19 Introducing inference
So far, you have learnt to ask a RQ, design a study, describe and summarise the data, and understand sampling variation. In this chapter, you will be introduced to the two big ideas in inference: confidence intervals and hypothesis testing. You will learn to:
- explain the purpose of a confidence interval.
- explain the purpose of hypothesis testing.
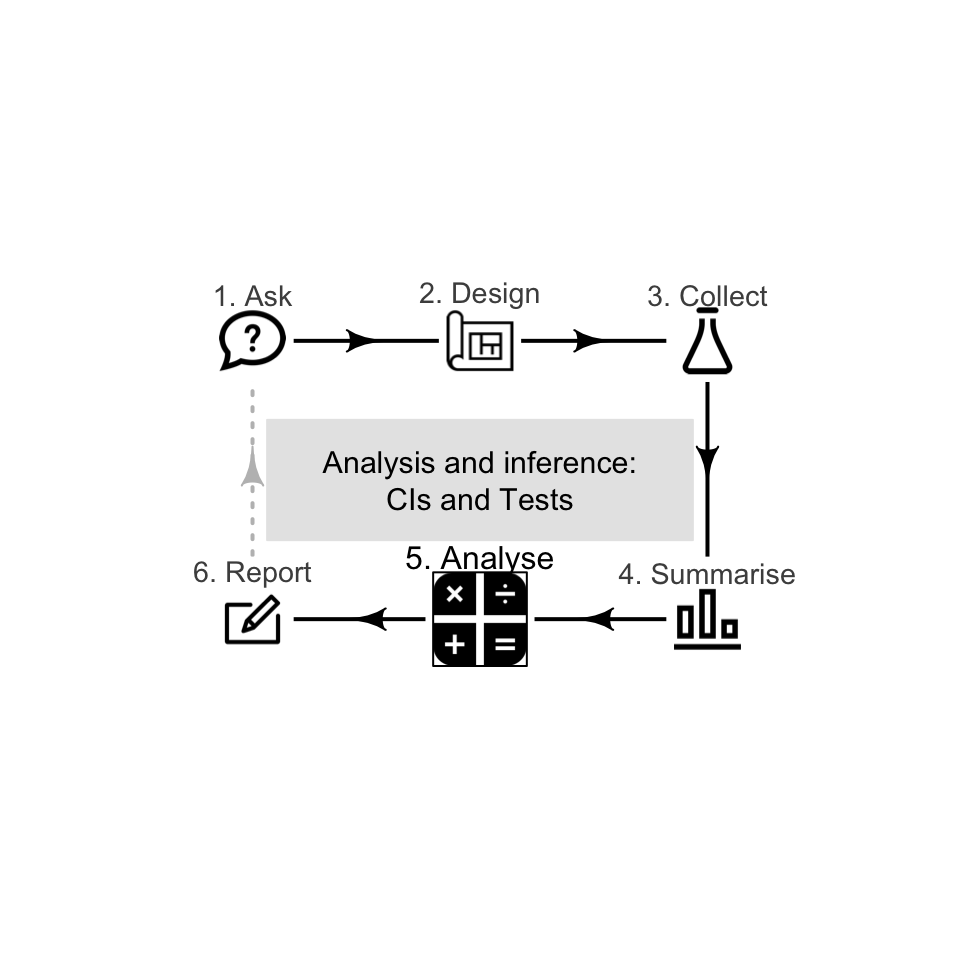
After posing a RQ (Chap. 2), a study is designed (Chaps. 3--9) to gather the evidence to answer the RQ (Chap. 10). Then the data are classified (Chap. 11) and summarised (Chaps. 13 to 18) in preparation for answering the RQ.
This Part introduces analysis: where the data are used to answer the research question. Answering the RQ is difficult, since we only study one of the countless possible samples, and hence observe only one of the countless possible values for the statistic. This is called sampling variation (Chap. ??). Analysis provides the tools for learning about a population parameter, based on observing one of the numerous possible values of a sample statistic. The appropriate type of analysis depends upon the number and types of variables. The analysis depends on the purpiose of the RQ (Sect. 2.8):
- Confidence intervals answer estimation RQ, where the interest is in how precisely a statistic estimates a parameter.
- Hypothesis tests answer decision-making RQs, where decisions are required.
Different scenarios require different confidence intervals and hypothesis tests; those discussed in this book are shown in Table 19.1.
| (Confidence intervals) | (Hypothesis tests) | |
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive RQs | ||
| Proportions for one sample | Chap. 20 | Chap. 27 |
| Means for one sample | Chap. 21 | Chap. 28 |
| Repeated-measures RQs | ||
| Mean differences (paired data) | Chap. 23 | Chap. 30 |
| Relational RQs | ||
| Comparing two means | Chap. 24 | Chap. 31 |
| Comparing two odds | Chap. 25 | Chap. 32 |
| Correlational RQs | ||
| Correlation | Sect. 34.2 | |
| Regression | Sect. 35.6 | Sect. 35.6 |