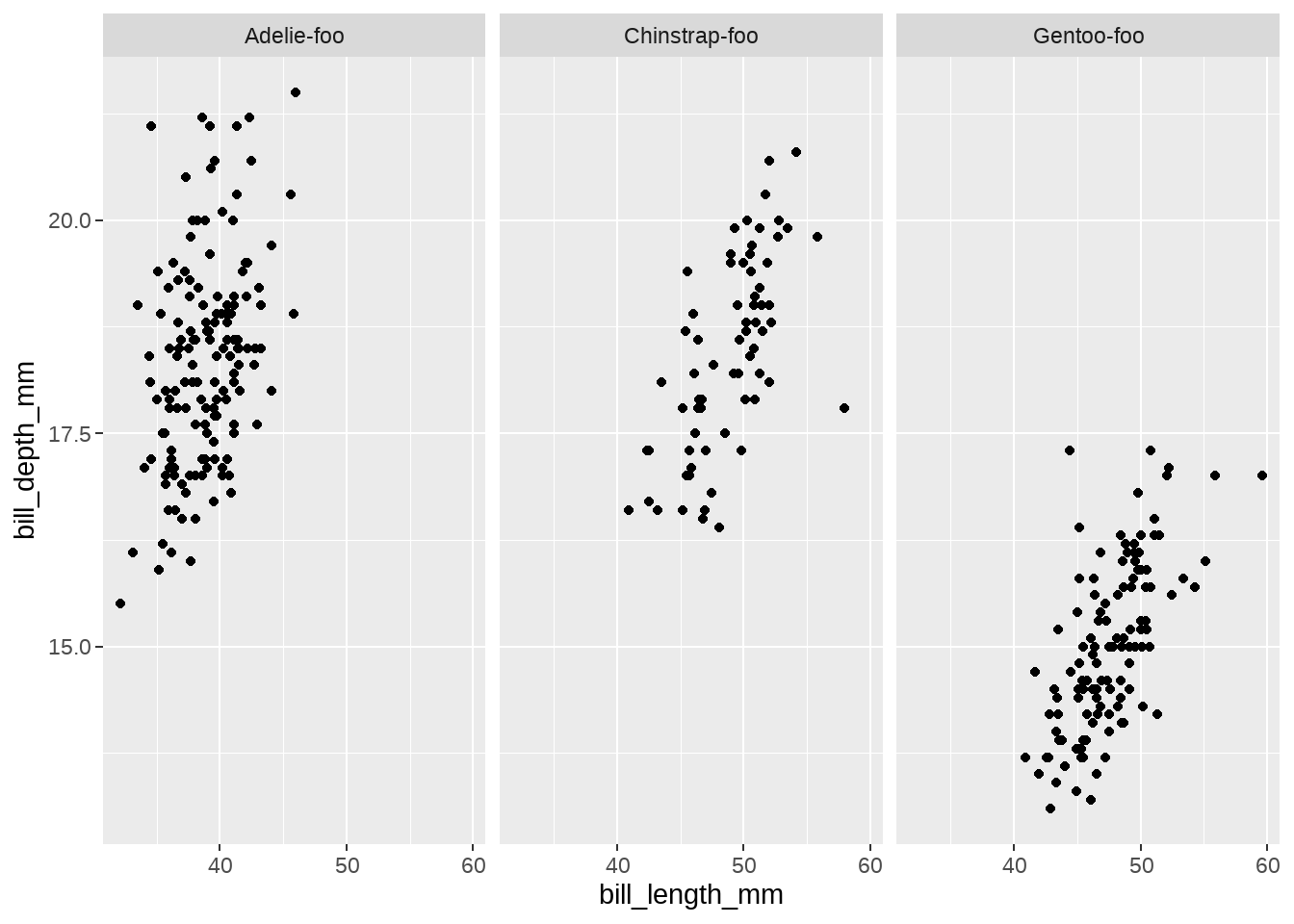
fun <- function(string) str_sub(string, 1, 1)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species), labeller = as_labeller(fun))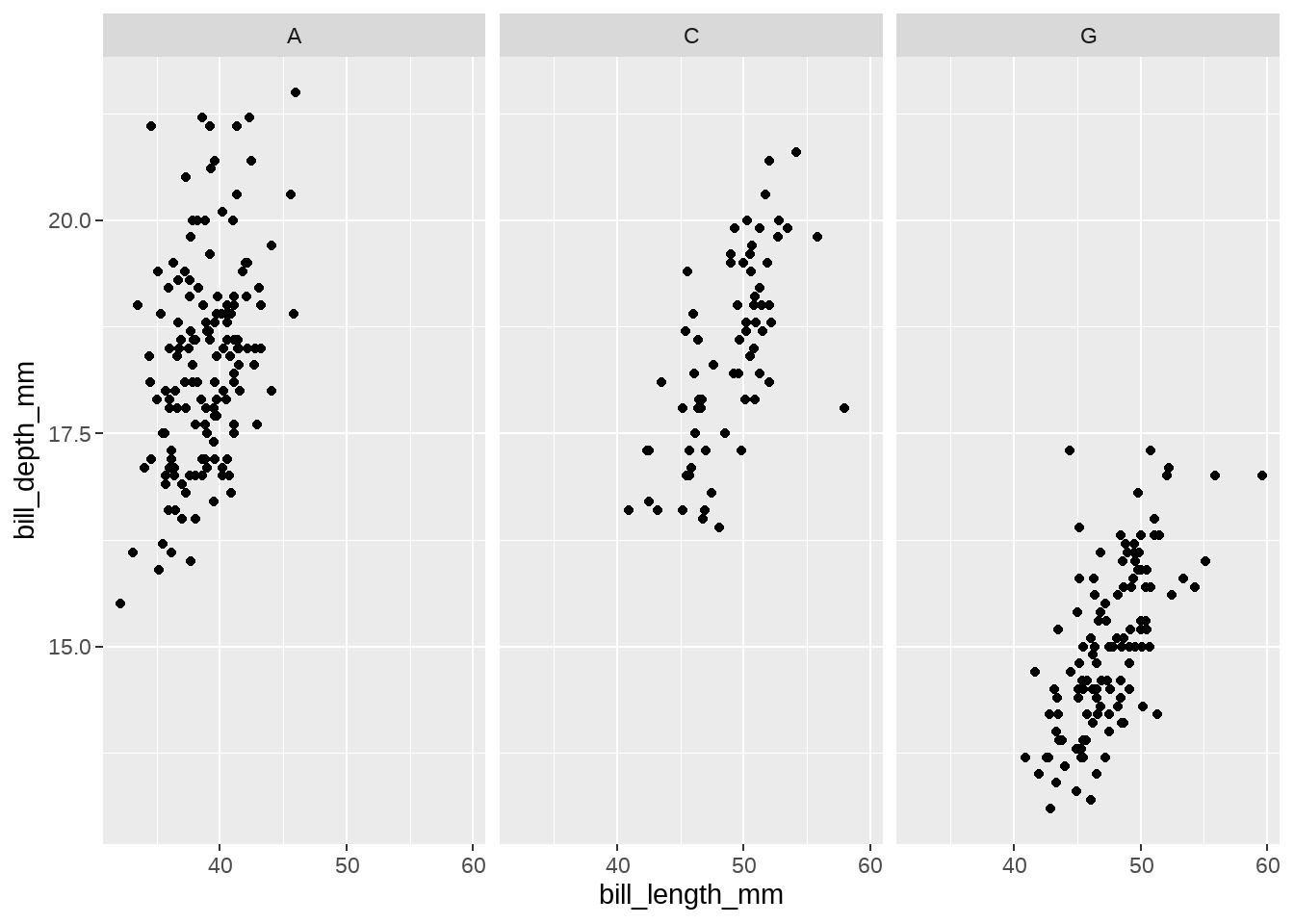
34.7.2 多个分组变量
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species, island))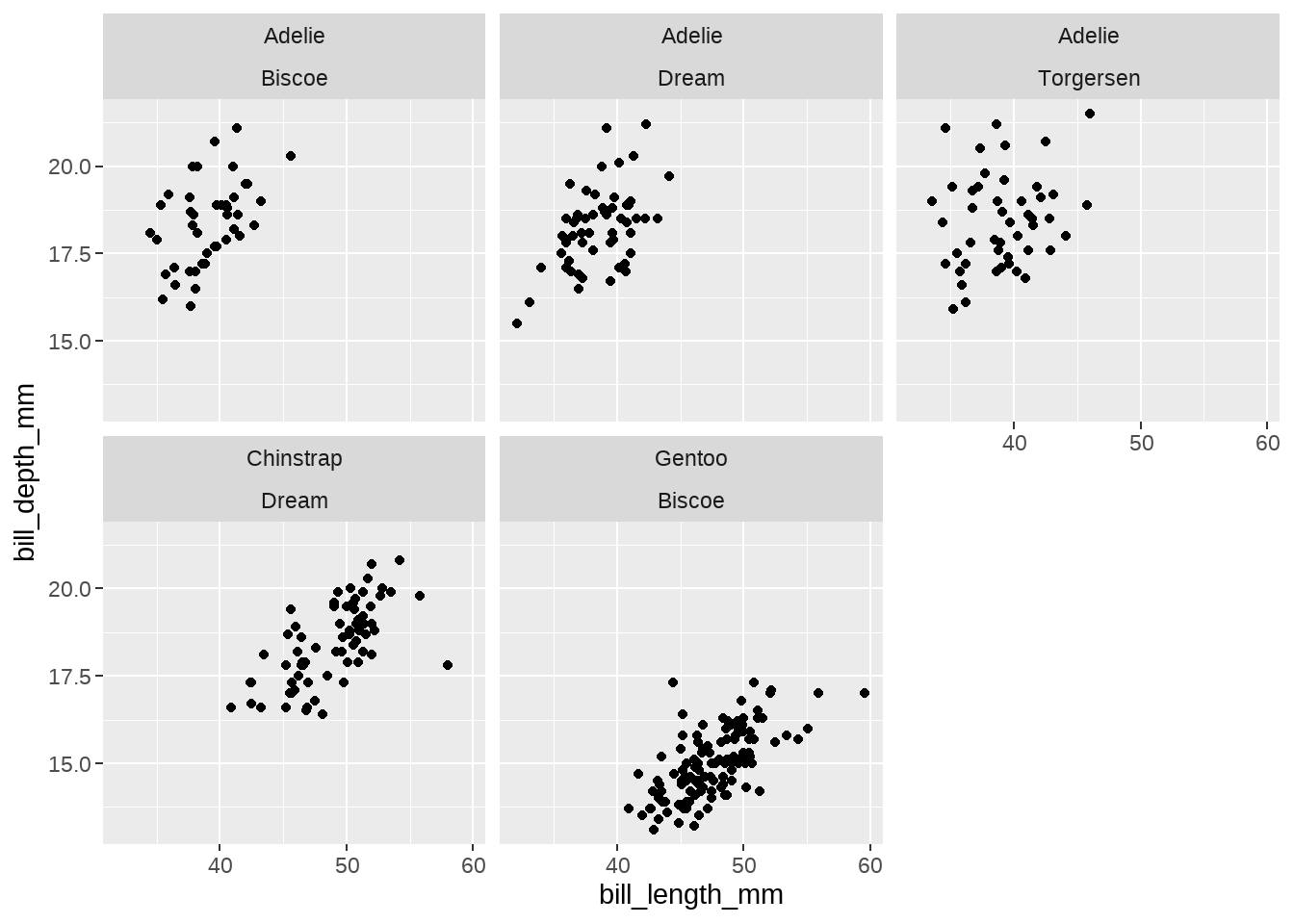
## # A tibble: 5 × 2
## species island
## <fct> <fct>
## 1 Adelie Biscoe
## 2 Adelie Dream
## 3 Adelie Torgersen
## 4 Chinstrap Dream
## 5 Gentoo Biscoe
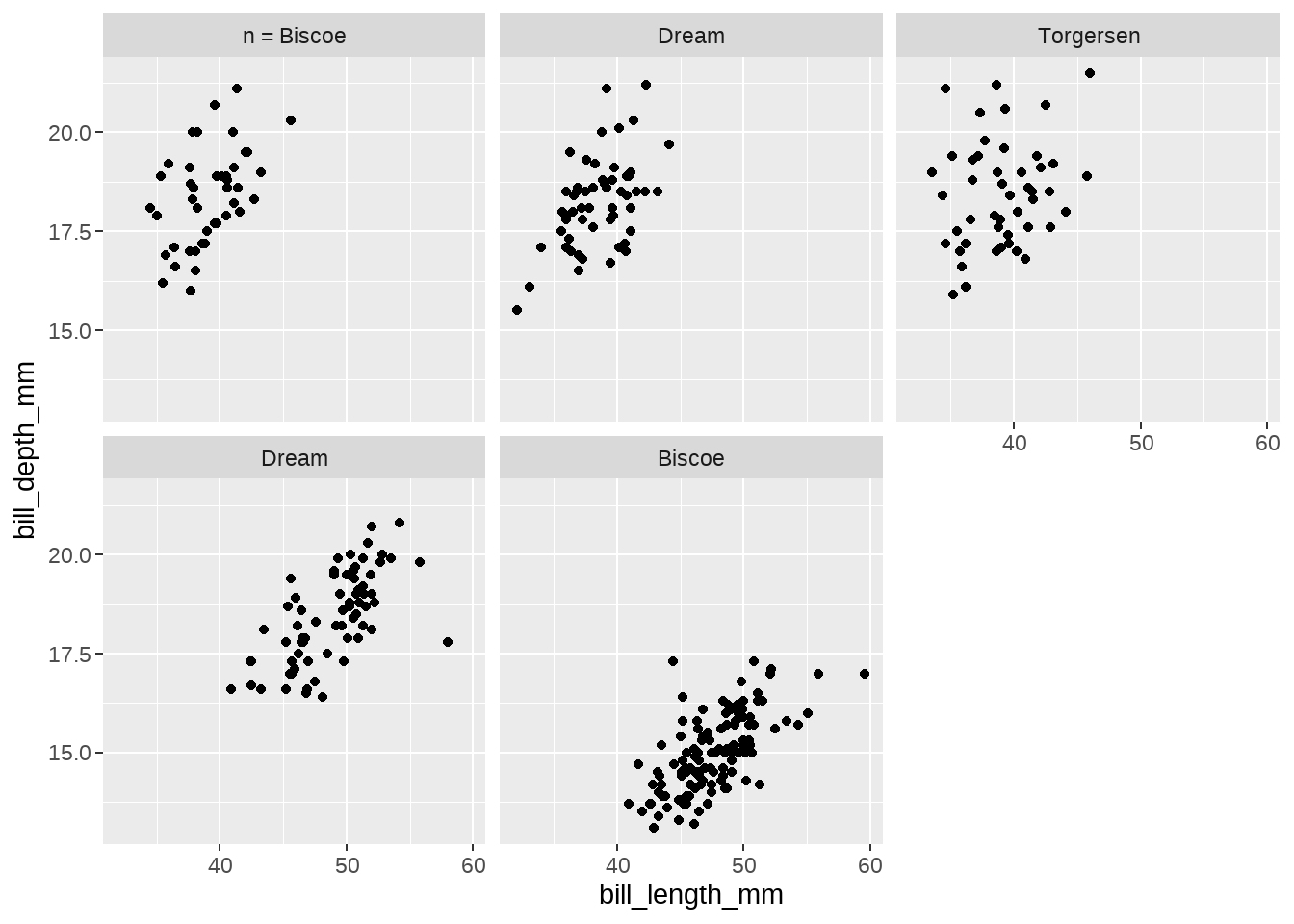
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(~ species + island, # or vars(species, island),
labeller = function(df) {
ls <- as.character(df[, 2])
ls[1] <- paste0("n = ", ls[1])
list(ls)
}
)
species_names <- list(
"Adelie" = "Adelie, n =146",
"Chinstrap" = "Chinstrap, n =68",
"Gentoo" = "Gentoo, n =119"
)
island_names <- list(
"Biscoe" = "B",
"Dream" = "D",
"Torgersen" = "T"
)
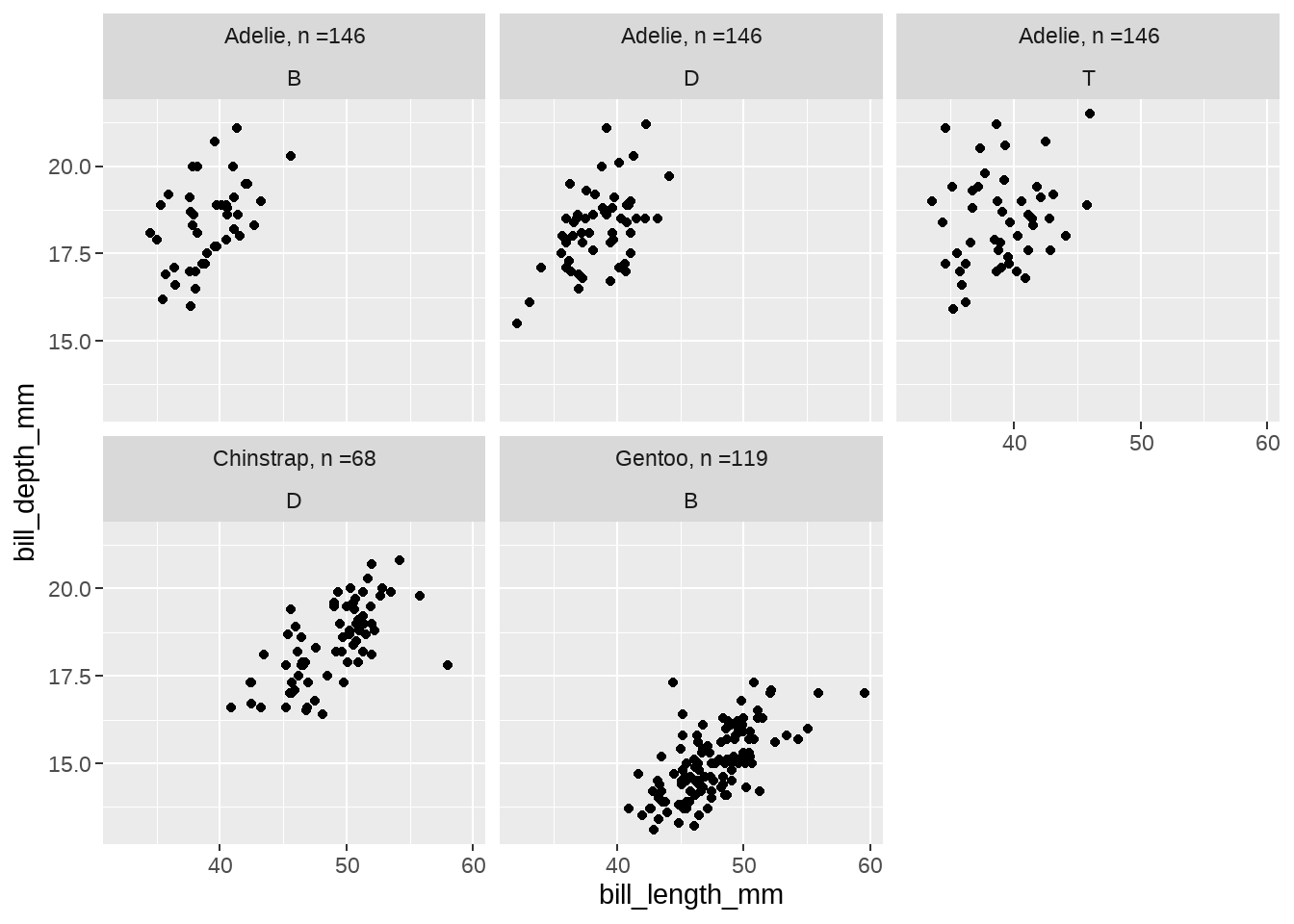
plot_labeller <- function(variable,value){
if (variable == 'species') {
return(species_names[value])
} else if (variable == 'island') {
return(island_names[value])
} else {
return(as.character(value))
}
}
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(~ species + island,
labeller = plot_labeller
)
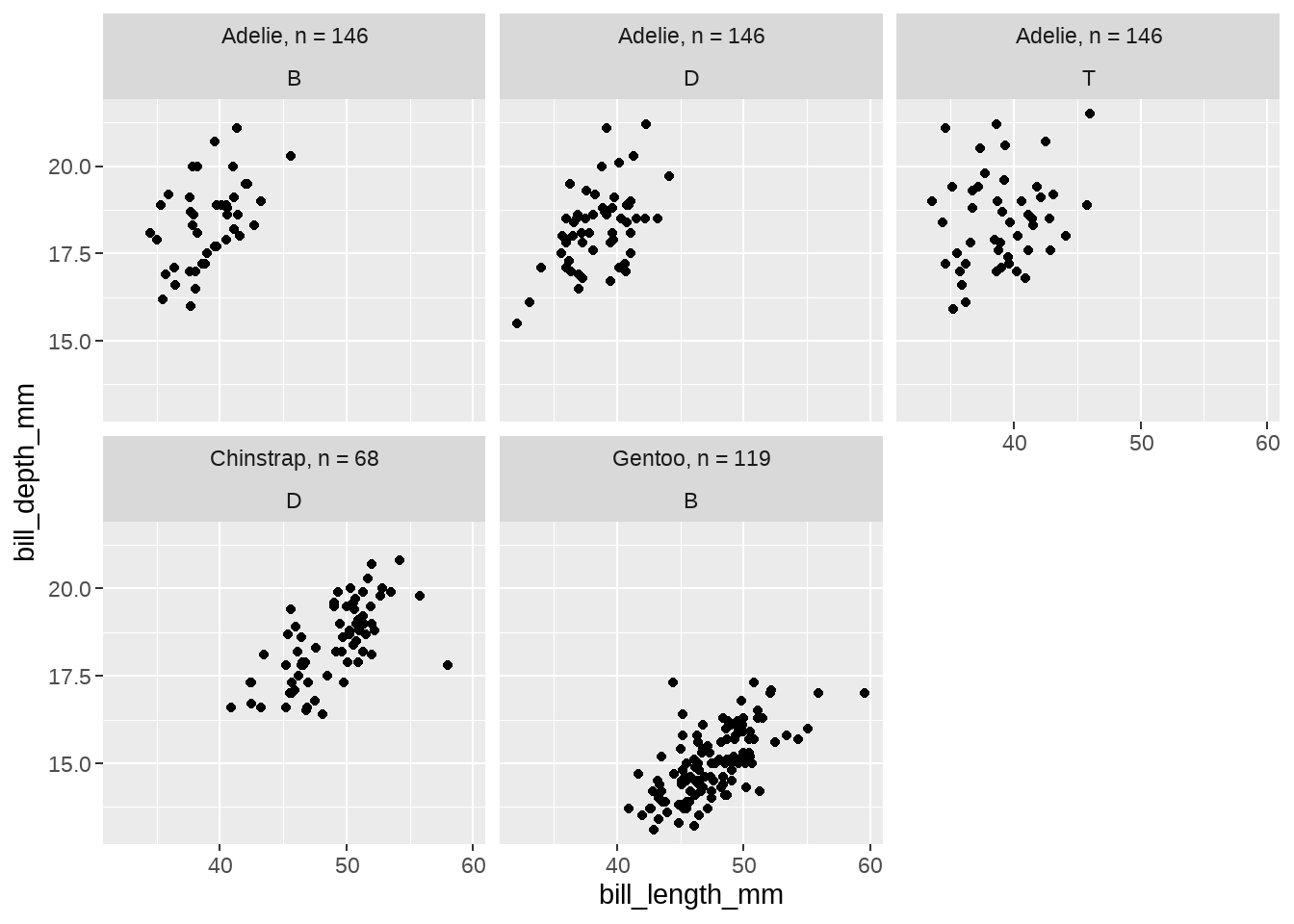
species_names <- c(
"Adelie" = "Adelie, n = 146",
"Chinstrap" = "Chinstrap, n = 68",
"Gentoo" = "Gentoo, n = 119"
)
fun <- function(string) stringr::str_sub(string, 1, 1)
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap(vars(species, island),
labeller = labeller(
species = as_labeller(species_names),
island = as_labeller(fun)
)
)
34.8 stat_function
df <- data.frame(x = 1:10, y = (1:10)^2)
ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) +
geom_point() +
stat_function(fun = ~ .x^2)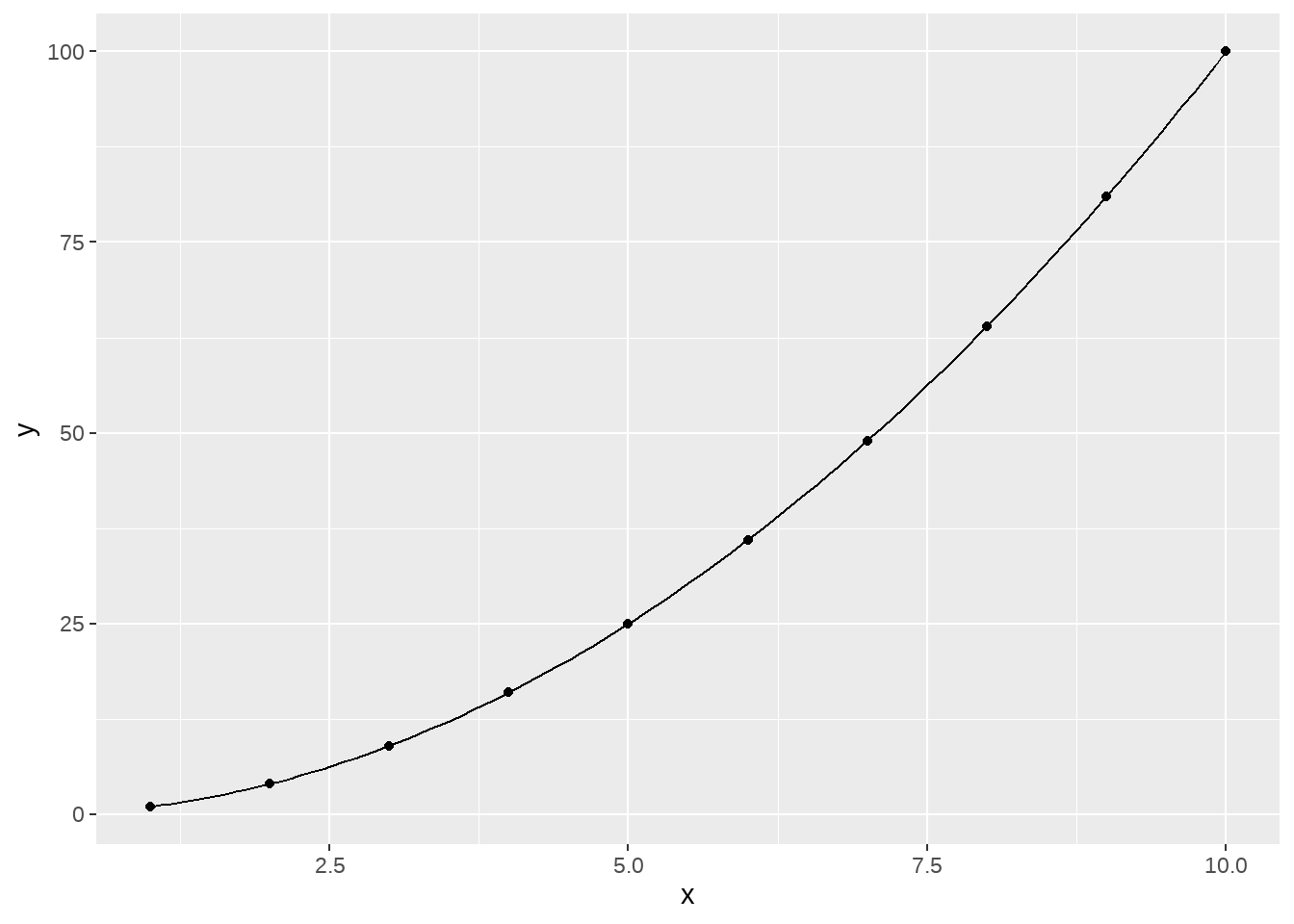
logisic <- function(x) {
exp(1)^x / (1 + exp(1) ^ x)
}
ggplot() +
xlim(-5, 5) +
geom_function(fun = logisic, color = "orange") +
theme_minimal()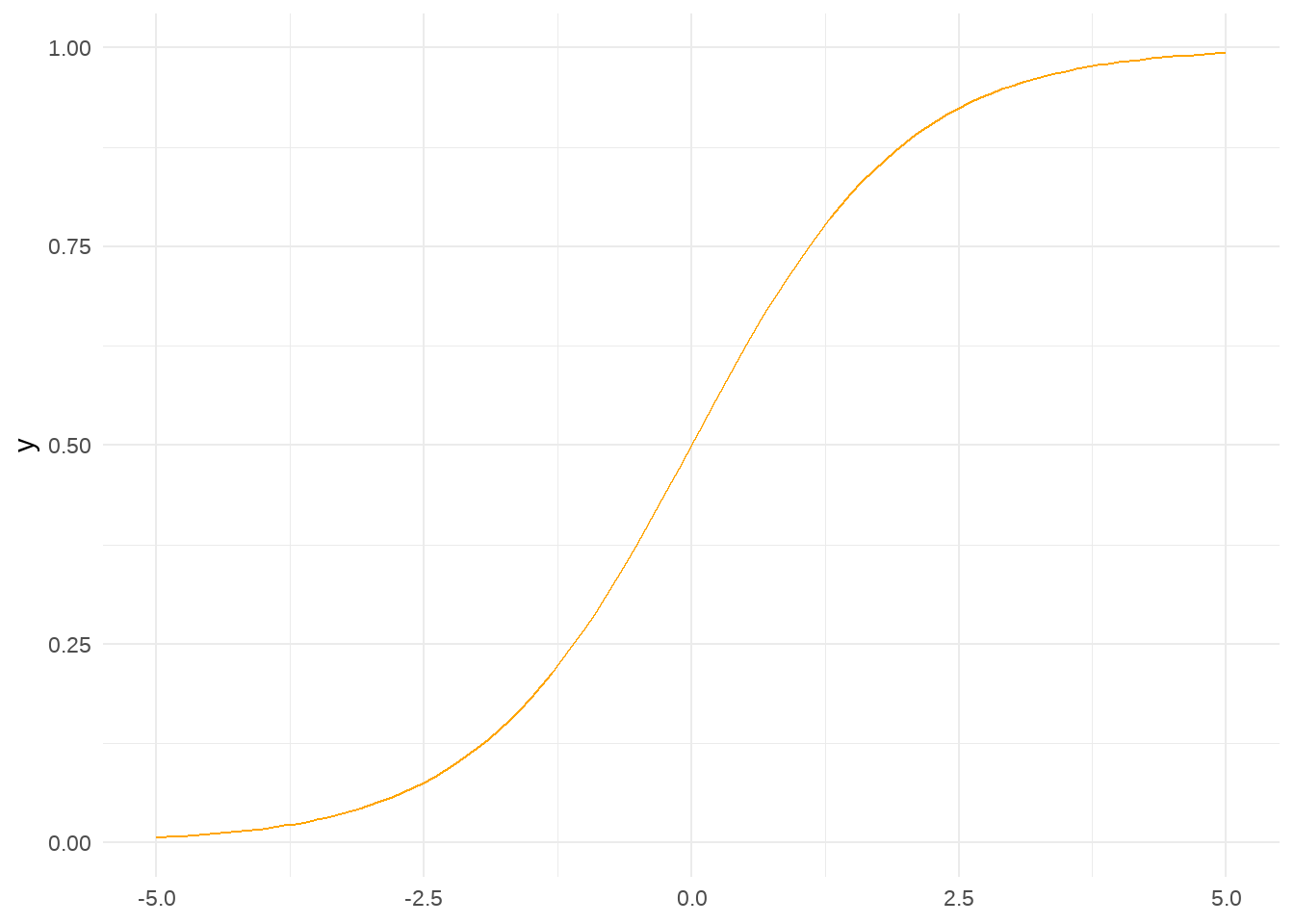
34.9 stat layer
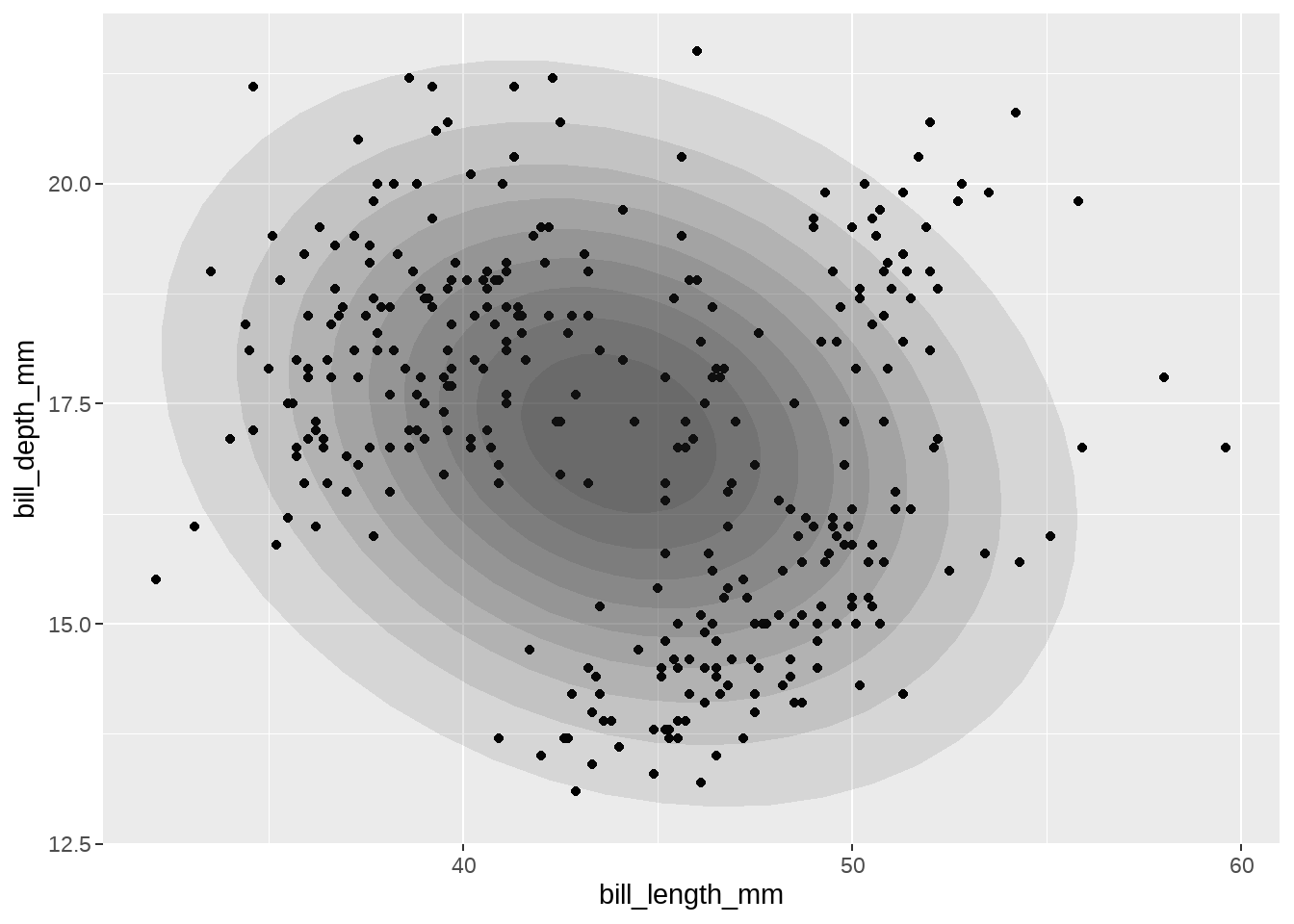
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point() +
purrr::map(
.x = seq(0.1, 0.9, by = 0.1),
.f = function(level) {
stat_ellipse(
geom = "polygon", type = "norm",
size = 0, alpha = 0.1, fill = "gray10",
level = level
)
}
)
layers <- penguins %>%
group_split(species) %>%
map(function(df) {
geom_point(
aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm),
alpha = 0.5,
data = df
)
})
ggplot() +
layers