Topic 10 Lipids I
Lipids perform a variety of basic functions within the body (see figure 10.1), including but not limited to:
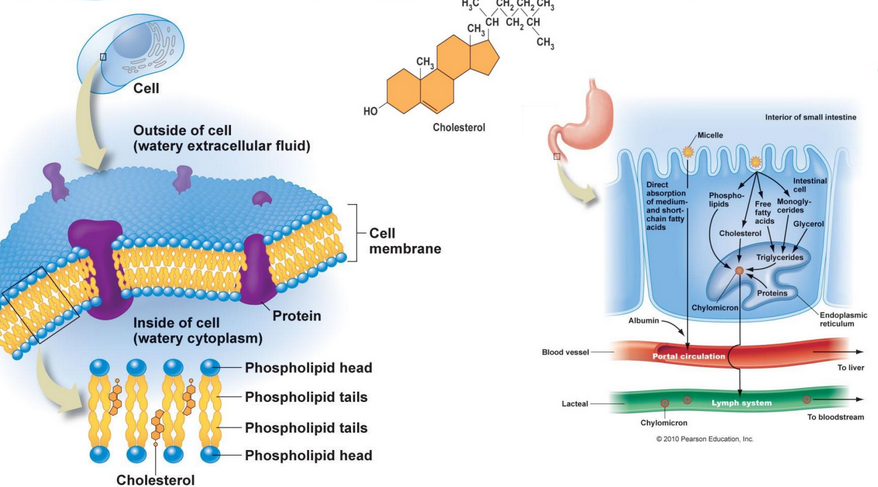
Figure 10.1: Functions of Lipids
Storing fat and providing energy
Fats can provide up to 9 kcal per kilogram; carbohydrates can only yield up to 4 kcal per kilogram!
Provide insulation
Help manufacture steroids and bile salts
Signalling
Play a role in transporting fat-soluble nutrients in blood
Manufacturing sex hormones (i.e., estrogen and testosterone)
Cell membrane synthesis
Figure 10.2: Types of Membrane Lipids
Figure 10.2 shows the five general types of membrane liipds:
- Glycerophospholipids
- Sphingolipids
- Galactolipids and sulfolipids
- Archaebacteria tetraether lipids
- Sterols (i.e., compounds with a rigid system of four fused hydrocarbon rings)
Furthermore, several diseases are also attributed with the abnormal chemistry or metabolism of lipids:
- Obesity
- Artherosclerosis
- Hypolipoporteinemia
- Hyperlipoporteinemia
- Steatosis (i.e., fatty liver)
- Lipidosis (i.e., lipid storage diseases)