Capítulo 15 Sistemas de Equacoes Lineares
Modelo \(\mathbf{y_i} = \mathbf{ X_i \beta + u_i}\)
onde: \(y_i\) é Gx1, \(X_i\) é GxK, \(\beta\) é Kx1 e \(u_i\) é Gx1.Sendo que \(K = k_1 + ... + K_G\)
15.0.1 SUR
Exemplo para dois indivíduos, 2 equações e 2 variáveis em cada equação
Nesse contexto \(x\) possui três dimensões: \(x_{ikg}\)
\[ \begin{bmatrix}y_{i1}\\ y_{i2} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}x_{i11} & x_{i21} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & x_{i12} & x_{i22} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \beta_{11} \\ \beta_{21} \\ \beta_{12} \\ \beta_{22} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} u_{i1} \\ u_{i2} \end{bmatrix}\]
\[ \begin{bmatrix}y_{i1}\\ y_{i2} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}x_{i11} \beta_{11} + x_{i21} \beta_{21} \\ x_{i12} \beta_{12} + x_{i22} \beta_{22} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} u_{i1} \\ u_{i2} \end{bmatrix}\]
Para uma Amostra N
\(Y = X\beta + U\)
onde: \(Y\) é um vetor NGx1, \(X\) uma matriz NGxK, \(\beta\) um vetor Kx1 e \(U\) um vetor NGx1.
Definir as variáveis explicativas do modelo
n = 1000
set.seed(1)
x1 = rnorm(n)
x2 = rnorm(n)Definir os termos de erros, independentes porém correlacionados entre as equações.
library(mvtnorm)
sigma = matrix(c(4,3,3,30), ncol=2)
mv = rmvnorm(n, mean=c(0,0), sigma=sigma)
u1 = matrix(c(mv[,1]),ncol = 1)
u2 = matrix(c(mv[,2]),ncol = 1)
u = rbind(u1,u2)Vetor \(\beta\)
beta1 = matrix(c(5,2,-1),ncol = 1)
beta2 = matrix(c(-5,-2,1),ncol = 1)
beta = rbind(beta1,beta2)Organizando a matrix \(X\)
X1 = cbind(1,x1,x2)
X2 = cbind(1,x1,x2)
X = rbind(cbind(X1,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,X2))Criando o vetor \(Y\)
Y = X%*%beta + uEstimador SOLS
Sols = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Y
Sols## [,1]
## 5.085939
## x1 1.979317
## x2 -1.104254
## -5.068044
## -2.089895
## 1.113130Estimar Equação por Equação
y1 = X1%*%beta1 + u1
y2 = X2%*%beta2 + u2ols1 = solve(t(X1)%*%X1)%*%t(X1)%*%y1
ols1## [,1]
## 5.085939
## x1 1.979317
## x2 -1.104254ols2 = solve(t(X2)%*%X2)%*%t(X2)%*%y2
ols2## [,1]
## -5.068044
## x1 -2.089895
## x2 1.113130Matriz de Variância e Covariância
\(\hat V(\hat\beta_{SOLS} = (X^{'}X)^{-1}X^{'}DX(X^{'}X)\)
e_hat = Y - X%*%Sols
e = c(e_hat)
e = e * e
D = diag(e)
V_h = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%(t(X)%*%D%*%X)%*%solve(t(X)%*%X)
V_h = (n/(n-6)) * V_h
ep_h = sqrt(diag(V_h))
ep_h## x1 x2
## 0.06478291 0.05993167 0.06459487 0.18294688 0.17507186 0.17235189e_hat1 = y1 - X1%*%ols1
e1 = c(e_hat1)
e1 = e1 * e1
D1 = diag(e1)
V_h1 = solve(t(X1)%*%X1)%*%(t(X1)%*%D1%*%X1)%*%solve(t(X1)%*%X1)
V_h1 = (n/(n-3)) * V_h1
ep_h1 = sqrt(diag(V_h1))
ep_h1## x1 x2
## 0.06468537 0.05984143 0.06449761e_hat2 = y2 - X2%*%ols2
e2 = c(e_hat2)
e2 = e2 * e2
D2 = diag(e2)
V_h2 = solve(t(X2)%*%X2)%*%(t(X2)%*%D2%*%X2)%*%solve(t(X2)%*%X2)
V_h2 = (n/(n-3)) * V_h2
ep_h2 = sqrt(diag(V_h2))
ep_h2## x1 x2
## 0.1826714 0.1748083 0.172092415.1 FGLS
Estimar a matriz \(\Omega = E(\mathbf u_i \mathbf u_i^{'})\).
\(\hat\Omega = N^{-1} \sum_{i =1}^N u_i u_i^{'} = UU^{'}\)
e_hat1 = y1 - X1%*%Sols[c(1,2,3),1]
e_hat2 = y2 - X2%*%Sols[c(4,5,6),1]
e_hat = cbind(e_hat1,e_hat2)
sigma = t(e_hat)%*%e_hat\(S = (I_N \otimes \Omega^{-1})\)
I = diag(n)
S = kronecker(I,solve(sigma)) ## Wooldridge\(\hat\beta_{Fgls} = [X^{'}(\Omega^{-1} \otimes I_N)X]^{-1} [X^{'}(\Omega^{-1} \otimes I_N)Y]\)
Bfgls = solve(t(X)%*%(S)%*%X)%*%(t(X)%*%(S)%*%Y) ## Wooldridge
Bfgls## [,1]
## 4.982906
## x1 1.938422
## x2 -1.129926
## -5.211998
## -2.191069
## 1.046103V = solve(t(X)%*%S%*%X)%*%(t(X)%*%S%*%D%*%S%*%X)%*%solve(t(X)%*%S%*%X)
V = (1/(n-6)) * V
ep = sqrt(diag(V))
ep## x1 x2
## 0.002822832 0.002279409 0.002360631 0.007680877 0.006445076 0.006601576\(\hat V(\hat\beta_{Fgls}) = N^{-1} (X^{'}(\Omega^{-1} \otimes I_N)X)\)
V_h = solve(t(X)%*%(S)%*%X)
V_h = (1/(n-6)) * V_h
ep_h = sqrt(diag(V_h))
ep_h## x1 x2
## 0.09158073 0.07939336 0.07606356 0.09158073 0.07939336 0.0760635615.1.0.1 PAINEL
\[ \begin{bmatrix}y_{i1}\\ y_{i2} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}x_{i11} & x_{i21} \\ x_{i12} & x_{i22} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \beta_{1} \\ \beta_{2} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} u_{i1} \\ u_{i2} \end{bmatrix}\]
n = 1000
set.seed(1)
x1 = rnorm(n)
x2 = rnorm(n)sigma = matrix(c(4,3,3,30), ncol=2)
mv = rmvnorm(n, mean=c(0,0), sigma=sigma)
u1 = matrix(c(mv[,1]),ncol = 1)
u2 = matrix(c(mv[,2]),ncol = 1)
u = rbind(u1,u2)beta = matrix(c(5,2,-1),ncol = 1)X1 = cbind(1,x1,x2)
X2 = cbind(1,x1,x2)
y1 = X1%*%beta + u1
y2 = X2%*%beta + u2
X = rbind(X1,X2)
Y = X%*%beta + uPooled OLS
Pols = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Y
Pols## [,1]
## 5.0089472
## x1 1.9447113
## x2 -0.9955618e_hat = Y - X%*%Pols
e = c(e_hat)
e = e * e
D = diag(e)
V_h = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%(t(X)%*%D%*%X)%*%solve(t(X)%*%X)
V_h = (n/(n-3)) * V_h
ep_h = sqrt(diag(V_h))
ep_h## x1 x2
## 0.09694305 0.09244921 0.09192699FGLS
e_hat1 = y1 - X1%*%Pols
e_hat2 = y2 - X2%*%Pols
e_hat = cbind(e_hat1,e_hat2)sigma = t(e_hat)%*%e_hat
I = diag(n)
S = kronecker(I,solve(sigma)) ## WooldridgeBfgls = solve(t(X)%*%(S)%*%X)%*%(t(X)%*%(S)%*%Y) ## Wooldridge
Bfgls## [,1]
## 4.885780
## x1 1.873816
## x2 -1.041929V_h = solve(t(X)%*%(S)%*%X)
V_h = (1/(n)) * V_h
ep_h = sqrt(diag(V_h))
ep_h## x1 x2
## 0.06470610 0.05614001 0.0537869815.2 Sistema de Equações com Variávies Instrumentais
15.2.1 2SLS
n = 1000
set.seed(1)
# Create independent variables
z1 = rnorm(n)
z2 = rnorm(n)
# Create error
u1 = rnorm(n)
u2 = rnorm(n)
# Create endogenous variable
x1 = .5*z1 - z2 + u1 + rnorm(n)
x2 = 1.5*z1 - 2*z2 - u2 + rnorm(n)
x3 = rnorm(n)
# Create dependent variable
y1 = 5 + 2*x1 - x2 + x3 + u1*5 - u2*2
y2 = -5 - 2*x1 + x2 - 2*x3 + u2*5 - u1*1
#X = cbind(x1,x2,x3,1)
#Y = cbind(y1,y2)X = rbind(cbind(1,x1,x2,x3,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x1,x2,x3))
Z = rbind(cbind(1,x3,z1,z2,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x3,z1,z2))
Y = matrix(c(y1,y2),ncol=1)Estimar por SOLS
Sols = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Y
Sols## [,1]
## 5.0262660
## x1 3.8164234
## x2 -1.2994949
## x3 0.8788473
## -4.9438961
## -1.5682791
## 0.1883747
## -1.9464426sols = function(n){
# Create independent variables
z1 = rnorm(n)
z2 = rnorm(n)
# Create error
u1 = rnorm(n)
u2 = rnorm(n)
# Create endogenous variable
x1 = .5*z1 - z2 + u1 + rnorm(n)
x2 = 1.5*z1 - 2*z2 - u2 + rnorm(n)
x3 = rnorm(n)
# Create dependent variable
y1 = 5 + 2*x1 - x2 + x3 + u1*5 - u2*2
y2 = -5 - 2*x1 + x2 - 2*x3 + u2*5 - u1*1
X = rbind(cbind(1,x1,x2,x3,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x1,x2,x3))
Z = rbind(cbind(1,x3,z1,z2,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x3,z1,z2))
Y = matrix(c(y1,y2),ncol=1)
Sols = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Y
Sols
}
z = replicate(10000, expr = sols(1000))
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
plot(density(z[2, 1, ]), xlim = c(0,4))
abline(v = 2)
plot(density(z[3, 1, ]), xlim = c(-2,0))
abline(v = -1)
plot(density(z[6, 1, ]), xlim = c(-4,0))
abline(v = -2)
plot(density(z[7, 1, ]), xlim = c(0,2))
abline(v = 1)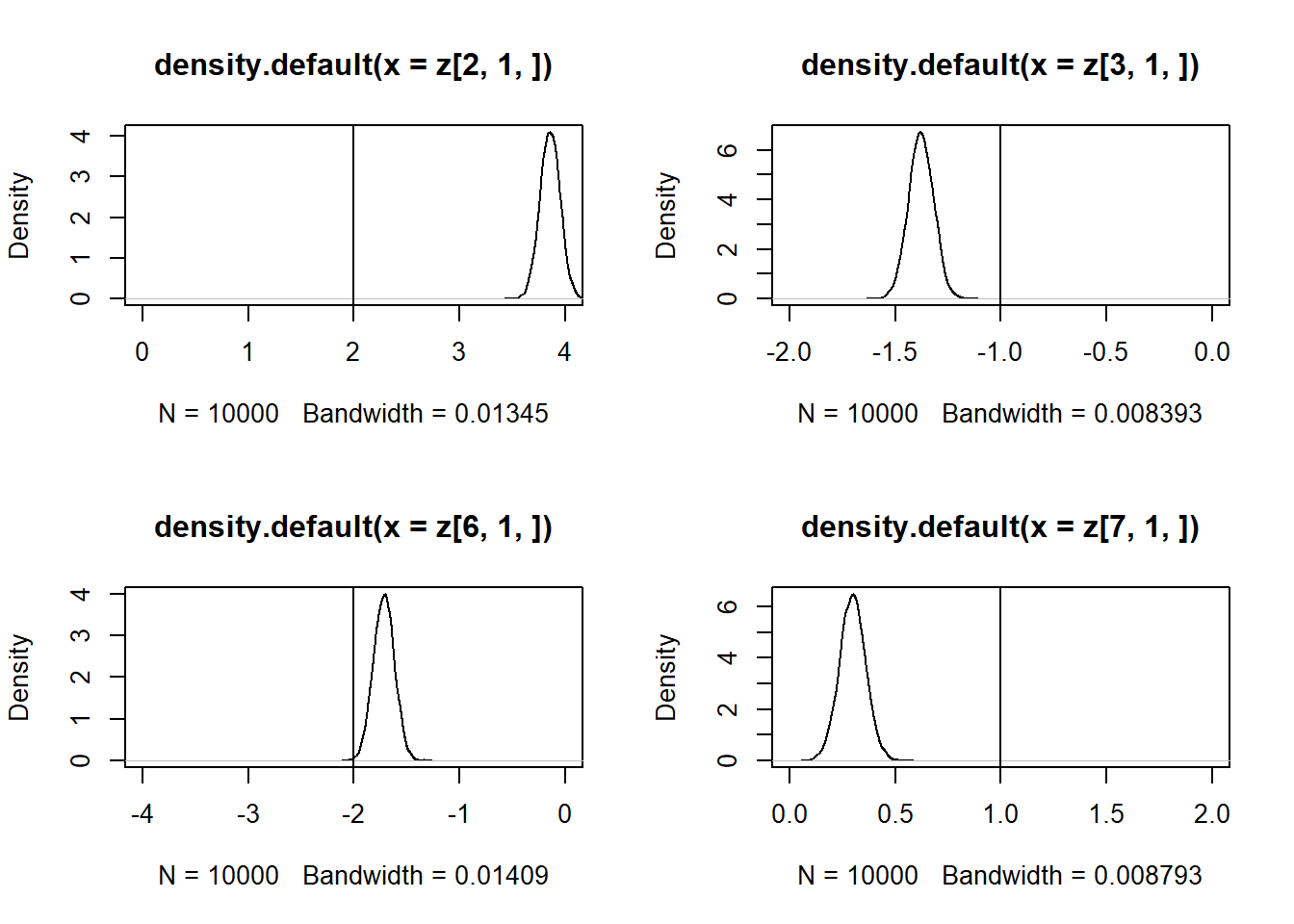
\(\hat\beta(2sls) = [X^{'}Z(Z^{'}Z)^{-1}Z^{'}X]^{-1}\)
SIV = solve(t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%Y
SIV## [,1]
## 5.0540920
## x1 0.6846211
## x2 -0.4035435
## x3 0.7844303
## -4.9229999
## -2.5418566
## 1.2379796
## -1.8822475sols = function(n){
# Create independent variables
z1 = rnorm(n)
z2 = rnorm(n)
# Create error
u1 = rnorm(n)
u2 = rnorm(n)
# Create endogenous variable
x1 = .5*z1 - z2 + u1 + rnorm(n)
x2 = 1.5*z1 - 2*z2 - u2 + rnorm(n)
x3 = rnorm(n)
# Create dependent variable
y1 = 5 + 2*x1 - x2 + x3 + u1*5 - u2*2
y2 = -5 - 2*x1 + x2 - 2*x3 + u2*5 - u1*1
X = rbind(cbind(1,x1,x2,x3,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x1,x2,x3))
Z = rbind(cbind(1,x3,z1,z2,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x3,z1,z2))
Y = matrix(c(y1,y2),ncol=1)
SIV = solve(t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%Y
SIV
}
z = replicate(10000, expr = sols(1000))
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
plot(density(z[2, 1, ]), xlim = c(0,4))
abline(v = 2)
plot(density(z[3, 1, ]), xlim = c(-2,0))
abline(v = -1)
plot(density(z[6, 1, ]), xlim = c(-4,0))
abline(v = -2)
plot(density(z[7, 1, ]), xlim = c(0,2))
abline(v = 1)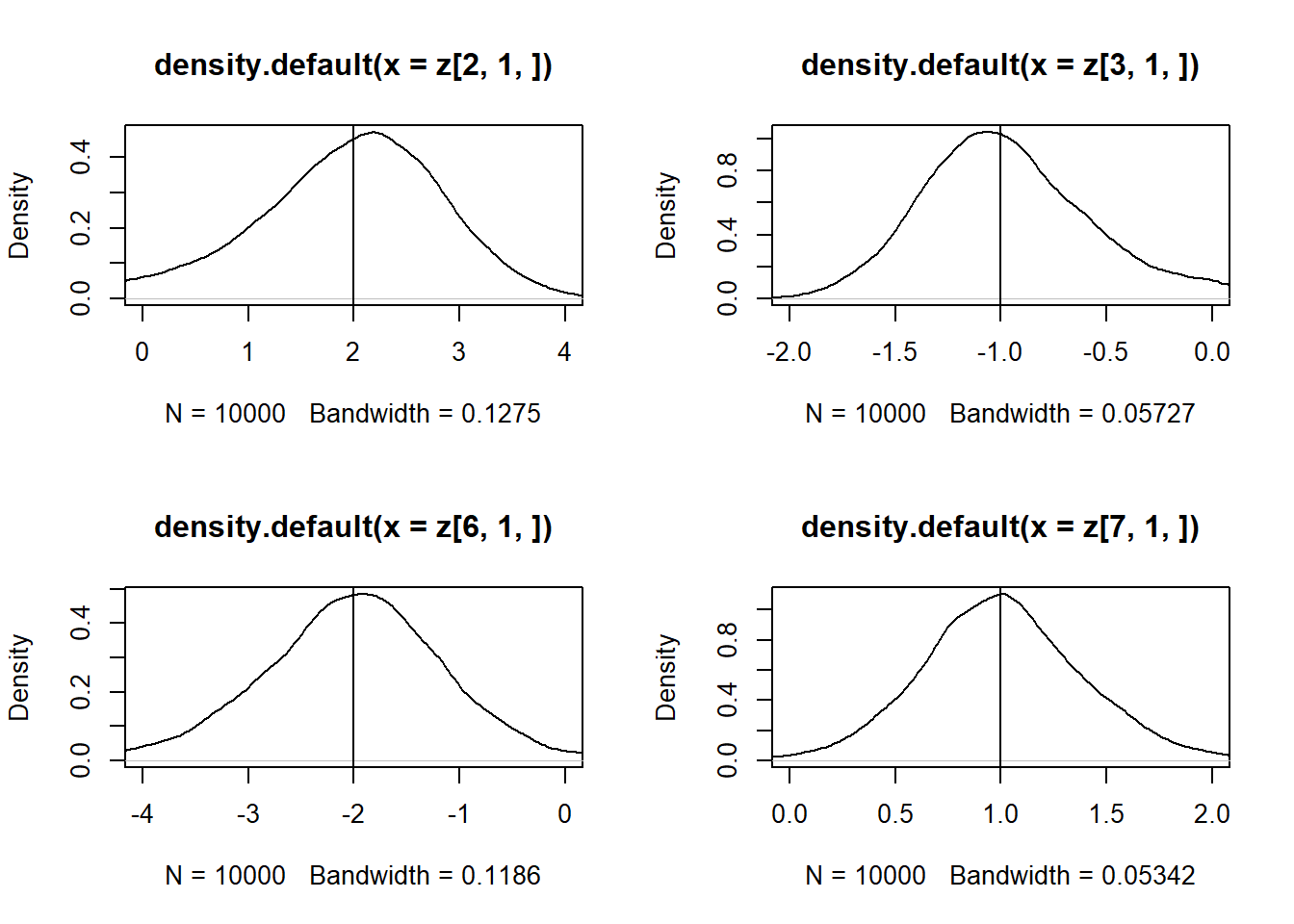
e_hat = Y - X%*%SIV
e = c(e_hat)
e = e * e
D = diag(e)
V_h = solve(t(X)%*%X)%*%(t(X)%*%D%*%X)%*%solve(t(X)%*%X)
V_h = (n/(n-8)) * V_h ## Para comparar com a estimação equação por equação usa-se k = 4
ep_h = sqrt(diag(V_h))
ep_h## x1 x2 x3
## 0.21240194 0.20748985 0.09645245 0.20761424 0.17464545 0.12252813 0.08269950
##
## 0.17908589Equção por equação
X = cbind(1,x1, x2, x3)
Y = cbind(y1,y2)
Z = cbind(1,x3, z1, z2)IV1 = solve(t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%y1
IV1## [,1]
## 5.0540920
## x1 0.6846211
## x2 -0.4035435
## x3 0.7844303IV2 = solve(t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%y2
IV2## [,1]
## -4.923000
## x1 -2.541857
## x2 1.237980
## x3 -1.88224715.2.2 FGLS - 3SLS
X1 = cbind(1,x1,x2,x3)
X2 = cbind(1,x1,x2,x3)
X = rbind(cbind(1,x1,x2,x3,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x1,x2,x3))
Z = rbind(cbind(1,x3,z1,z2,0,0,0,0),cbind(0,0,0,0,1,x3,z1,z2))
Y = matrix(c(y1,y2),ncol=1)e_hat1 = y1 - X1%*%SIV[c(1,2,3,4),1]
e_hat2 = y2 - X2%*%SIV[c(5,6,7,8),1]
e_hat = cbind(e_hat1,e_hat2)sigma = t(e_hat)%*%e_hat
I = diag(n)
S1 = kronecker(I,solve(sigma)) Bfgls1 = solve(t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%S1%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%X)%*%t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%S1%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%Y
Bfgls1## [,1]
## 5.0540920
## x1 0.6846211
## x2 -0.4035435
## x3 0.7844303
## -4.9229999
## -2.5418566
## 1.2379796
## -1.8822475S2 = kronecker(I,sigma)
V_h = solve(t(X)%*%Z%*%solve(t(Z)%*%S2%*%Z)%*%t(Z)%*%X)
V_h = (1/(n)) * V_h
ep_h = sqrt(diag(V_h))
ep_h## x1 x2 x3
## 0.1669931 1.1803355 0.5236078 0.1840325 0.1669931 1.1803355 0.5236078 0.1840325