6.1 Predictive Data Analysis (PDA)
Human has a long history of obsessed with production. A magic crystal ball was used to predict the future.

Figure 6.1: Human is obsessed with prediction using a crystal ball.
In data science, Predictive data analysis (PDA) can not be accomplished alone. It needs to encompass both of DDA and EDA, to analyse historical and current data, and then to make predictions about future or unknown data.
A classic example of a predictive model is customer scoring as shown in Figure 6.2. The customer scoring model factors together individual customer’s attributes (properties or attributes), weight them, and adds them up to produce an overall score.
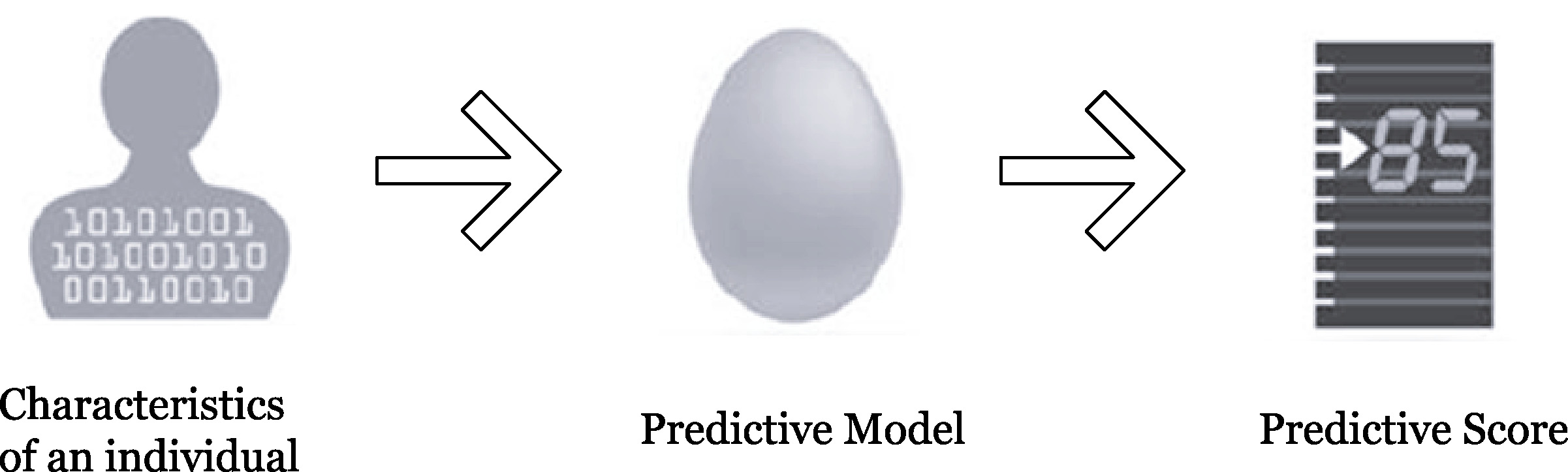
Figure 6.2: Example of predictive model for customer score
The typical way to build a predictive model is through training on the training dataset. The model built is then tested with the testing dataset, so its performance can be tested and evaluated, improved to satisfactory. Finally, the model can be applied to the unknown datasets for predictions and applications.