Chapter 40: group theory
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hm4y1v75R
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Group_(mathematics)
40.1 matrix group
subset of two-by-two matrices at least excluding zero matrix
\[ \mathcal{M}=\left(\mathcal{M},\cdot\right)\subset\left(\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{C}\right)-\left\{ 0\right\} ,\cdot\right)=\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{C}\right)-\left\{ \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right\} \]
matrix multiplication
\[ \begin{aligned} & \forall\left\langle M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}},M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right\rangle \in\mathcal{M}^{2},\exists M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\in\mathcal{M}\left[M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}=M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\cdot M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right]\\ \Leftrightarrow & \cdot:\mathcal{M}\times\mathcal{M}=\mathcal{M}^{2}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}\\ \Leftrightarrow & \cdot:\mathcal{M}\times\mathcal{M}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}\\ \Leftrightarrow & \mathcal{M}\times\mathcal{M}\overset{\cdot}{\rightarrow}\mathcal{M}\\ \Leftrightarrow & \mathcal{M}^{2}\overset{\cdot}{\rightarrow}\mathcal{M} \end{aligned} \]
matrix group
\[ \begin{aligned} & \begin{cases} \forall\left\langle M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}},M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}},M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\right\rangle \in\mathcal{M}^{3}\left[M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\left(M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\right)=\left(M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)M_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\right] & \text{associativity}\\ \exists I=I_{2}=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\in\mathcal{M},\forall M\in\mathcal{M}\left[IM=M\right] & \text{left unit element}\\ \forall M\in\mathcal{M},\exists M^{-1}\in\mathcal{M}\left[M^{-1}M=I\right] & \text{left inverse (element)} \end{cases}\\ \Rightarrow & \mathcal{M}=\left(\mathcal{M},\cdot\right)\text{ is a matrix group} \end{aligned} \]
40.2 group definition and basic theorem
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Group_(mathematics)#Elementary_consequences_of_the_group_axioms
Definition 40.1 (group) group definition by a set and a binary operation on the set
\[ \begin{aligned} & \begin{cases} \circ:G\times G=G^{2}\rightarrow G & \text{binary operation}\\ \forall\left\langle g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}},g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}},g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\right\rangle \in G^{3}\left[g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\circ\left(g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\circ g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\right)=\left(g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\circ g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)\circ g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\right] & \text{associativity}\\ \exists e=\in G,\forall g\in G\left[e\circ g=g\right] & \text{left unit element}\\ \forall g\in G,\exists g^{-1}\in G\left[g^{-1}\circ g=e\right] & \text{left inverse (element)} \end{cases}\\ \Leftrightarrow & G=\left(G,\circ\right)\text{ is a group} \end{aligned} \]
Theorem 40.1 group left inverses equal right inverses
\[ \ \]
Proof:
\[ \text{to be proved} \]
\[ \tag*{$\Box$} \]
40.3 EpicOrganism = AIRoswell = Pan, Yi-Wen10
https://space.bilibili.com/14316464/video
https://space.bilibili.com/14316464/channel/collectiondetail?sid=1768137
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1mC4y1Z78k
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Sp4y1w76M
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cc411o7Hc
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1d8411v7t9
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Rw411e7km
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Q84y127ZQ
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hm4y1g7A9
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1s94y1L7MU
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1j84y1d7eY
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18z4y1P7oB
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cN4y1m77z
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18N4y1a7a3
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ma4y1r7nT
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV11N4y187QW
40.7 complex group representation
40.7.1 complex basis group
\[ \begin{aligned} G= & \left\{ 1,\mathrm{i},-1,-\mathrm{i}\right\} \\ = & \left\{ \mathrm{i}^{0},\mathrm{i}^{1},\mathrm{i}^{2},\mathrm{i}^{3}\right\} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \forall\left\langle g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}},g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right\rangle \in G^{2},\exists g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\in G\left[g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}=g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\cdot g_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right]\\ \Leftrightarrow & \cdot:G\times G=G^{2}\rightarrow G \end{aligned} \]
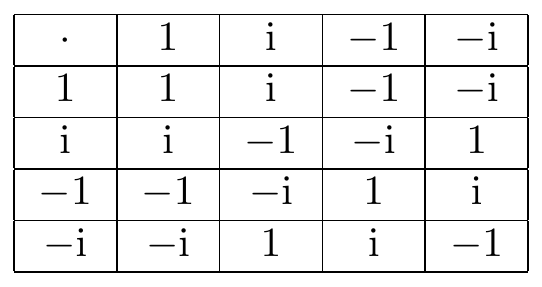
Fig. 17.1: complex basis group table
40.7.2 \(\mathbb{C}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{R}\right)\)
\[ 1\leftrightarrow\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}=I_{2}=I \]
\[ \begin{aligned} c_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+c_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix}= & x\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+y\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix},\left\langle a,b,c,d\right\rangle \in\mathbb{R}^{4}\\ = & xI+yJ,J=\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix}\in\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{R}\right),\left\langle x,y\right\rangle \in\mathbb{R}^{2} \end{aligned} \]
\[ J^{2}=-I \]
\[ \begin{aligned} J^{2}= & -I\\ \begin{pmatrix}a^{2}+bc & ab+bd\\ ca+cd & cb+d^{2} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix}= & -\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{cases} a^{2}+bc=-1 & b=0\Rightarrow a^{2}=-1\Rightarrow\Leftarrow a\in\mathbb{R}\Rightarrow b\ne0\\ ab+bd=0 & \left(b=0\right)\vee\left(a=-d\right)\overset{b\ne0}{\Rightarrow}a=-d\\ ca+cd=0\\ cb+d^{2}=-1 & a^{2}=d^{2}\Rightarrow\left(a=d\right)\vee\left(a=-d\right) \end{cases} & \overset{\text{if }a=d}{\Rightarrow}\begin{cases} a=d\\ a=-d \end{cases}\\ & \Rightarrow a=d=0\Rightarrow bc=-1 \end{aligned} \] \[ J=\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ \dfrac{-a^{2}-1}{b} & -a \end{pmatrix}=J\left(a,b\right),b\ne0 \]
\[ \begin{aligned} J\left(a,b\right)=\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ \dfrac{-a^{2}-1}{b} & -a \end{pmatrix},b\ne0 \end{aligned} \]
\[ J\left(a=1,b\right)=\begin{pmatrix}1 & b\\ \dfrac{-2}{b} & -1 \end{pmatrix}\Rightarrow J^{2}\left(a=1,b\right)=\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}=-I \]
\[ \begin{aligned} xI+yJ\left(a=1,b\right)=\begin{pmatrix}x+y & yb\\ y\cdot\dfrac{-2}{b} & x-y \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned} \]
\[ J\left(a=0,b\right)=\begin{pmatrix}0 & b\\ \dfrac{-1}{b} & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ J\left(a=0,b=1\right)=\begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} J\left(a=0,b=-1\right)= & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=-\begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=-J\left(a=0,b=1\right)\\ \Rightarrow J^{2}\left(a=0,b=-1\right)= & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}=-I \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} J=J\left(a=0,b=-1\right)= & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \Rightarrow & \begin{cases} 1\leftrightarrow I=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{i}\leftrightarrow J=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{cases}\\ \Rightarrow x+y\mathrm{i}\leftrightarrow & xI+yJ\\ = & x\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+y\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}x & -y\\ y & x \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned} \]
\[ x+y\mathrm{i}\leftrightarrow\begin{pmatrix}x & -y\\ y & x \end{pmatrix}=xI+yJ \]
realizing
\[ \mathbb{C}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{R}\right)=\mathcal{M}_{2}\left(\mathbb{R}\right) \]
40.7.3 ( determinant of complex group representation ) equivalent to ( squared modulus of complex number )
\[ \det\left(xI+yJ\right)=\det\begin{pmatrix}x & -y\\ y & x \end{pmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix}x & -y\\ y & x \end{vmatrix}=x^{2}+y^{2}=\left|x+y\mathrm{i}\right|^{2} \]
40.7.3.1 Lagrange identity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lagrange's_identity
generalization of Brahmagupta–Fibonacci identity
specialization of Binet–Cauchy identity
cf. Euler identity[40.8.1.1]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \det\left[\left(aI+bJ\right)\left(cI+dJ\right)\right]\\ = & \det\left[\begin{pmatrix}a & -b\\ b & a \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}c & -d\\ d & c \end{pmatrix}\right]\\ = & \det\begin{pmatrix}ac-bd & -ad-bc\\ ad+bc & ac-bd \end{pmatrix}=\left|\left(ac-bd\right)+\left(ad+bc\right)\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}=\left(ac-bd\right)^{2}+\left(ad+bc\right)^{2}\\ = & \left[\det\begin{pmatrix}a & -b\\ b & a \end{pmatrix}\right]\left[\det\begin{pmatrix}c & -d\\ d & c \end{pmatrix}\right]=\left|a+b\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}\left|c+d\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}=\left(a^{2}+b^{2}\right)\left(c^{2}+d^{2}\right) \end{aligned} \]
\[ \left|a+b\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}\left|c+d\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}=\left(a^{2}+b^{2}\right)\left(c^{2}+d^{2}\right)=\left(ac-bd\right)^{2}+\left(ad+bc\right)^{2} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \det\left[\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}I+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}J\right)\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}I+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}J\right)\right]\\ = & \det\left[\begin{pmatrix}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}} & -y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\\ y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}} & x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}} \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} & -y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\\ y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} & x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} \end{pmatrix}\right]\\ = & \det\begin{pmatrix}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}-y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} & -x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}-y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\\ x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} & x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}-y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} \end{pmatrix}=\left|\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}-y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)+\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}=\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}-y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)^{2}+\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)^{2}\\ = & \left[\det\begin{pmatrix}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}} & -y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\\ y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}} & x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}} \end{pmatrix}\right]\left[\det\begin{pmatrix}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} & -y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\\ y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} & x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}} \end{pmatrix}\right]=\left|x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}\left|x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}=\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}^{2}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}^{2}\right)\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}^{2}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}^{2}\right) \end{aligned} \]
\[ \left|x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}\left|x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\mathrm{i}\right|^{2}=\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}^{2}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}^{2}\right)\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}^{2}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}^{2}\right)=\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}-y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)^{2}+\left(x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}+y_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}\right)^{2} \]
40.7.4 Euler formula proved by complex group representation
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1mM4y1J79a
\[ \begin{aligned} \begin{pmatrix}x^{\prime}\\ y^{\prime} \end{pmatrix}= & \begin{pmatrix}\cos\theta & -\sin\theta\\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}=R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \theta}}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \begin{pmatrix}\cos n\frac{\theta}{n} & -\sin n\frac{\theta}{n}\\ \sin n\frac{\theta}{n} & \cos n\frac{\theta}{n} \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\cos\frac{\theta}{n} & -\sin\frac{\theta}{n}\\ \sin\frac{\theta}{n} & \cos\frac{\theta}{n} \end{pmatrix}^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}=R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}=\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\begin{pmatrix}\cos\frac{\theta}{n} & -\sin\frac{\theta}{n}\\ \sin\frac{\theta}{n} & \cos\frac{\theta}{n} \end{pmatrix}= & \begin{pmatrix}1 & -\frac{\theta}{n}\\ \frac{\theta}{n} & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+\dfrac{\theta}{n}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+\dfrac{\theta}{n}\begin{pmatrix}\cos\frac{\pi}{2} & -\sin\frac{\pi}{2}\\ \sin\frac{\pi}{2} & \cos\frac{\pi}{2} \end{pmatrix}\\ = & I+\dfrac{\theta}{n}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\pi}{2}}} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}=\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\begin{pmatrix}\cos\frac{\theta}{n} & -\sin\frac{\theta}{n}\\ \sin\frac{\theta}{n} & \cos\frac{\theta}{n} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}1 & -\frac{\theta}{n}\\ \frac{\theta}{n} & 1 \end{pmatrix}=I+\dfrac{\theta}{n}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\pi}{2}}} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} \begin{pmatrix}x^{\prime}\\ y^{\prime} \end{pmatrix}=\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\begin{pmatrix}x^{\prime}\\ y^{\prime} \end{pmatrix}= & \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}=\left[\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}^{n}\right]\left[\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}\right]=\left[\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}^{n}\right]\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\left[\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\theta}{n}}}\right]^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}=\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\left[I+\dfrac{\theta}{n}R_{{\scriptscriptstyle \frac{\pi}{2}}}\right]^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\left[I+\dfrac{\theta}{n}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right]^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}=\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty}\left[I+\dfrac{\theta J}{n}\right]^{n}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix},J=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \mathrm{e}^{J\theta}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \begin{cases} \begin{pmatrix}x^{\prime}\\ y^{\prime} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\cos\theta & -\sin\theta\\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}x^{\prime}\\ y^{\prime} \end{pmatrix}=\mathrm{e}^{J\theta}\begin{pmatrix}x\\ y \end{pmatrix} \end{cases}\\ \Rightarrow & \mathrm{e}^{J\theta}=\begin{pmatrix}\cos\theta & -\sin\theta\\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta \end{pmatrix}\overset{x+y\mathrm{i}\leftrightarrow\begin{pmatrix}x & -y\\ y & x \end{pmatrix}=xI+yJ}{\Rightarrow}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}\theta}=\cos\theta+\mathrm{i}\sin\theta \end{aligned} \]
\[ \ \tag*{$\Box$} \]
40.8 quaternion group representation
\[ \begin{aligned} & q=a+b\mathrm{i}+c\mathrm{j}+d\mathrm{k}=a+\mathrm{i}b+\mathrm{j}c+\mathrm{k}d,\begin{cases} q\in\mathbb{H}\\ a,b,c,d\in\mathbb{R} & \Leftrightarrow\left\langle a,b,c,d\right\rangle \in\mathbb{R}^{4} \end{cases}\\ = & w=t+x\mathrm{i}+y\mathrm{j}+z\mathrm{k}=t+\mathrm{i}x+\mathrm{j}y+\mathrm{k}z,\begin{cases} w\in\mathbb{H}\\ t,x,y,z\in\mathbb{R} & \Leftrightarrow\left\langle t,x,y,z\right\rangle \in\mathbb{R}^{4} \end{cases}\\ = & a1+b\mathrm{i}+c\mathrm{j}+d\mathrm{k}=t1+x\mathrm{i}+y\mathrm{j}+z\mathrm{k}=x_{{\scriptscriptstyle 0}}1+\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle i}}x_{{\scriptscriptstyle i}} \end{aligned} \]
40.8.1 \(\mathbb{H}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{C}\right)\)
\[ 1=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}=1_{2}=1 \]
\[ \begin{aligned} \boldsymbol{e}= & \begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ c & d \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ \dfrac{-a^{2}-1}{b} & -a \end{pmatrix}\\ = & \begin{cases} \begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ \dfrac{-a^{2}-1}{b} & -a \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & b\\ \dfrac{-1}{b} & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & \beta\\ -\beta & 0 \end{pmatrix}\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}=J=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\mathrm{j} & a=0\\ \begin{pmatrix}a & b\\ \dfrac{-a^{2}-1}{b} & -a \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix} & a\ne0 \end{cases} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} \begin{pmatrix}\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2} & 0\\ 0 & \beta^{2}+\alpha^{2} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix}=\boldsymbol{e}^{2}= & -1=-\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \Downarrow\\ \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}= & -1\Leftrightarrow\beta^{2}+\alpha^{2}=-1 \end{aligned} \]
\[ \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}=-1\Rightarrow\left\langle \alpha,\beta\right\rangle \notin\mathbb{R}^{2}\Rightarrow\Leftarrow\left\langle \alpha,\beta\right\rangle \in\mathbb{R}^{2}\Rightarrow\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}\ge0 \]
quaternion group has no irreducible two-dimensional representation over the reals 11
\[ \left\langle \alpha,\beta\right\rangle \in\mathbb{C}^{2}-\mathbb{R}^{2} \]
\[ \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}=-1=\beta^{2}+\alpha^{2} \]
\[ \begin{pmatrix}\beta & \alpha\\ \alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}\beta & \alpha\\ \alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\beta^{2}+\alpha^{2} & 0\\ 0 & \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}=-\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}=-1 \]
\[ 1=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix},\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix},\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ 1=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix},\mathrm{i}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix},\mathrm{j}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ \mathrm{i}\mathrm{j}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\beta & -\alpha\\ -\alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix}=\mathrm{k} \]
\[ 1=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix},\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix},\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix},\boldsymbol{e}_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}=\begin{pmatrix}\beta & -\alpha\\ -\alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix} \] \[ 1=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix},\mathrm{i}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix},\mathrm{j}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix},\mathrm{k}=\begin{pmatrix}\beta & -\alpha\\ -\alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ \mathrm{j}\mathrm{k}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}\beta & -\alpha\\ -\alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix}=\mathrm{i} \]
\[ \begin{array}{ccccc} & \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}=-1 & \begin{cases} \alpha=\sqrt{-1}\\ \beta=0 \end{cases} & \begin{cases} \alpha=\sqrt{-2}\\ \beta=1 \end{cases} & \beta=\alpha^{2},n\in\left\{ 1,2,4,5\right\} \\ 1 & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ -1 & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{i} & \begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\sqrt{-1} & 0\\ 0 & -\sqrt{-1} \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\sqrt{-2} & 1\\ 1 & -\sqrt{-2} \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}}\\ \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & -\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{i} & \begin{pmatrix}-\alpha & -\beta\\ -\beta & \alpha \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\sqrt{-1} & 0\\ 0 & \sqrt{-1} \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\sqrt{-2} & -1\\ -1 & \sqrt{-2} \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & -\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}}\\ -\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{j} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{j} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{k} & \begin{pmatrix}\beta & -\alpha\\ -\alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -\sqrt{-1}\\ -\sqrt{-1} & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & -\sqrt{-2}\\ -\sqrt{-2} & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & -\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}}\\ -\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & -\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{k} & \begin{pmatrix}-\beta & \alpha\\ \alpha & \beta \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & \sqrt{-1}\\ \sqrt{-1} & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & \sqrt{-2}\\ \sqrt{-2} & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}}\\ \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} & \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{2n}{3}\sqrt{-1}} \end{pmatrix} \end{array} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} -1= & \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}\\ \overset{\beta=\alpha^{2}}{=} & \alpha^{2}+\alpha^{4}\\ \alpha^{4}+\alpha^{2}+1= & 0,\alpha^{4}+\alpha^{2}+1=\left(\alpha^{2}+\alpha+1\right)\left(\alpha^{2}-\alpha+1\right)\\ \left(\alpha^{2}-1\right)\left(\alpha^{4}+\alpha^{2}+1\right)= & 0\\ \alpha^{6}-1= & 0\\ \alpha^{6}= & 1=\mathrm{e}^{2\pi k\sqrt{-1}},k\in\mathbb{Z}\\ \alpha= & \mathrm{e}^{2\pi\frac{n}{6}\sqrt{-1}},n\in\left\{ 0,1,2,3,4,5\right\} -\left\{ 0,3\right\} \\ = & \mathrm{e}^{\pi\frac{n}{3}\sqrt{-1}},n\in\left\{ 1,2,4,5\right\} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{array}{ccccc} & \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}=-1 & \begin{cases} \alpha=i\\ \beta=0 \end{cases} & \begin{cases} \alpha=\sqrt{2}i\\ \beta=1 \end{cases} & \omega=\mathrm{e}^{i\pi\frac{n}{3}},n\in\left\{ 1,2,4,5\right\} \\ 1 & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ -1 & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{i} & \begin{pmatrix}\alpha & \beta\\ \beta & -\alpha \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\sqrt{2}i & 1\\ 1 & -\sqrt{2}i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\omega & \omega^{2}\\ \omega^{2} & -\omega \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{i} & \begin{pmatrix}-\alpha & -\beta\\ -\beta & \alpha \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-i & 0\\ 0 & i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\sqrt{2}i & -1\\ -1 & \sqrt{2}i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\omega & -\omega^{2}\\ -\omega^{2} & \omega \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{j} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{j} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{k} & \begin{pmatrix}\beta & -\alpha\\ -\alpha & -\beta \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & -\sqrt{2}i\\ -\sqrt{2}i & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\omega^{2} & -\omega\\ -\omega & -\omega^{2} \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{k} & \begin{pmatrix}-\beta & \alpha\\ \alpha & \beta \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & i\\ i & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & \sqrt{2}i\\ \sqrt{2}i & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\omega^{2} & \omega\\ \omega & \omega^{2} \end{pmatrix} \end{array} \]
realizing
\[ \mathbb{H}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2\times2}\left(\mathbb{C}\right)=\mathcal{M}_{2}\left(\mathbb{C}\right) \]
40.8.1.1 Euler identity
cf. Lagrange identity[40.7.3.1]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \det\left(a+b\mathrm{i}+c\mathrm{j}+d\mathrm{k}\right)\\ = & \det\left[a\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+b\begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix}+c\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}+d\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right]\\ = & \det\begin{pmatrix}a+bi & -c-di\\ c-di & a-bi \end{pmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix}a+bi & -c-di\\ c-di & a-bi \end{vmatrix}\\ = & \left(a^{2}+b^{2}\right)+\left(c^{2}+d^{2}\right)=a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \det\left(a+b\mathrm{i}+c\mathrm{j}+d\mathrm{k}\right)=\det\begin{pmatrix}a+bi & -c-di\\ c-di & a-bi \end{pmatrix}=a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \det\left[\left(q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 10}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 11}}\mathrm{i}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 12}}\mathrm{j}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 13}}\mathrm{k}\right)\left(q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 20}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 21}}\mathrm{i}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 22}}\mathrm{j}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 23}}\mathrm{k}\right)\right]=\det\left[\left(a+b\mathrm{i}+c\mathrm{j}+d\mathrm{k}\right)\left(\alpha+\beta\mathrm{i}+\gamma\mathrm{j}+\delta\mathrm{k}\right)\right]\\ = & \det\Biggl\{\left[q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 10}}\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 11}}\begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 12}}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 13}}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right]\\ & \left[q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 20}}\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 21}}\begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 22}}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 23}}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right]\Biggr\}\\ = & \det\Biggl\{\left[a\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+b\begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix}+c\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}+d\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right]\\ & \left[\alpha\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}+\beta\begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix}+\gamma\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}+\delta\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\right]\Biggr\}\\ = & \det\left\{ \begin{pmatrix}a+bi & -c-di\\ c-di & a-bi \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}\alpha+\beta i & -\gamma-\delta i\\ \gamma-\delta i & \alpha-\beta i \end{pmatrix}\right\} \\ & =\det\begin{pmatrix}a+bi & -c-di\\ c-di & a-bi \end{pmatrix}\det\begin{pmatrix}\alpha+\beta i & -\gamma-\delta i\\ \gamma-\delta i & \alpha-\beta i \end{pmatrix}=\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2}\right)\left(\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}+\delta^{2}\right)\\ = & \det\left\{ \begin{pmatrix}\left[a+bi\right]\left[\alpha+\beta i\right]-\left[c+di\right]\left[\gamma-\delta i\right] & \left[a+bi\right]\left[-\gamma-\delta i\right]-\left[c+di\right]\left[\alpha-\beta i\right]\\ \left[c-di\right]\left[\alpha+\beta i\right]+\left[a-bi\right]\left[\gamma-\delta i\right] & \left[c-di\right]\left[-\gamma-\delta i\right]+\left[a-bi\right]\left[\alpha-\beta i\right] \end{pmatrix}\right\} \\ = & \det\left\{ \begin{pmatrix}\left(a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right)+i\left(a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right) & -\left(a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right)-i\left(a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right)\\ \left(a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right)-i\left(a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right) & \left(a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right)-i\left(a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right) \end{pmatrix}\right\} \\ = & \det\left\{ \left(a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right)+\left(a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right)\mathrm{i}+\left(a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right)\mathrm{j}+\left(a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right)\mathrm{k}\right\} \\ = & \left(a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right)^{2}+\left(a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right)^{2}+\left(a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right)^{2}+\left(a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right)^{2}\\ = & \left(q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 10}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 20}}-q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 11}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 21}}-q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 12}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 22}}-q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 13}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 23}}\right)^{2}+\left(q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 10}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 21}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 11}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 20}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 12}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 23}}-q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 13}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 22}}\right)^{2}\\ + & \left(q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 10}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 22}}-q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 11}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 23}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 12}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 20}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 13}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 21}}\right)^{2}+\left(q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 10}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 23}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 11}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 22}}-q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 12}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 21}}+q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 13}}q_{{\scriptscriptstyle 20}}\right)^{2} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} & \left(a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2}\right)\left(\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}+\delta^{2}\right)\\ = & \left(a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right)^{2}+\left(a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right)^{2}\\ & +\left(a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right)^{2}+\left(a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right)^{2} \end{aligned} \]
Theorem 26.2 For any two integers greater than zero, their multiplication can be the summation of squared four integers greater than zero.
\[ \forall\left\langle m_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}},m_{2}\right\rangle \in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{2},\exists\left\langle k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}},k_{2},k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}},k_{4}\right\rangle \in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4}\left[m_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}m_{2}=k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}^{2}+k_{2}^{2}+k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}^{2}+k_{4}^{2}\right] \]
Proof:
Let \(\begin{cases} m_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}=a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2} & \left\langle a,b,c,d\right\rangle \in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4}\\ m_{{\scriptscriptstyle 2}}=\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}+\delta^{2} & \left\langle \alpha,\beta,\gamma,\delta\right\rangle \in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4} \end{cases}\overset{\text{closure property}}{\Rightarrow}\begin{pmatrix}m_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\\ m_{2} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2}\\ \alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}+\delta^{2} \end{pmatrix}\in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{2}\),
\[ \begin{aligned} m_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}m_{2} & =\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}+d^{2}\right)\left(\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}+\delta^{2}\right)\\ & \overset{\text{Euler identity}}{=}\left(a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right)^{2}+\left(a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right)^{2}\\ & +\left(a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right)^{2}+\left(a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right)^{2}\\ & =\left|a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right|^{2}\\ & +\left|a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right|^{2}\\ & +\left|a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right|^{2}\\ & +\left|a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right|^{2}\\ & =k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}^{2}+k_{2}^{2}+k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}^{2}+k_{4}^{2},\begin{pmatrix}k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 1}}\\ k_{2}\\ k_{{\scriptscriptstyle 3}}\\ k_{4} \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}\left|a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right|\\ \left|a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right|\\ \left|a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right|\\ \left|a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right| \end{pmatrix}\in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4} \end{aligned} \]
\[ \begin{aligned} \because & \begin{cases} \left\langle a,b,c,d\right\rangle \in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4}\\ \left\langle \alpha,\beta,\gamma,\delta\right\rangle \in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4} \end{cases}\\ \overset{\text{closure property}}{\Rightarrow} & \begin{pmatrix}\left|a\alpha-b\beta-c\gamma-d\delta\right|\\ \left|a\beta+b\alpha+c\delta-d\gamma\right|\\ \left|a\gamma-b\delta+c\alpha+d\beta\right|\\ \left|a\delta+b\gamma-c\beta+d\alpha\right| \end{pmatrix}\in\left(\mathbb{N}\cup\left\{ 0\right\} \right)^{4} \end{aligned} \] \[ \ \tag*{$\Box$} \]
40.8.2 \(\mathbb{H}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{4\times4}\left(\mathbb{R}\right)\)
\[ \mathbb{H}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2}\left(\mathbb{C}\right)\overset{\mathbb{C}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2}\left(\mathbb{R}\right)}{\rightarrow}\mathcal{M}_{4\times4}\left(\mathbb{R}\right)=\mathcal{M}_{4}\left(\mathbb{R}\right) \]
\[ \mathbb{C}\rightarrow\mathcal{M}_{2}\left(\mathbb{R}\right)\Leftarrow\begin{cases} 1\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ i\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{cases} \]
\[ 1\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ -1\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ \mathrm{i}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ -\mathrm{i}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}-i & 0\\ 0 & i \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ \mathrm{j}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ -\mathrm{j}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ \mathrm{k}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
\[ -\mathrm{k}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & i\\ i & 0 \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{pmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
some examinations
\[ \mathrm{i}\mathrm{j}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\leftarrow\mathrm{k} \]
\[ \mathrm{j}\mathrm{i}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\leftarrow-\mathrm{k} \]
\[ \mathrm{i}^{2}=\mathrm{i}\mathrm{i}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\leftarrow-1 \]
\[ \begin{array}{ccccc} & \begin{cases} \alpha=i\\ \beta=0 \end{cases} & \begin{cases} 1\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ i\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{cases} & \begin{cases} \alpha=\sqrt{2}i\\ \beta=1 \end{cases} & \begin{cases} 1\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ i\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \end{cases}\\ 1 & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\\ -1 & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{i} & \begin{pmatrix}i & 0\\ 0 & -i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}\sqrt{2}i & 1\\ 1 & -\sqrt{2}i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -\sqrt{2} & 1 & 0\\ \sqrt{2} & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 1 & -\sqrt{2} & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{i} & \begin{pmatrix}-i & 0\\ 0 & i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-\sqrt{2}i & -1\\ -1 & \sqrt{2}i \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1 & -1 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & -1 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{j} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{j} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathrm{k} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & -i\\ -i & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ -1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & -\sqrt{2}i\\ -\sqrt{2}i & -1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}1 & 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 1 & -\sqrt{2} & 0\\ 0 & \sqrt{2} & -1 & 0\\ -\sqrt{2} & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\\ -\mathrm{k} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & i\\ i & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & \sqrt{2}i\\ \sqrt{2}i & 1 \end{pmatrix} & \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0 & 0 & -\sqrt{2}\\ 0 & -1 & \sqrt{2} & 0\\ 0 & -\sqrt{2} & 1 & 0\\ \sqrt{2} & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \end{array} \]
some examinations
\[ \mathrm{i}\mathrm{j}\rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}0 & -\sqrt{2} & 1 & 0\\ \sqrt{2} & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 1 & -\sqrt{2} & 0 \end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}1 & 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 1 & -\sqrt{2} & 0\\ 0 & \sqrt{2} & -1 & 0\\ -\sqrt{2} & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\leftarrow\mathrm{k} \]