n = 10
lambda = 2
w = rexp(n, rate = lambda)
t = cumsum(c(0, w))
plot(t, 0:n,
type = "s",
xlab = "time, t", ylab = "Number of events, N(t)",
main = paste("Sample path of Poisson process with rate", lambda))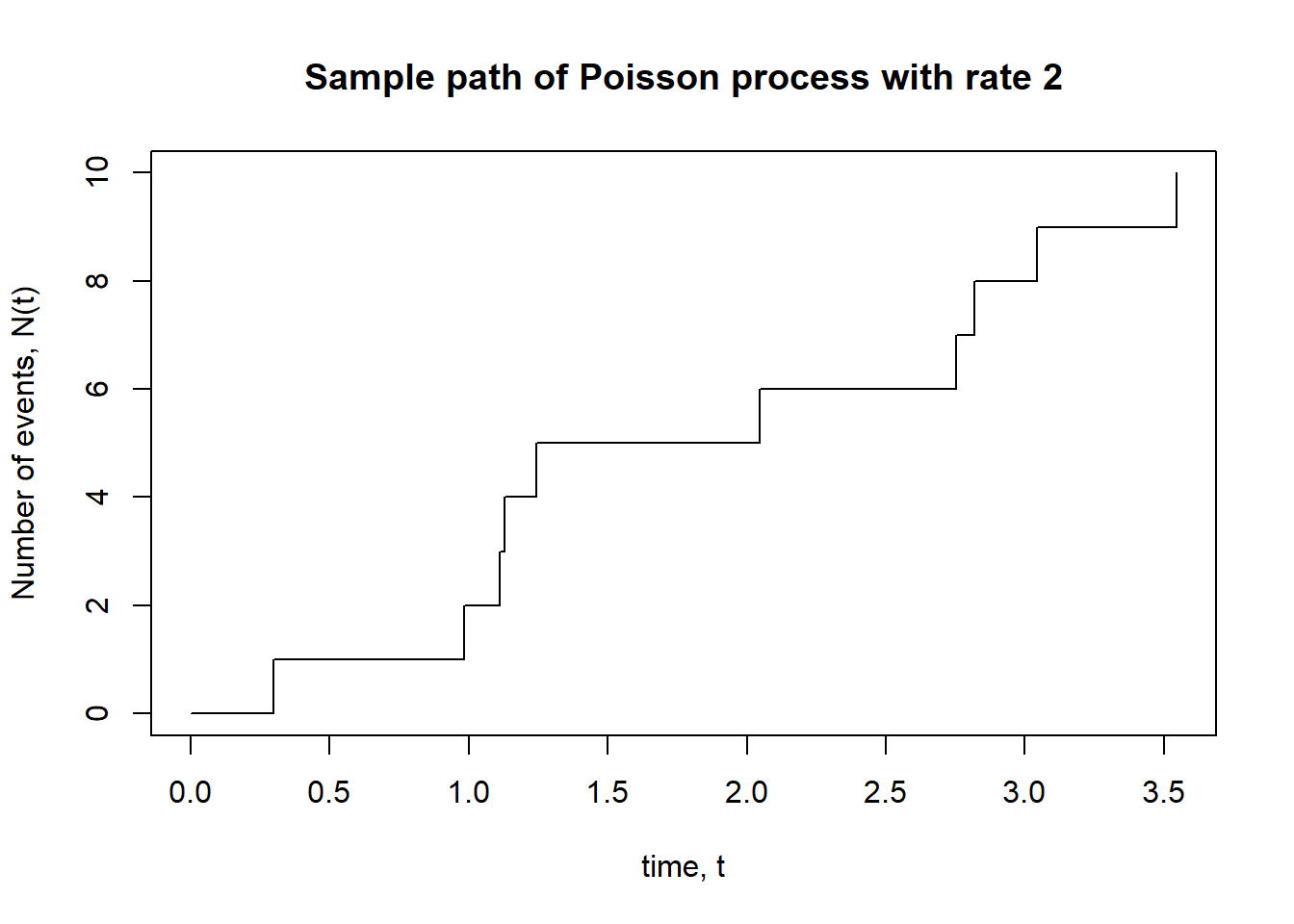
Simulate times between events as i.i.d. Exponential
n = 10
lambda = 2
w = rexp(n, rate = lambda)
t = cumsum(c(0, w))
plot(t, 0:n,
type = "s",
xlab = "time, t", ylab = "Number of events, N(t)",
main = paste("Sample path of Poisson process with rate", lambda))
T = 10
lambda = 2
N_T = rpois(1, lambda * T)
u = runif(N_T, 0, T)
t = c(0, sort(u))
plot(t, 0:N_T,
type = "s",
xlab = "time, t", ylab = "Number of events, N(t)",
main = paste("Sample path of Poisson process with rate", lambda))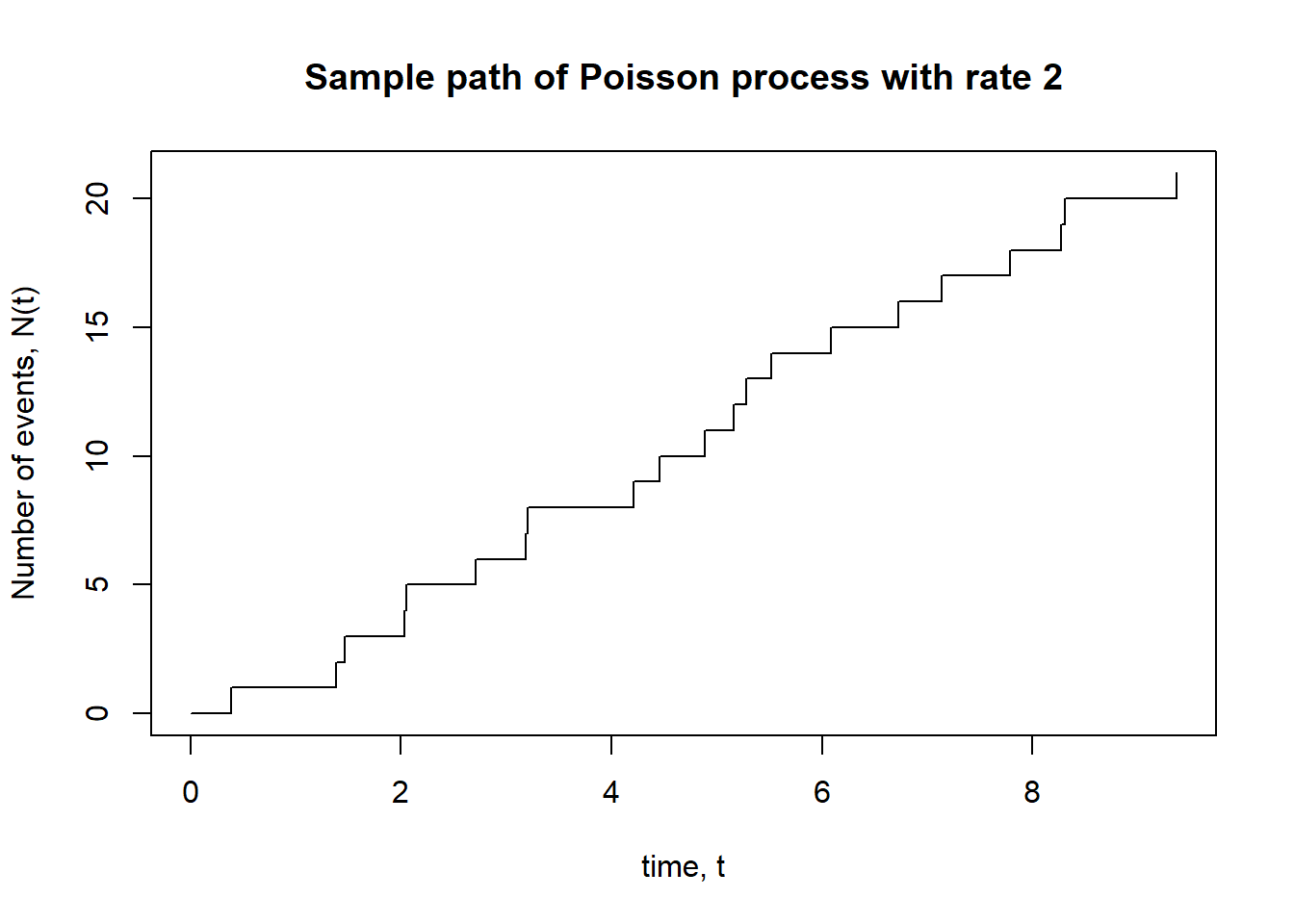
from symbulate import *
from matplotlib import pyplot as pltP = PoissonProcessProbabilitySpace(rate = 2)
N = RV(P)plt.figure()
N.sim(5).plot()
plt.show();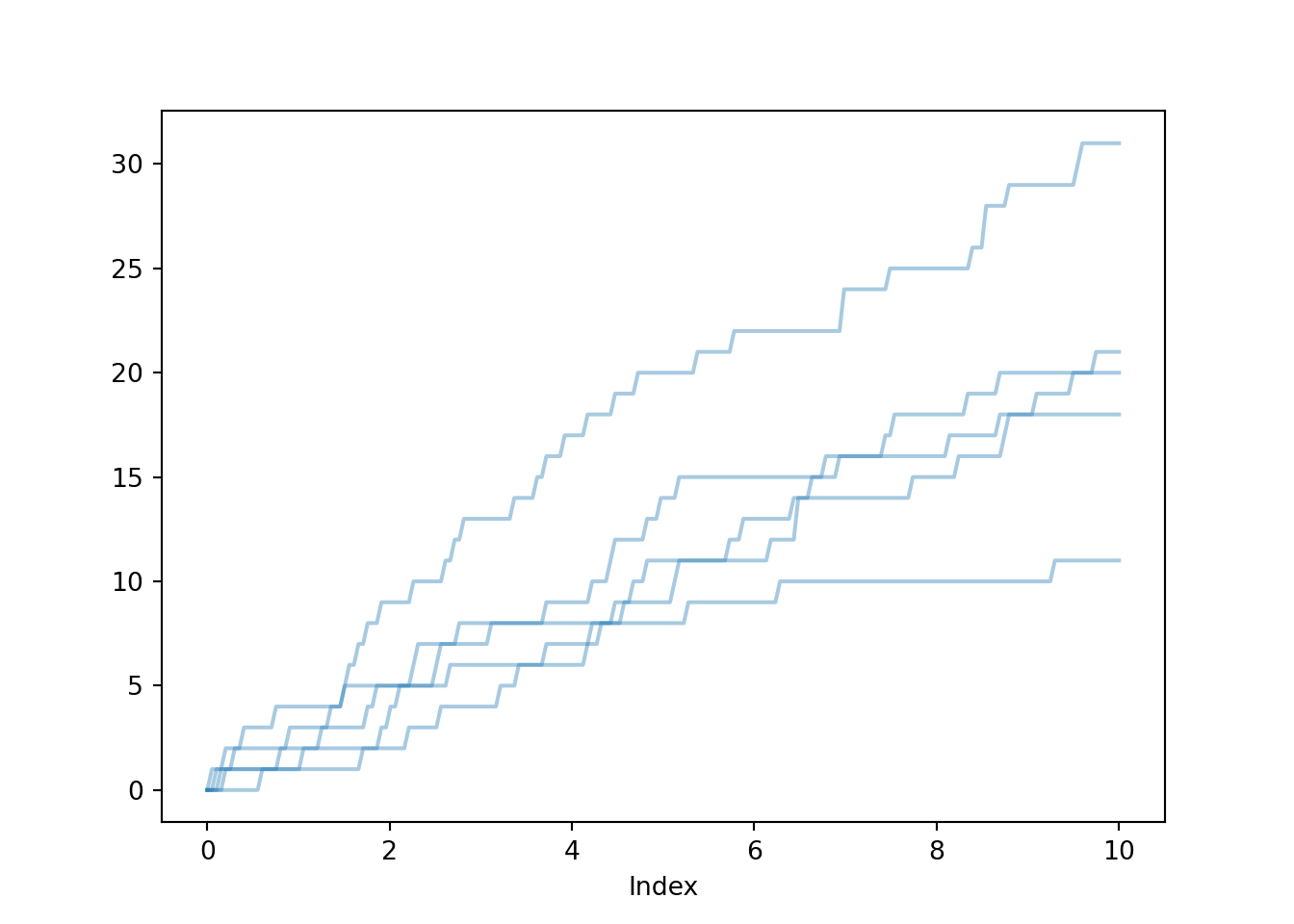
plt.figure()
N.sim(100).plot()
plt.show();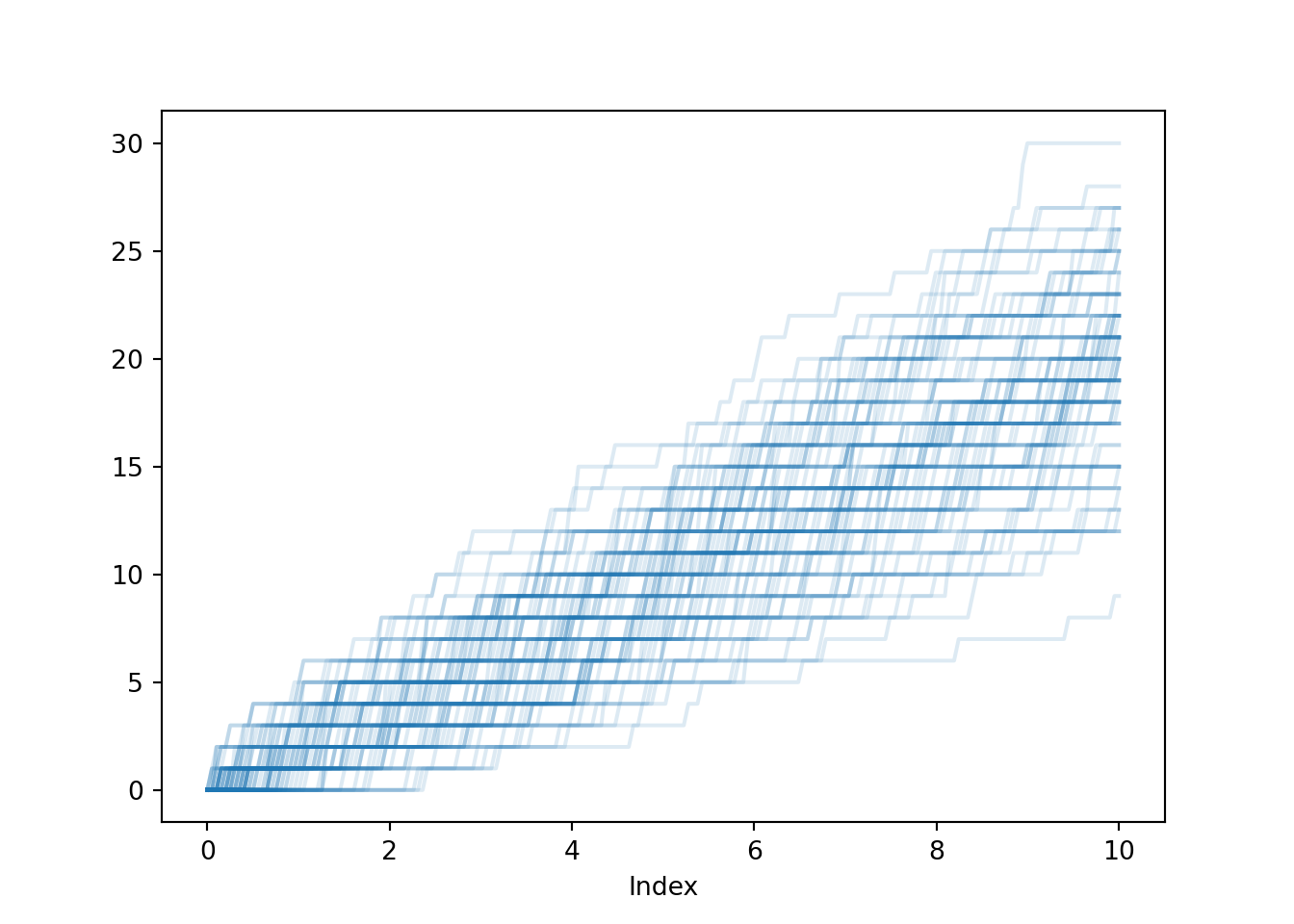
plt.figure();
N[5].sim(10000).plot()
Poisson(2 * 5).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Poisson object at 0x0000017B651B2E50>plt.show()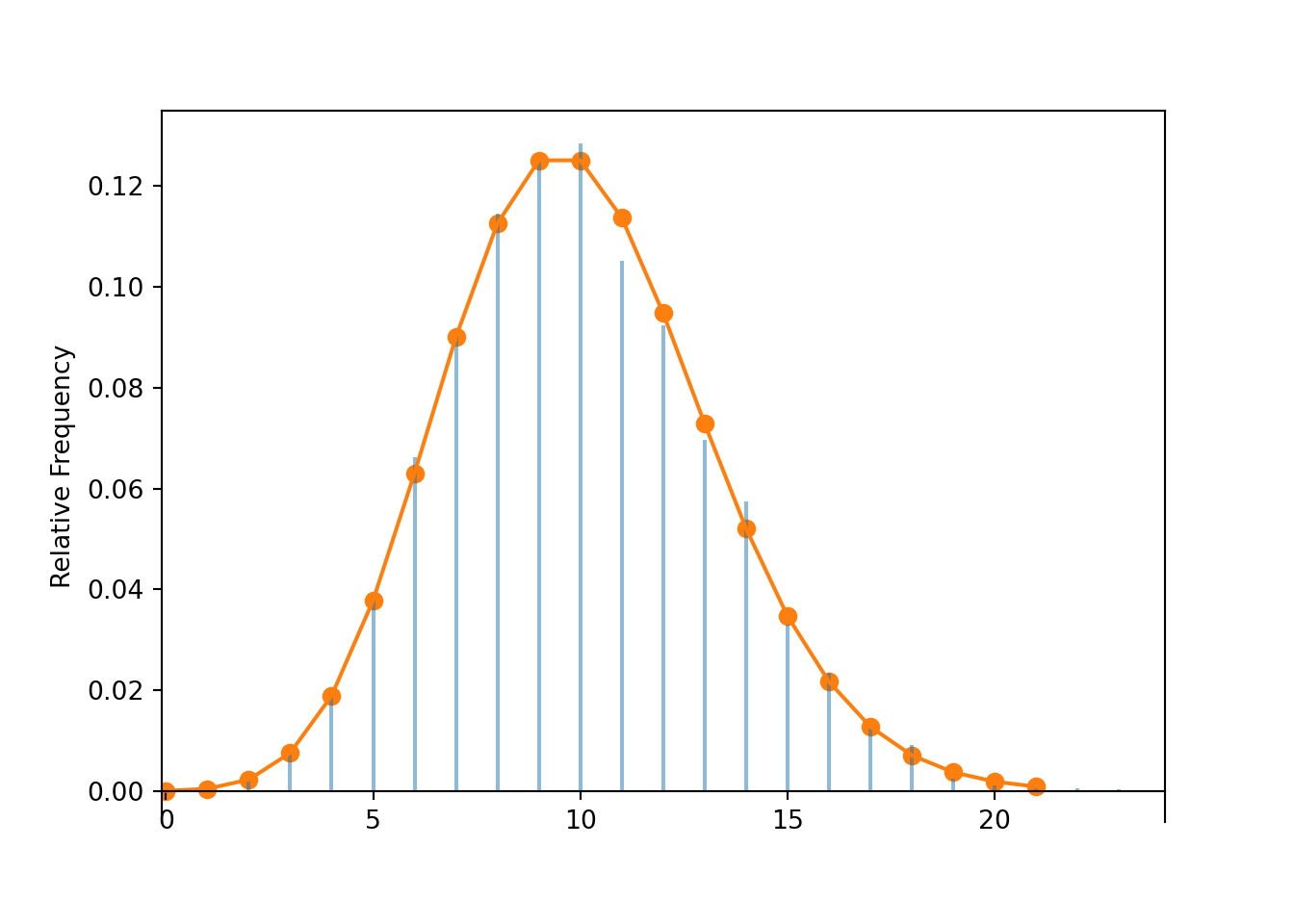
plt.figure();
(N[5] - N[3]).sim(10000).plot()
Poisson(2 * (5 - 3)).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Poisson object at 0x0000017B65293850>plt.show()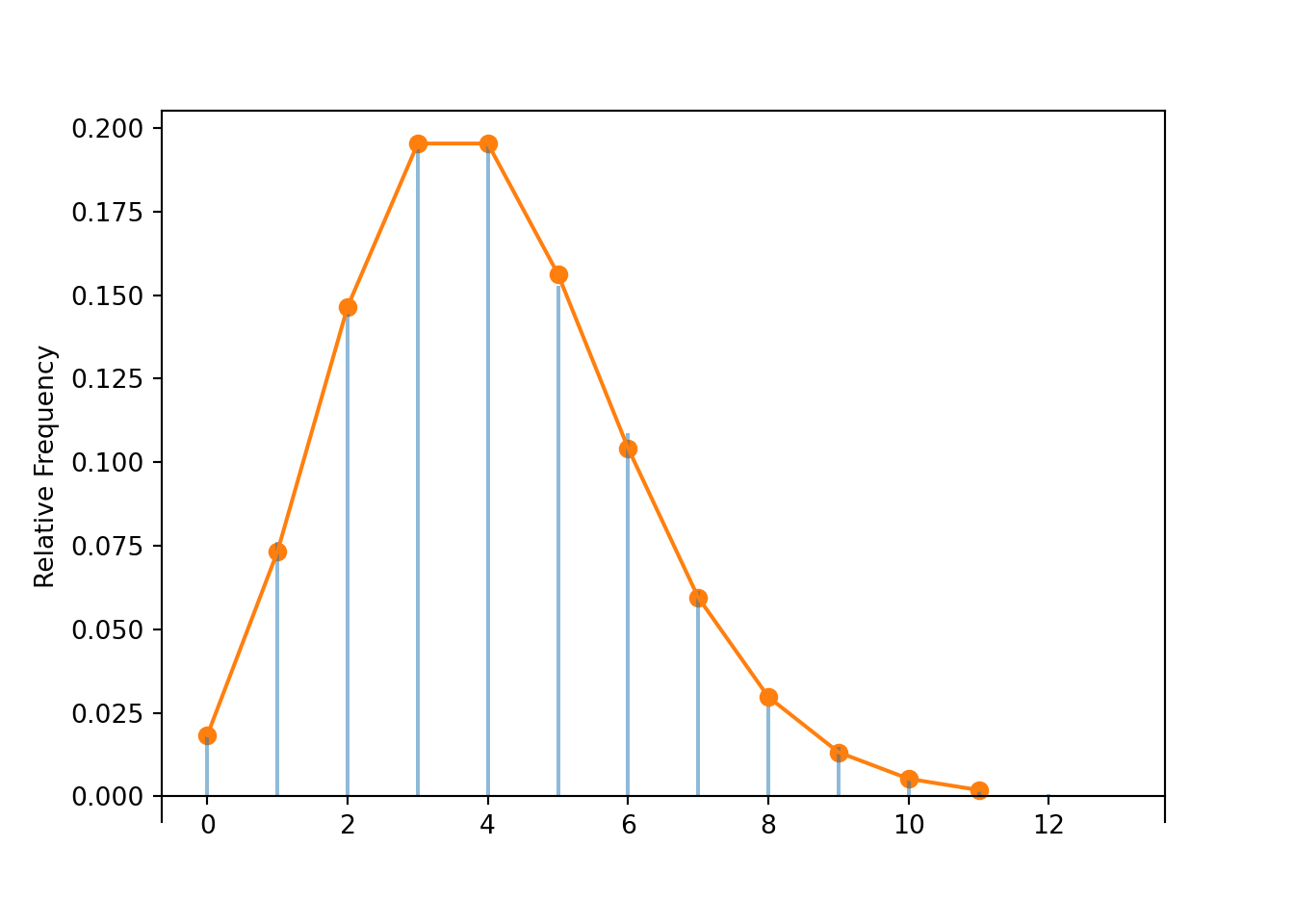
W = RV(P, interarrival_times)plt.figure();
W[0].sim(10000).plot()
Exponential(rate = 2).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Exponential object at 0x0000017B6549BA10>plt.show();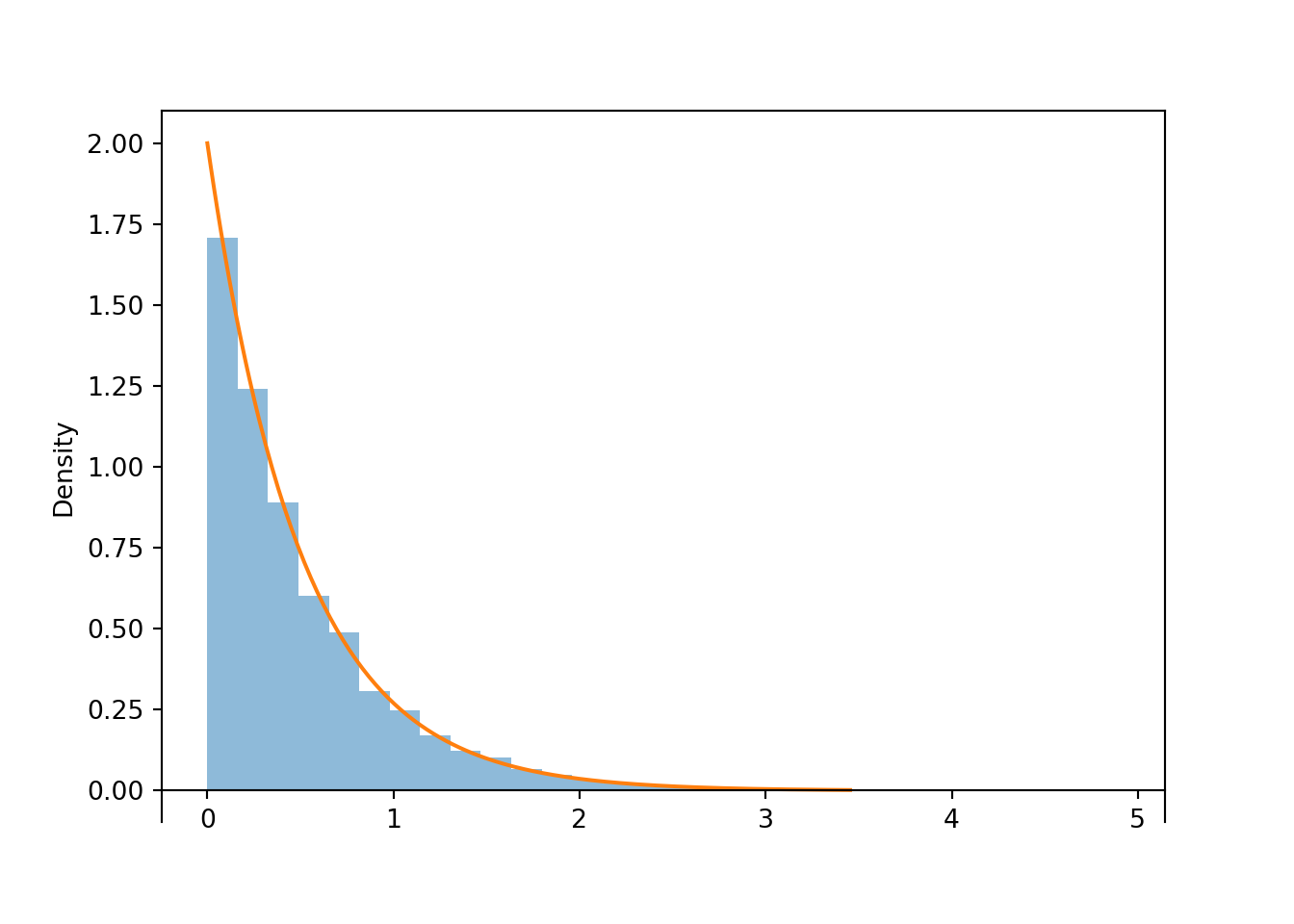
plt.figure();
(W[0] & W[1]).sim(10000).plot()
plt.show();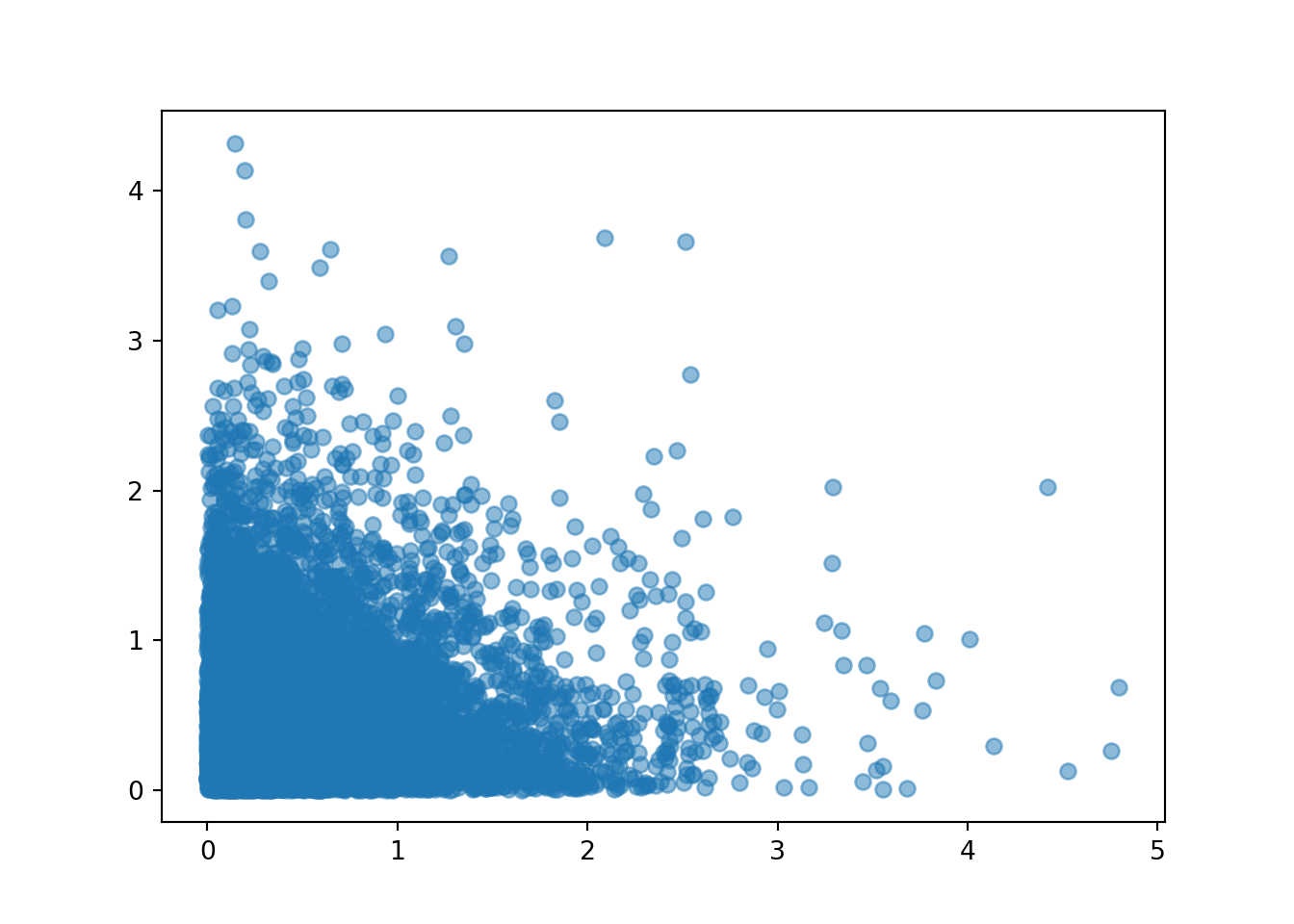
T = RV(P, arrival_times)plt.figure();
T[0].sim(10000).plot()
Gamma(shape = 1, rate = 2).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Gamma object at 0x0000017B64300410>plt.show();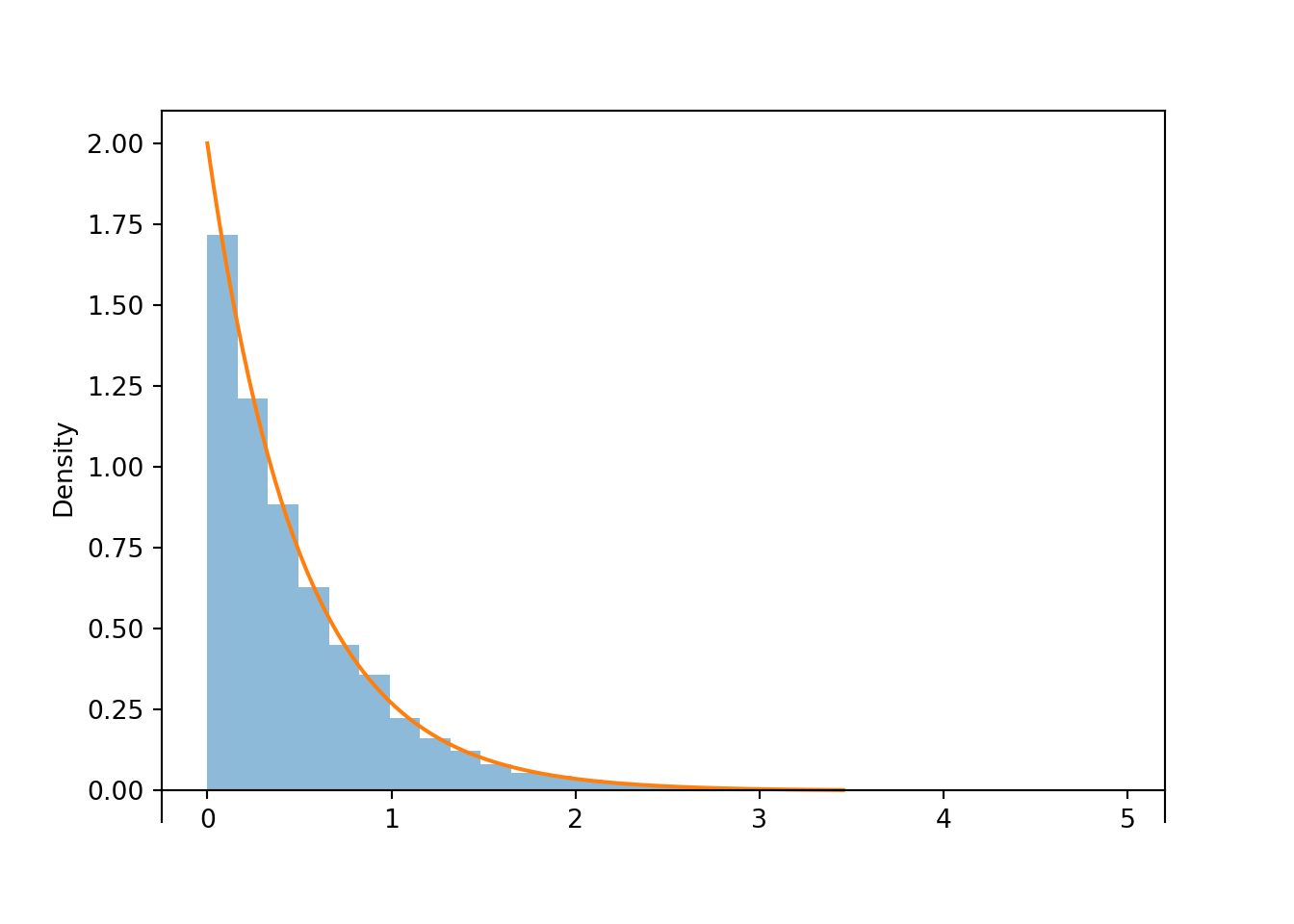
plt.figure();
T[1].sim(10000).plot()
Gamma(shape = 2, rate = 2).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Gamma object at 0x0000017B642467D0>plt.show();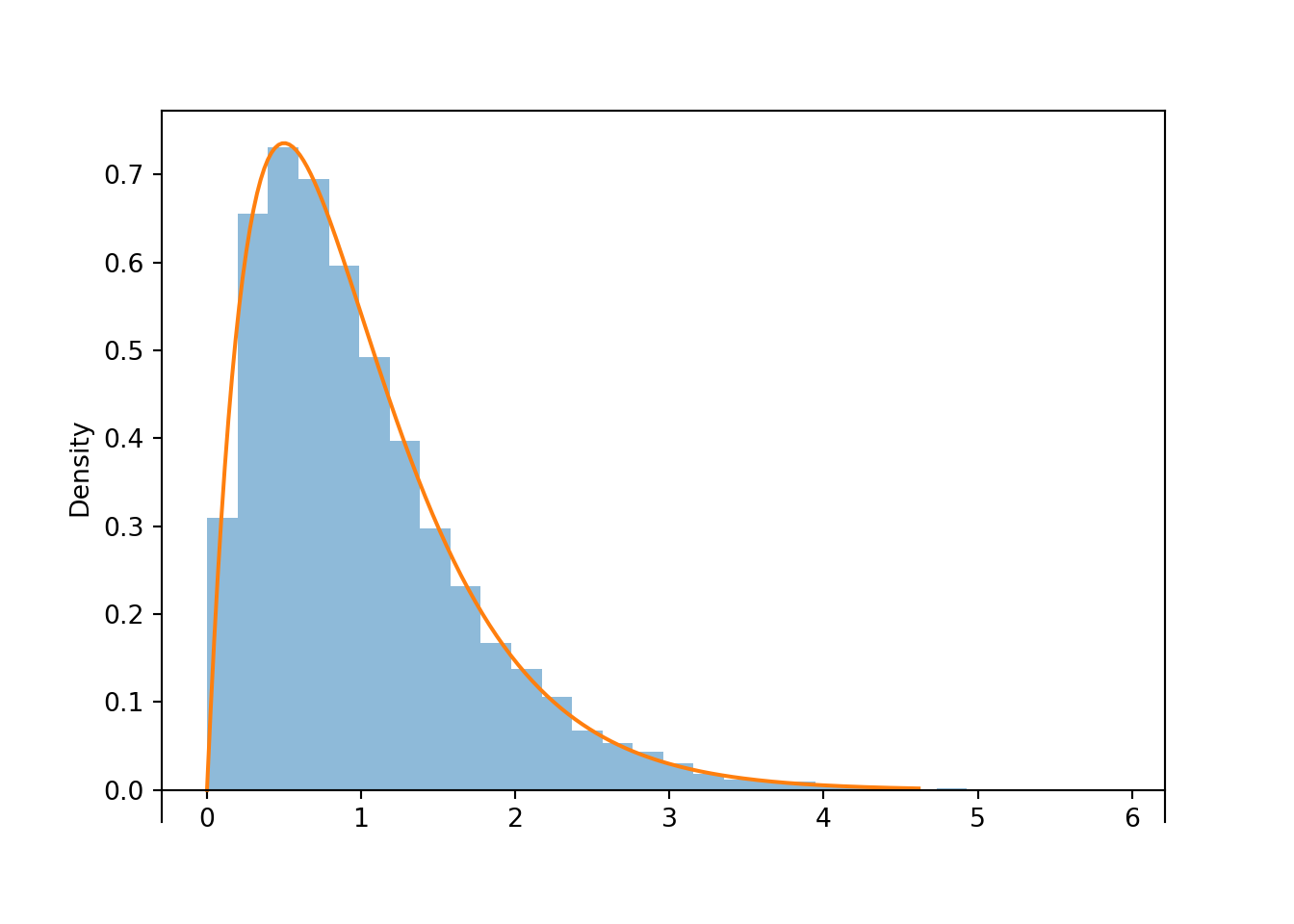
plt.figure();
N[0.05].sim(10000).plot()
plt.show();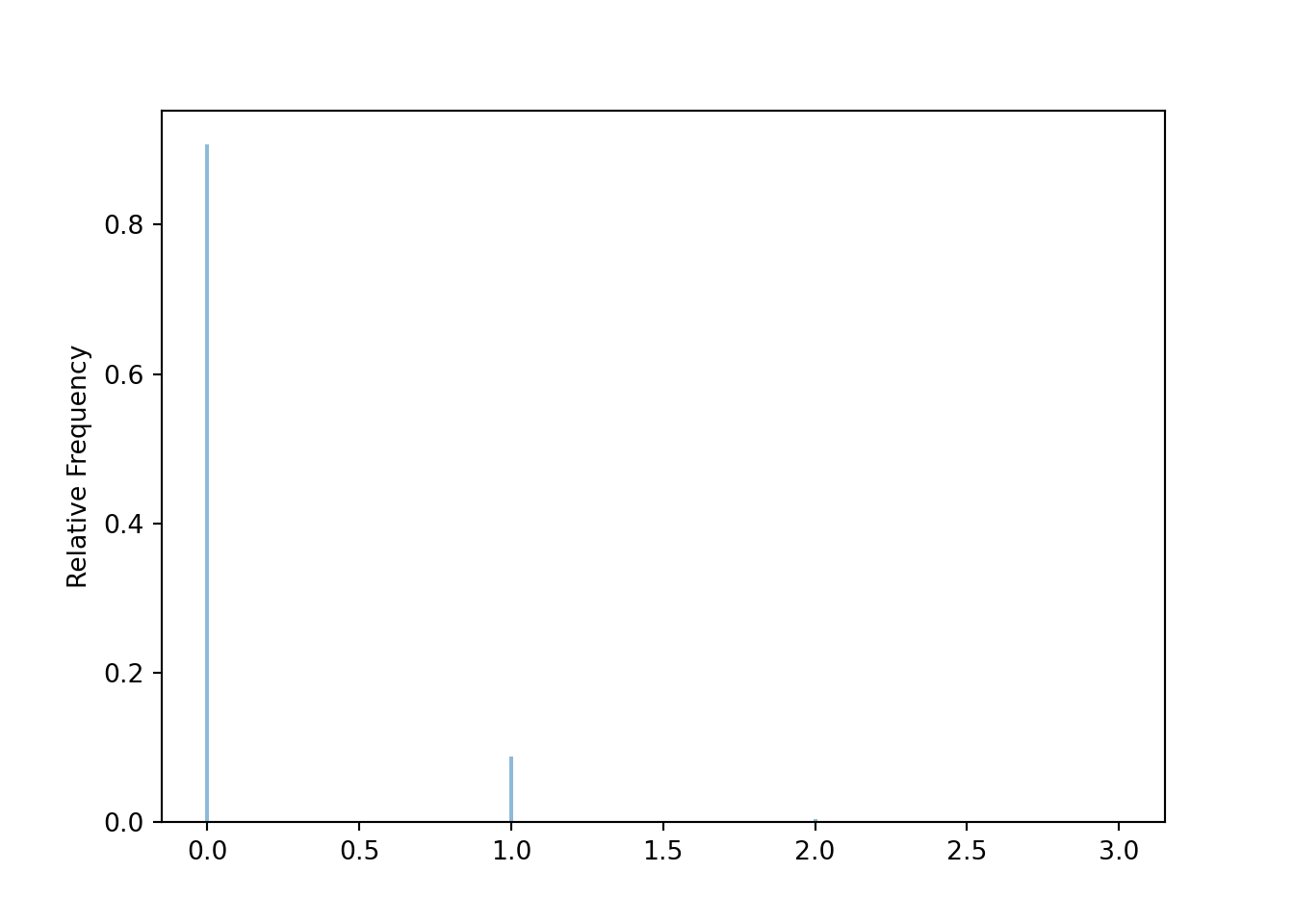
plt.figure();
(N[2] | (N[5] == 10) ).sim(10000).plot()
Binomial(10, 2 / 5).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Binomial object at 0x0000017B63D13910>plt.show();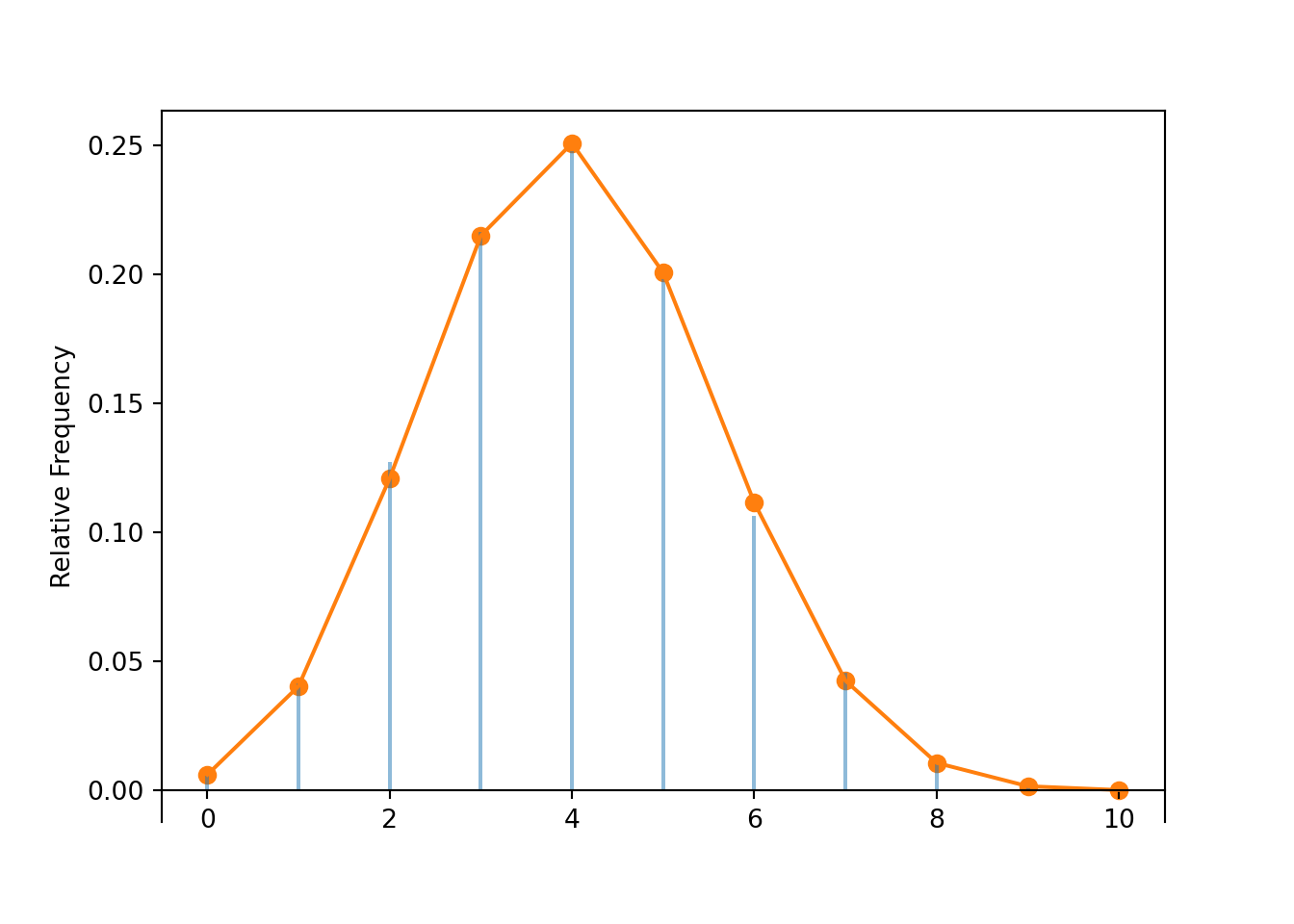
plt.figure();
(T[0] | (N[2] == 1) ).sim(10000).plot()
Uniform(0, 2).plot()<symbulate.distributions.Uniform object at 0x0000017B64302E50>plt.show();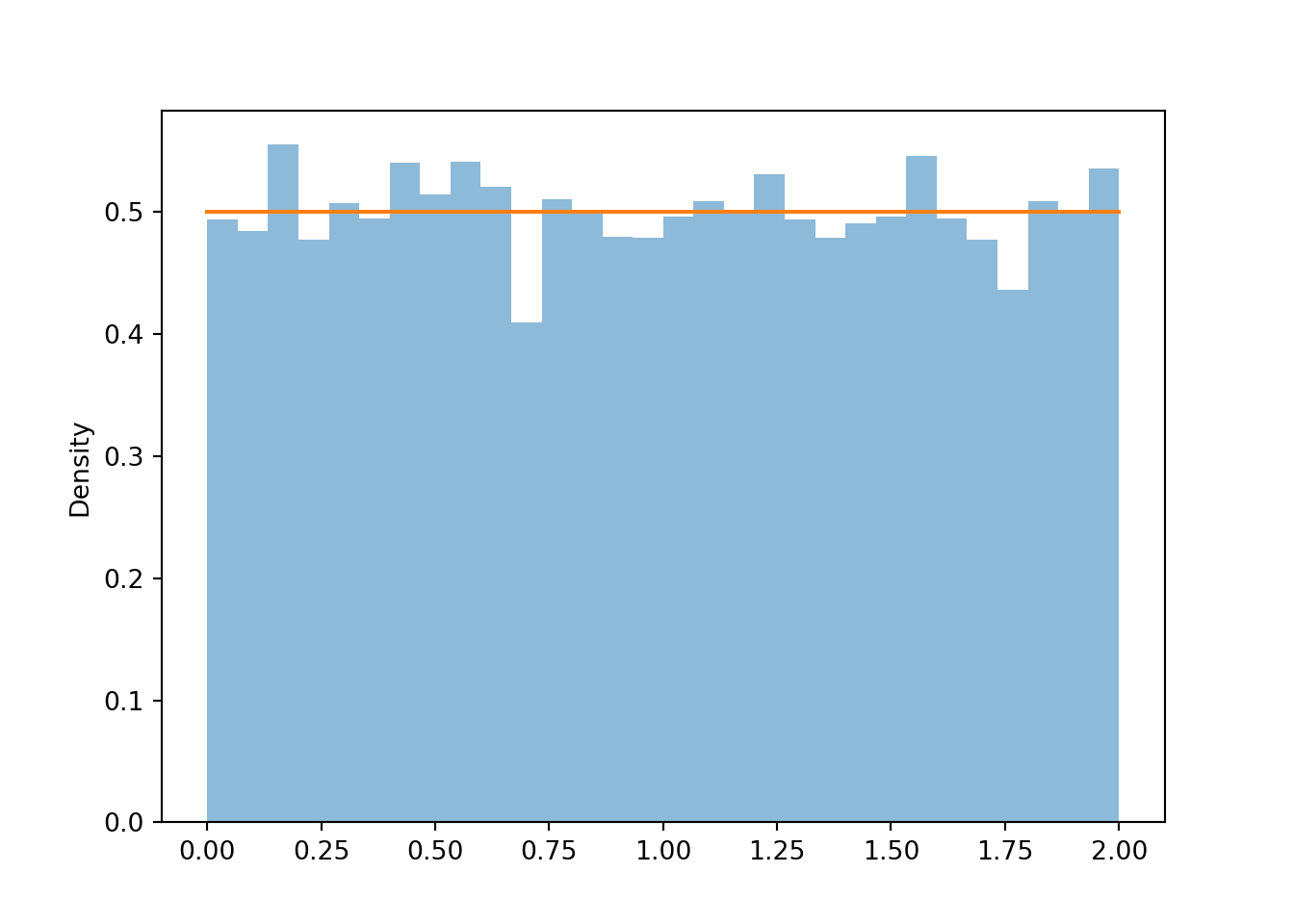
plt.figure();
((T[0] & T[1]) | (N[2] == 2) ).sim(1000).plot()
plt.show();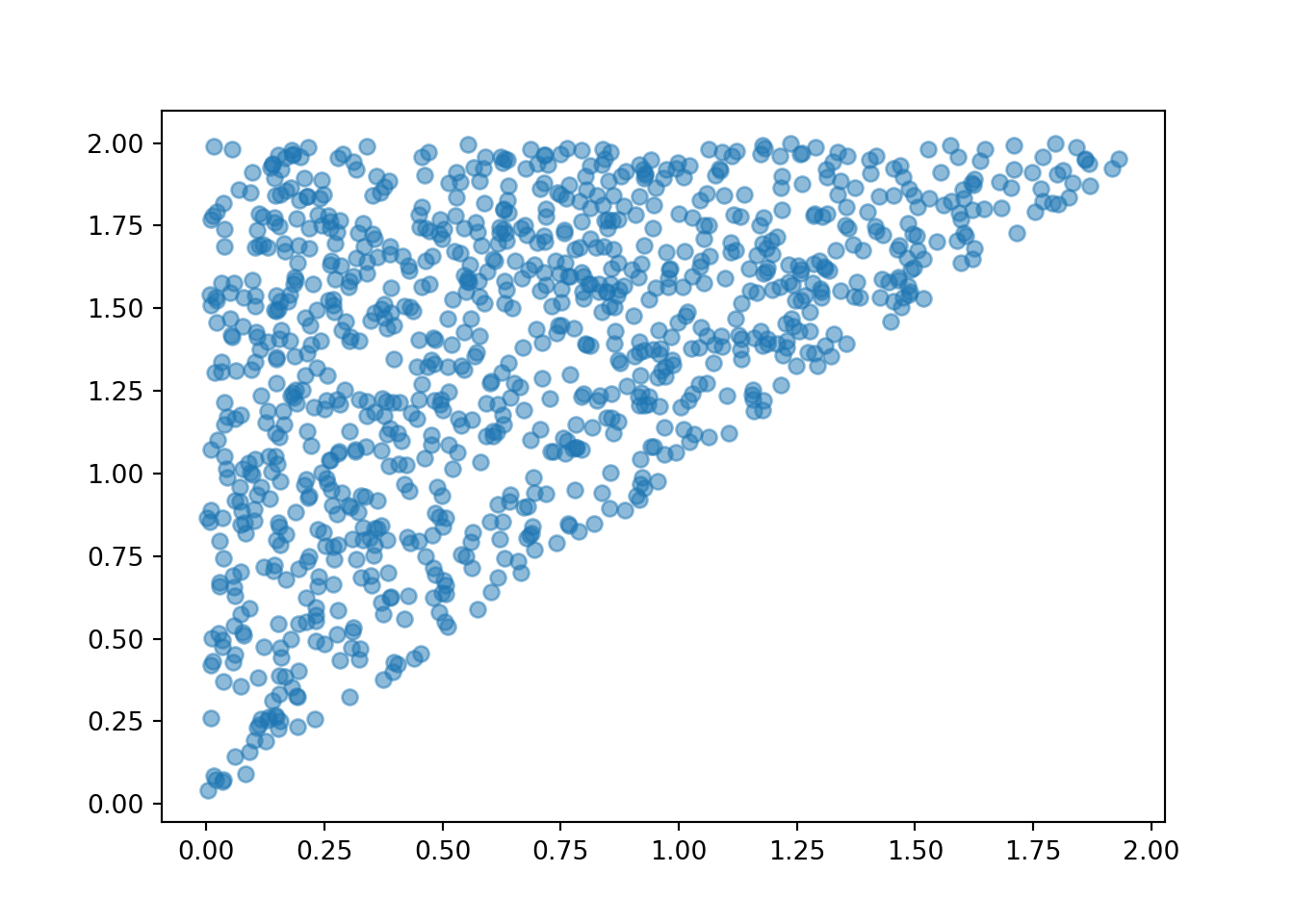
Order statistics of Uniform
plt.figure();
P = Uniform(0, 2) ** 2
U1 = RV(P, min)
U2 = RV(P, max)
(U1 & U2).sim(1000).plot()
plt.show();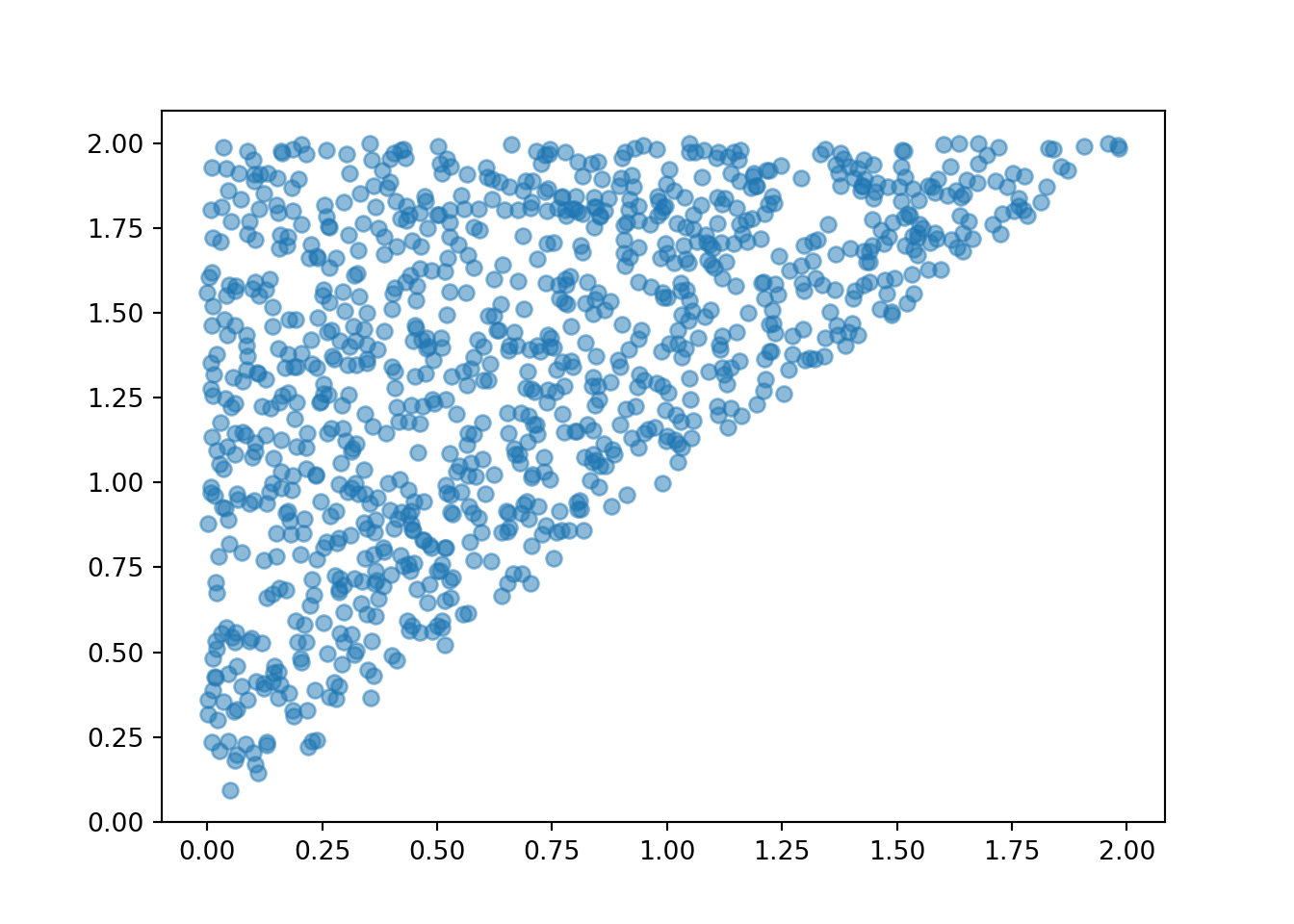
Tmax = 10000
T = 5 #mean time between buses
lambda = 2
N_commuters = rpois(1, lambda * Tmax)
W_commuters = sort(runif(N_commuters, 0 , Tmax))
N_buses = rpois(1, Tmax / T)
W_buses = sort(runif(N_buses, 0 , Tmax))
waiting_time = rep(NA, N_commuters)
for (i in 1:N_commuters){
if (W_commuters[i] < max(W_buses)){
waiting_time[i] = min(W_buses[W_buses > W_commuters[i]]) - W_commuters[i]
}
}
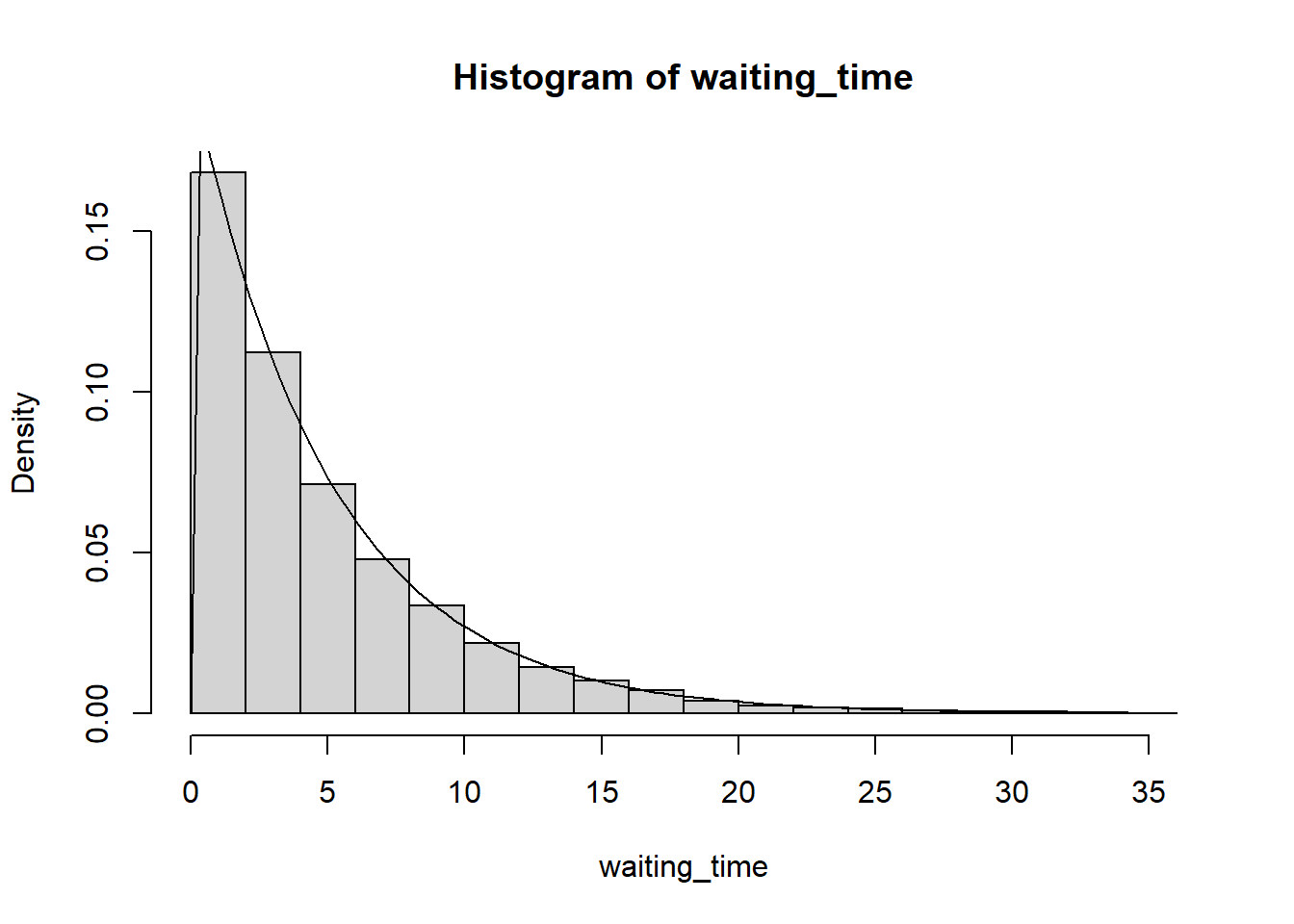
mean(waiting_time, na.rm = TRUE)[1] 4.908867hist(waiting_time, freq = FALSE)
curve(dexp(x, 1 / T), add = TRUE)