第 74 章 抽样数据的规整与可视化
library(tidyverse)
library(tidybayes)
library(ggdist)
library(rstan)
rstan_options(auto_write = TRUE)
options(mc.cores = parallel::detectCores())在贝叶斯抽样样本量比较大,我们需要规整和可视化,就需要借助一些函数。这里简单介绍tidybayes宏包和它的姊妹宏包 ggdist,更多的技术参数见官方手册。
74.1 企鹅案例
问题简化,我们只挑选Gentoo类企鹅
## # A tibble: 119 × 8
## species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
## 1 Gentoo Biscoe 46.1 13.2 211 4500
## 2 Gentoo Biscoe 50 16.3 230 5700
## 3 Gentoo Biscoe 48.7 14.1 210 4450
## 4 Gentoo Biscoe 50 15.2 218 5700
## 5 Gentoo Biscoe 47.6 14.5 215 5400
## 6 Gentoo Biscoe 46.5 13.5 210 4550
## 7 Gentoo Biscoe 45.4 14.6 211 4800
## 8 Gentoo Biscoe 46.7 15.3 219 5200
## 9 Gentoo Biscoe 43.3 13.4 209 4400
## 10 Gentoo Biscoe 46.8 15.4 215 5150
## # ℹ 109 more rows
## # ℹ 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>先看下两个变量的关系
gentoo %>%
ggplot(aes(x = bill_length_mm, bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point()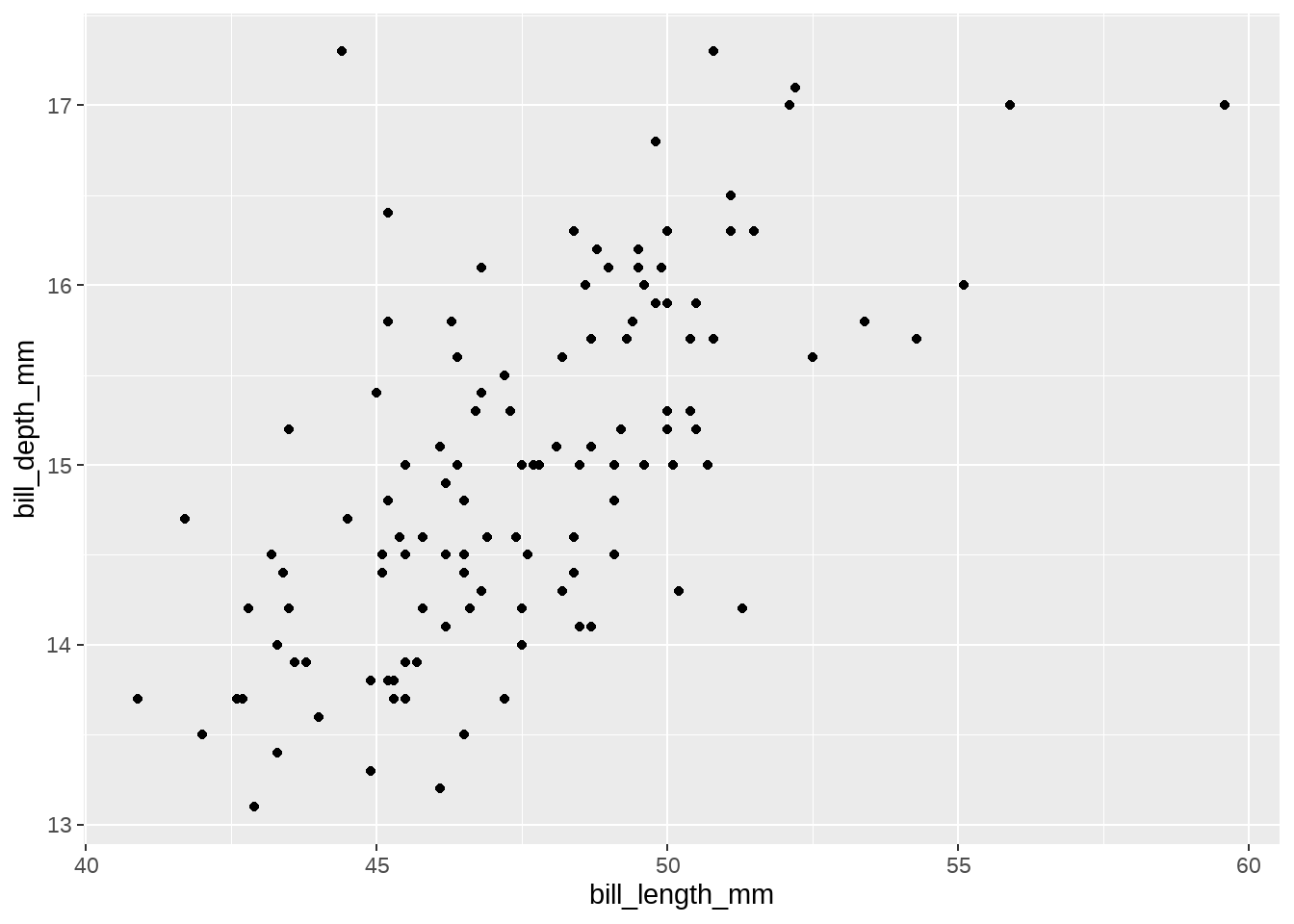
74.2 Stan模型
假设我们建立最简单的线性模型,其中预测因子bill_length_mm,被解释变量是 bill_depth_mm
\[ \begin{align} y_n &\sim \operatorname{normal}(\mu_n, \,\, \sigma)\\ \mu_n &= \alpha + \beta x_n \end{align} \]
stan_program <- "
data {
int<lower=0> N;
vector[N] y;
vector[N] x;
int<lower=0> M;
vector[M] new_x;
}
parameters {
real alpha;
real beta;
real<lower=0> sigma;
}
model {
y ~ normal(alpha + beta * x, sigma);
alpha ~ normal(0, 10);
beta ~ normal(0, 10);
sigma ~ exponential(1);
}
generated quantities {
vector[M] y_fit;
vector[M] y_rep;
for (n in 1:M) {
y_fit[n] = alpha + beta * new_x[n];
y_rep[n] = normal_rng(alpha + beta * new_x[n], sigma);
}
}
"
library(modelr)
newdata <- gentoo %>%
data_grid(
bill_length_mm = seq_range(bill_length_mm, 100)
)
# or
# newdata <- data.frame(
# bill_length_mm = seq(min(gentoo$bill_length_mm), max(gentoo$bill_length_mm), length.out = 100)
# )
stan_data <- list(
N = nrow(gentoo),
x = gentoo$bill_length_mm,
y = gentoo$bill_depth_mm,
M = nrow(newdata),
new_x = newdata$bill_length_mm
)
fit <- stan(model_code = stan_program, data = stan_data)74.3 抽样
draws <- fit %>%
tidybayes::gather_draws(alpha, beta, sigma)
draws## # A tibble: 12,000 × 5
## # Groups: .variable [3]
## .chain .iteration .draw .variable .value
## <int> <int> <int> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 1 1 1 alpha 3.53
## 2 1 2 2 alpha 3.10
## 3 1 3 3 alpha 3.32
## 4 1 4 4 alpha 3.21
## 5 1 5 5 alpha 3.61
## 6 1 6 6 alpha 3.87
## 7 1 7 7 alpha 2.63
## 8 1 8 8 alpha 3.99
## 9 1 9 9 alpha 3.91
## 10 1 10 10 alpha 4.76
## # ℹ 11,990 more rows74.4 统计汇总
## # A tibble: 6 × 7
## .variable .value .lower .upper .width .point .interval
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
## 1 alpha 5.06 4.07 6.00 0.65 mean qi
## 2 beta 0.209 0.189 0.229 0.65 mean qi
## 3 sigma 0.755 0.709 0.801 0.65 mean qi
## 4 alpha 5.06 3.33 6.76 0.89 mean qi
## 5 beta 0.209 0.173 0.245 0.89 mean qi
## 6 sigma 0.755 0.682 0.836 0.89 mean qi74.5 可视化
-
geom_slabinterval() / stat_slabinterval()family
draws %>%
ggplot(aes(x = .value, y = .variable)) +
ggdist::stat_interval()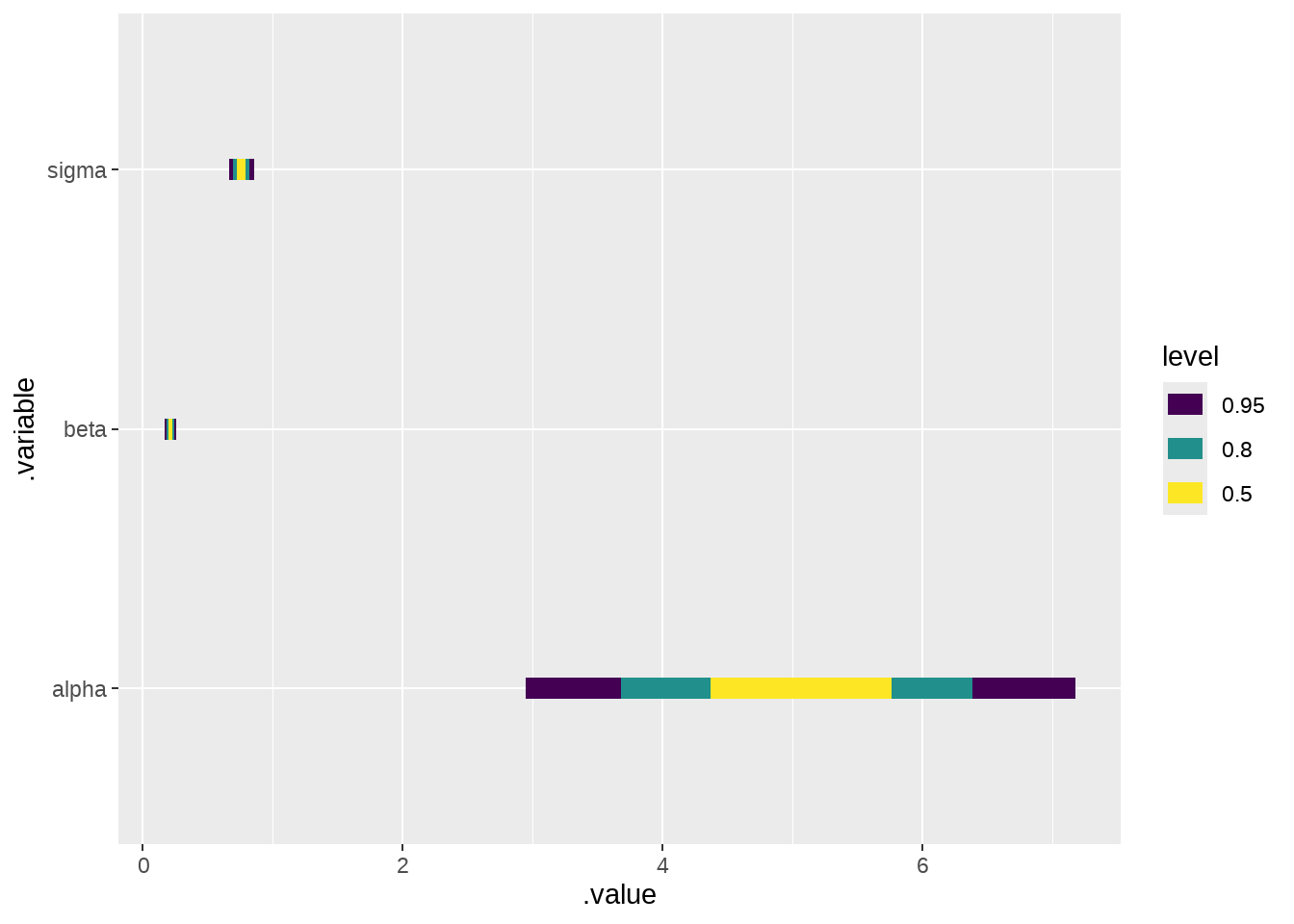
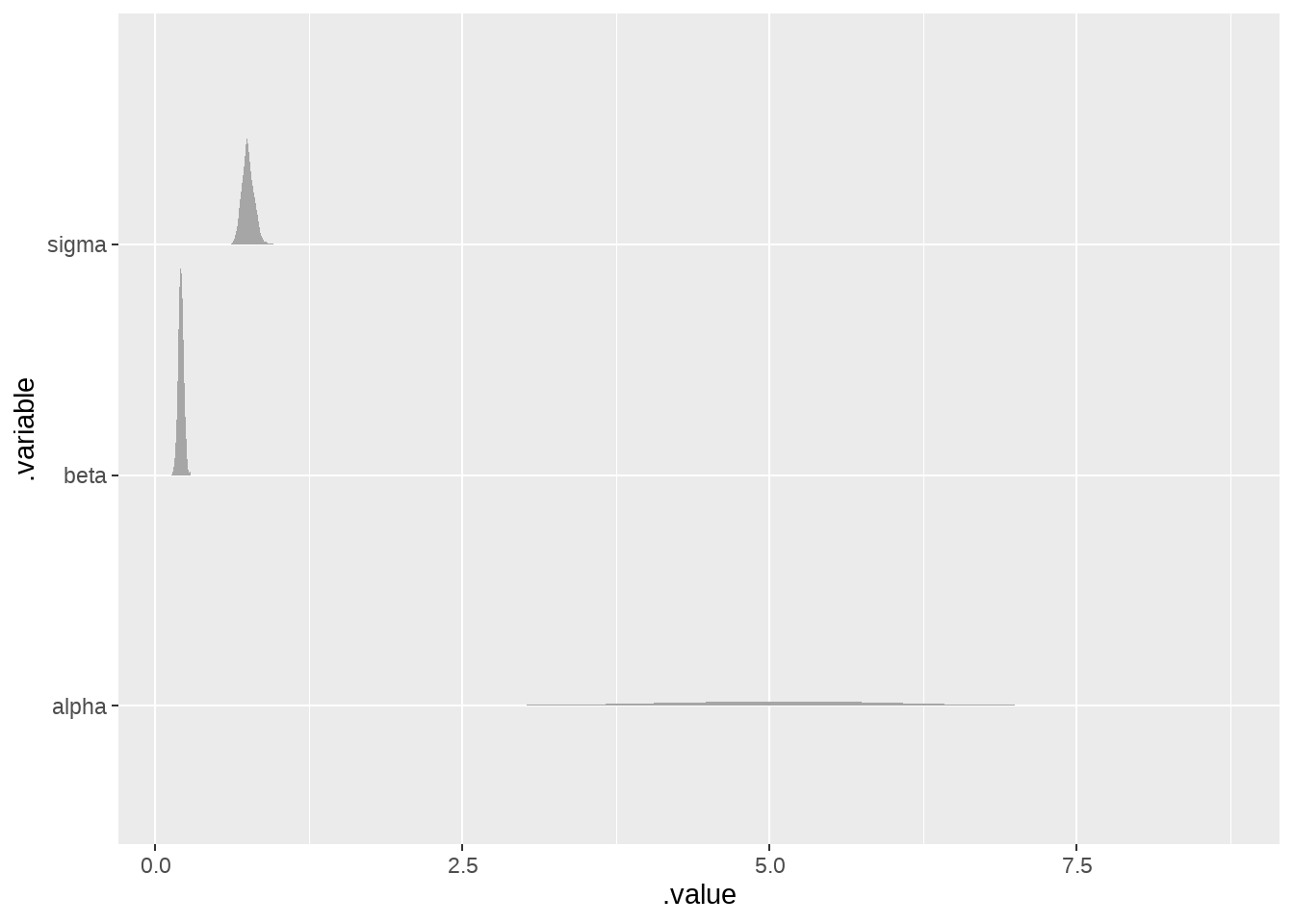
draws %>%
ggplot(aes(x = .value, y = .variable)) +
ggdist::stat_slabinterval()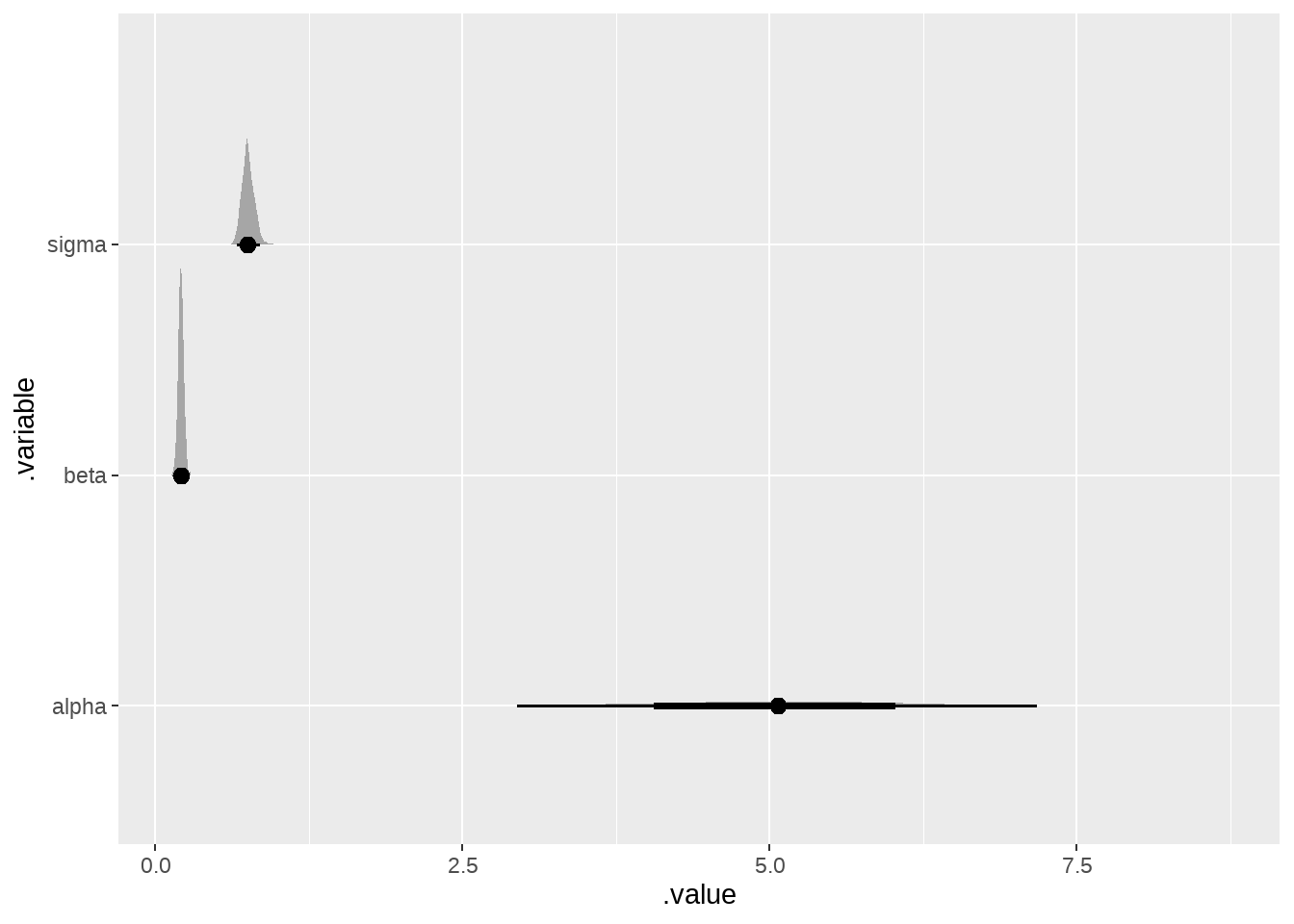
draws %>%
filter(.variable %in% c("beta", "sigma")) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = .value, y = .variable)) +
ggdist::stat_slabinterval() +
facet_grid(~ .variable, labeller = "label_both", scales = "free") 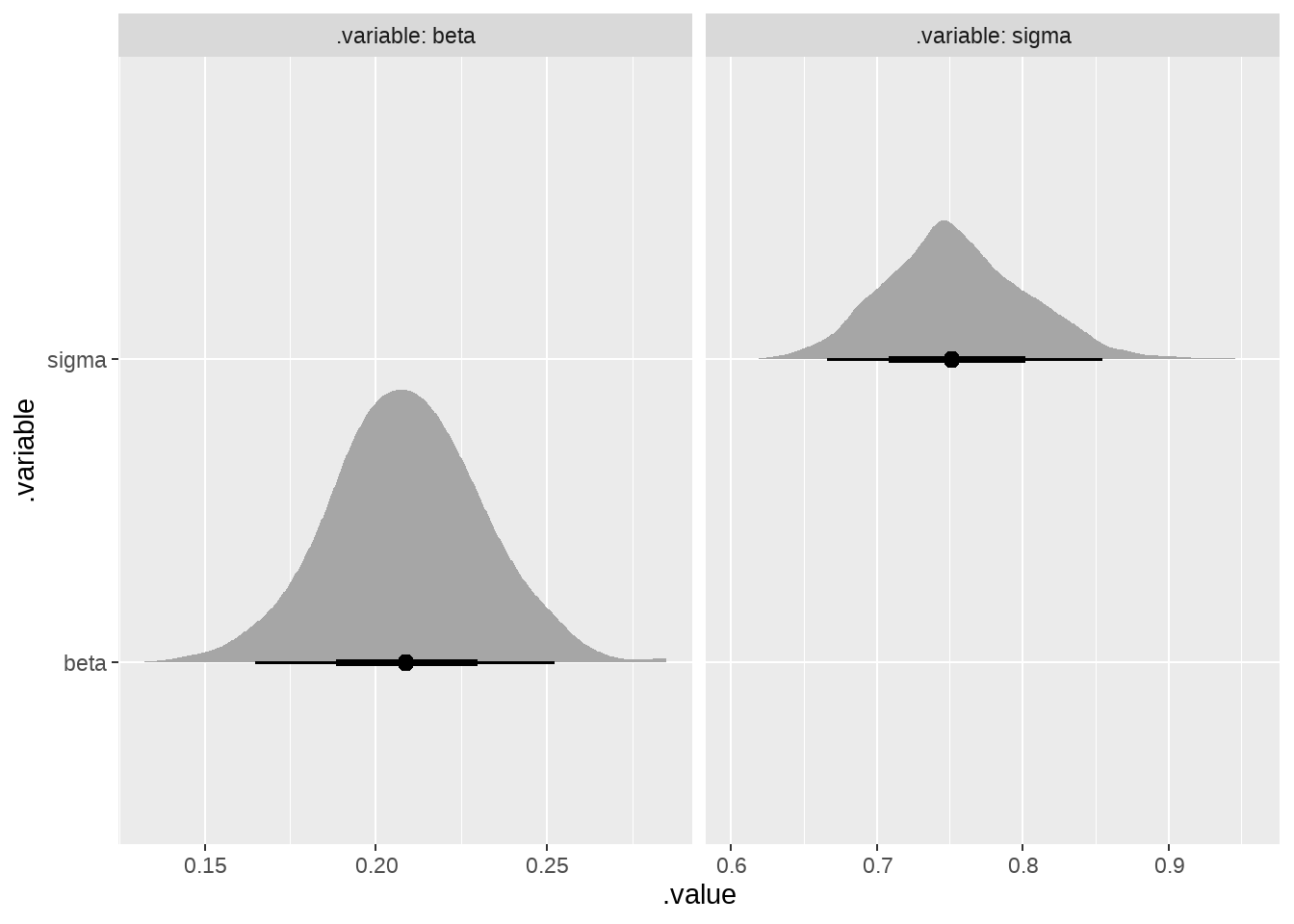
-
geom_dotsinterval() / stat_dotsinterval()family
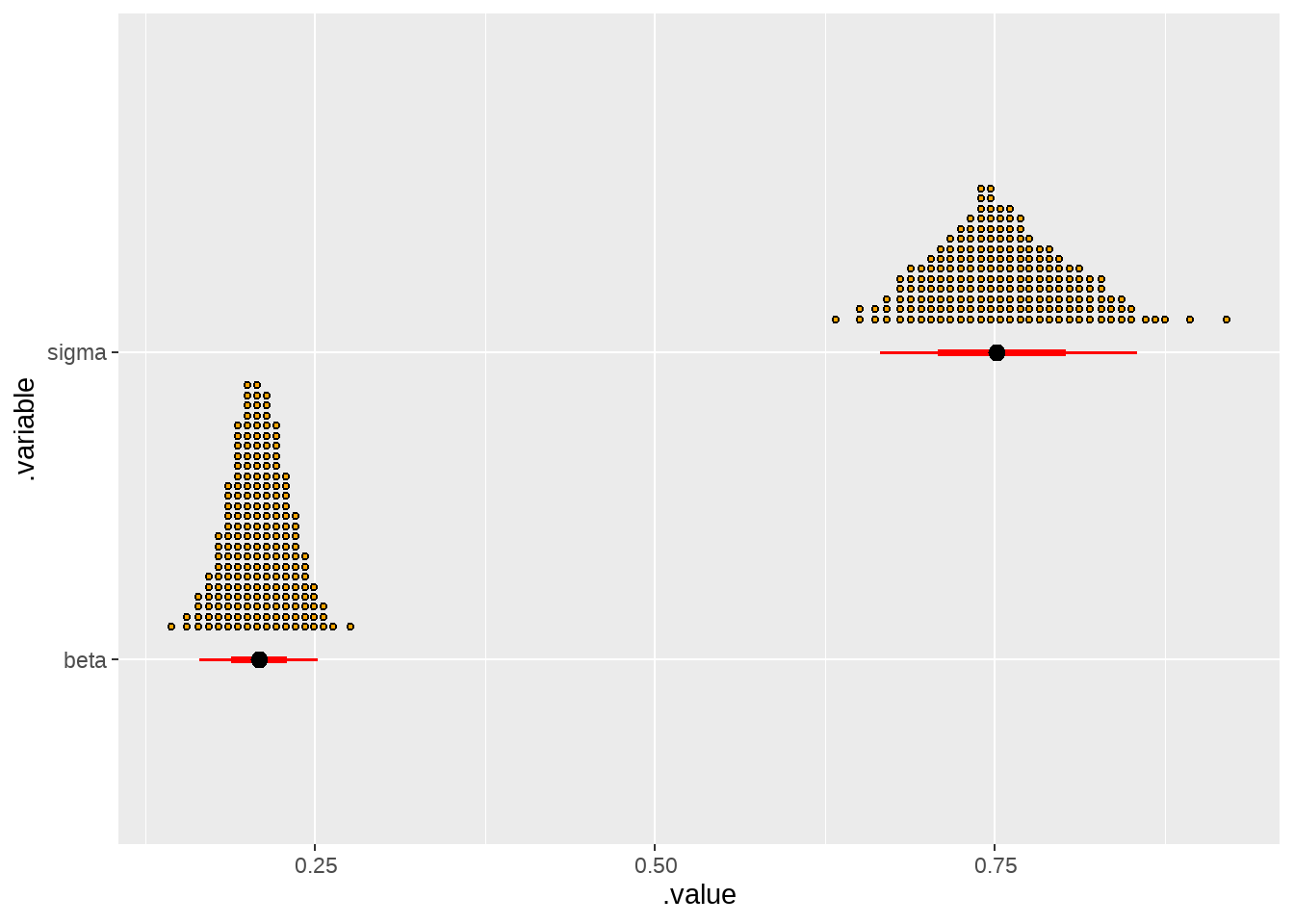
draws %>%
filter(.variable %in% c("beta", "sigma")) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = .value, y = .variable)) +
stat_dotsinterval(
quantiles = 200,
justification = -0.1,
slab_color = "black",
slab_fill = "orange",
interval_color = "red"
) 
-
geom_lineribbon() / stat_lineribbon()family
fit %>%
tidybayes::gather_draws(y_fit[i]) %>%
ggdist::median_qi(.width = c(0.89)) %>%
bind_cols(newdata) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_point(
data = gentoo,
aes(bill_length_mm, bill_depth_mm)
) +
geom_lineribbon(
aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = .value, ymin = .lower, ymax = .upper),
alpha = 0.3,
fill = "gray50"
) +
theme_classic() +
scale_fill_brewer(direction = -1)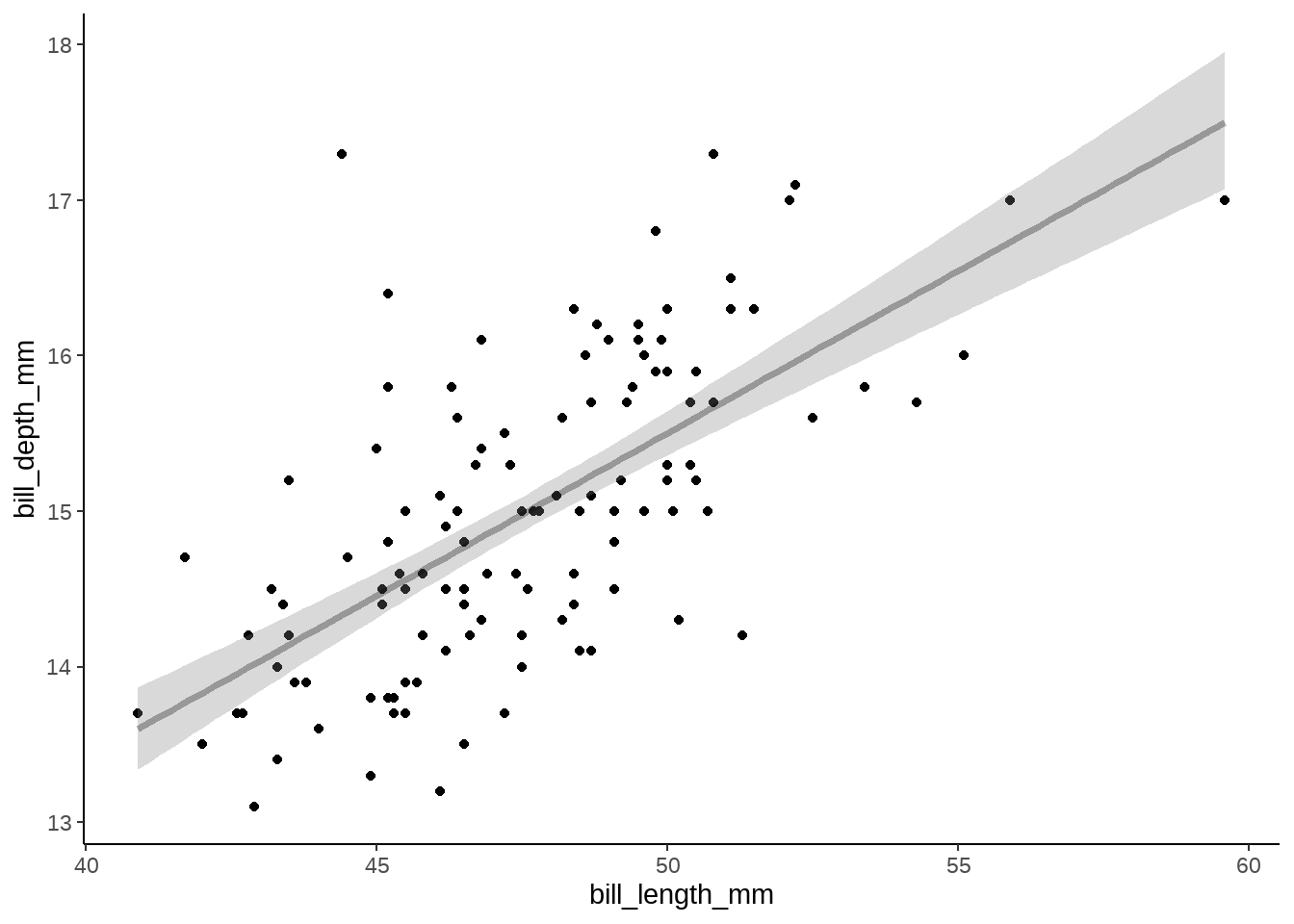
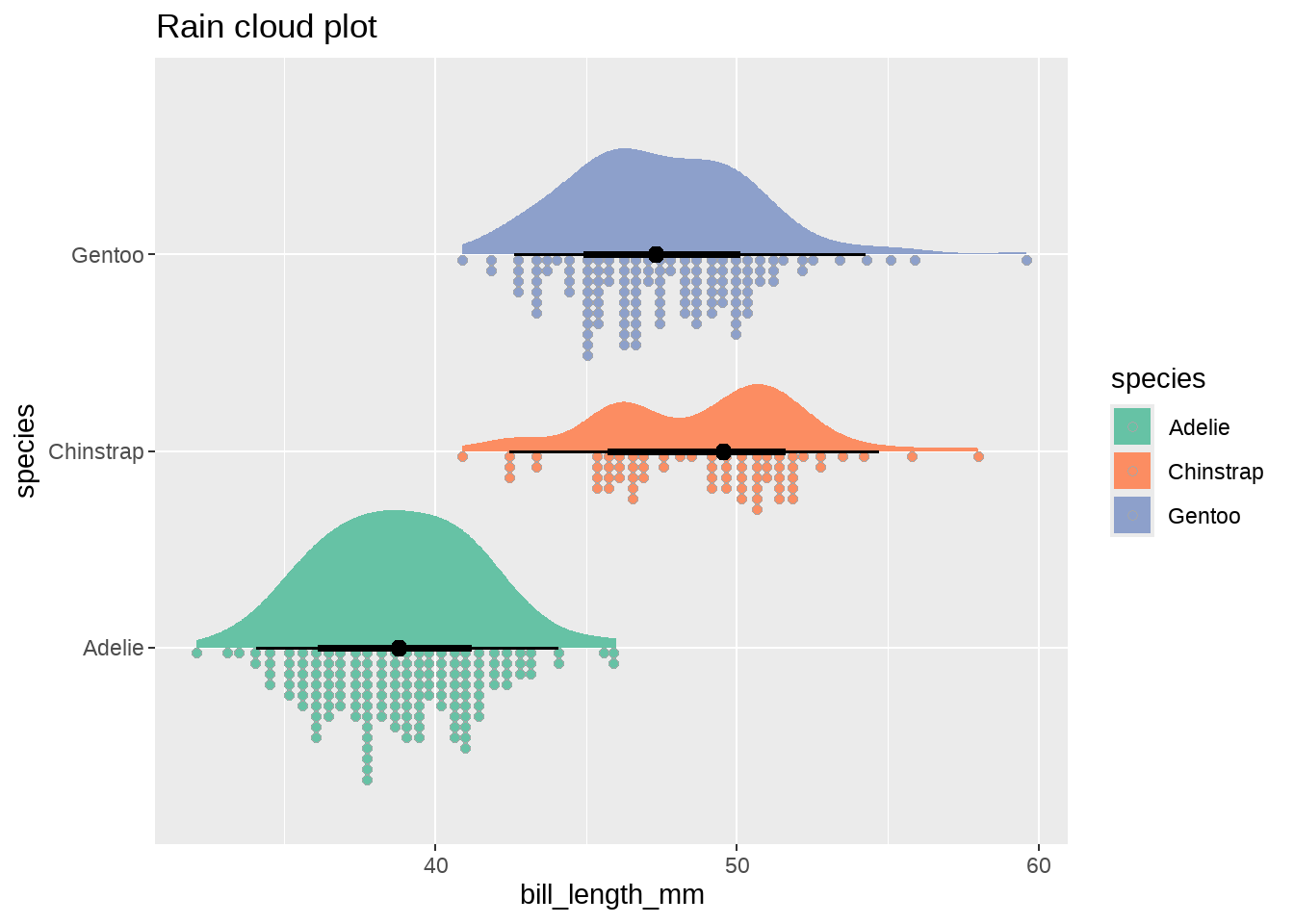
- 组合
penguins %>%
ggplot(aes(y = species, x = bill_length_mm, fill = species)) +
stat_slab(aes(thickness = after_stat(pdf*n)), scale = 0.7) +
stat_dotsinterval(side = "bottom", scale = 0.7, slab_size = NA) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set2") +
ggtitle("Rain cloud plot")