0.10 Key Elements of a Ritual Lens
Project RISE uses a ritual lens to achieve several inter-related outcomes. One direct outcome is a rich and complete description of the rituals, behaviors, beliefs, and practices that exemplify the perinatal experience in Bihar. The ritual lens helps achieve a deeper and more meaningful understanding of the factors that affect behavior because it includes the behavior, the stated reason for it, and a source of influence. Additionally, we benefit from the perspectives gained by trying to document and understand the form and function of ritual. The objective focused on ritual content is presented in Chapter 11 and the additional consequences of this perspective are discussed in Chapter 12.
Figure 0.3 gives an example of two rituals and their associated content, roles in fostering collective action, and their reinforcing mechanisms.
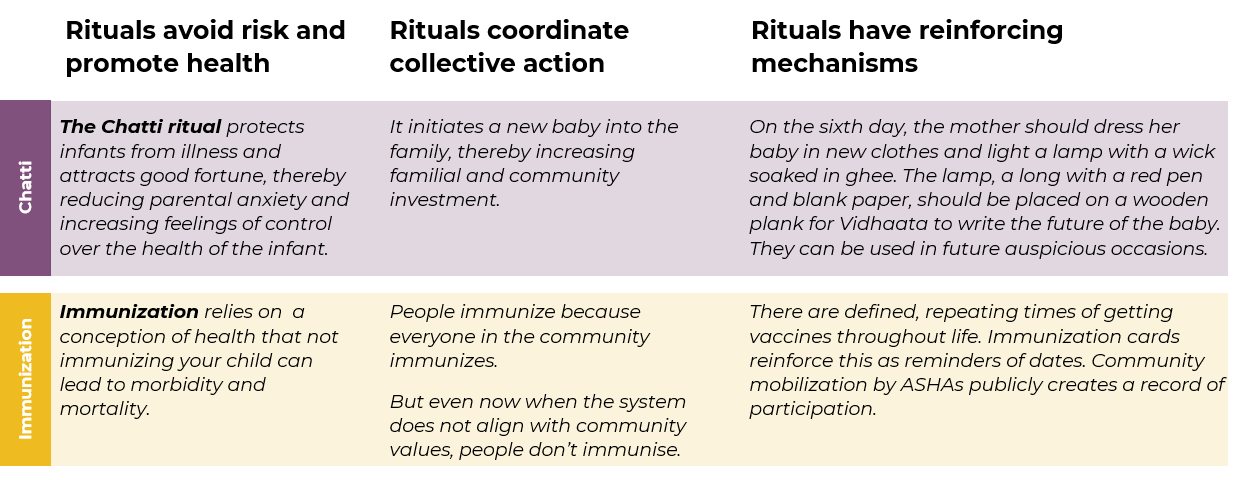
Figure 0.3: Key ritual elements for the examples of Chhathi and immunization.
Distinguishing between ritual awareness and ritual leveraging: rituals, beliefs, practices, habits, and behaviors are all examples of complex cultural phenomena that do not exist in isolation. A ritual awareness examines these things for how they connect so that solutions may come in the form of tweaks or the potential of changing a seemingly non-health-related ritual because of its influence on another. Ritual leveraging is more direct in that it modifies or directly applies a ritual to health behaviors of interest. Applying such distinctions to certain behaviors or contexts can only be done after extensive analysis and synthesis.
Ritual taxonomy and ritual friction are concepts the represent the shift from organization to diagnosis.
A ritual taxonomy tries to identify these factors:
function or functions of the ritual/behavior/belief
influencers, those who inform the woman about the behavior and especially those who affect the probability that she actually does or doesn’t do it
obstacles that may stem from other behaviors/practices that are connected or adjacent to the ritual, or perhaps a physical distancing that occurs due to the ritual that makes messaging difficult
how the practice is transmitted, meaning identifying if it is learned from parents/neighbors, if it is sacred/religious, or derived from some other source
Ritual friction is a measure of resistance that incorporates beliefs and values of culture and norms. In some cases, ritual could make cultural system have less friction toward a new idea or practice. A cultural setting with high friction is one that connects to lots of reinforcing meanings and beliefs or is widely practiced, or is key to showing your affiliation to an important group. Basically, these are hard to change because they are highly valued, connected to multiple value systems, or are strongly influenced by important cultural figures. If we are introducing a behavior that is similar to one that people already like to do and does not conflict with any core values, then the friction is low (and the behavior relatively easier to change). If we are introducing a behavior that is tied to many core beliefs and must actually displace or re-align some of those beliefs, then friction is high. In Project RISE there may be some cases where we are confronting both impurity and evil eye and tightly held values.