2 August 20
2.1 Announcements
- Assignment #1 due Friday at 5 pm
- Office hours 9:30 - 10:30 today
- PDF/PMF handout
-Reading Assignment
- By next Thursday read pgs. 77 - 106 in Wikle et al. (2019)
2.2 Statistical models
- What is a model?
- Simplification of something that is real designed to serve a purpose
- What is a statistical model?
- Simplification of a real data generating mechanism
- Constructed from deterministic mathematical equations and Probability density /mass functions
- Capable of generating data
- What is the purpose of a statistical model
- See section 1.2 on pg. 7 and pg. 77 of Wikle et al. (2019)
- Capable of making predictions, forecasts, and hindcasts
- Enables statistical inference about observable and unobservable quantities
- Reliability quantify and communicate uncertainty
- Example using simple linear regression
2.3 Matrix review
- Column vectors
- \(\mathbf{y}\equiv(y_{1},y_{2},\ldots,y_{n})^{'}\)
- \(\mathbf{x}\equiv(x_{1},x_{2},\ldots,x_{n})^{'}\)
- \(\boldsymbol{\beta}\equiv(\beta_{1},\beta_{2},\ldots,\beta_{p})^{'}\)
- \(\boldsymbol{1}\equiv(1,1,\ldots,1)^{'}\)
- In R
## [,1] ## [1,] 1 ## [2,] 2 ## [3,] 3 - Matrices
- \(\mathbf{X}\equiv(\mathbf{x}_{1},\mathbf{x}_{2},\ldots,\mathbf{x}_{p})\)
- In R
## [,1] [,2] ## [1,] 1 4 ## [2,] 2 5 ## [3,] 3 6 - Vector multiplication
- \(\mathbf{y}^{'}\mathbf{y}\)
- \(\mathbf{1}^{'}\mathbf{1}\)
- \(\mathbf{1}\mathbf{1}^{'}\)
- In R
## [,1] ## [1,] 14 - Matrix by vector multiplication
- \(\mathbf{X}^{'}\mathbf{y}\)
- In R
## [,1] ## [1,] 14 ## [2,] 32 - Matrix by matrix multiplication
- \(\mathbf{X}^{'}\mathbf{X}\)
- In R
## [,1] [,2] ## [1,] 14 32 ## [2,] 32 77 - Matrix inversion
- \((\mathbf{X}^{'}\mathbf{X})^{-1}\)
- In R
## [,1] [,2] ## [1,] 1.4259259 -0.5925926 ## [2,] -0.5925926 0.2592593 - Determinant of a matrix
- \(|\mathbf{I}|\)
- In R
## [,1] [,2] [,3] ## [1,] 1 0 0 ## [2,] 0 1 0 ## [3,] 0 0 1## [1] 1 - \(|\mathbf{I}|\)
- Quadratic form
- \(\mathbf{y}^{'}\mathbf{S}\mathbf{y}\)
- Derivative of a quadratic form (Note \(\mathbf{S}\) is a symmetric matrix; e.g., \(\mathbf{X}^{'}\mathbf{X}\))
- \(\frac{\partial}{\partial\mathbf{y}}\mathbf{y^{'}\mathbf{S}\mathbf{y}}=2\mathbf{S}\mathbf{y}\)
- Other useful derivatives
- \(\frac{\partial}{\partial\mathbf{y}}\mathbf{\mathbf{x^{'}}\mathbf{y}}=\mathbf{x}\)
- \(\frac{\partial}{\partial\mathbf{y}}\mathbf{\mathbf{X^{'}}\mathbf{y}}=\mathbf{X}\)
2.4 Distribution theory review
- Probability density functions (PDF) and probability mass functions (PMF)
- Normal distribution (continuous support)
- Binomial distribution (discrete support)
- Poisson distribution (discrete support)
- And many more (see handout)
- Distributions in R
- PDF of the normal distribution \[[z|\mu,\sigma^2] = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}\textit{e}^{-\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}(z - \mu)^2}\]
- \(z\) is the random variable
- \(\mu\) and \(\sigma^2\) are the parameters
- PDFs & PMFs in R
?dnorm
- Generate random variables (\(z\)) from a PDF (e.g., \(z_i\sim\text{N}(\mu,\sigma^2)\))
## [1] 0.50403669 -1.75030666 -0.43050400 0.01207176 -0.24953909- Histogram representation of a PDF
library(latex2exp) z <- rnorm(n = 10000, mean = 0, sd = 1) hist(z,freq=FALSE,col="grey",main = "", xlab= TeX('$\\mathit{z}$'), ylab = TeX('$\\lbrack\\mathit{z}|\\mu,\\sigma^2\\rbrack$'))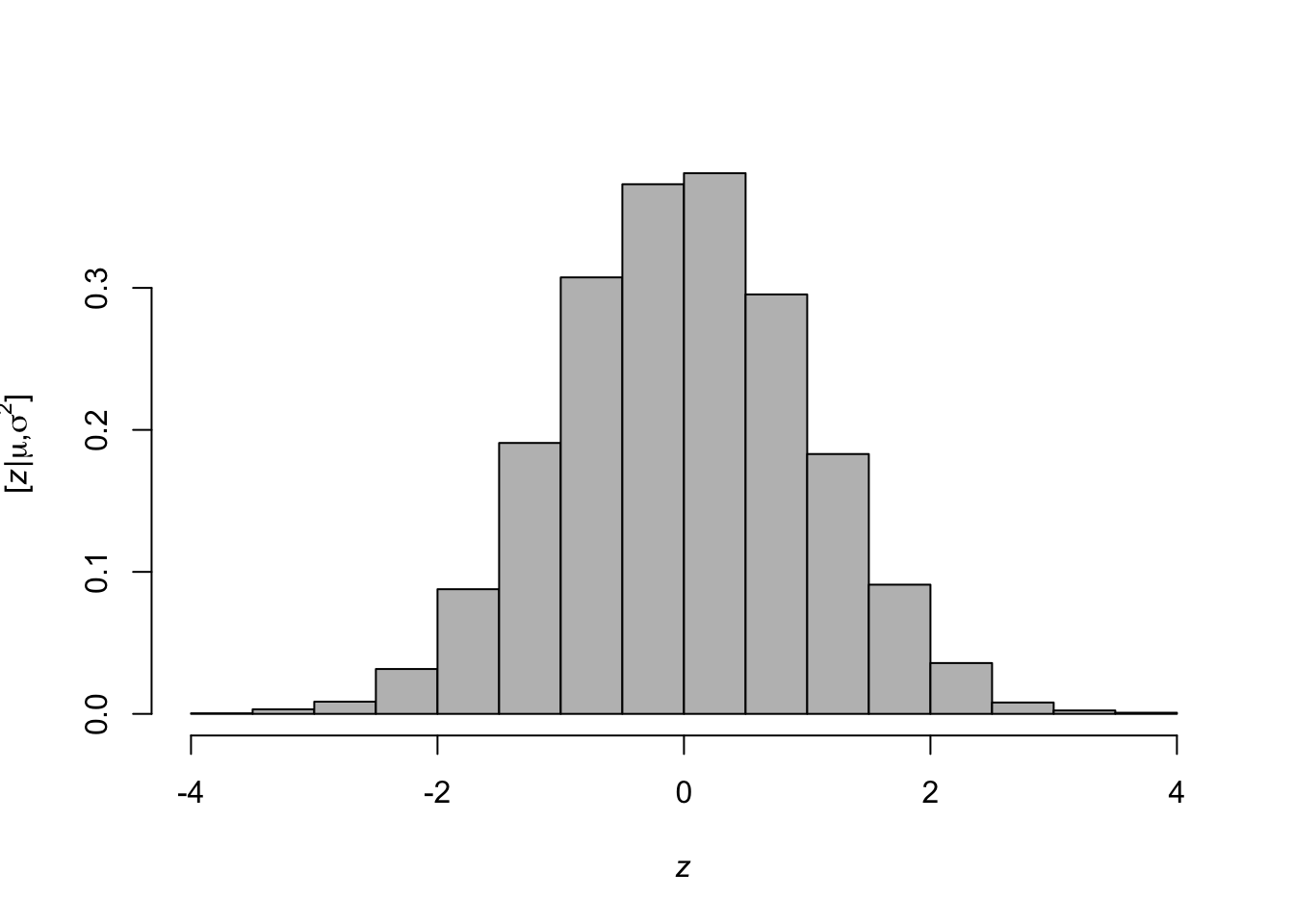
- Plot a PDF in R
curve(expr = dnorm(x = x, mean = 0, sd = 1), from = -10, to = 10, xlab= TeX('$\\mathit{z}$'), ylab = TeX('$\\lbrack\\mathit{z}|\\mu,\\sigma^2\\rbrack$'))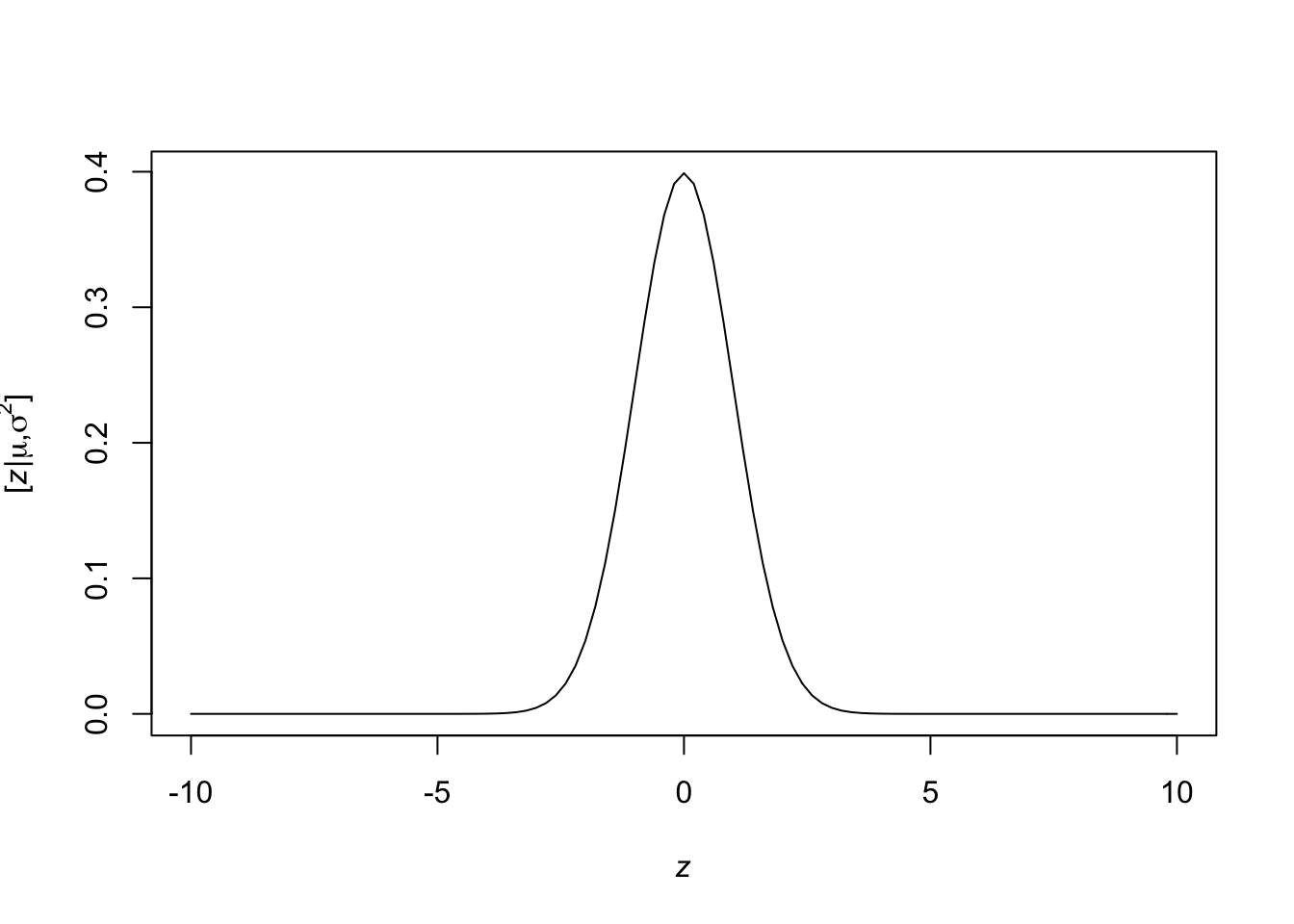
- Evaluate the “likelihood” at a given value of the parameters
## [1] 0.08492566- Other distributions
rpois(n = 5, lambda = 2) rbinom(n = 5, size = 10, prob = 0.5) runif(n = 5,min = 0,max = 3) rt(n = 5,df = 1) rcauchy(n = 5, location = 2, scale = 4)- See stats package for more information
- PDF of the normal distribution \[[z|\mu,\sigma^2] = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}\textit{e}^{-\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}(z - \mu)^2}\]
- Making your functions for a distribution
- PDF of the exponential distribution \[[z|\lambda] = \lambda\textit{e}^{-\lambda z}\]
- Make your own function for the PDF of the exponential distribution
- Make your own function to simulate random variables from the exponential distribution using the inverse probability integral transform
- Make histogram by sampling from
rexp()and overlay the PDF usingdexp()
z <- rexp(n = 10000, lambda = 1) hist(z,freq=FALSE,col="grey",main = "", xlab= TeX('$\\mathit{z}$'), ylab = TeX('$\\lbrack\\mathit{z}|\\lambda\\rbrack$')) curve(expr = dexp(z = x,lambda = 1), from = 0, to = 10, add = TRUE,col = "deepskyblue",lwd = 3)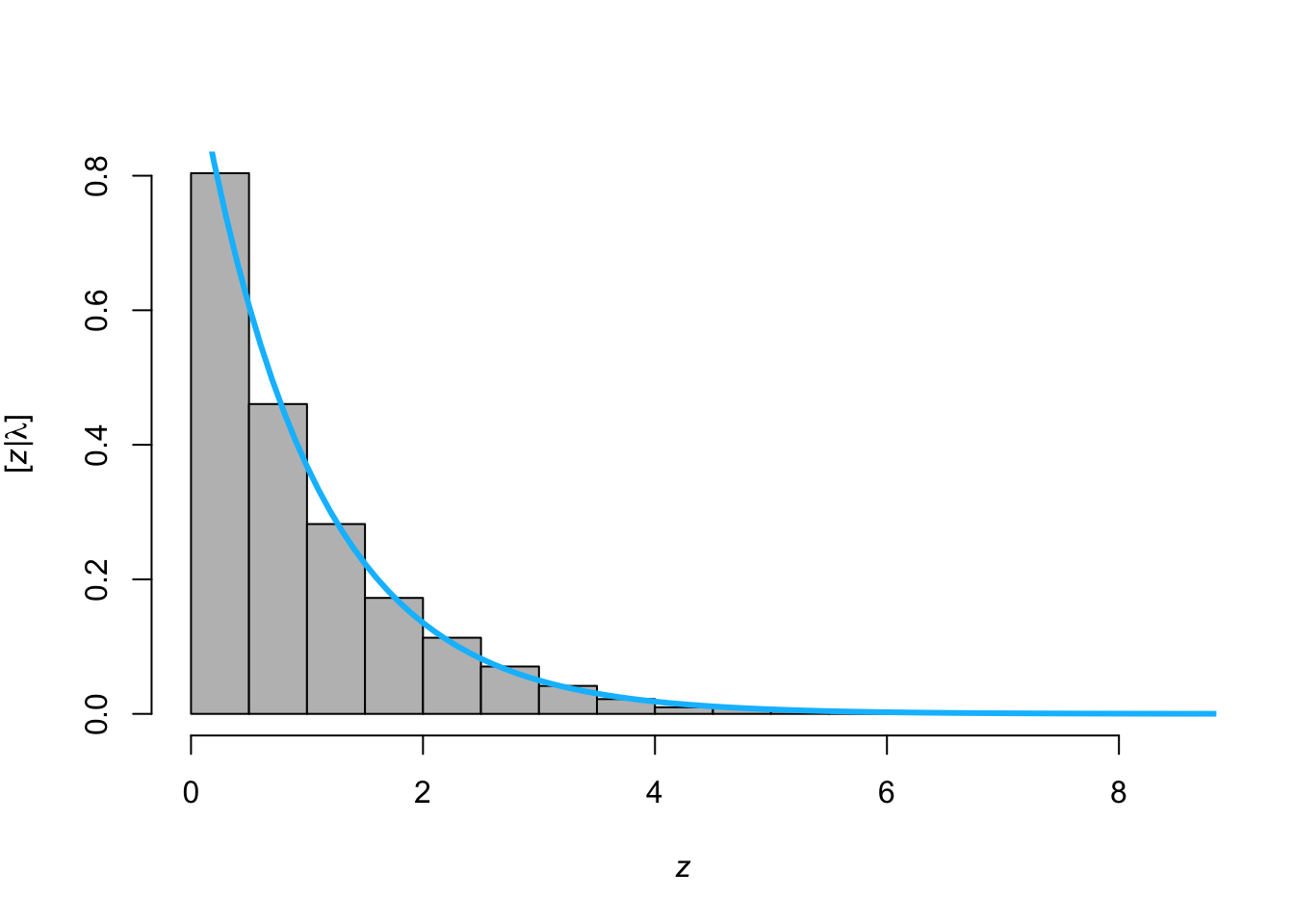
- Moments of a distribution
- First moment: \(\text{E}(z) = \int z [z|\theta]dz\)
- Second central moment: \(\text{Var}(z) = \int (z -\text{E}(z))^2[z|\theta]dz\)
- Note that \([z|\theta]\) is an arbitrary PDF or PMF with parameters \(\theta\)
- Example normal distribution \[\begin{eqnarray} \text{E}(z) &=& \int_{-\infty}^\infty z\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}\textit{e}^{-\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}(z - \mu)^2}dz\\&=& \mu \end{eqnarray}\] \[\begin{eqnarray} \text{Var}(z) &=& \int_{-\infty}^\infty (z-\mu)^2\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}\textit{e}^{-\frac{1}{2\sigma^2}(z - \mu)^2}dz\\&=& \sigma^2 \end{eqnarray}\]
- Example exponential distribution\[\begin{eqnarray} \text{E}(z) &=& \int_{0}^\infty z\lambda\textit{e}^{-\lambda z}dz\\&=& \frac{1}{\lambda} \end{eqnarray}\]\[\begin{eqnarray}\text{Var}(z) &=& \int_{0}^\infty (z-\mu)^2\lambda\textit{e}^{-\lambda z}dz\\&=& \frac{1}{\lambda^2} \end{eqnarray}\]
2.5 Mathematical model review
- Mathematical models are deterministic equations that describe the relationship between input variables and an output variable
- Common types of mathematical models used for spatio-temporal statistics
- Linear equations
- Scalar form: \(\mu=\beta_{0}+\beta_{1}x_{1}+\beta_{2}x_{2}+\ldots+\beta_{p}x_{p}\)
- Vector form: \(\boldsymbol{\mu}=\beta_{0}+\beta_{1}\mathbf{x}_{1}+\beta_{2}\mathbf{x}_{2}+\ldots+\beta_{p}\mathbf{x}_{p}\)
- Matrix form: \(\boldsymbol{\mu}=\mathbf{X}\boldsymbol{\beta}\)
- Non-linear equations Scalar form: \(\mu = e^{\beta_{0}+\beta_{1}x_{1}+\beta_{2}x_{2}+\ldots+\beta_{p}x_{p}}\)
- Difference equations
- Scalar form: \(\mu_{t+1} = \phi\mu_{t}\)
- Differential equations
- Scalar form: \(\frac{d\mu(t)}{dt}=\gamma\mu(t)\)
- Linear equations
2.6 Summary and comments
- The material covered today should be review for you
- Probability distributions and mathematical models are the building block for most (parametric) statistical models
- Agent-based models simulation models are also widely used but rarely using statistical approaches (Epstein and Axtell 1996; Heard et al. 2015)
- Next class meeting we will build our first statistical model!