3.9 The Generalized DINA model
The generalized DINA model, or G-DINA model, is a general model framework (de la Torre, 2011).
G-DINA model is often called a saturated model because it subsumes many existing CDMs 1
A revisit of the DINA model
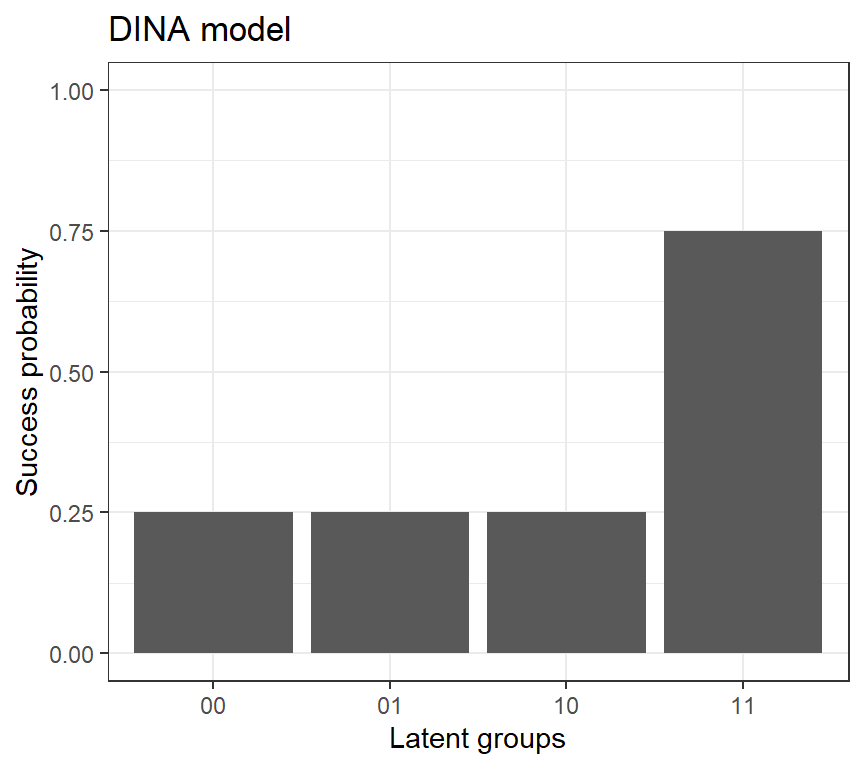
A generalization
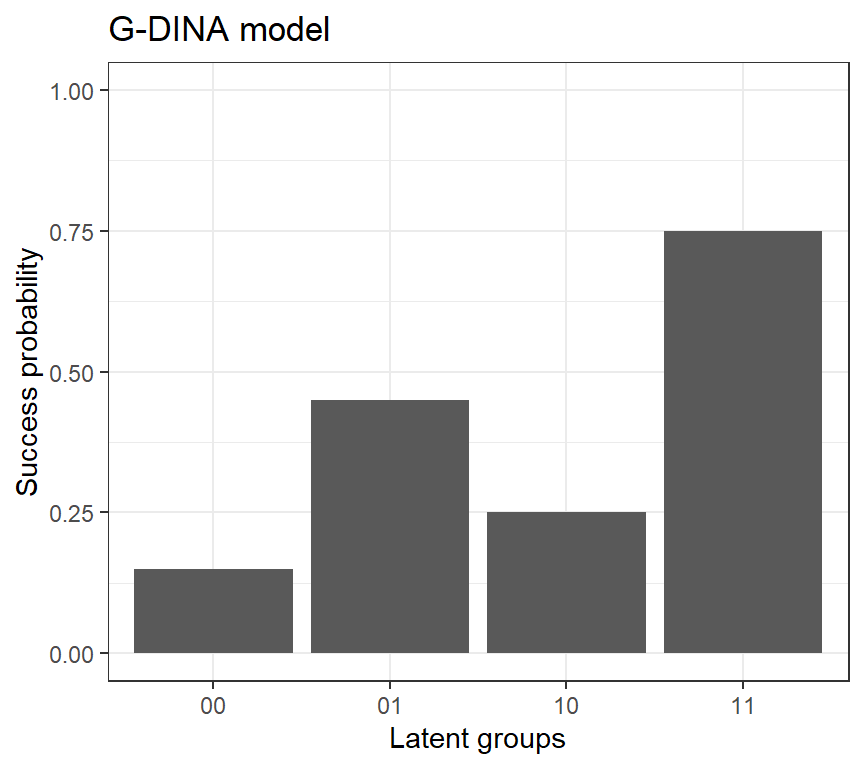
The IRF of the G-DINA model can be written by
\[ P(Y_{j}=1|\alpha_{lj}^*)=\pi_{lj} \]
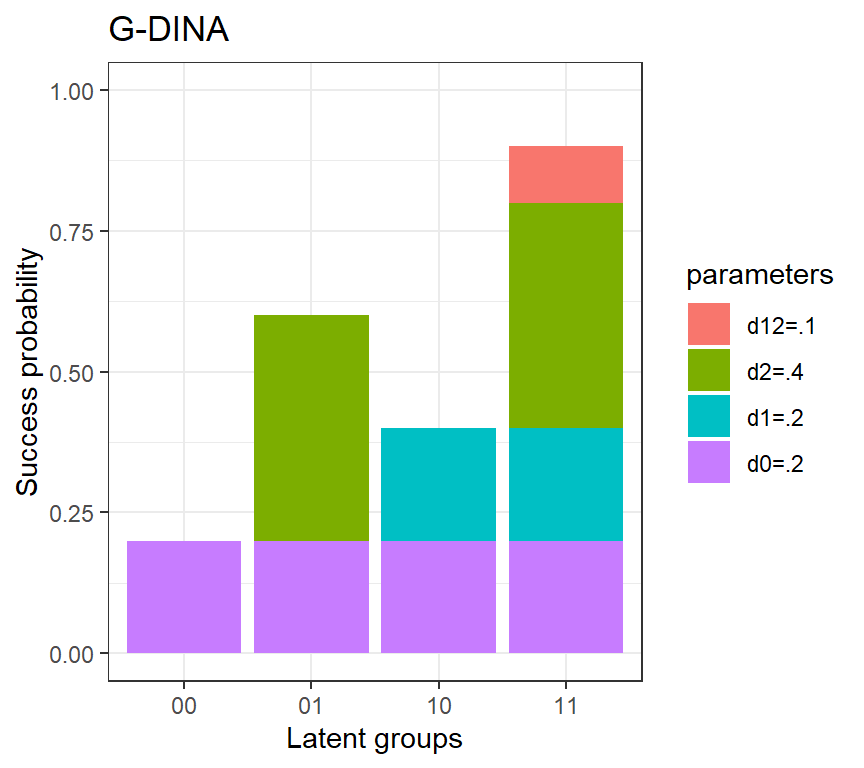
: Although the above IRF of the G-DINA model is very simple, researchers often reparmeterize it in a different, but equivalent, way:
\[ P(Y_{j}=1|\alpha_{lj}^*)=\delta_{j0}+\sum_k^{K_j^*}\delta_{jk}\alpha_{lk}+\ldots+\delta_{j1,2,\ldots,K_j^*}\prod_k^{K_j^*}\alpha_{lk} \]
Based on this parameterization, which is often referred to as the identity link of the G-DINA model, please calculate the following probabilities of success:
\[ \begin{aligned} P(Y_{j}=1|\alpha_{lj}^*=00) &= \delta_{j0} \\ P(Y_{j}=1|\alpha_{lj}^*=10) &= ? \\ P(Y_{j}=1|\alpha_{lj}^*=01) &= ? \\ P(Y_{j}=1|\alpha_{lj}^*=11) &= ? \\ \end{aligned} \]
References
Another two saturated CDMs are loglinear CDM (Henson et al., 2009) and the general diagnostic model (Davier, 2008)↩︎