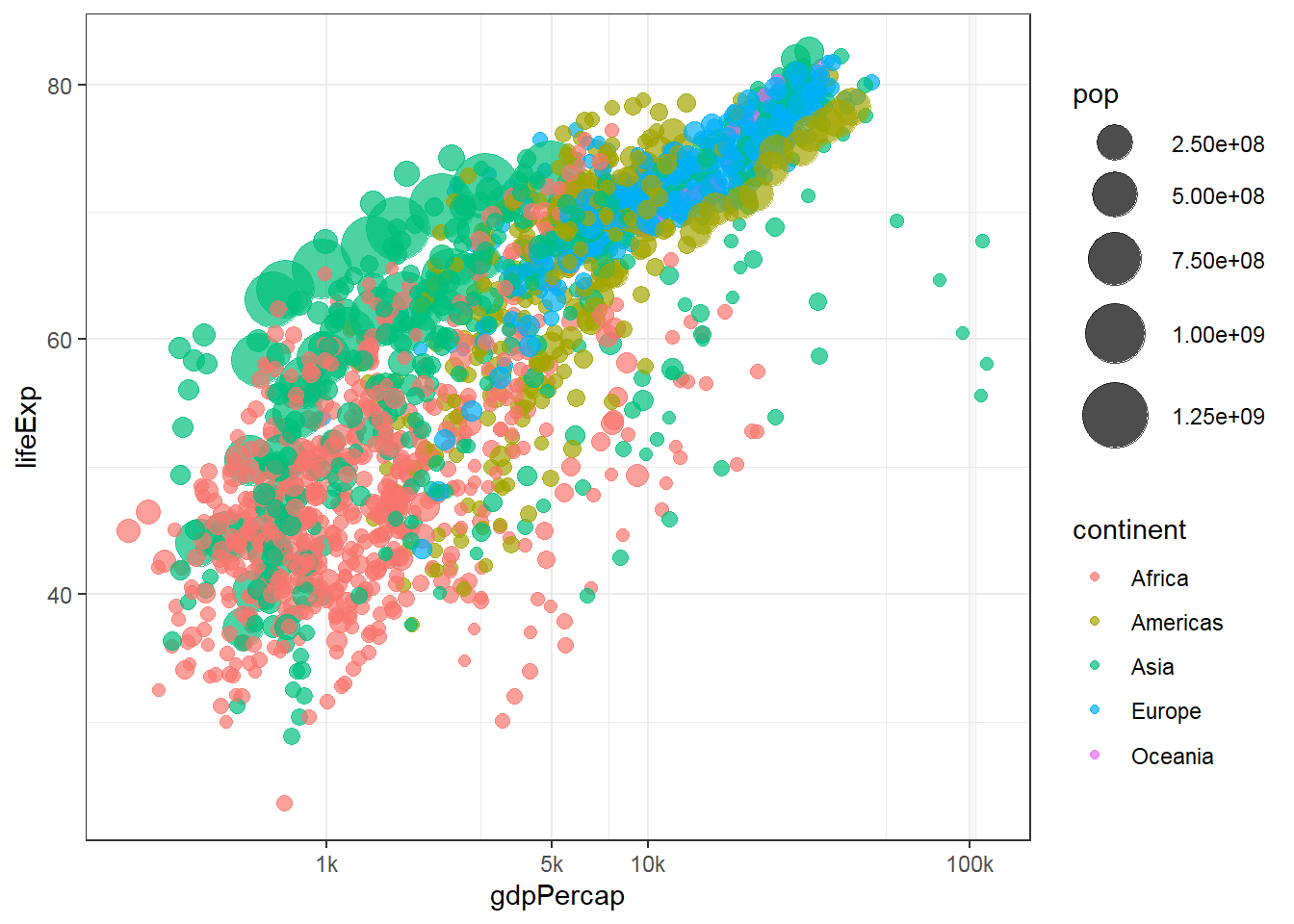
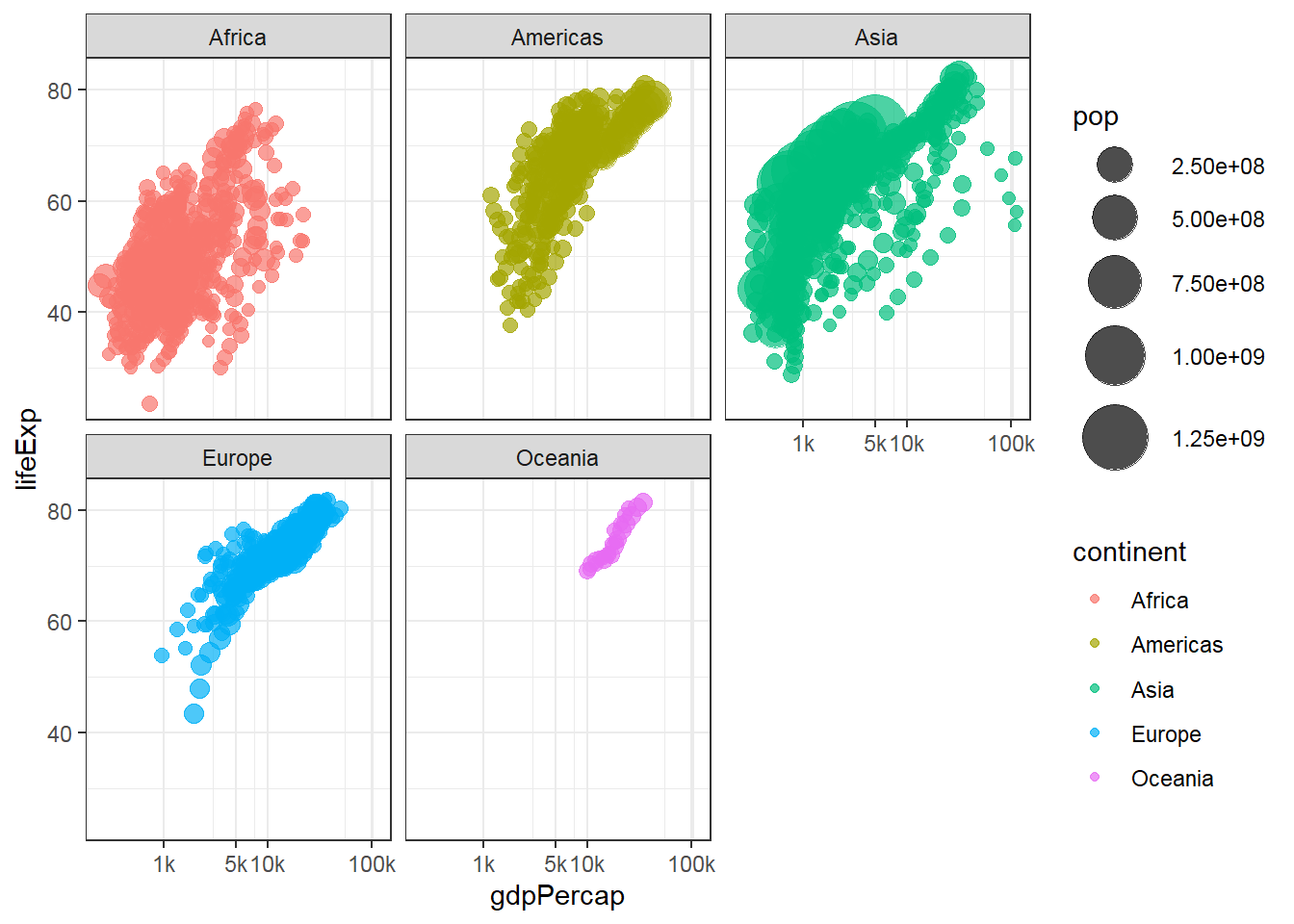
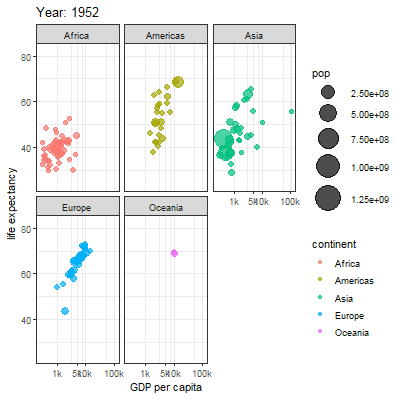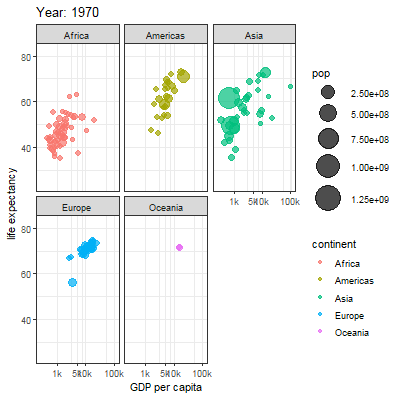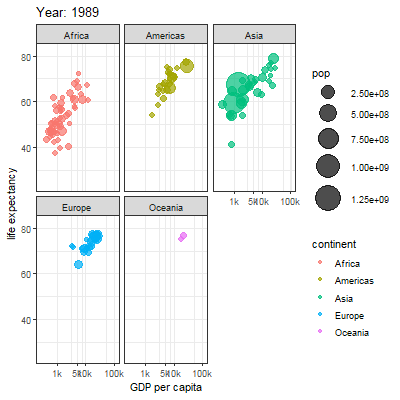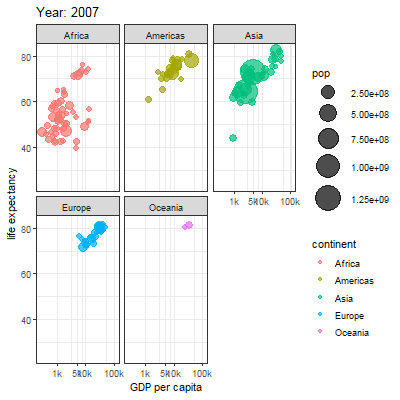
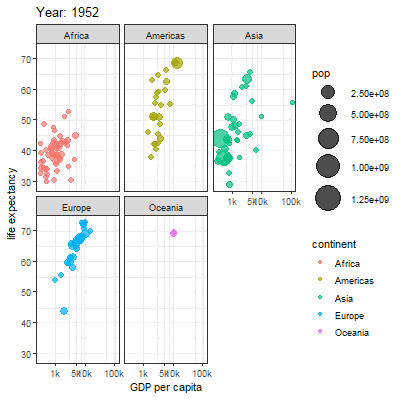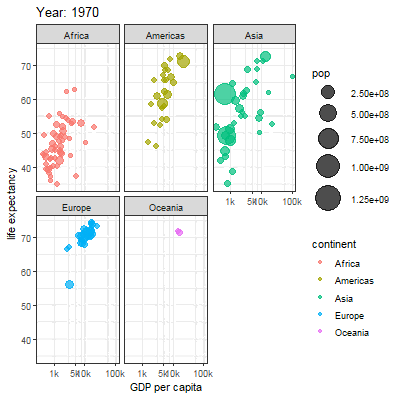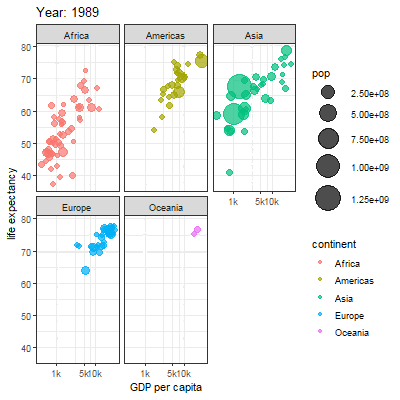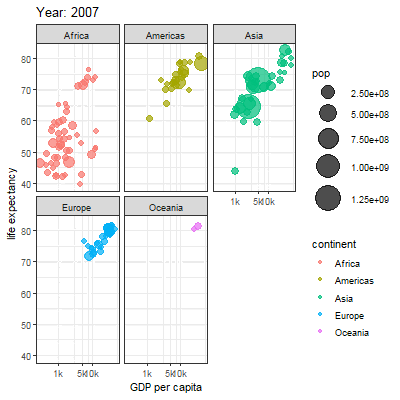
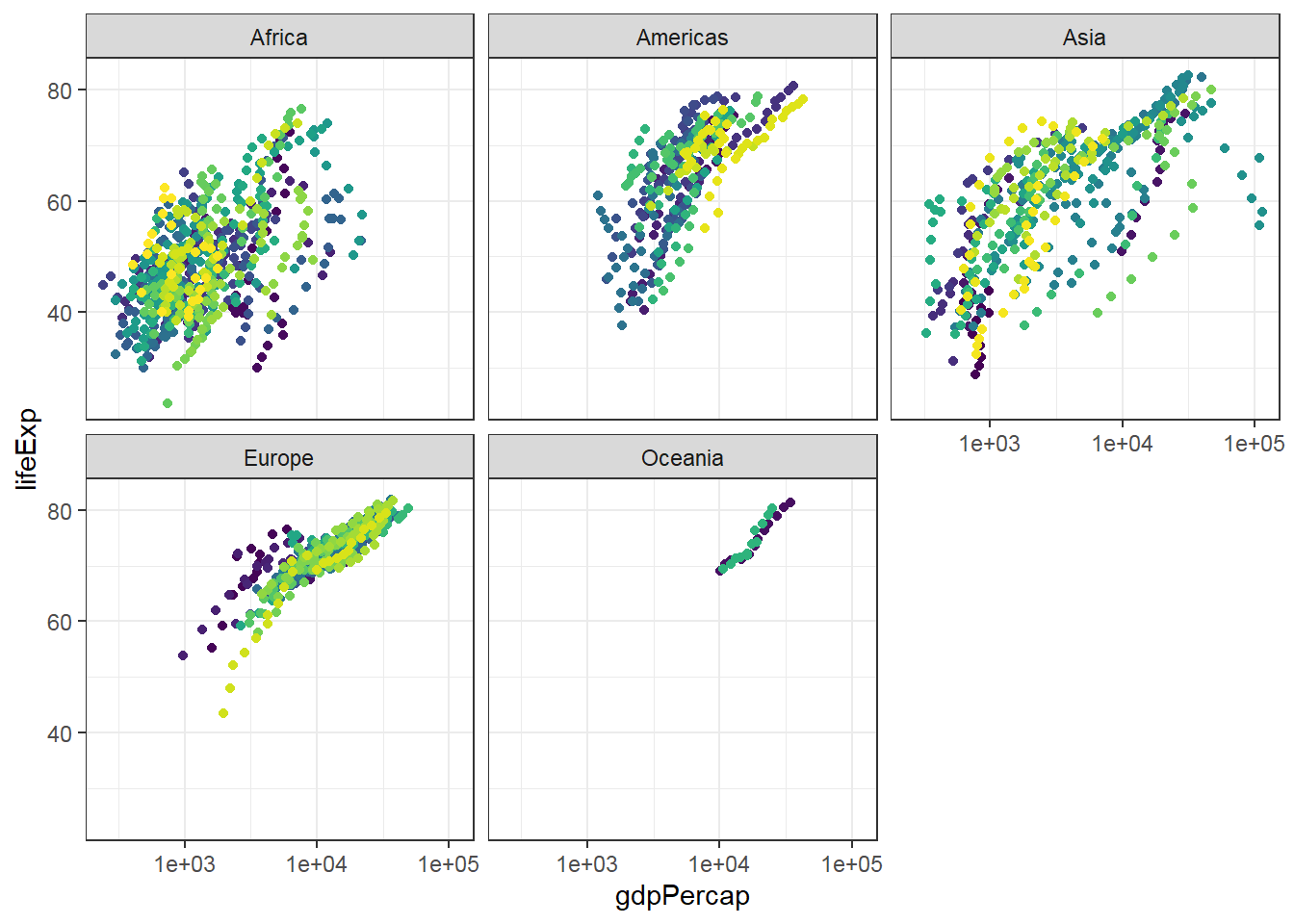
3.2.1 Main content
High-dimensional data
- Feature projection / Manifold learning
- 4 popular feature projection techniques: PCA, MDS, t-SNE, UMAP
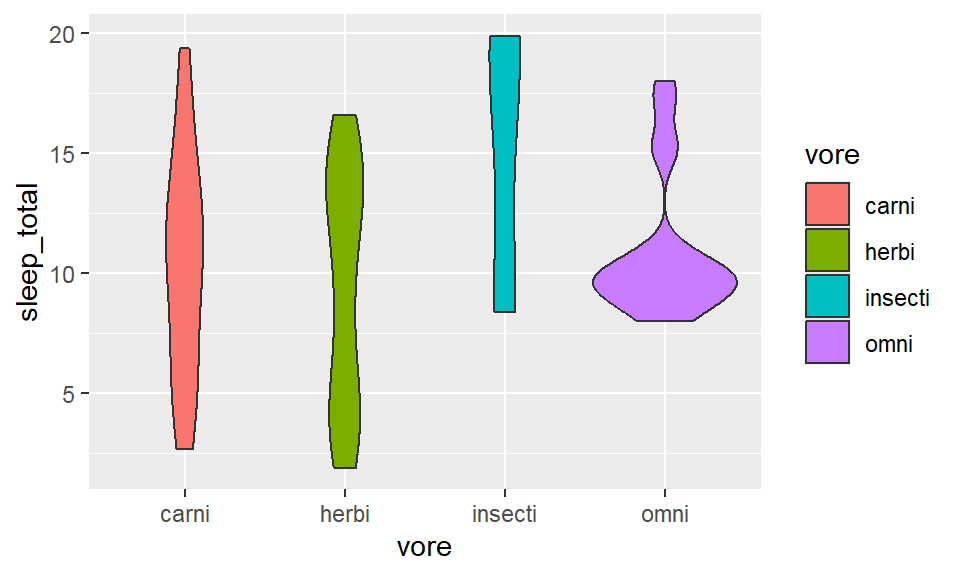
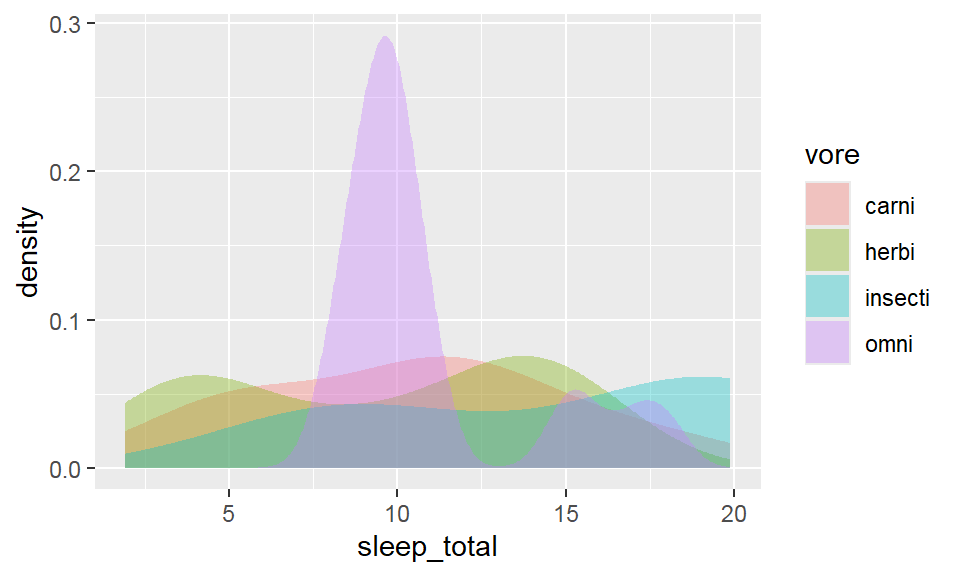
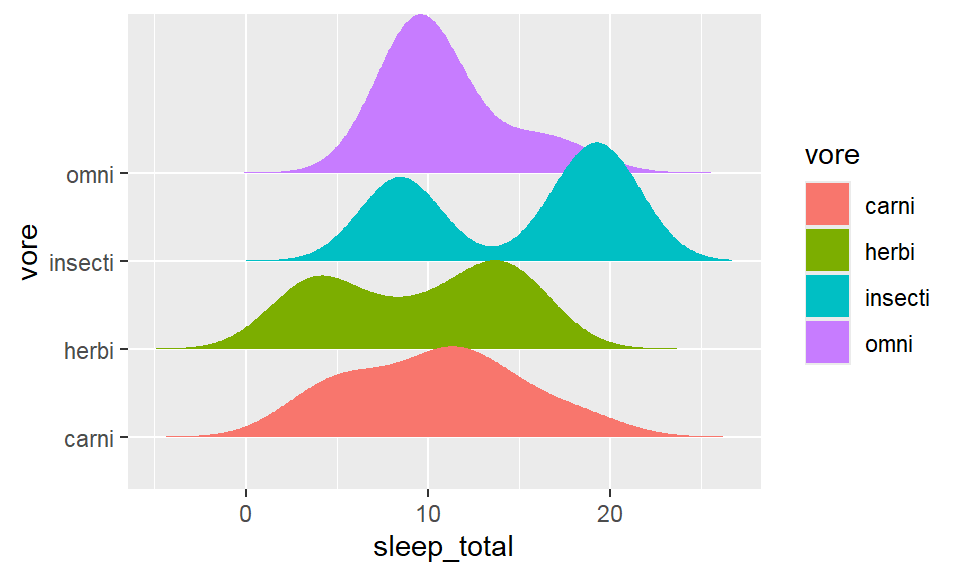
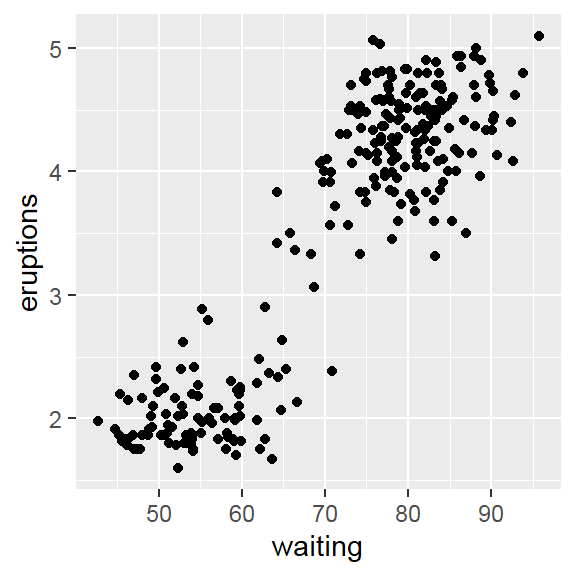
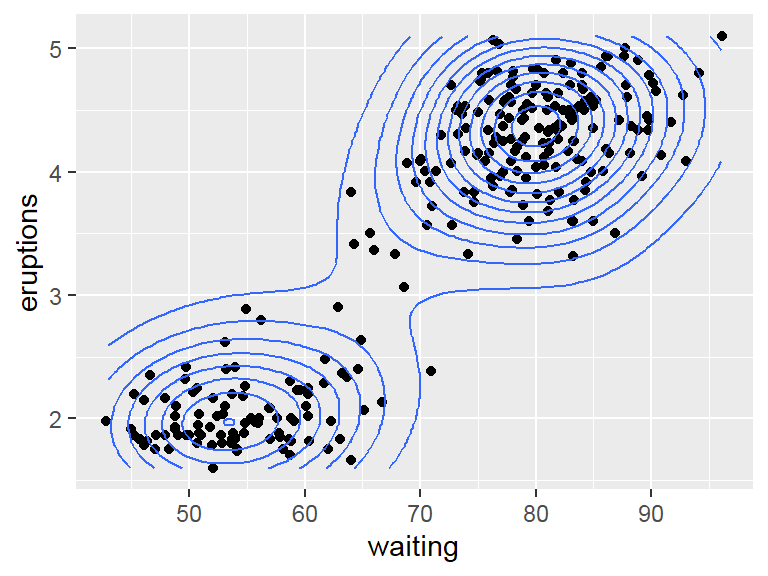
Distribution plot
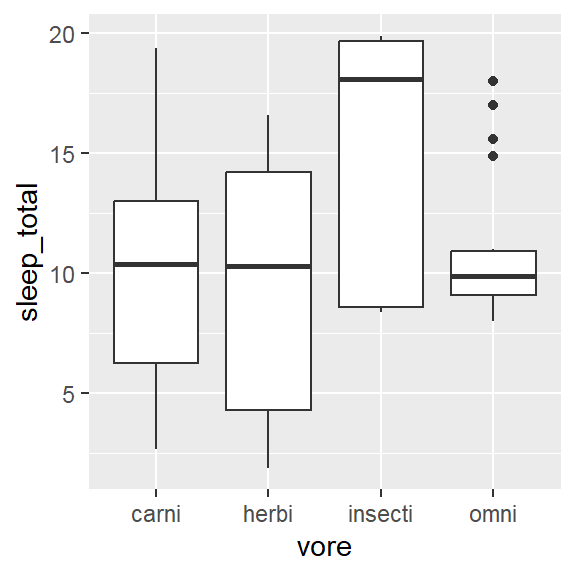
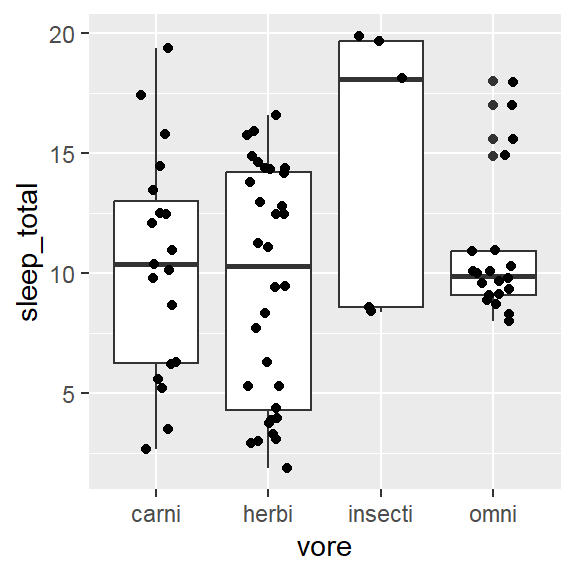
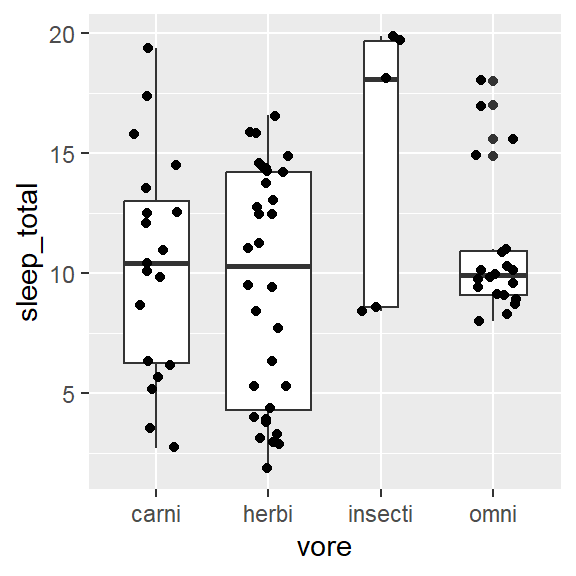
- Within 1 variable:
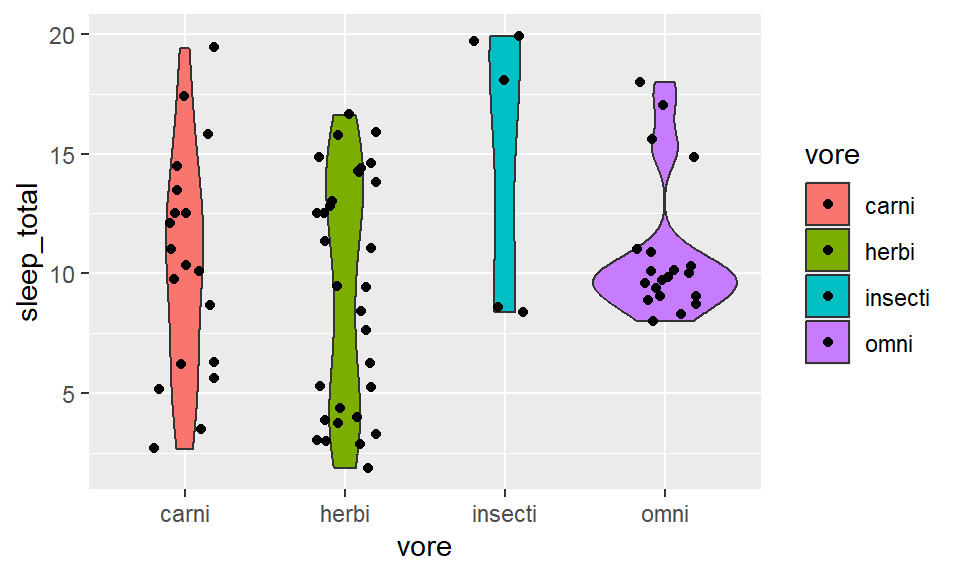
- Weighted box/ violin
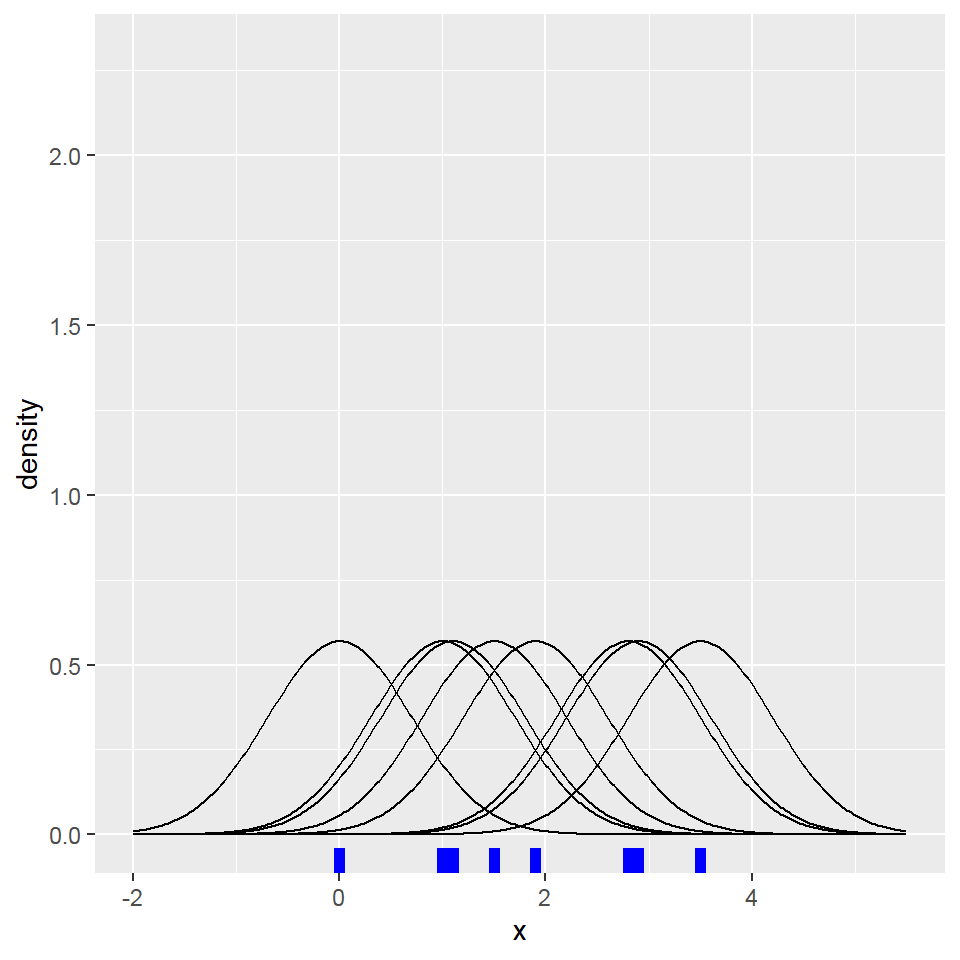
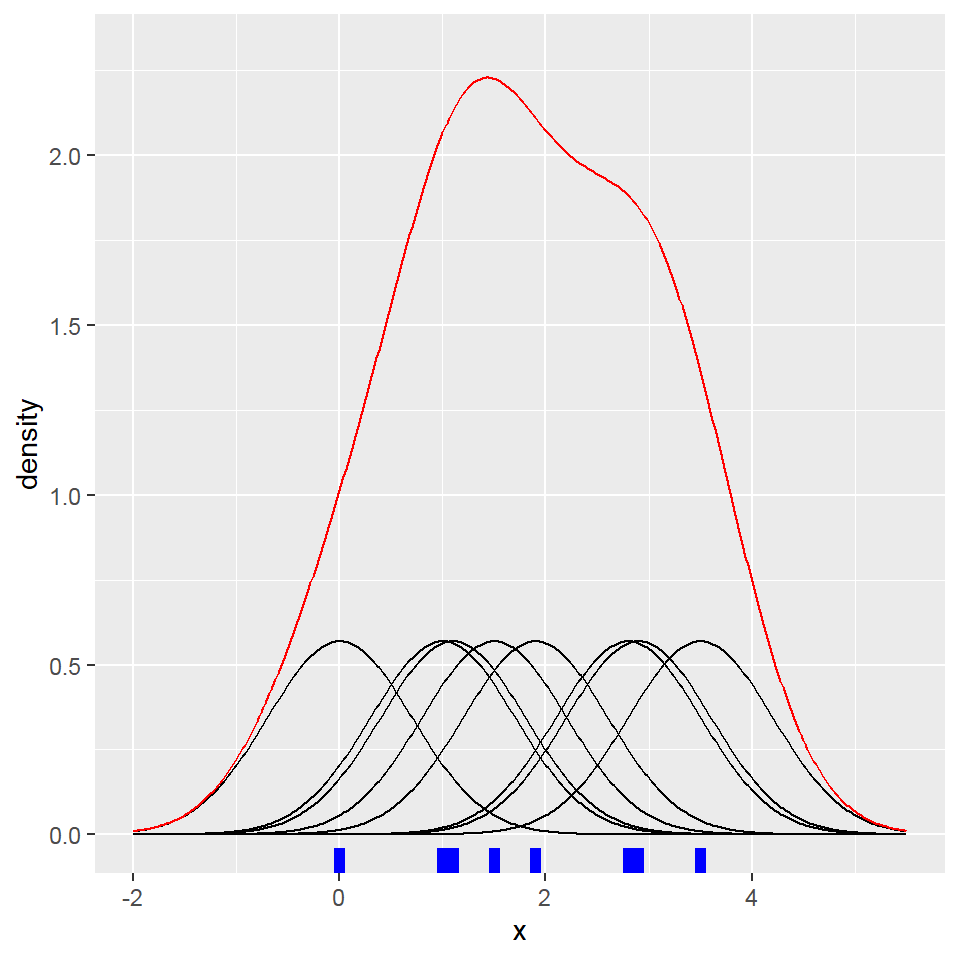
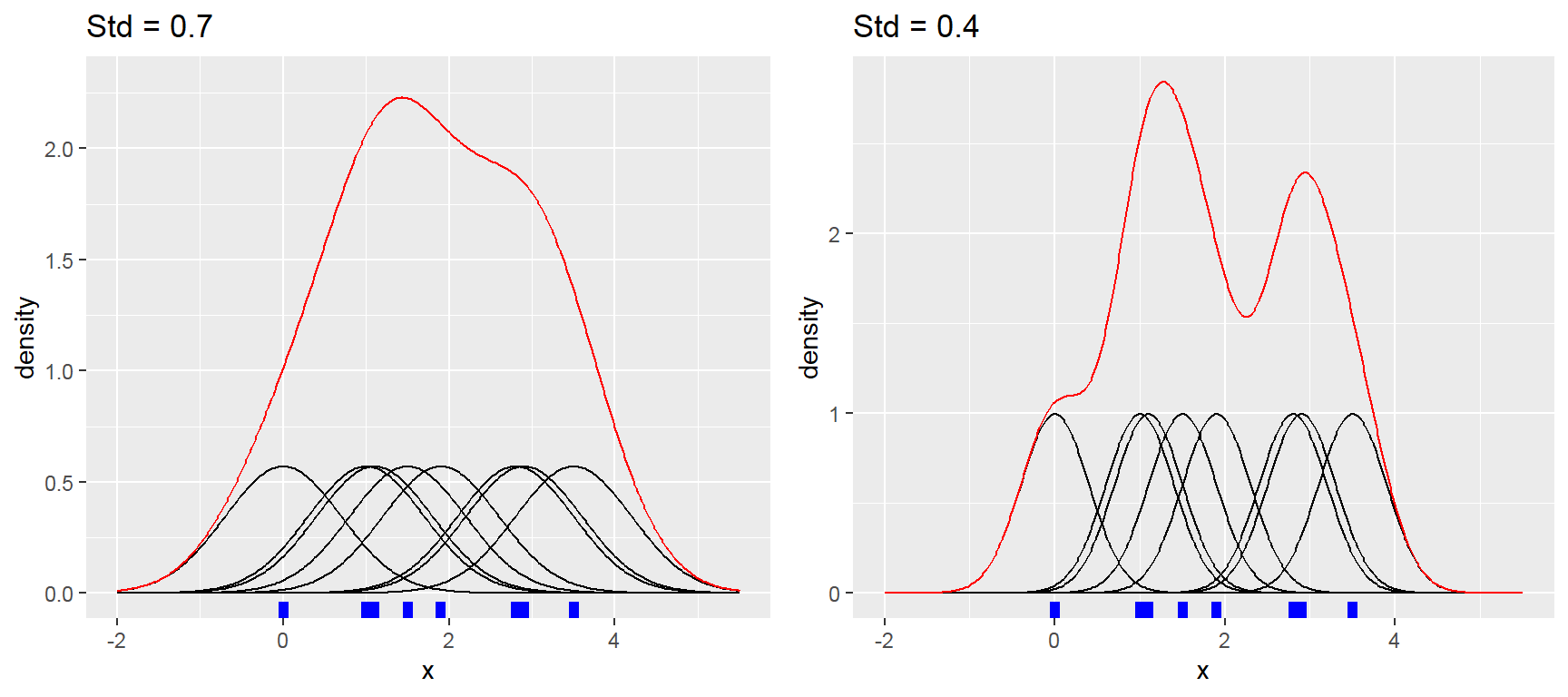
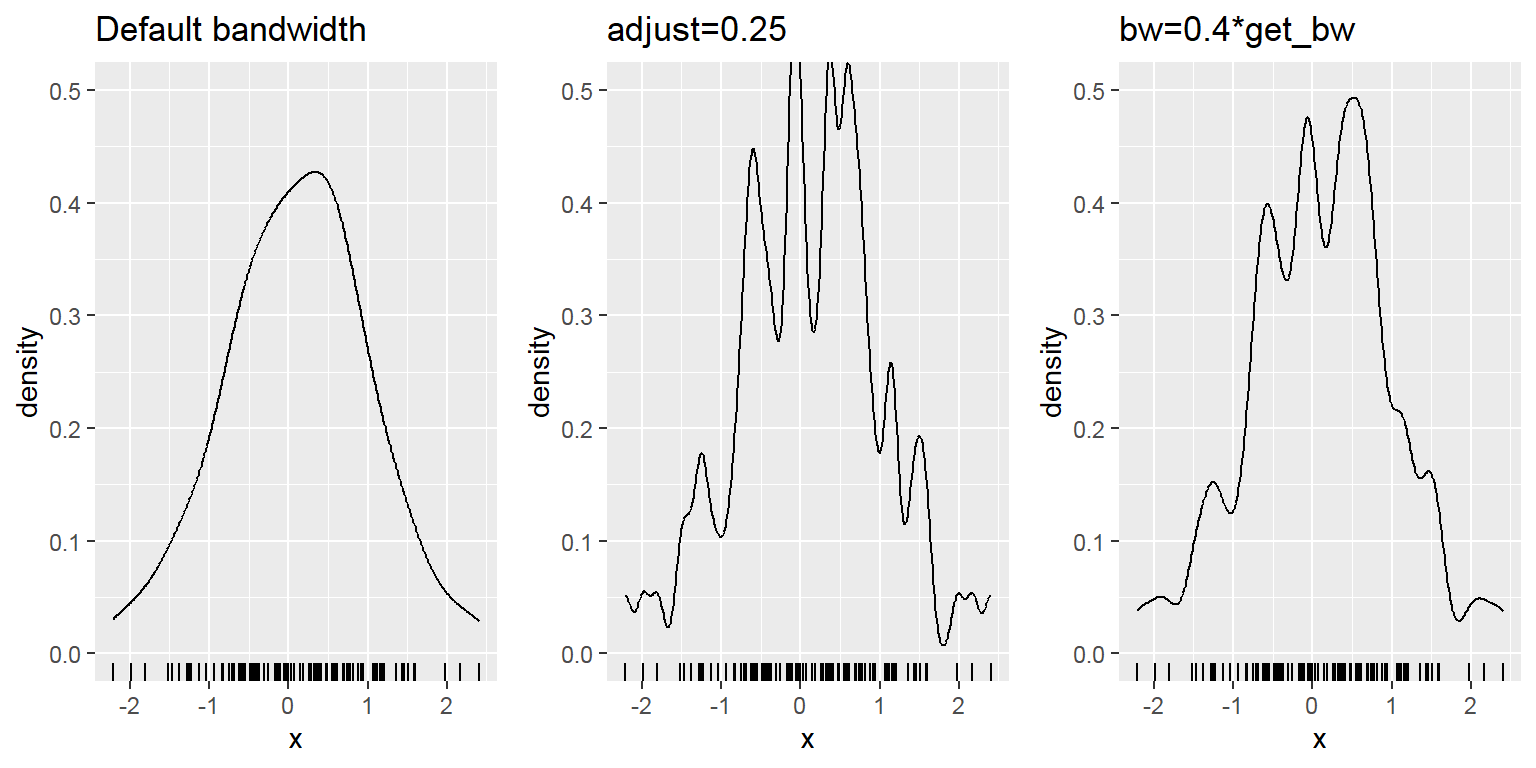
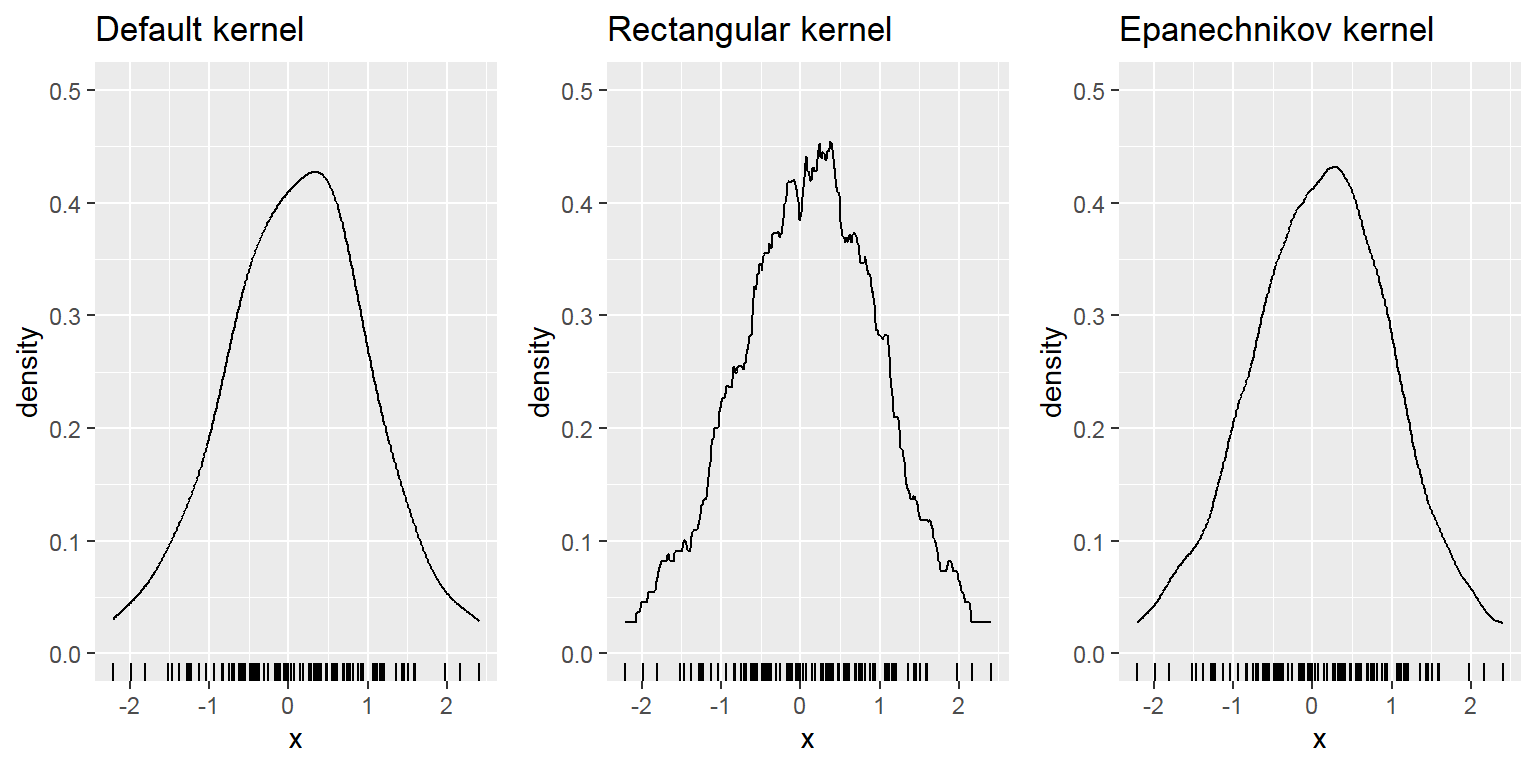
- Density
- 2 Separate variables:
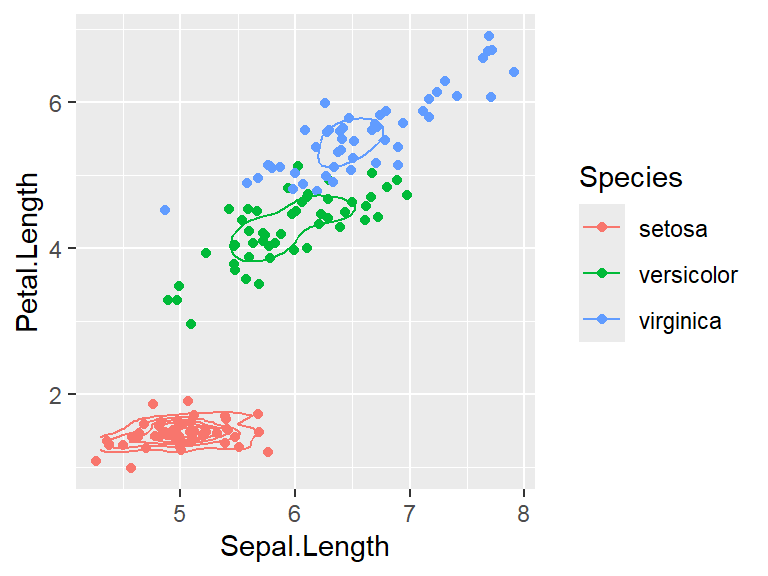
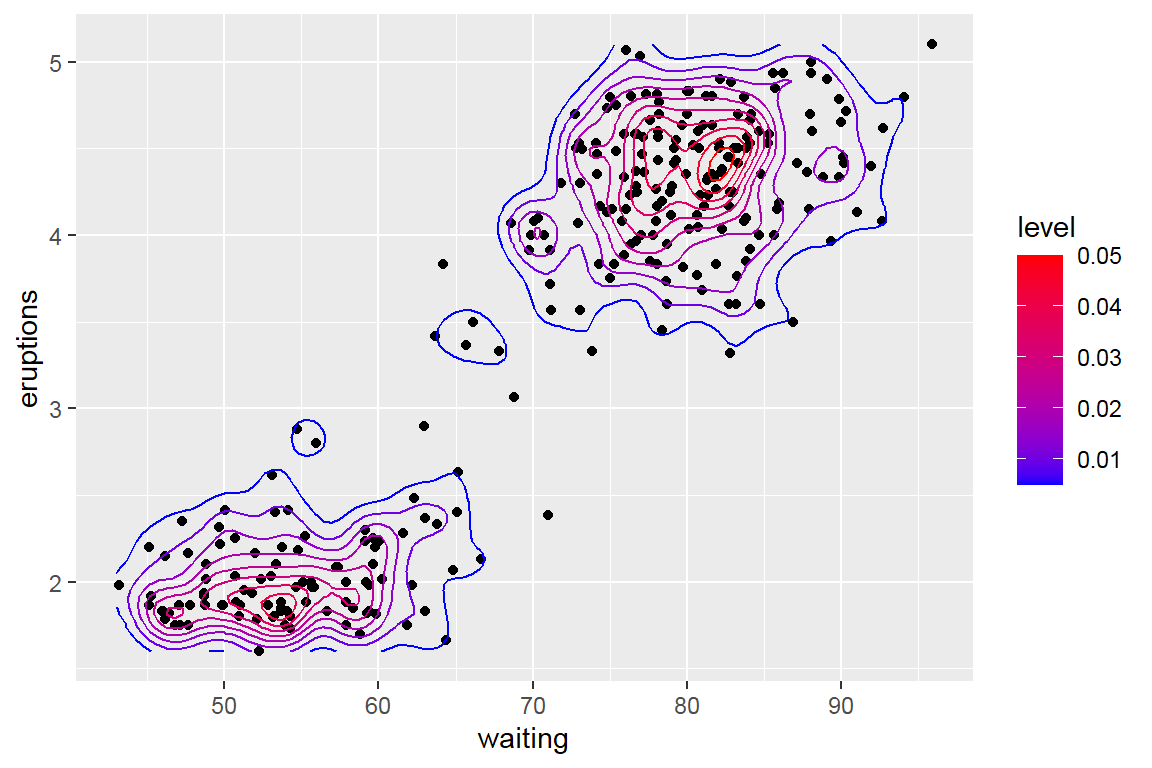
- 2D density
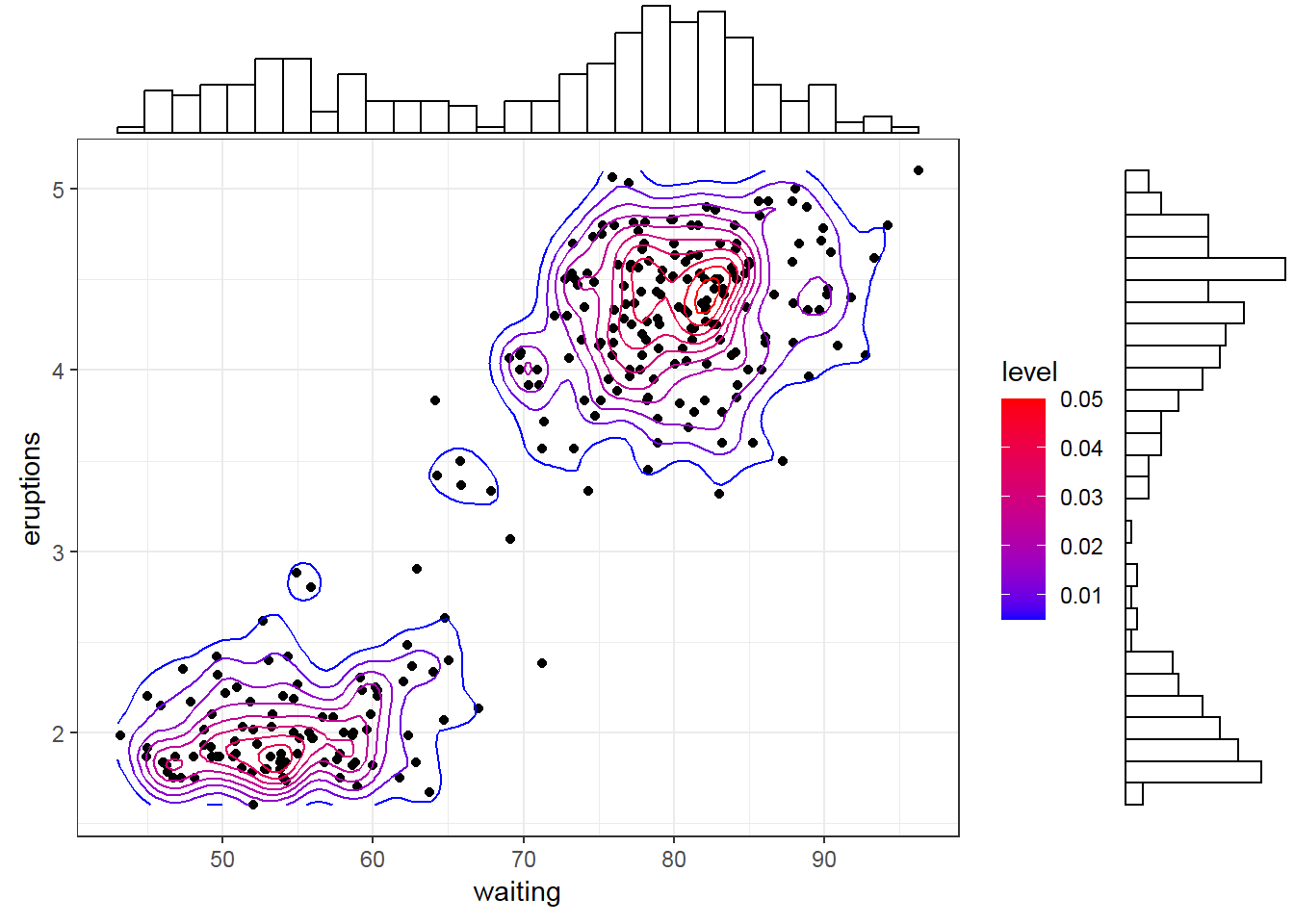
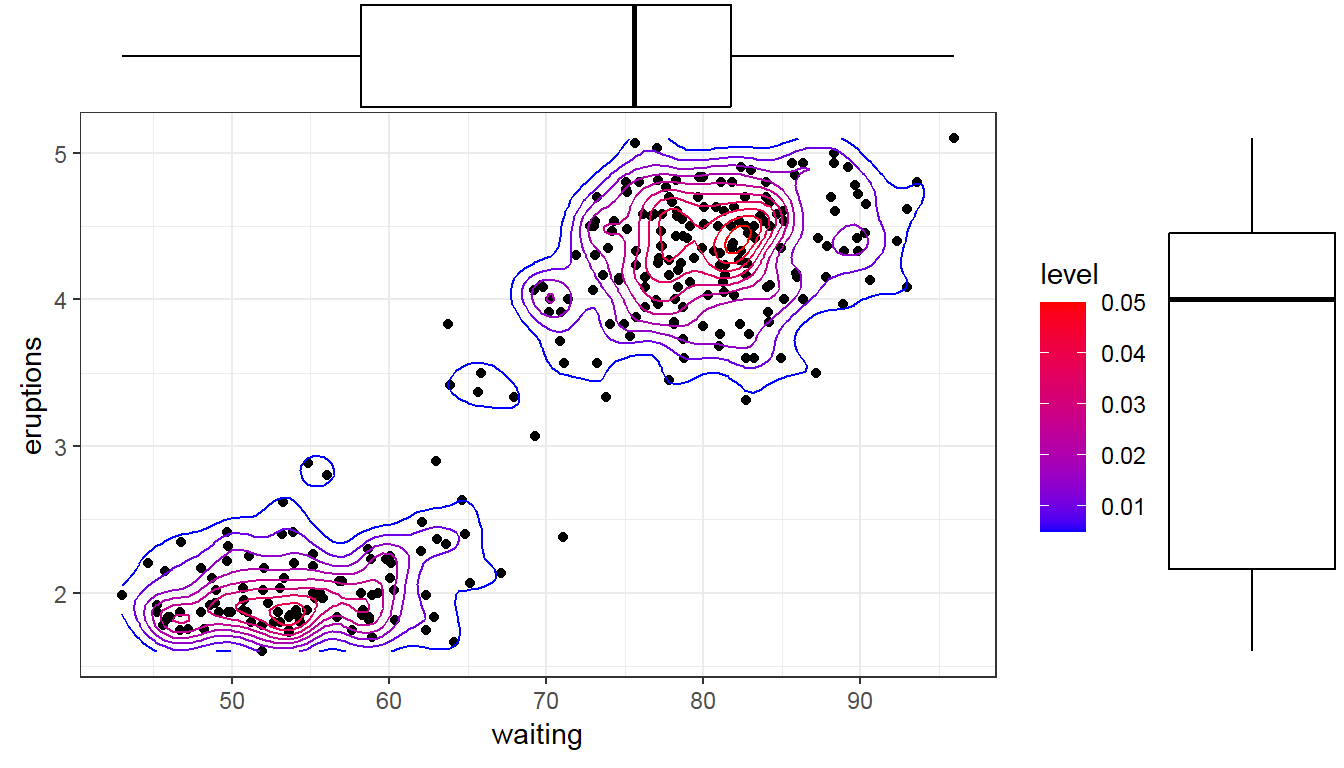
- Marginal histogram/ box plot
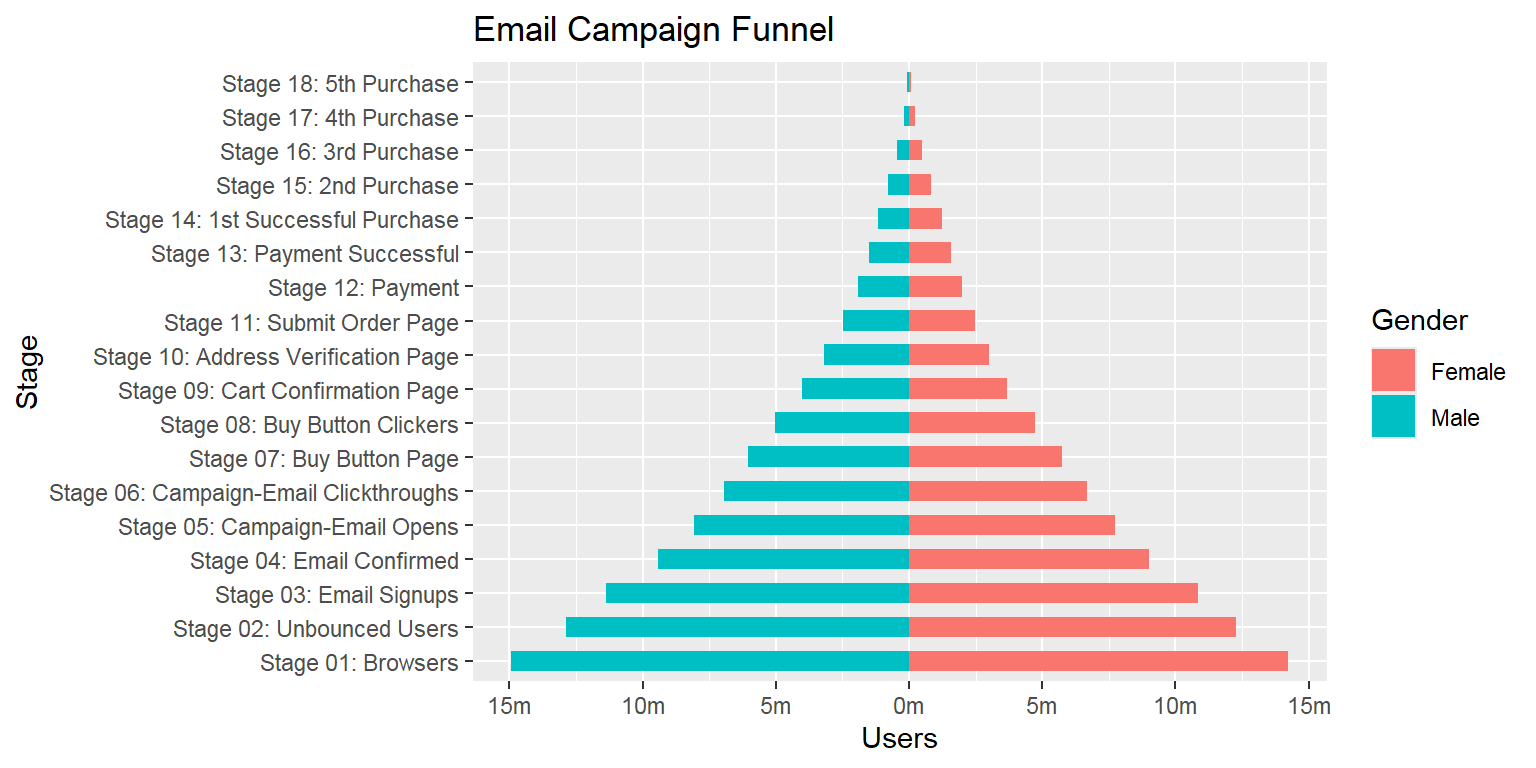
- Population pyramid
- Within 1 variable:
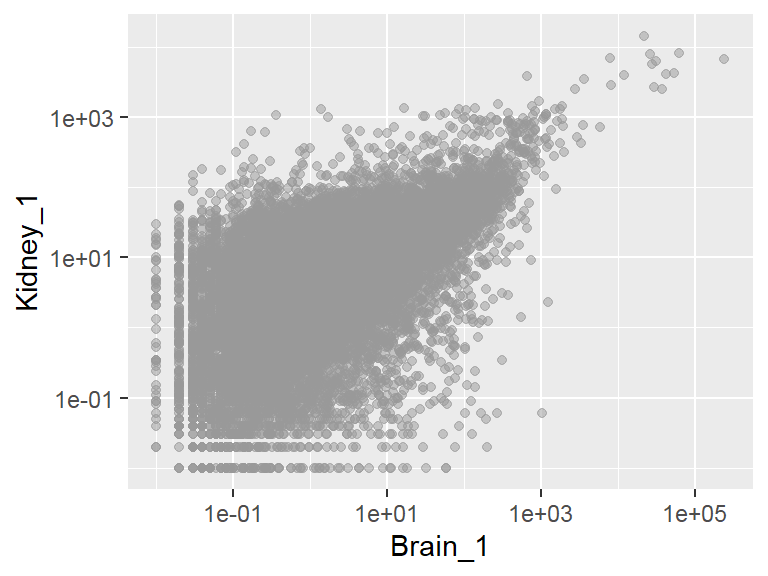
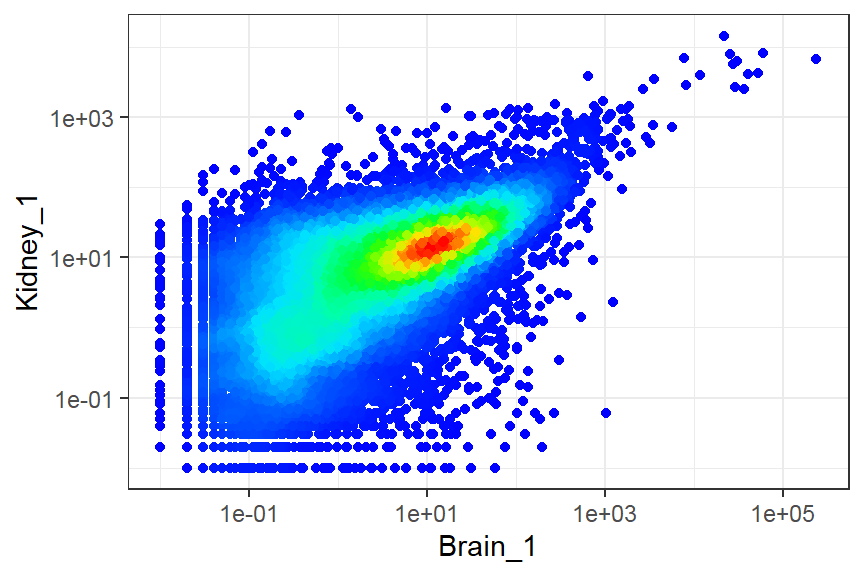
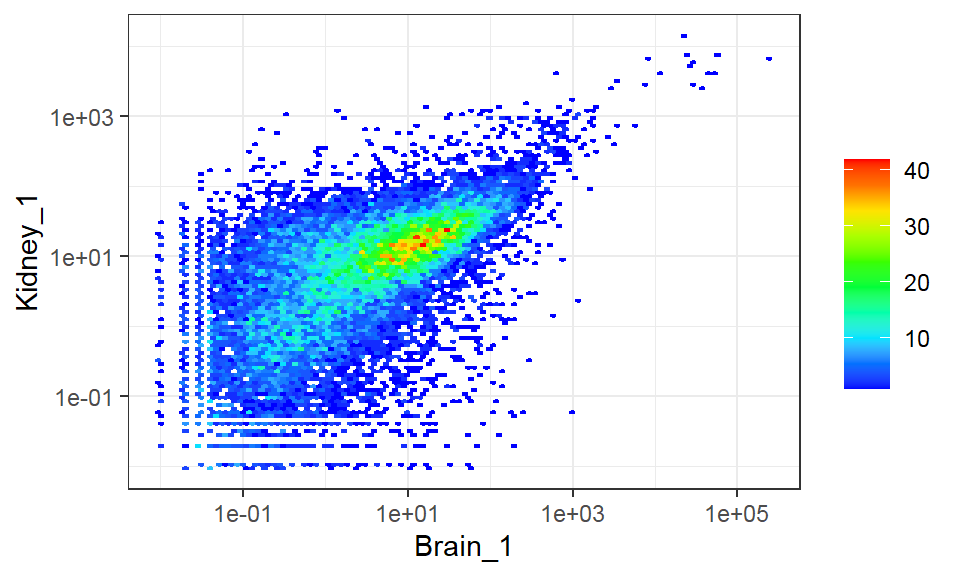
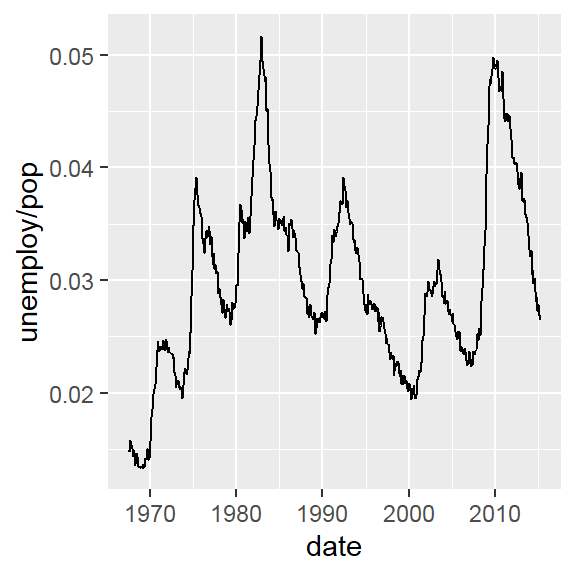
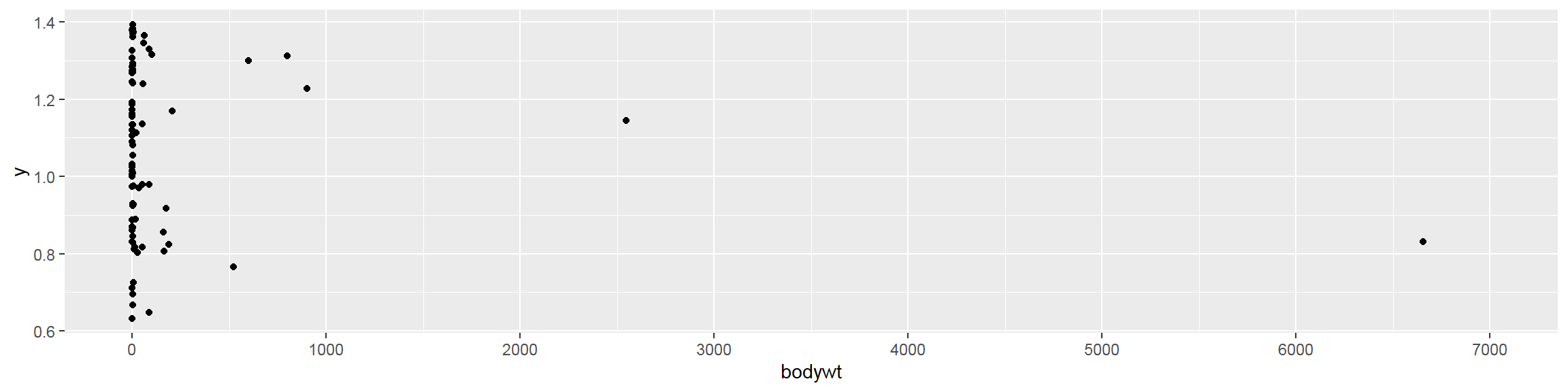
Deal with large number of observations
- Binned scatter
Deal with multi-dimensional data
- Feature projection/ Manifold learning >> high-dimensional
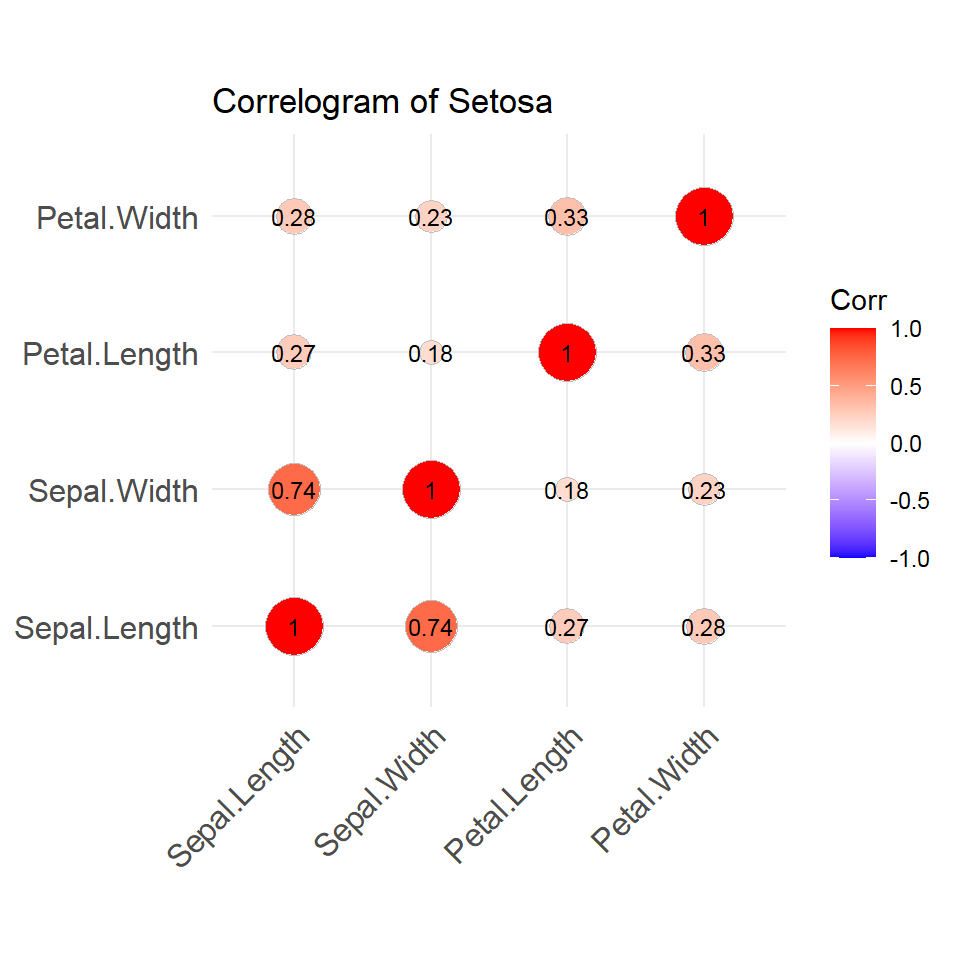
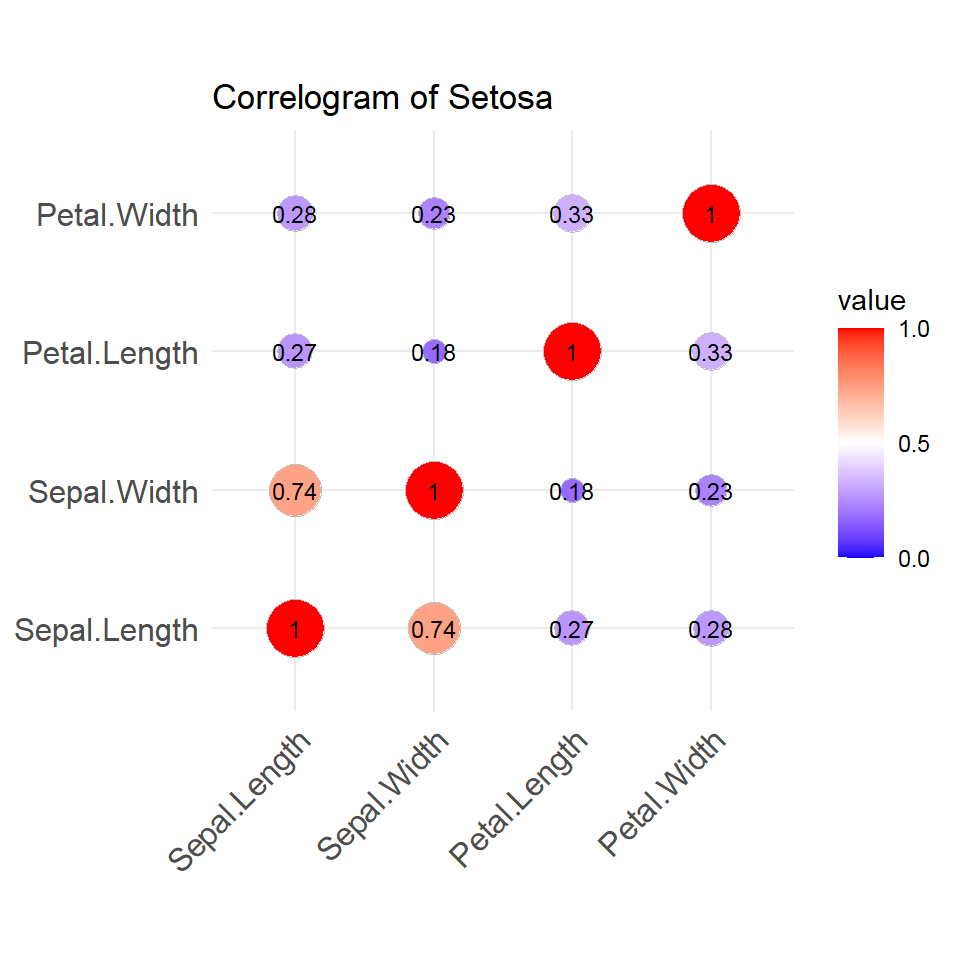
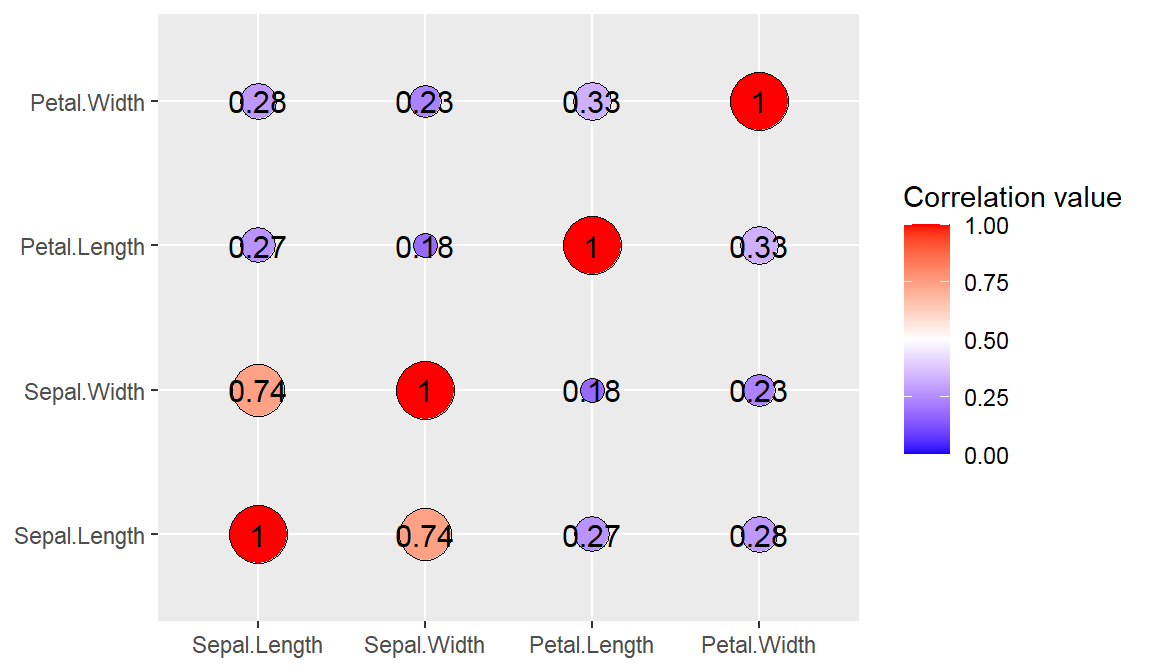
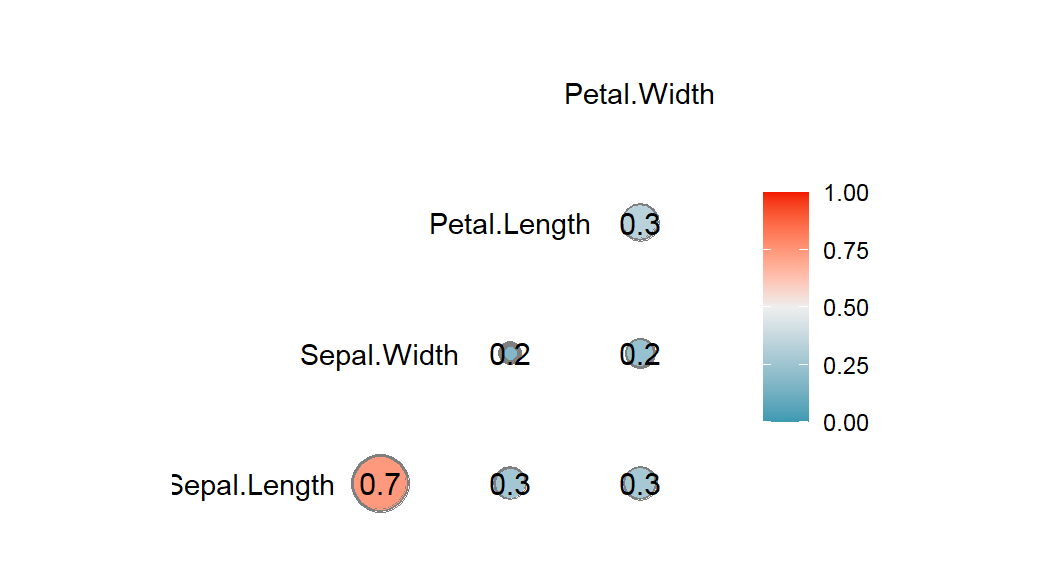
- Correlogram
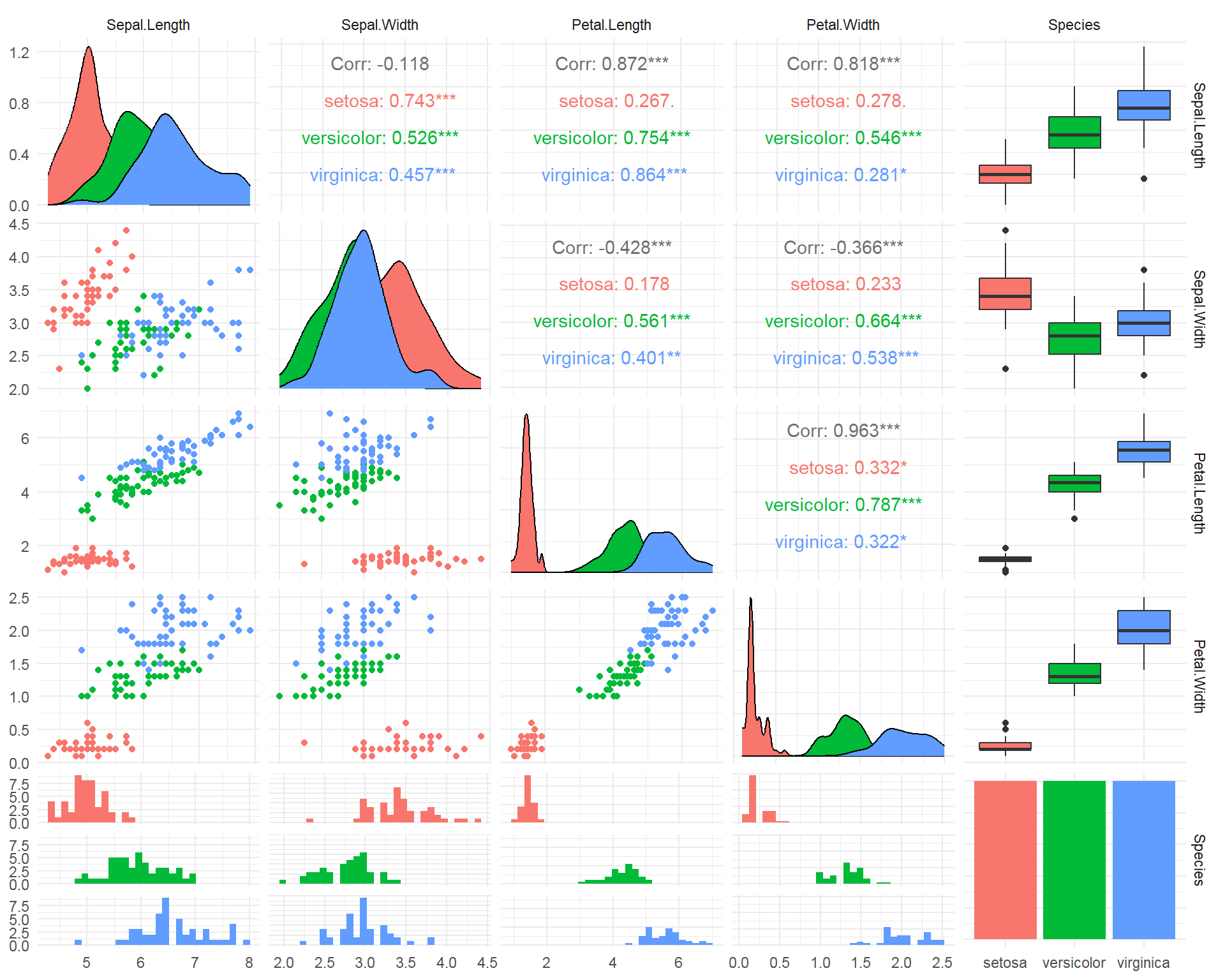
- SPLOM - Scatter PLOt Matrix
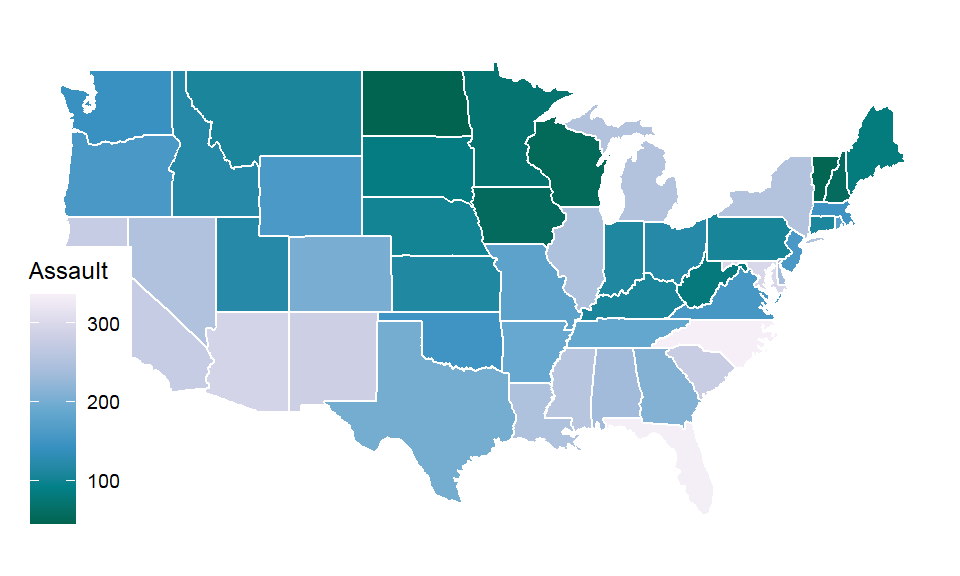
Map
- Chorophleth
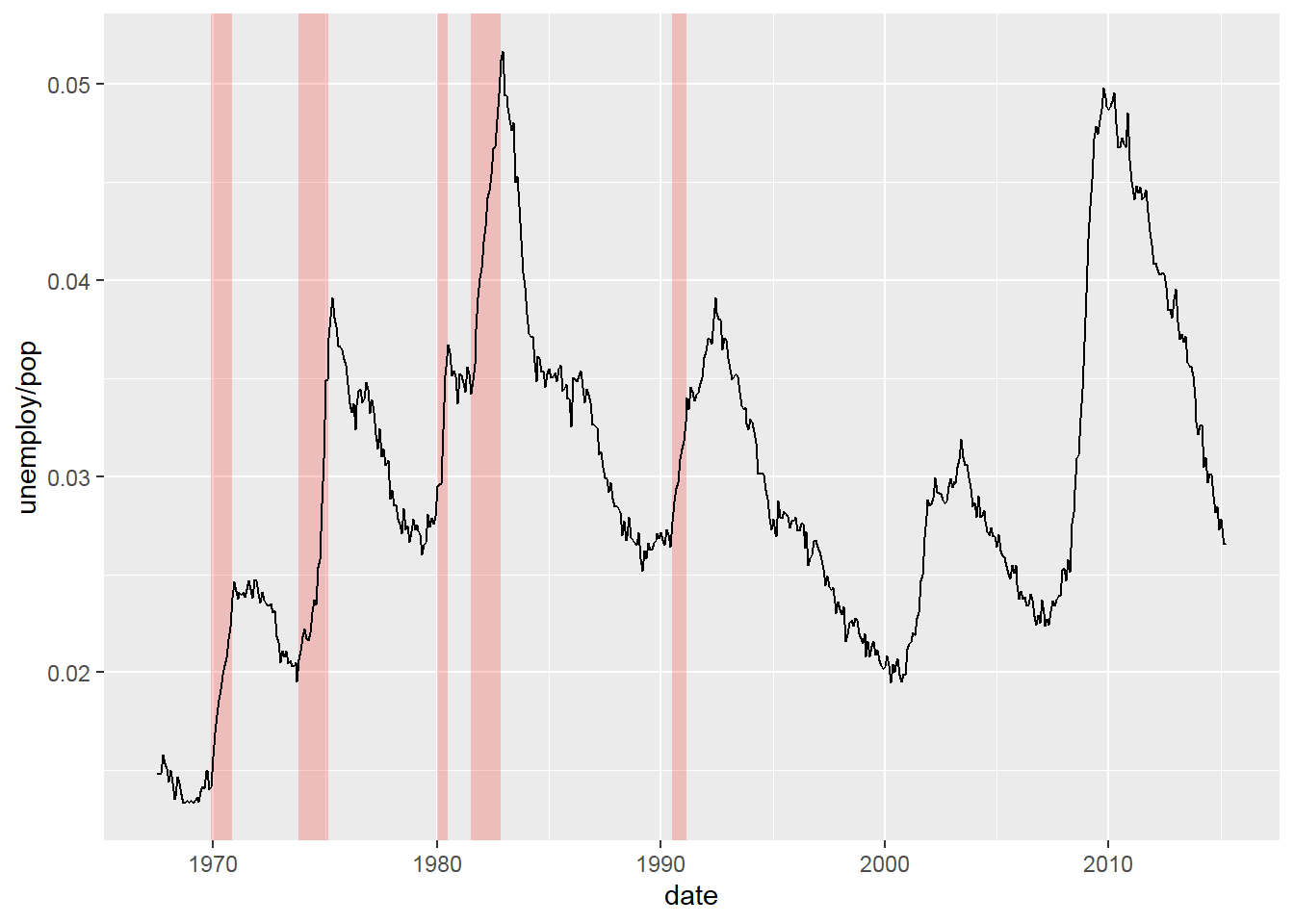
Animation
Honorable mentions
plotly
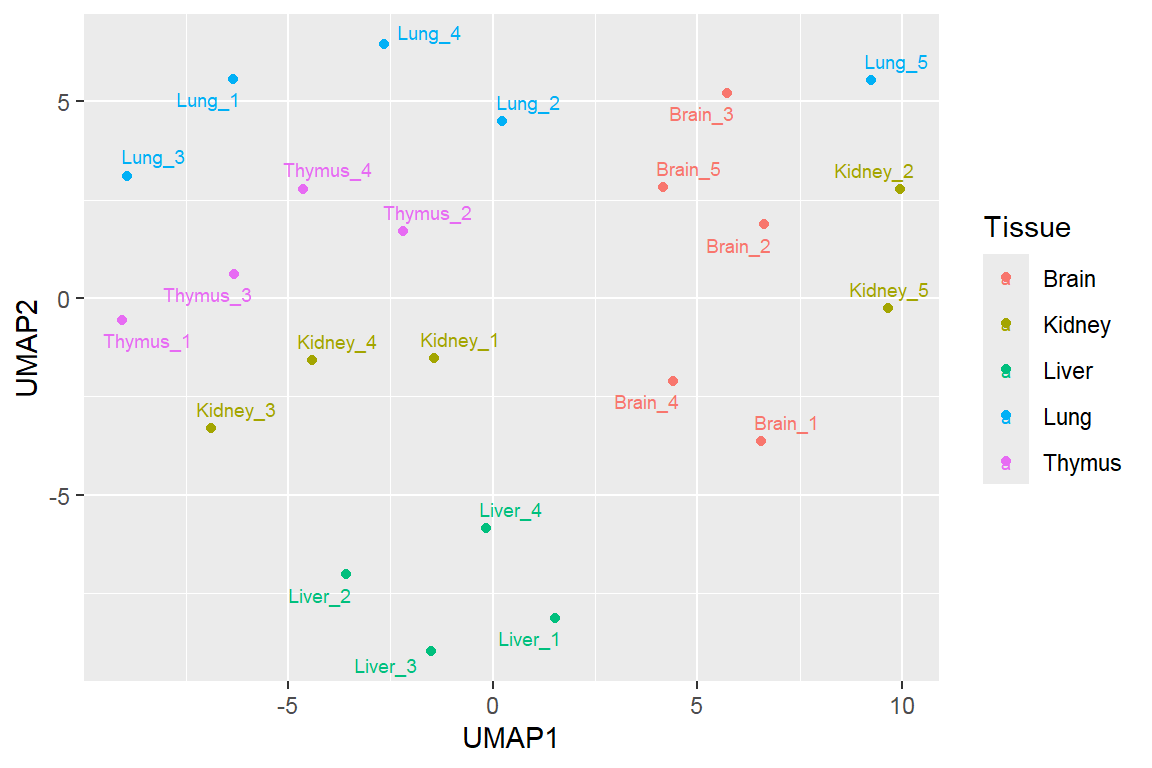
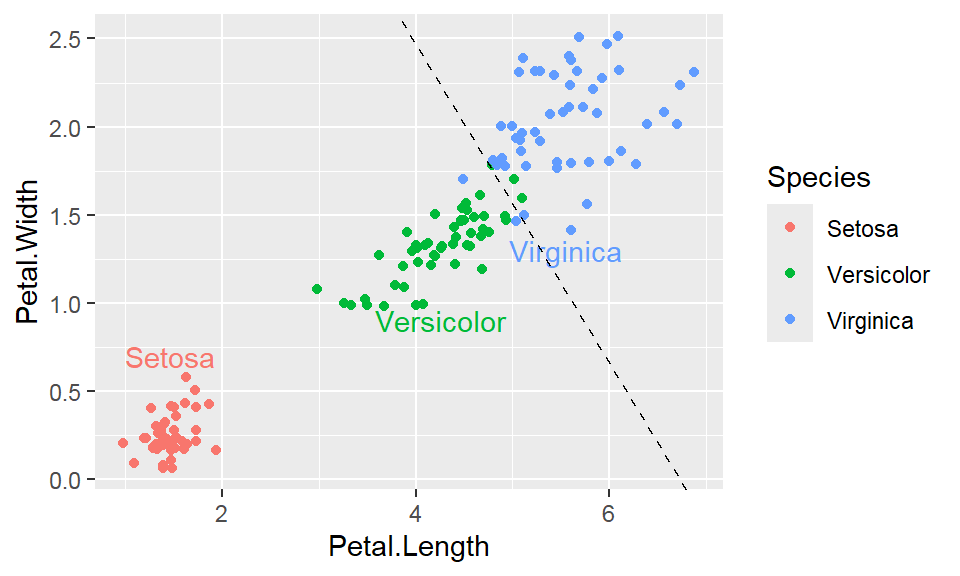
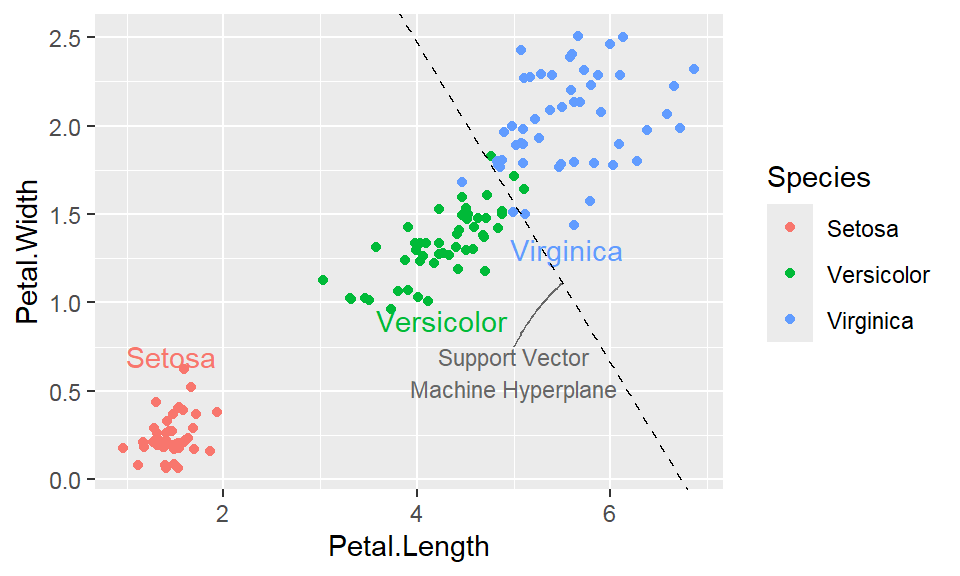
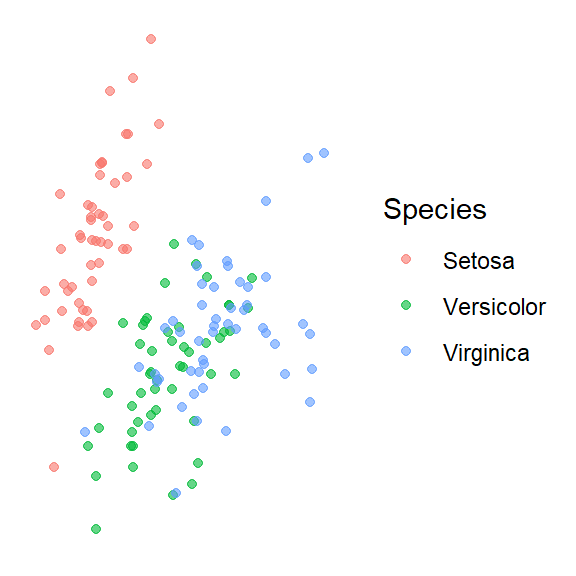
Feature projection/ Manifold learning
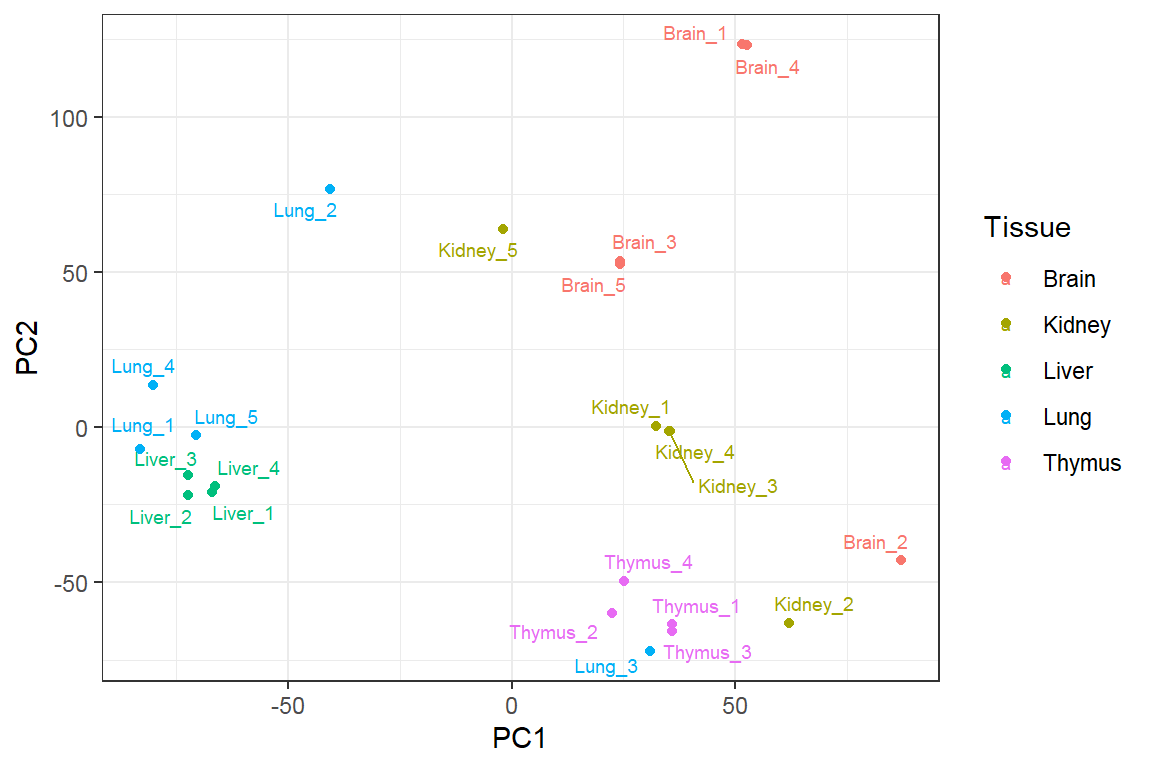
Principal Component Analysis
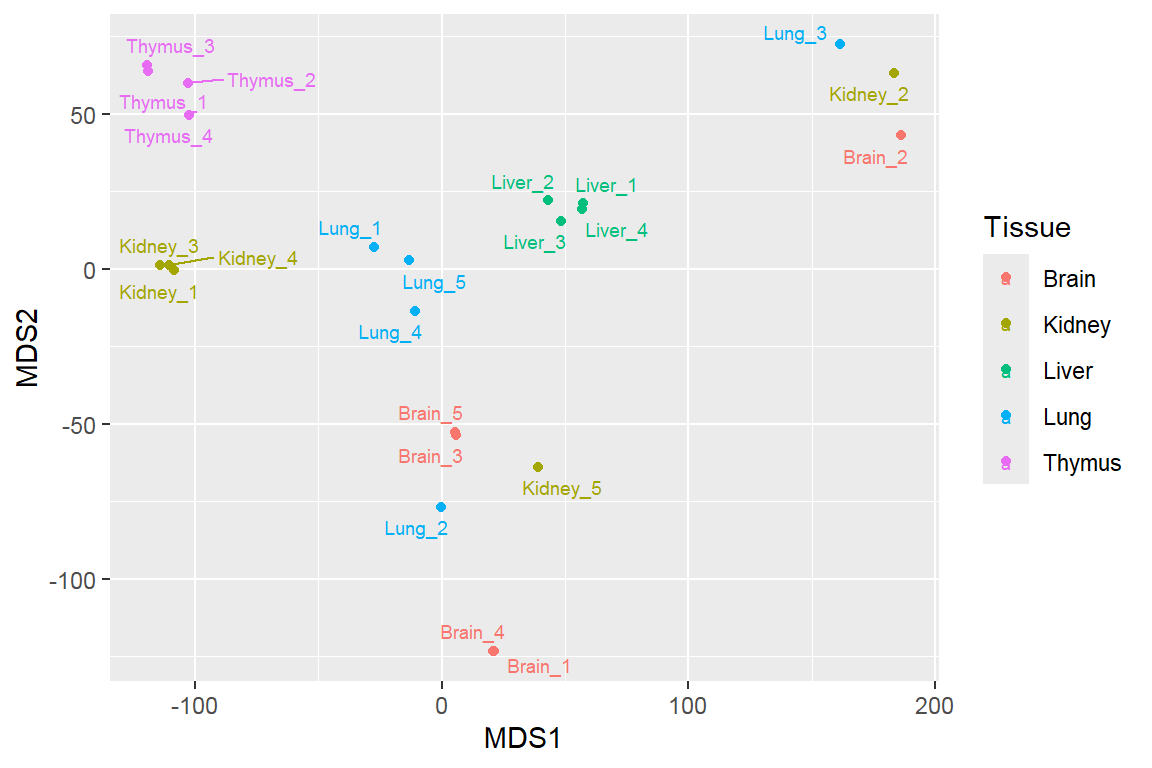
Multidimensional scaling
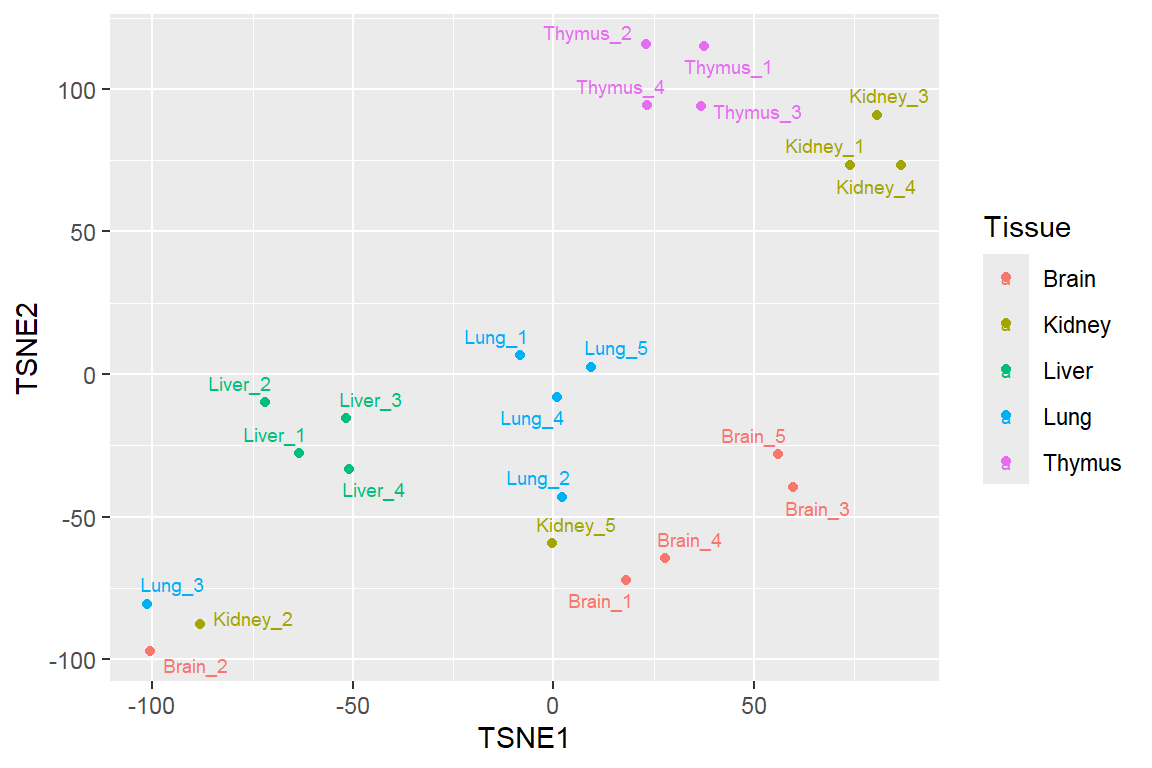
t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE)
Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP)
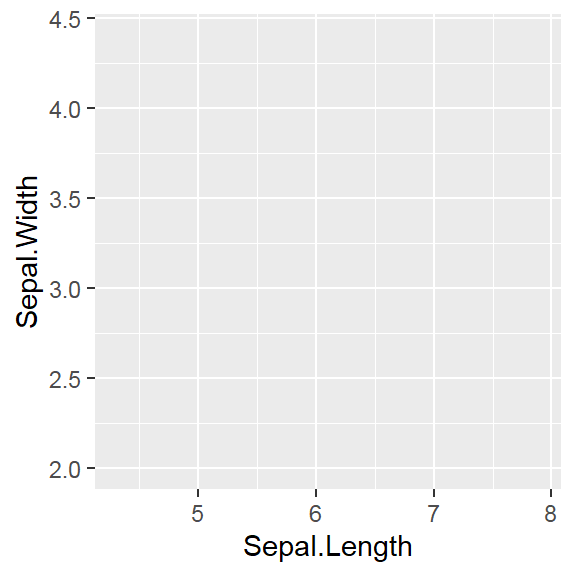
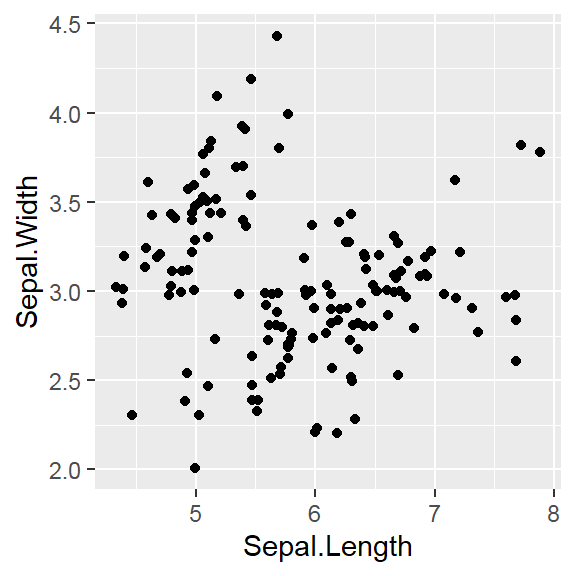
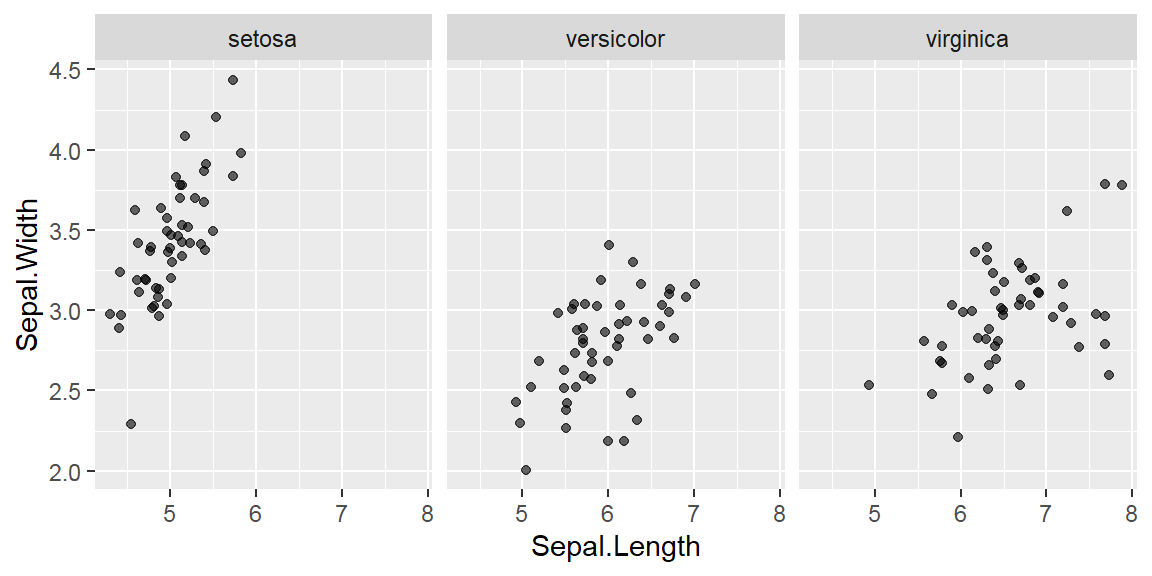
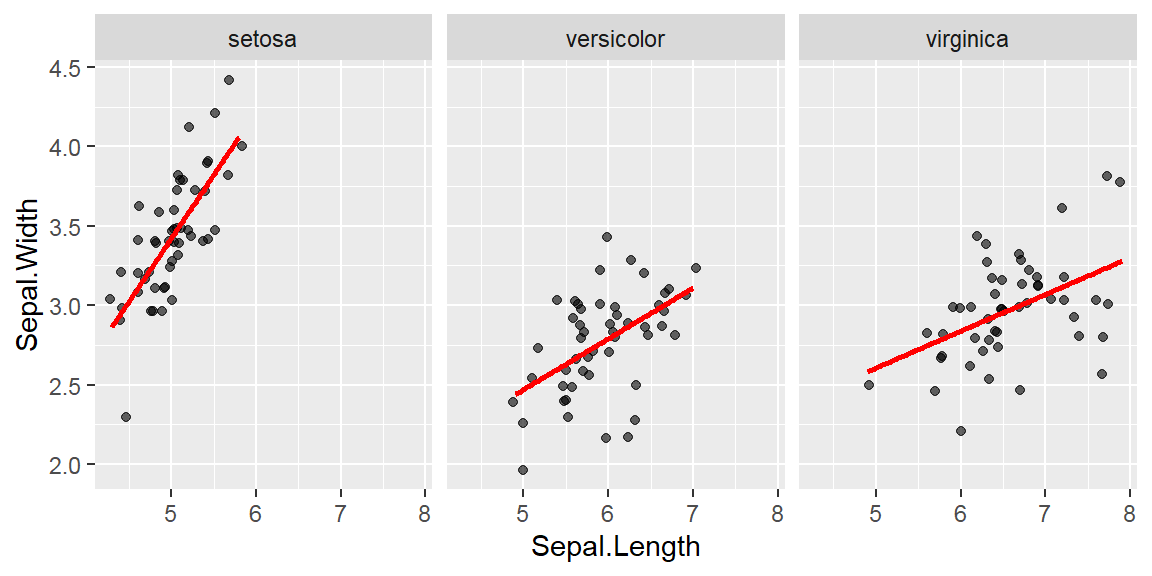
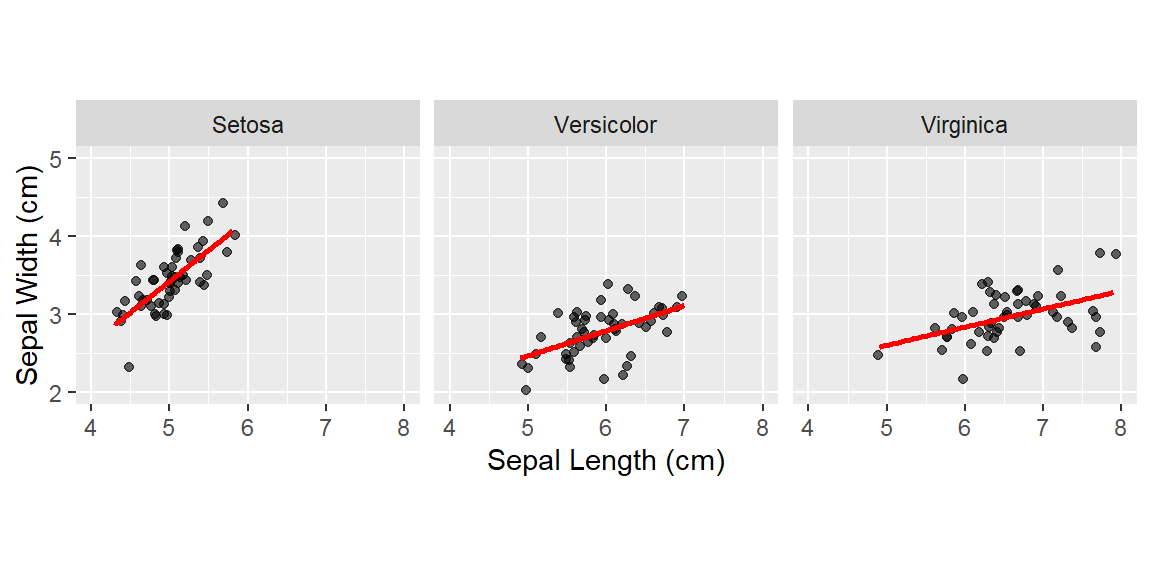
 They are discrete variables.
They are discrete variables.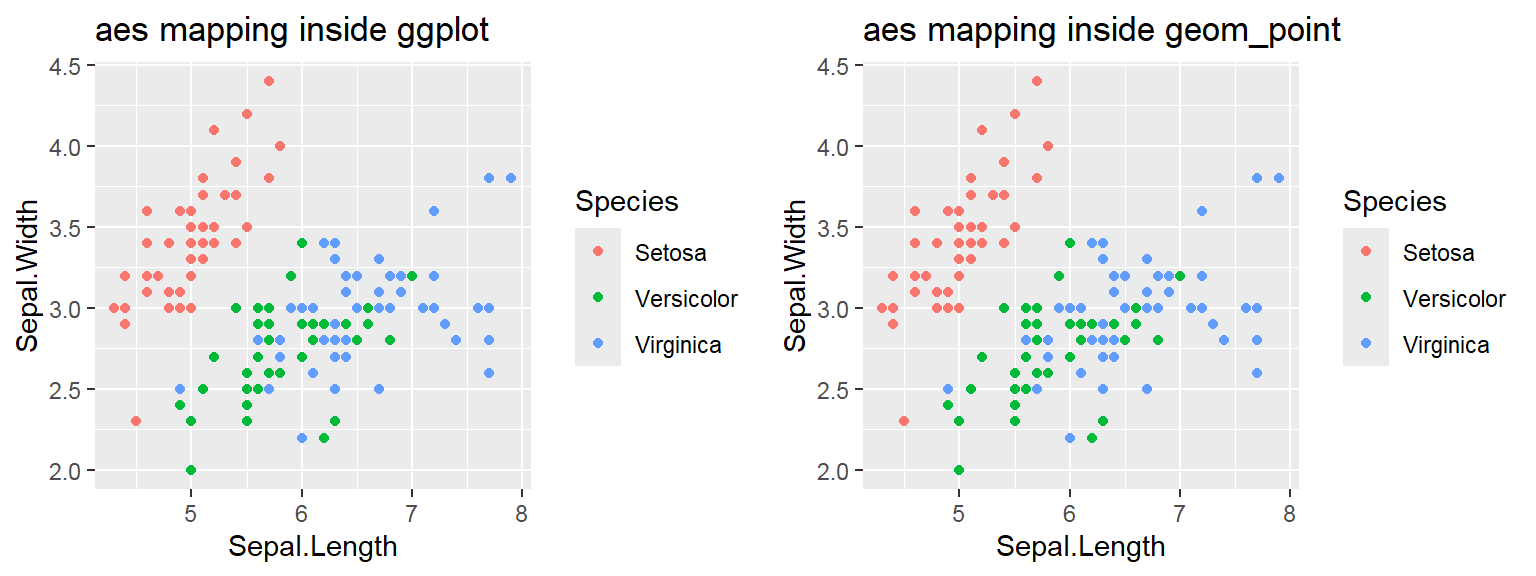
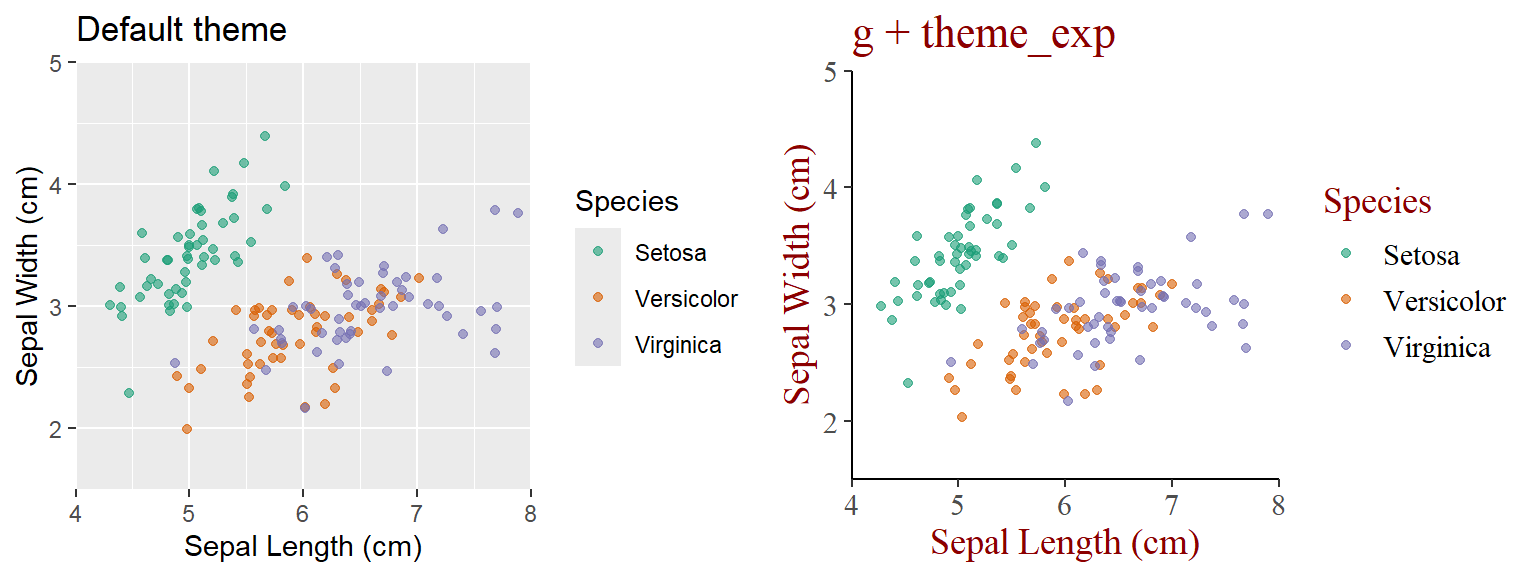
 The color attribute is set to “red”
Attribute is set inside geom_*() .
The color attribute is set to “red”
Attribute is set inside geom_*() .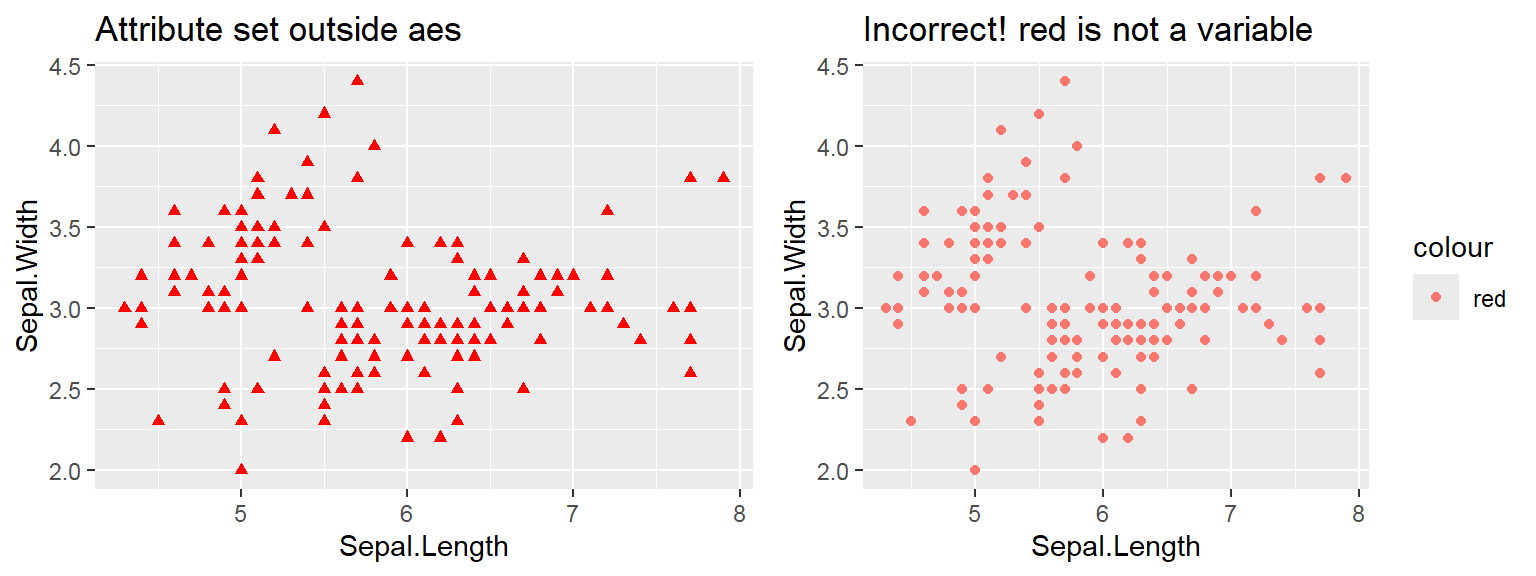
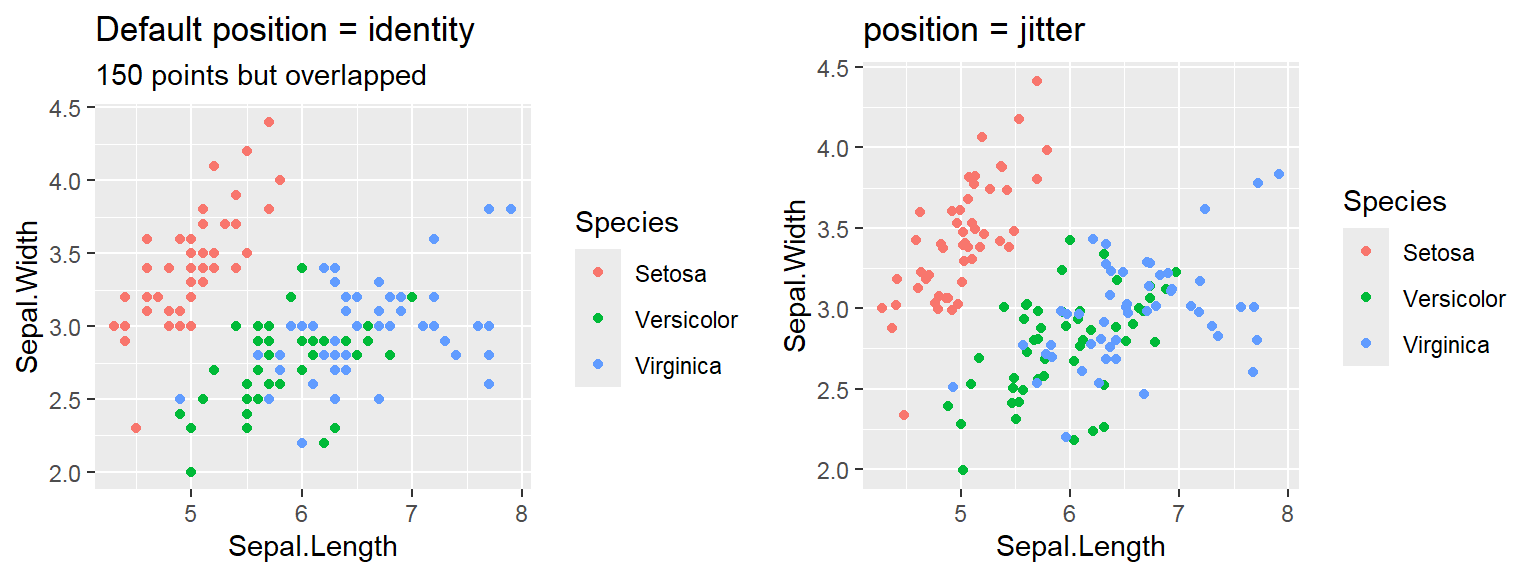
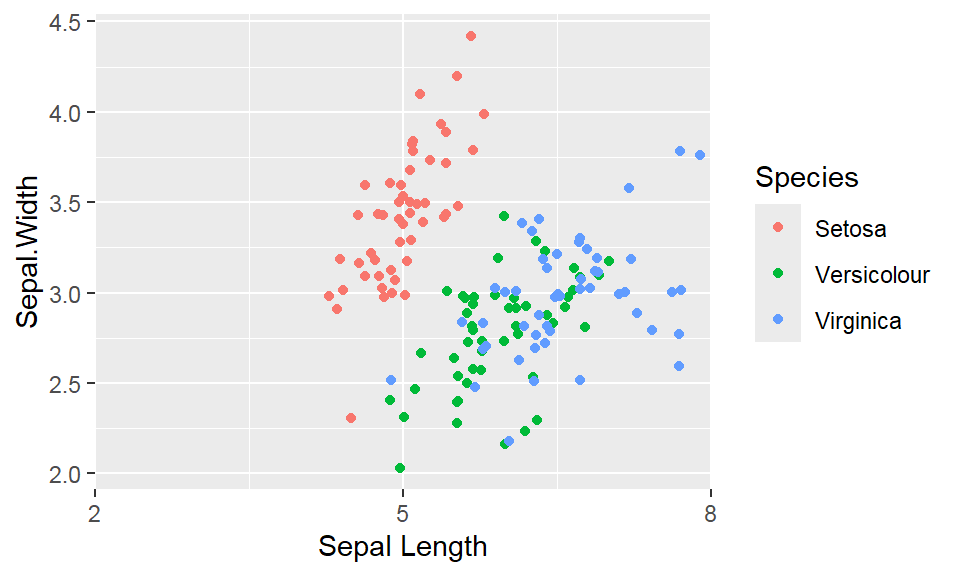
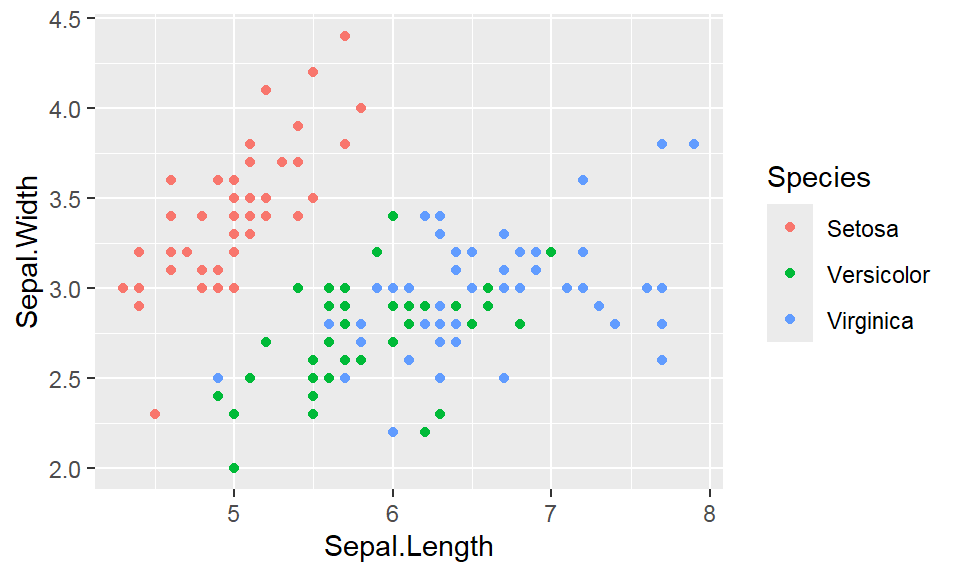
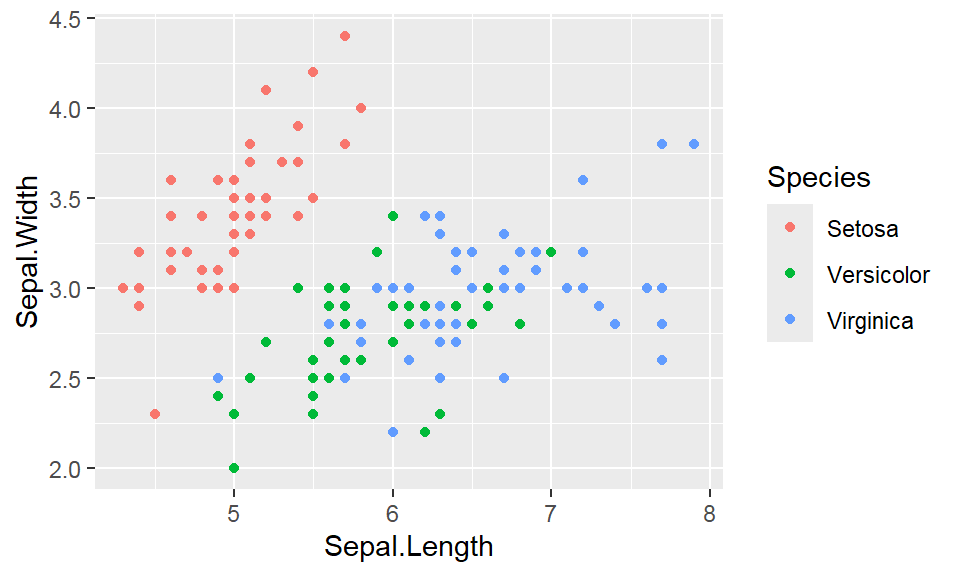
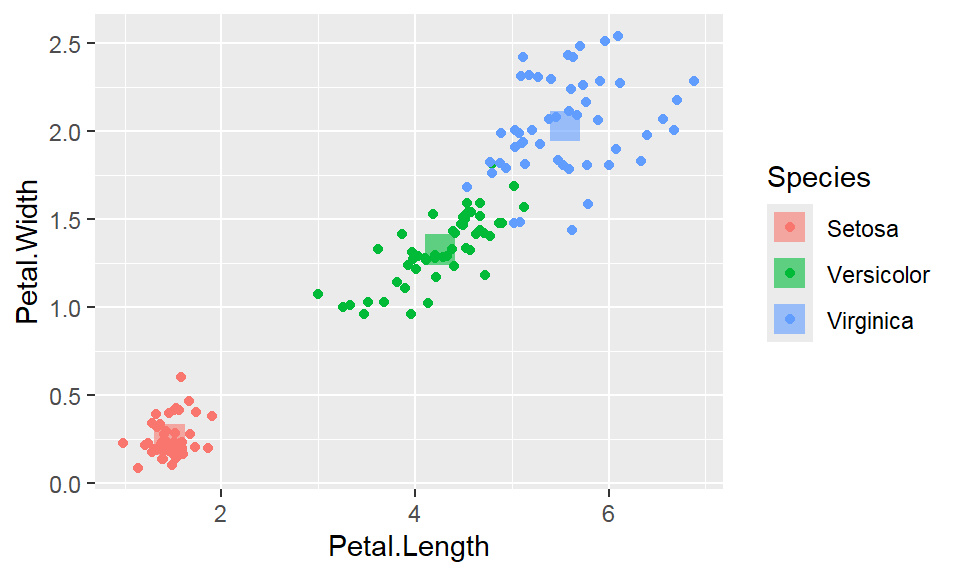
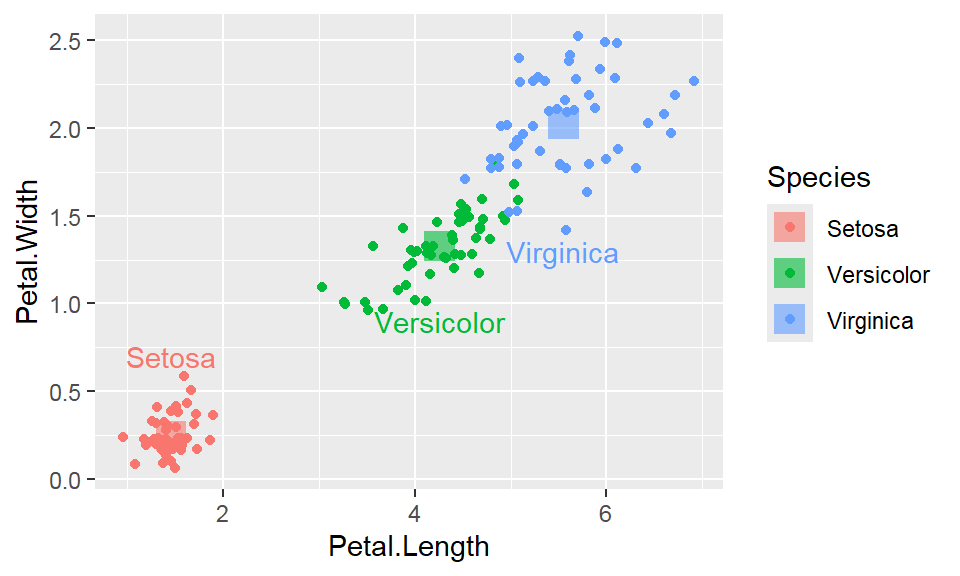
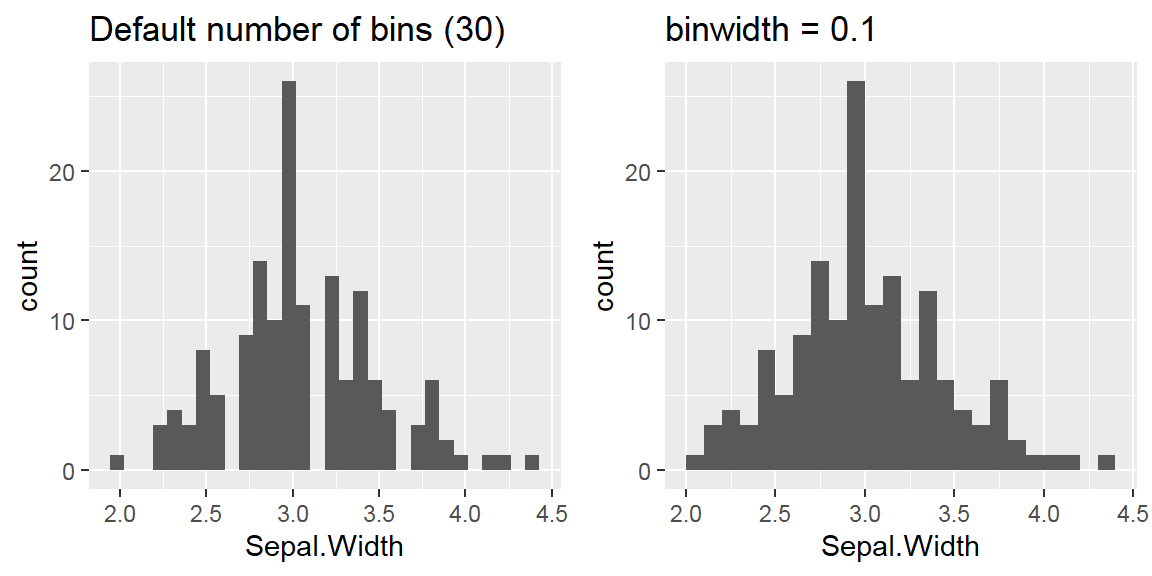
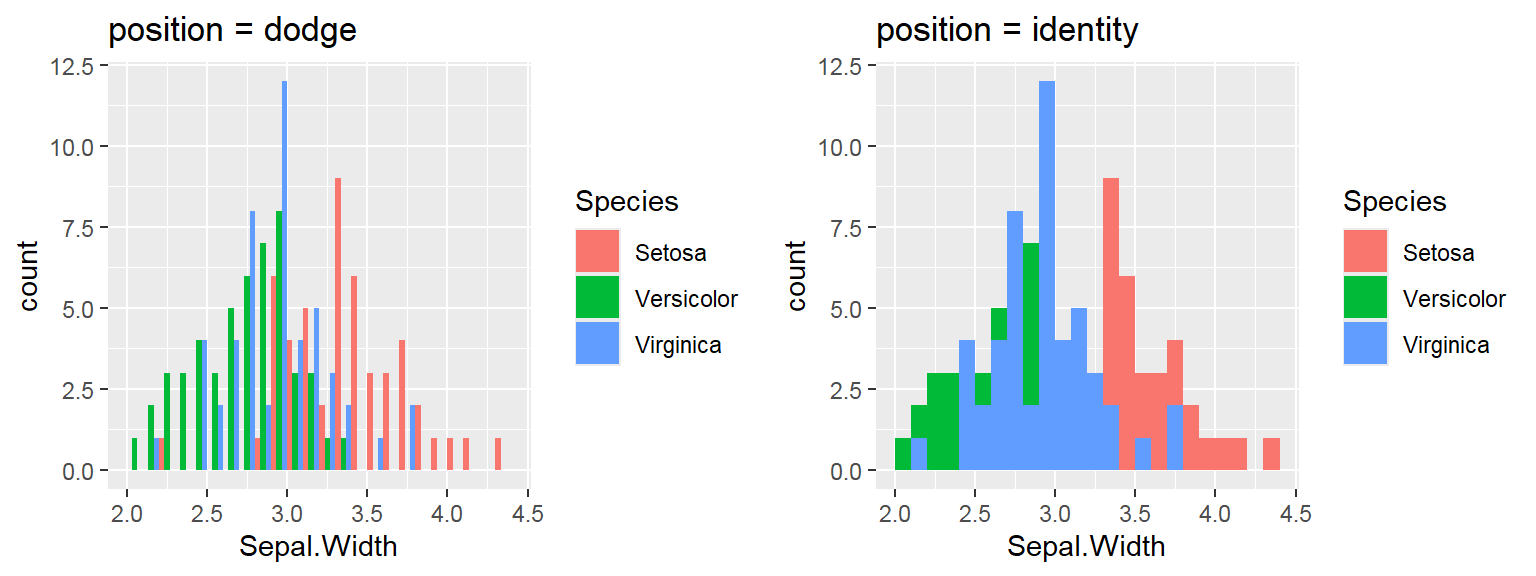
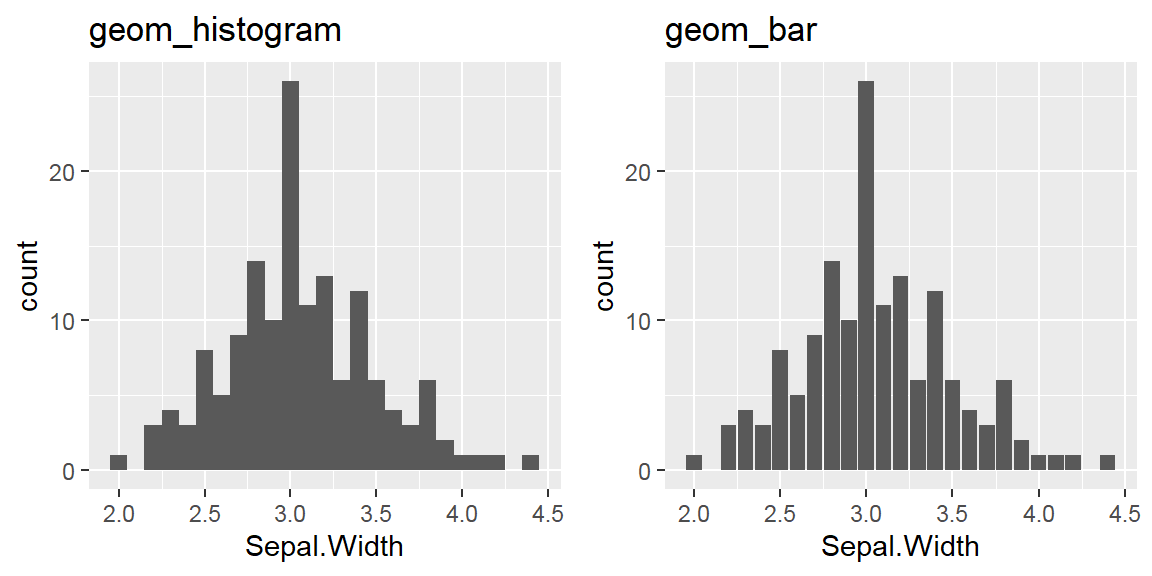
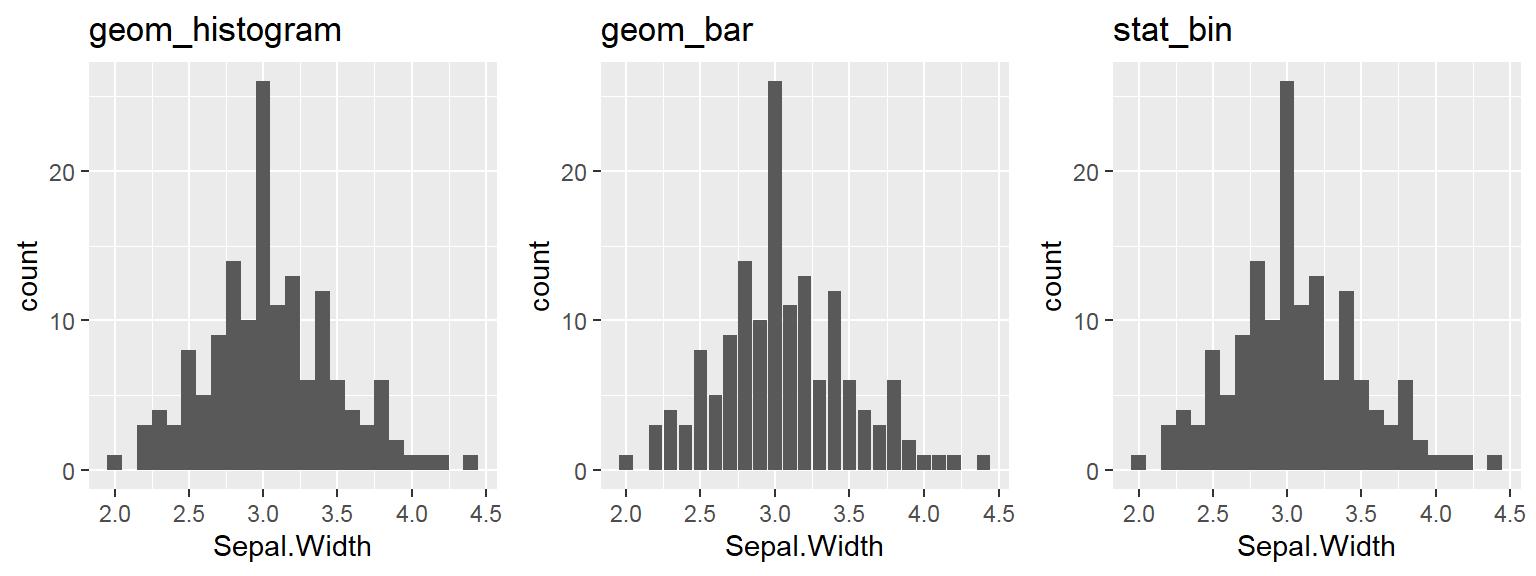
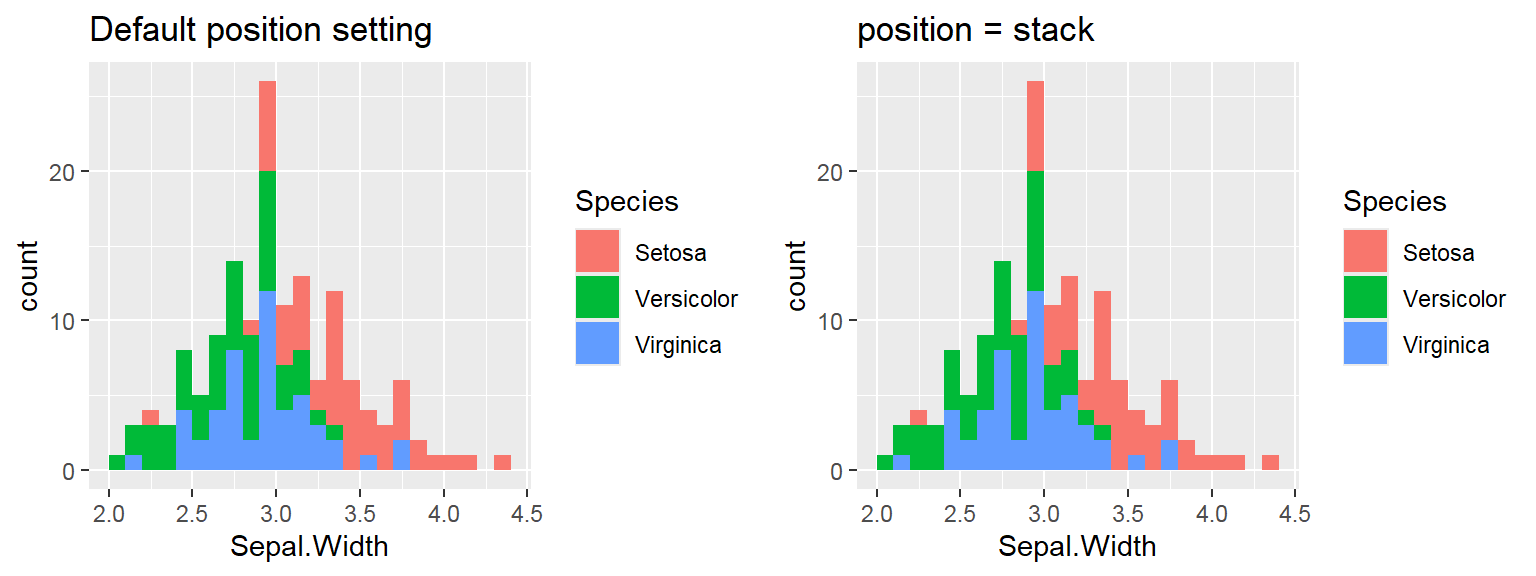 We cant say whether the histogram bars are stacked or overlapped onto each other
We cant say whether the histogram bars are stacked or overlapped onto each other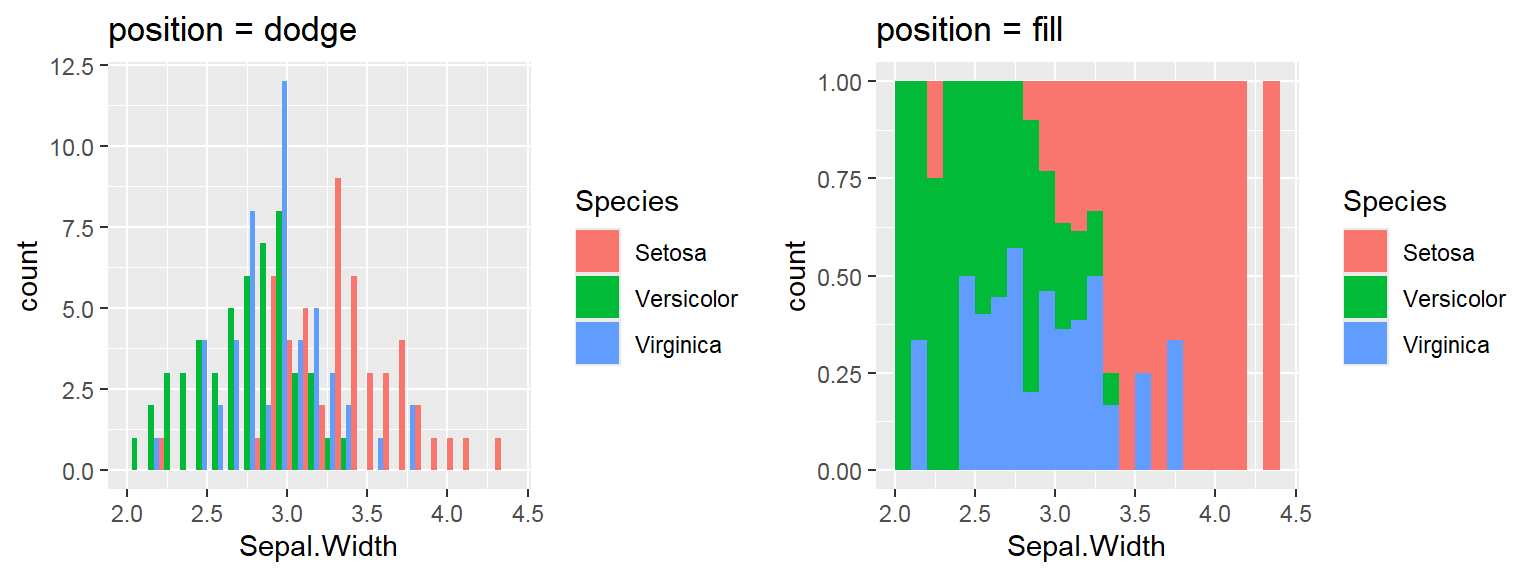
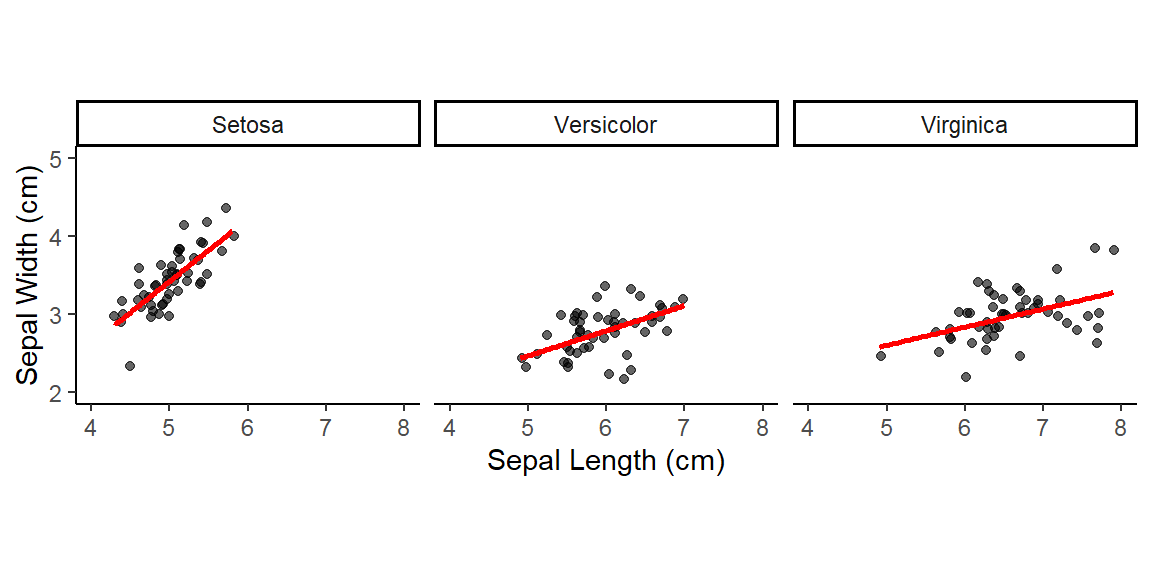
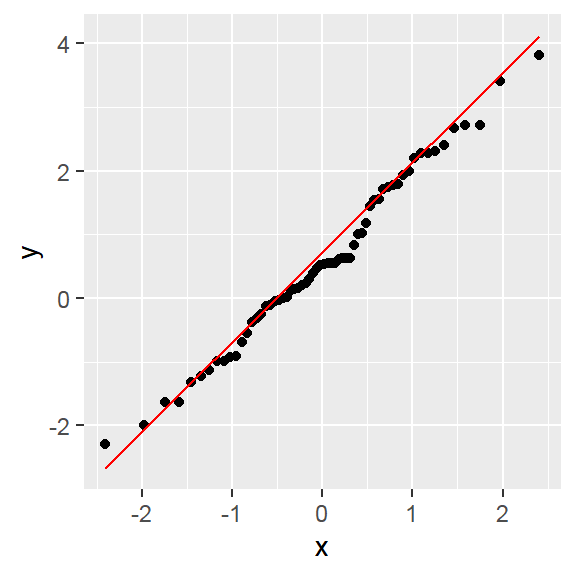
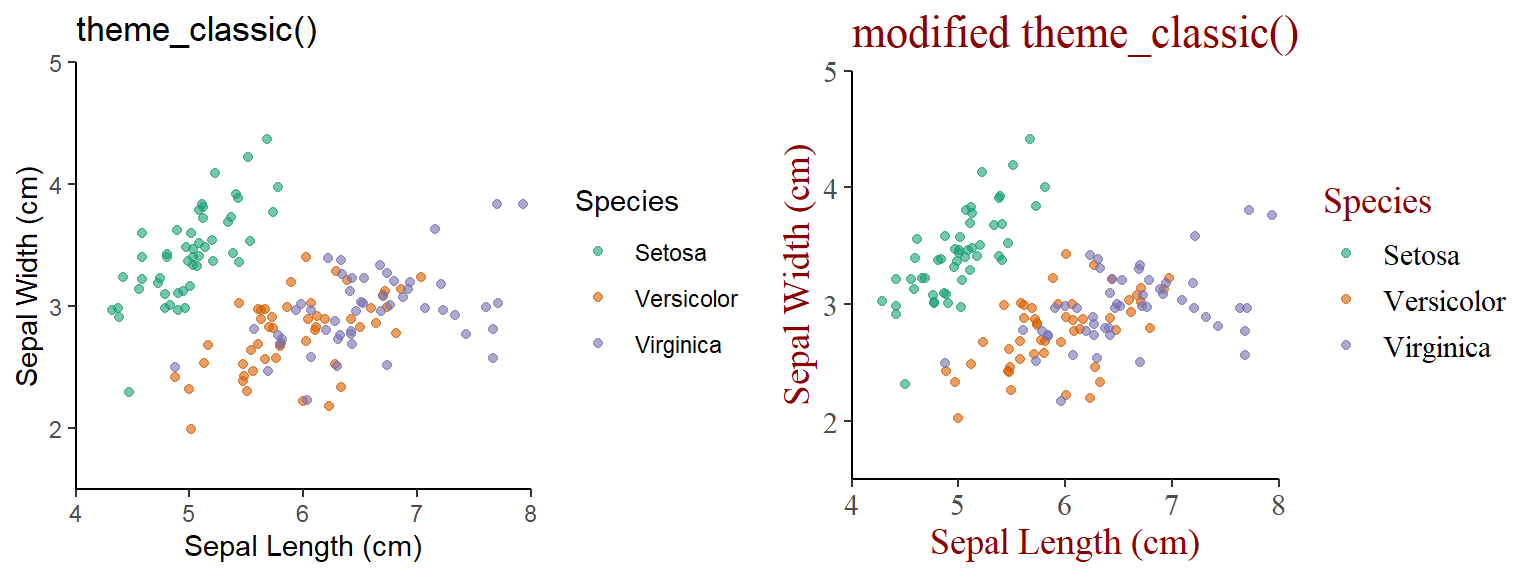
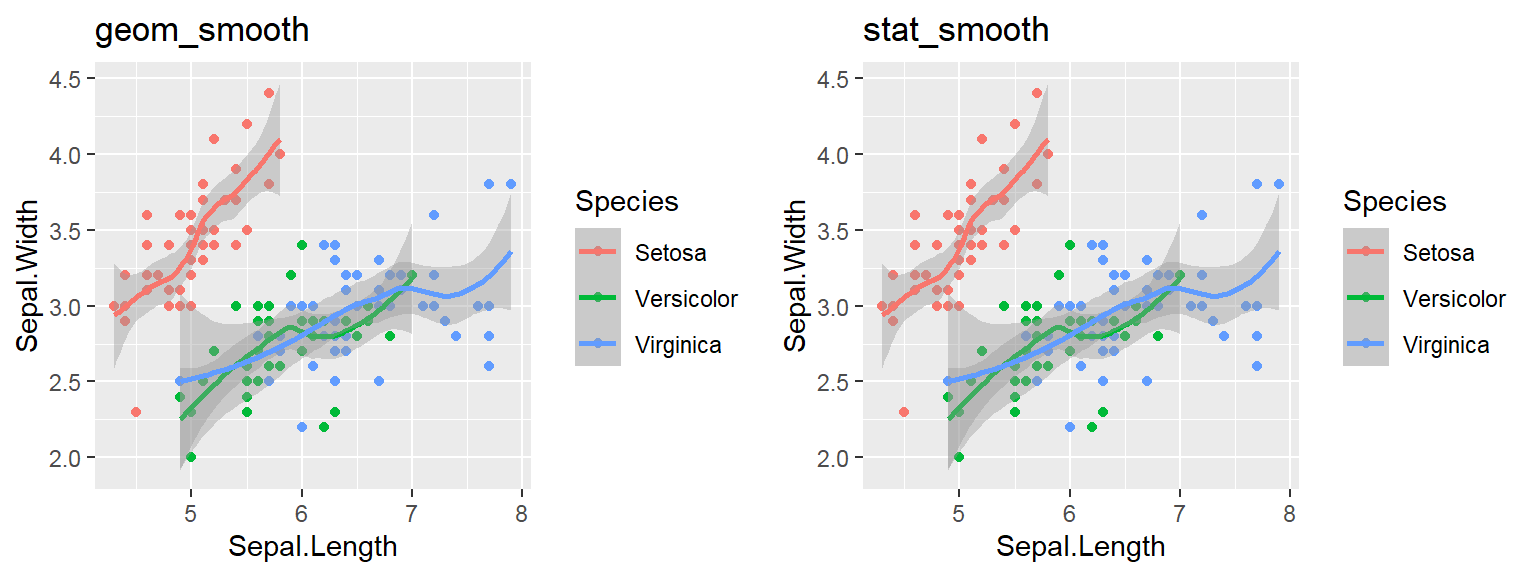 Note: By default, loess regression is used. It is a non-parametric methods where least squares regression is performed in localized subsets, and used when n < 1000. We can change smoothing method with the
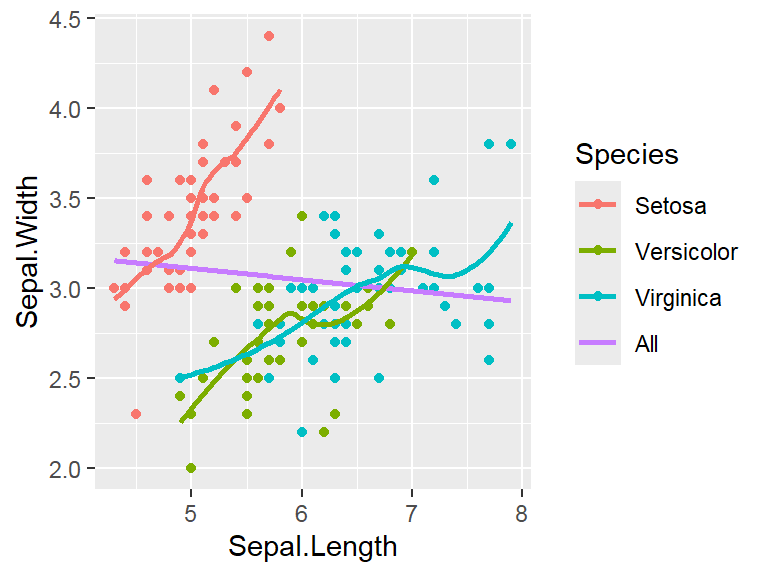
Note: By default, loess regression is used. It is a non-parametric methods where least squares regression is performed in localized subsets, and used when n < 1000. We can change smoothing method with the 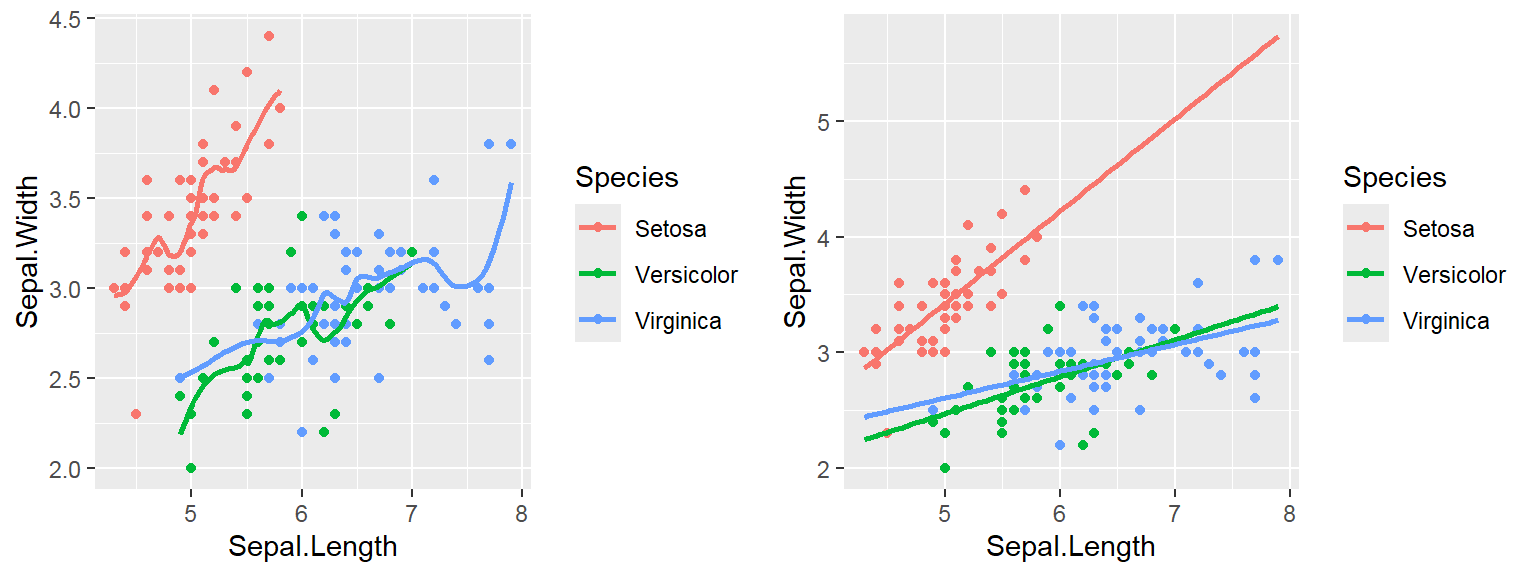
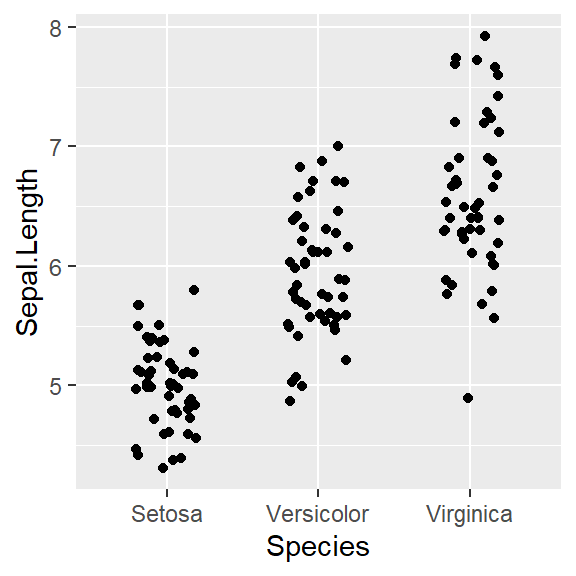
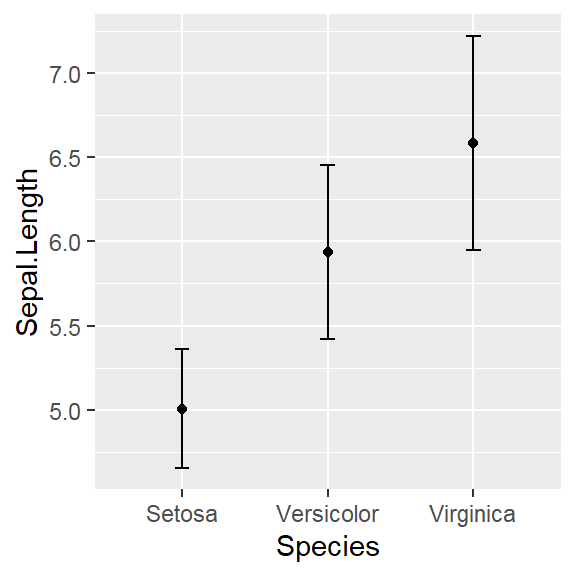
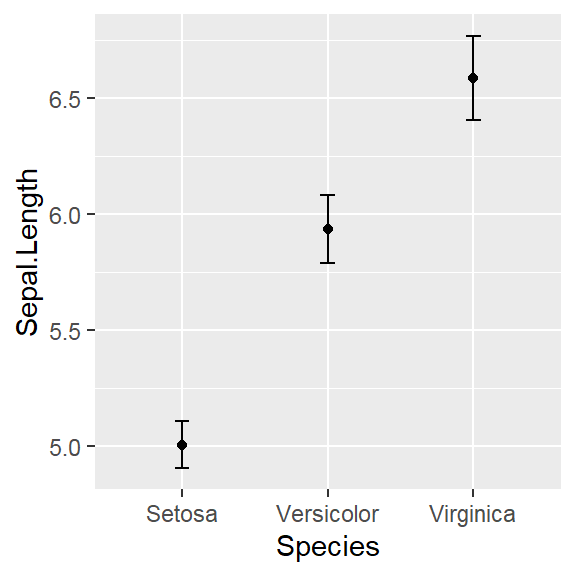
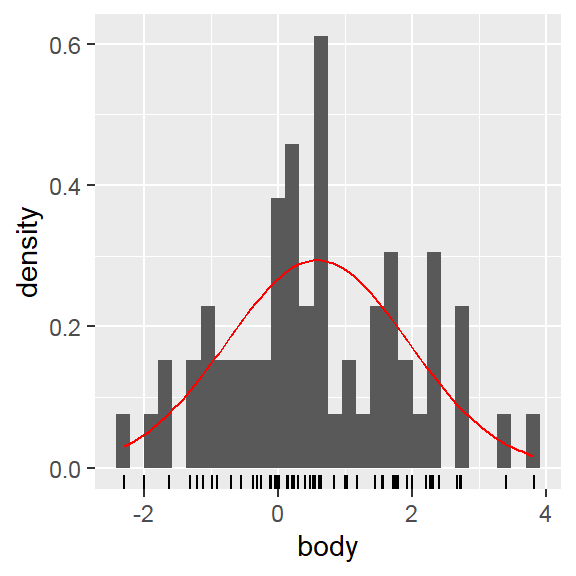
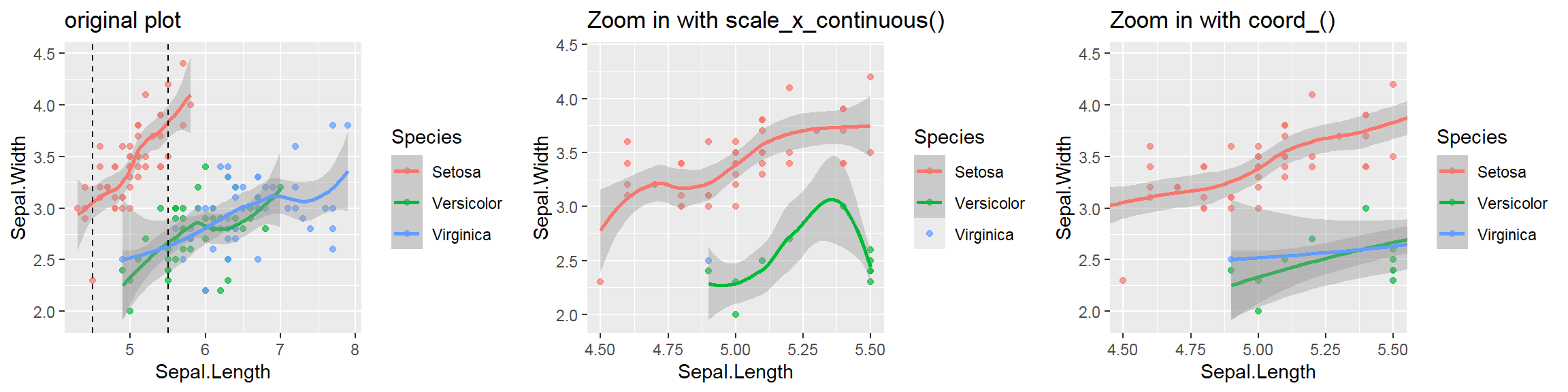
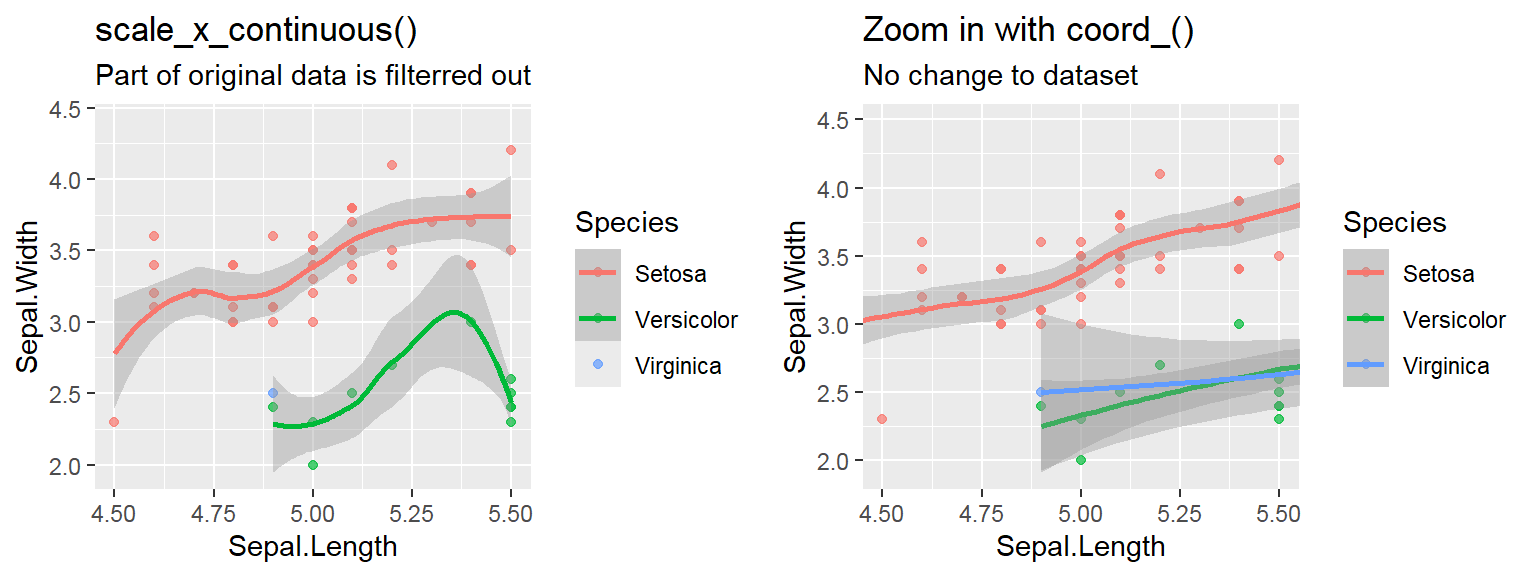
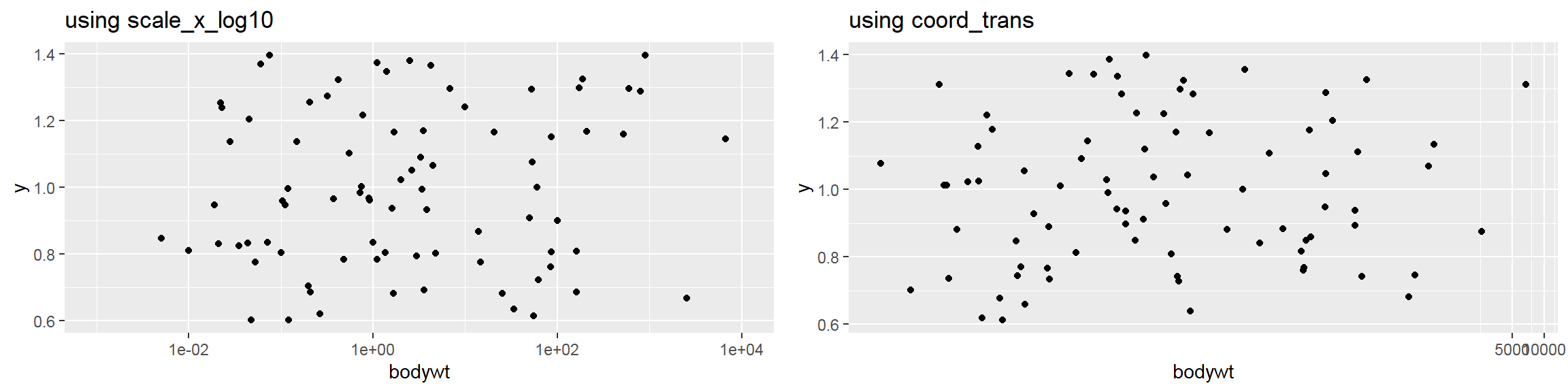
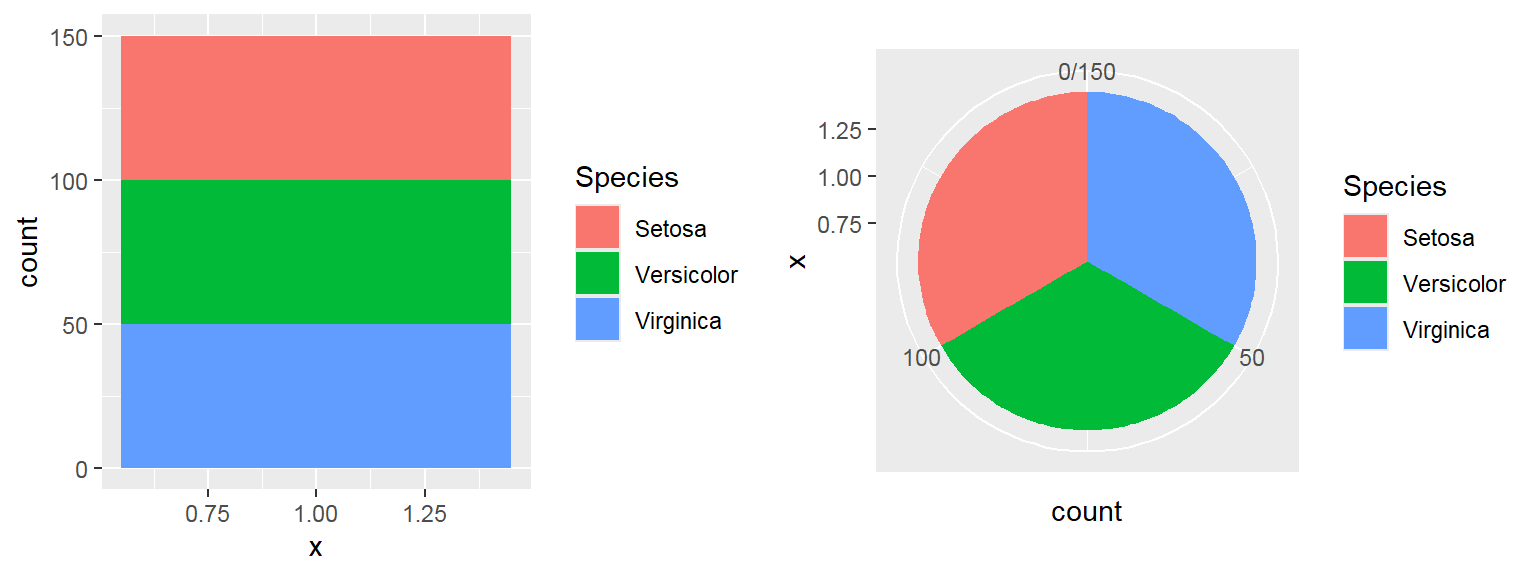

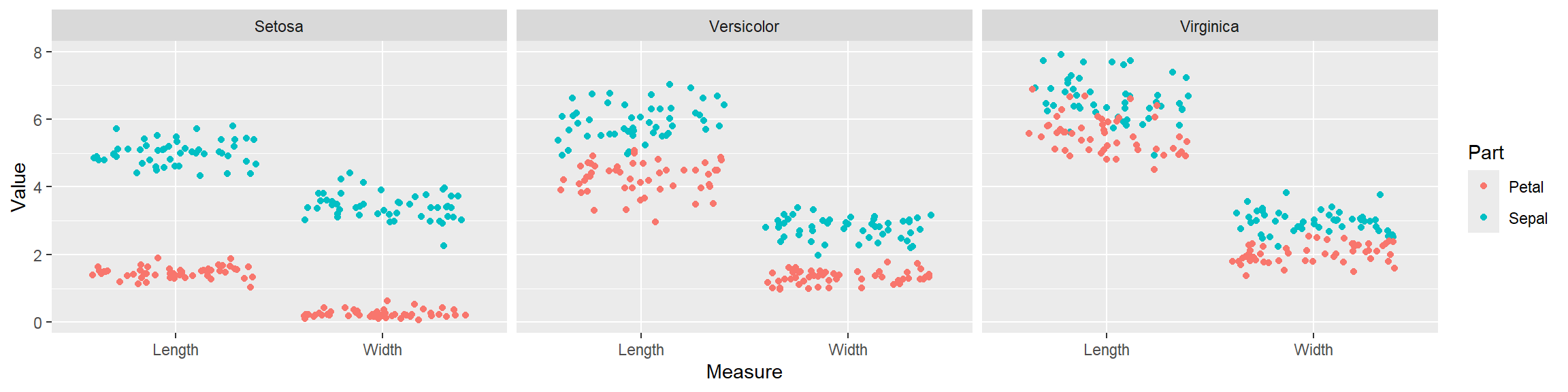
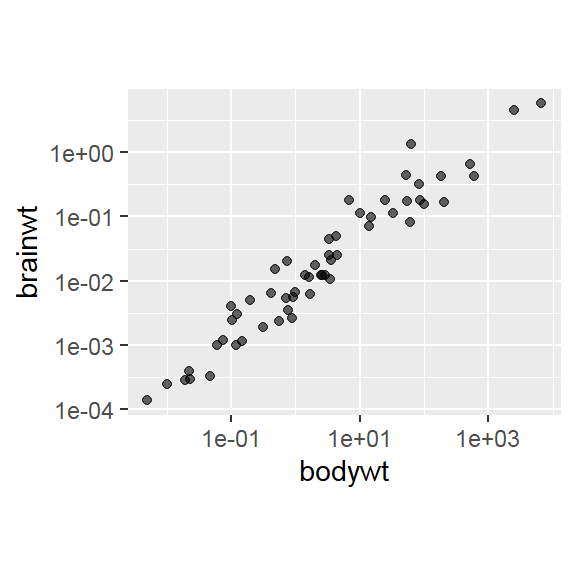
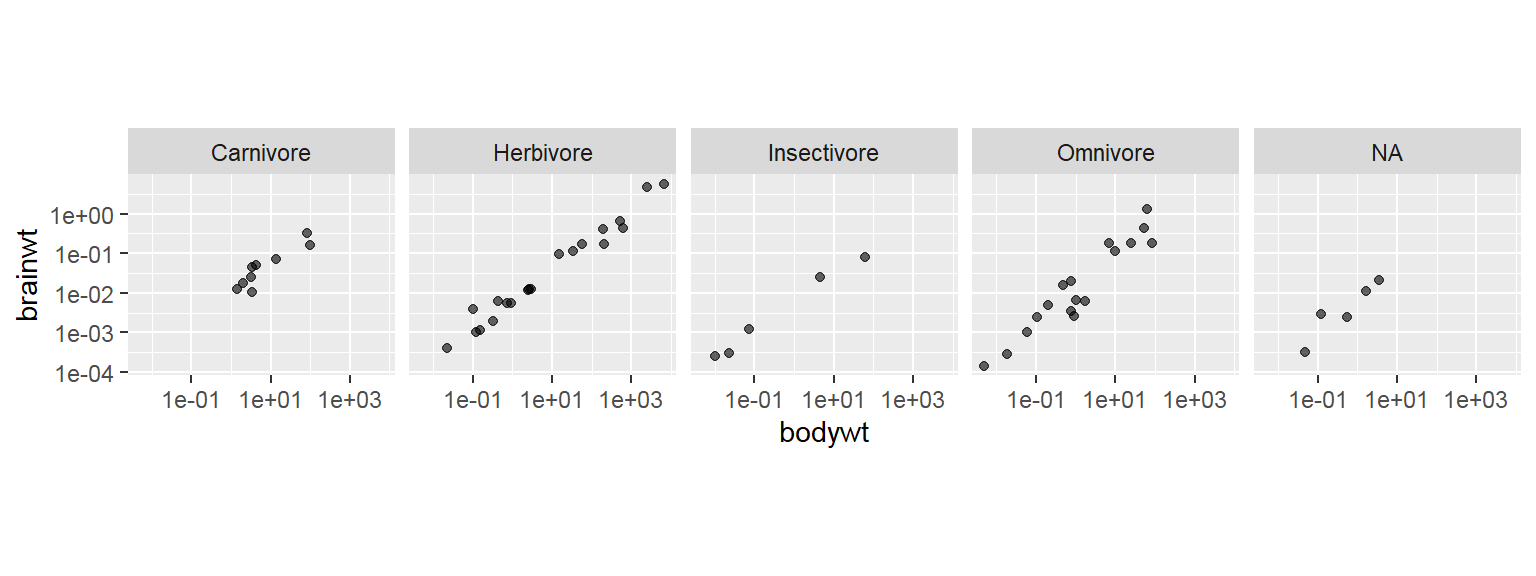
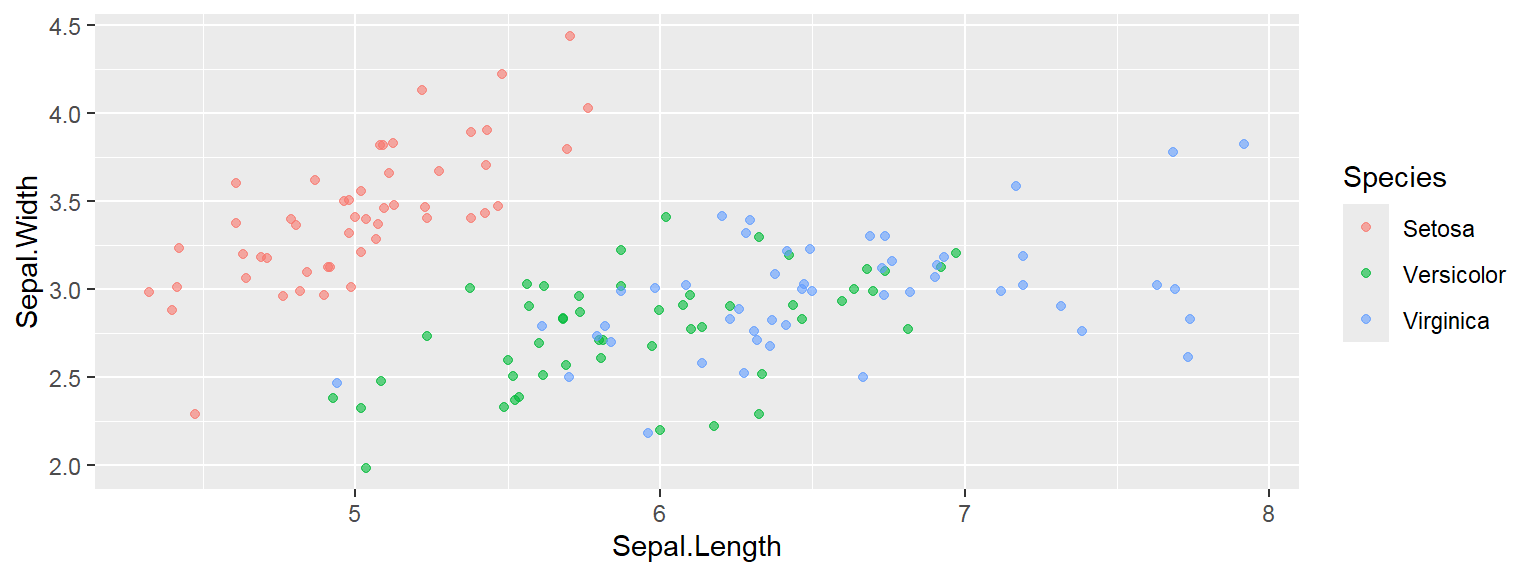
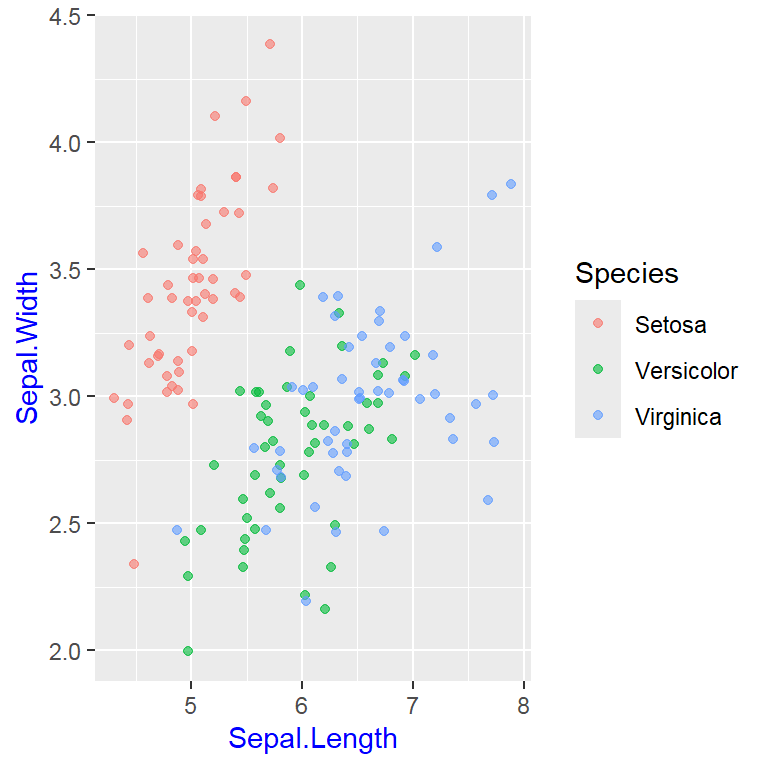
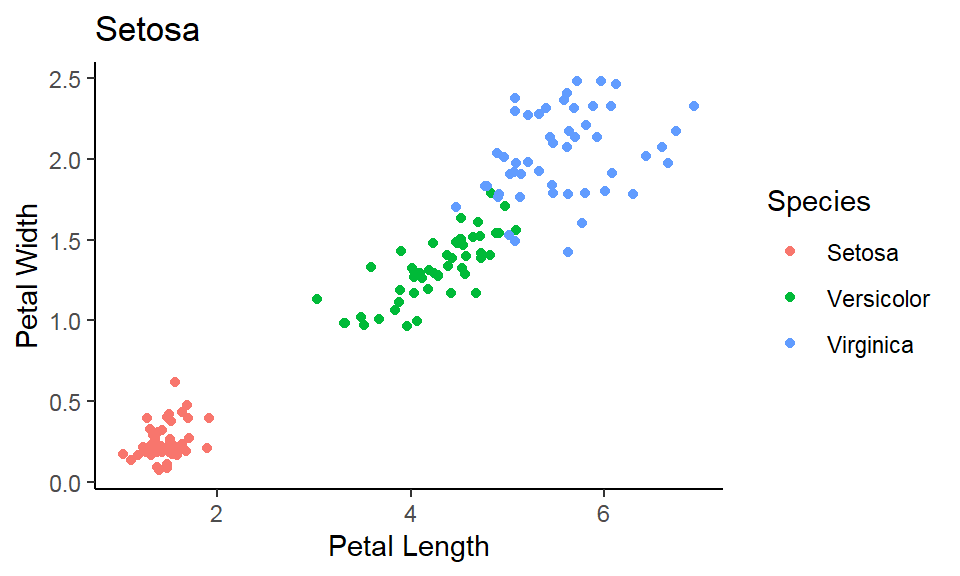
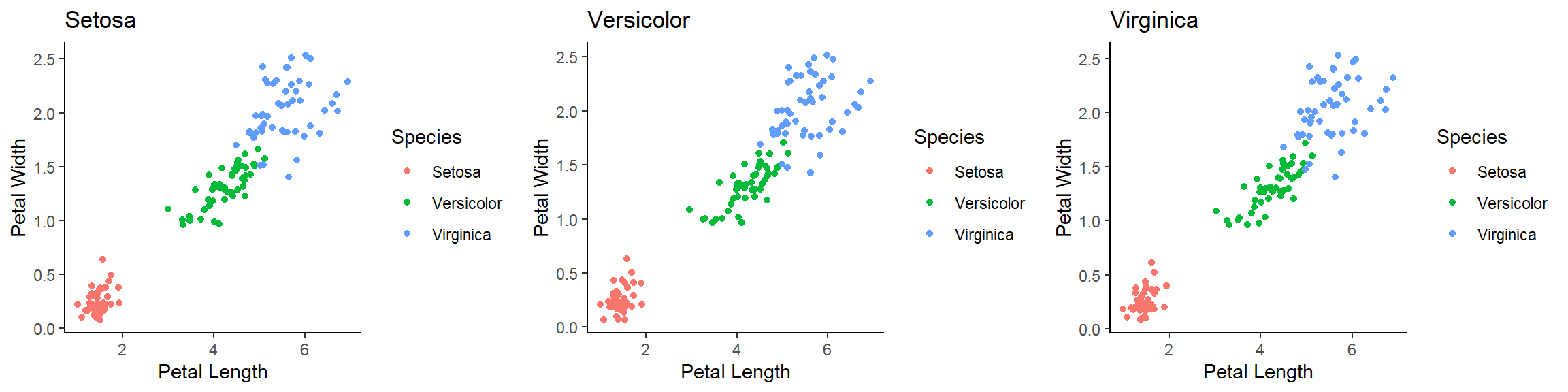
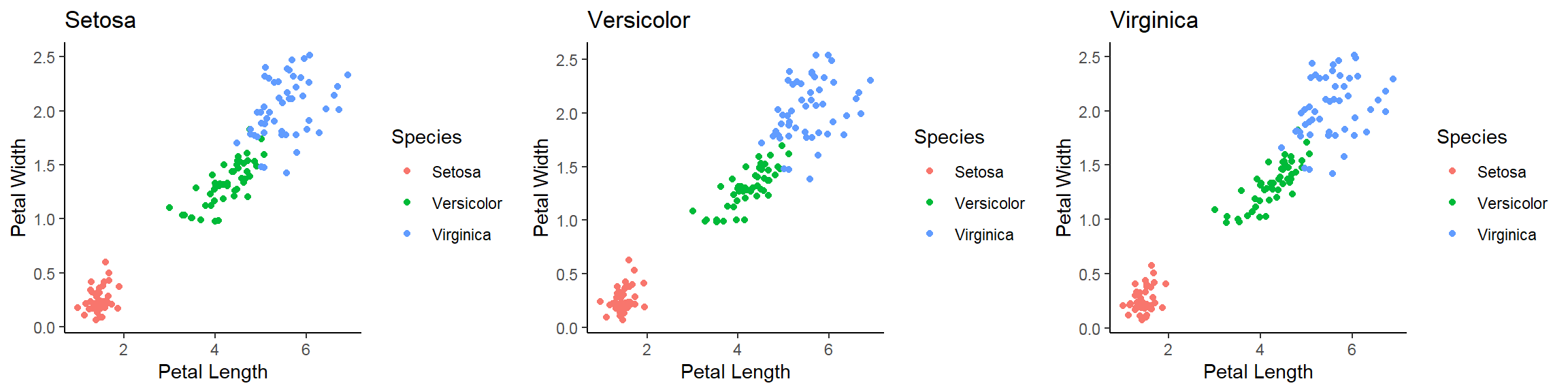
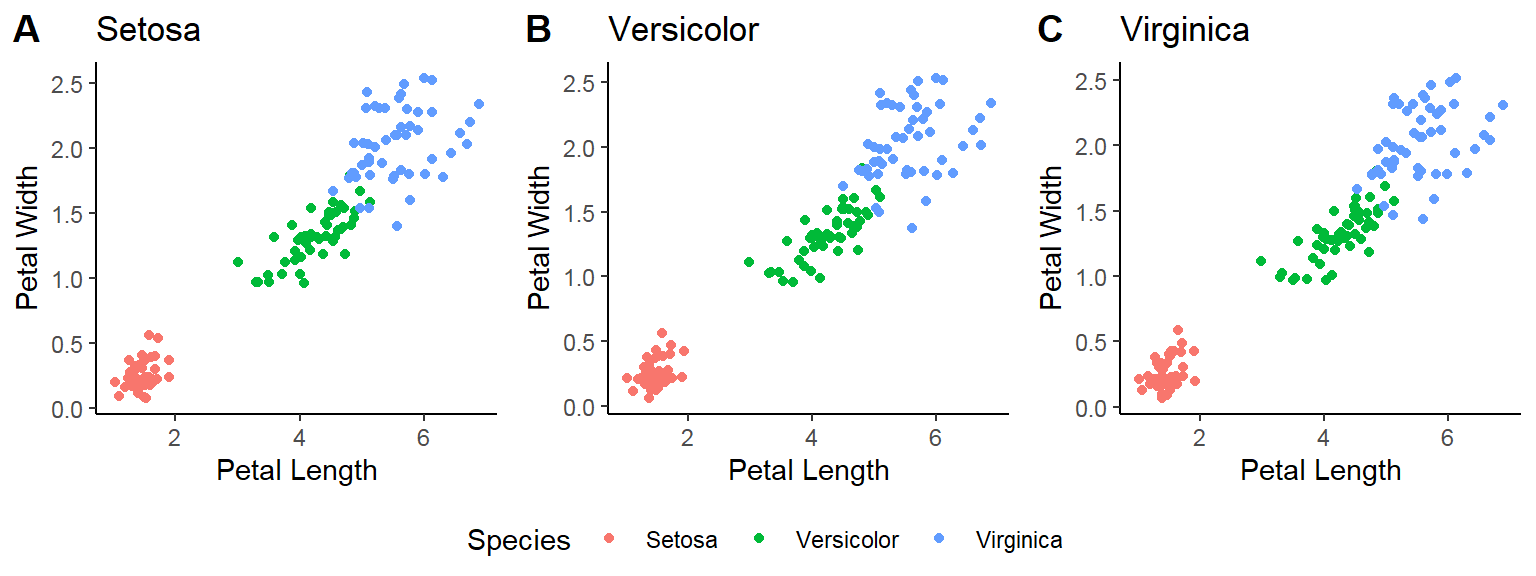
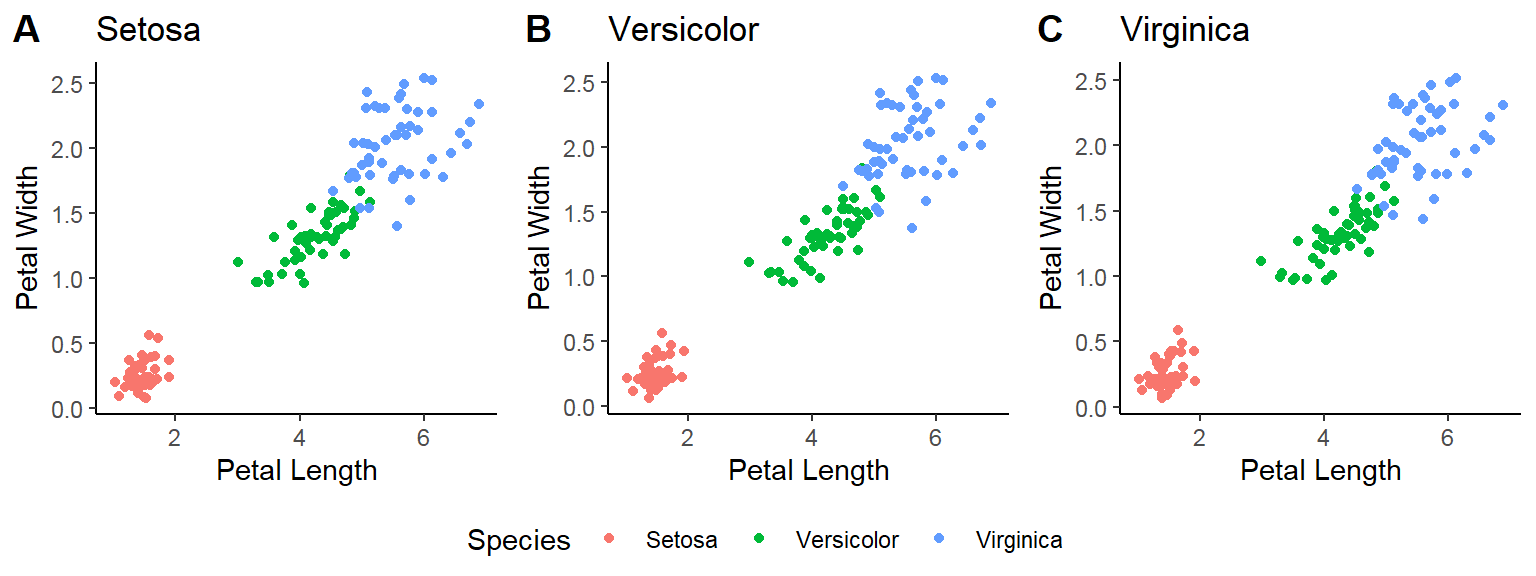
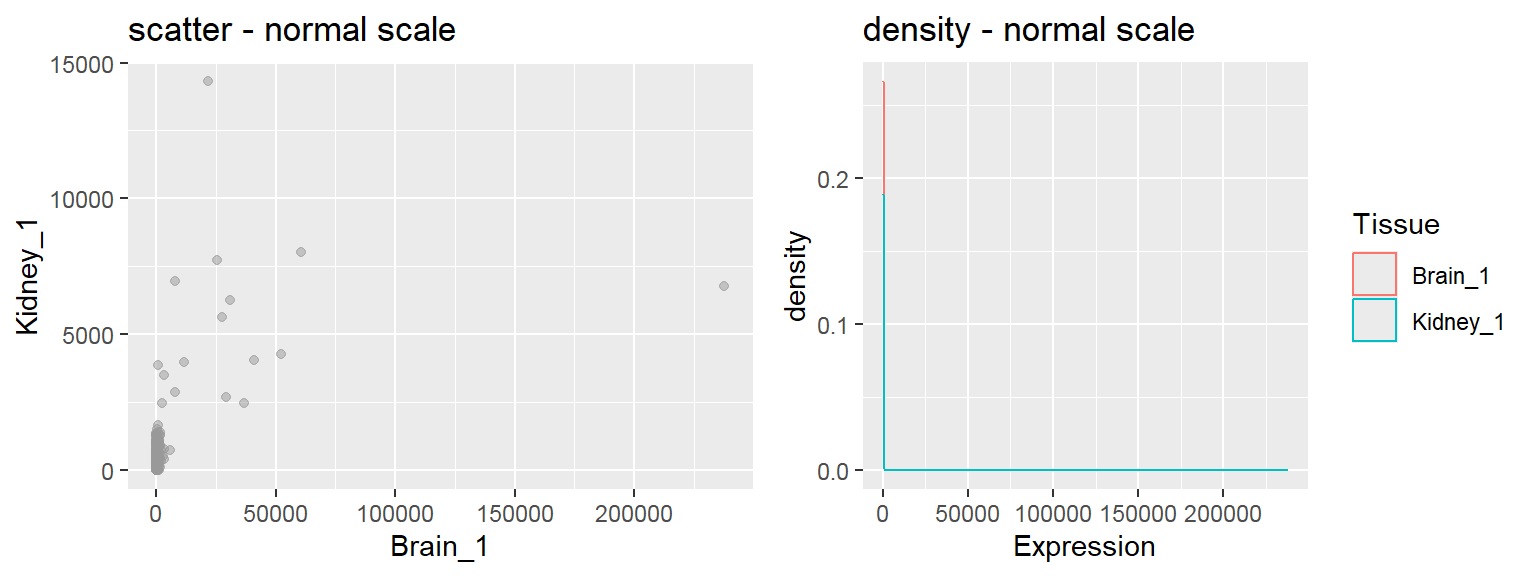
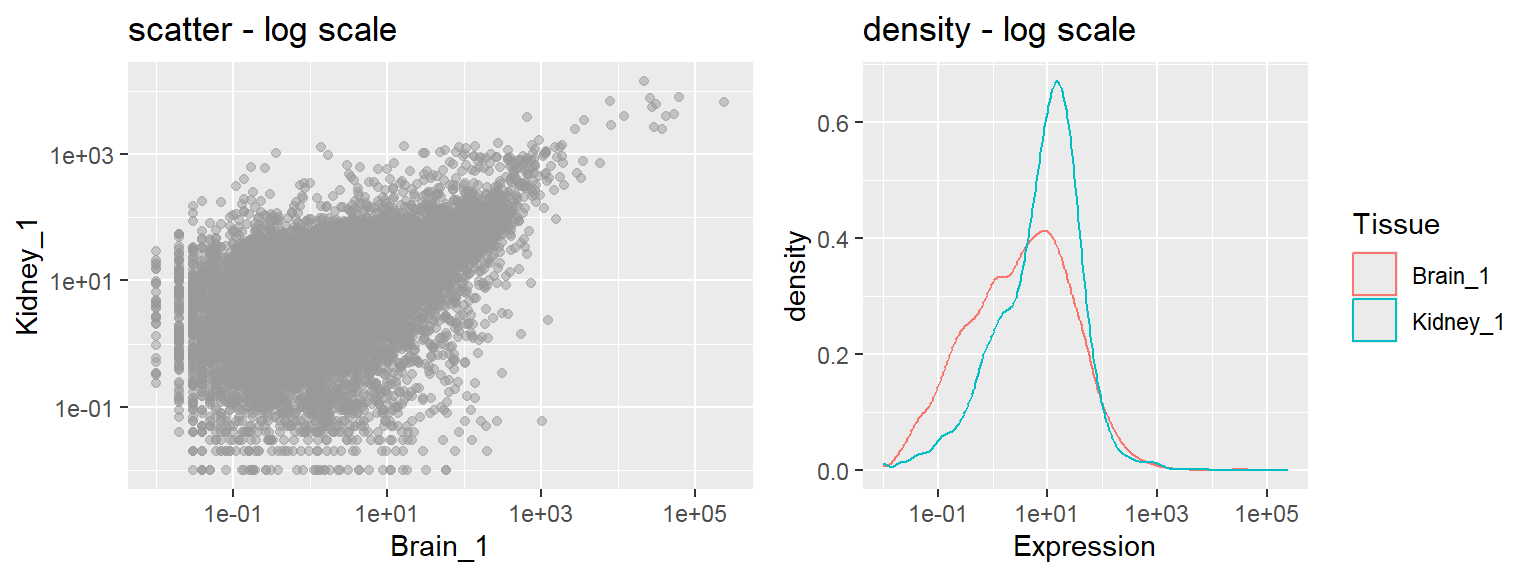
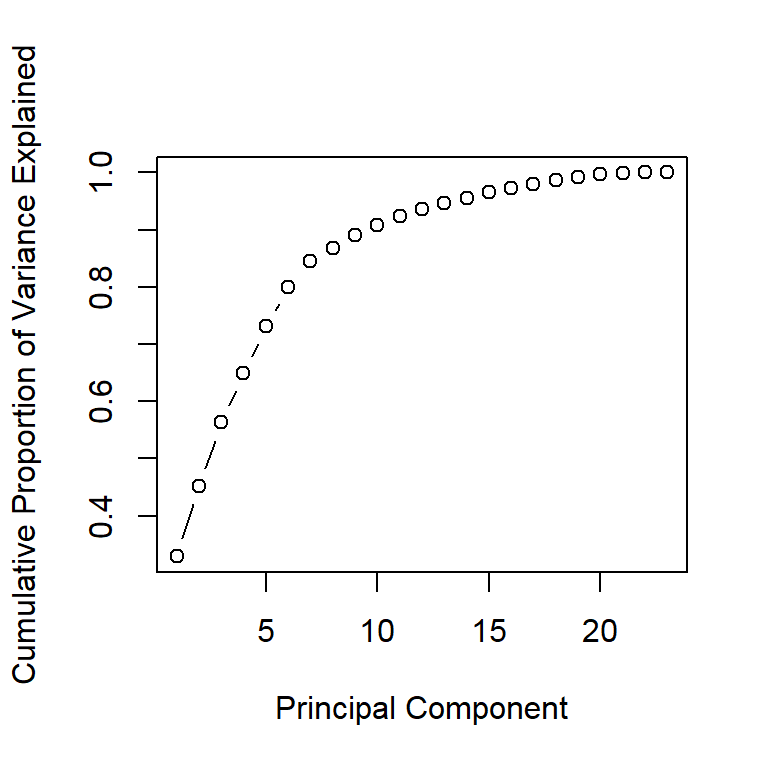
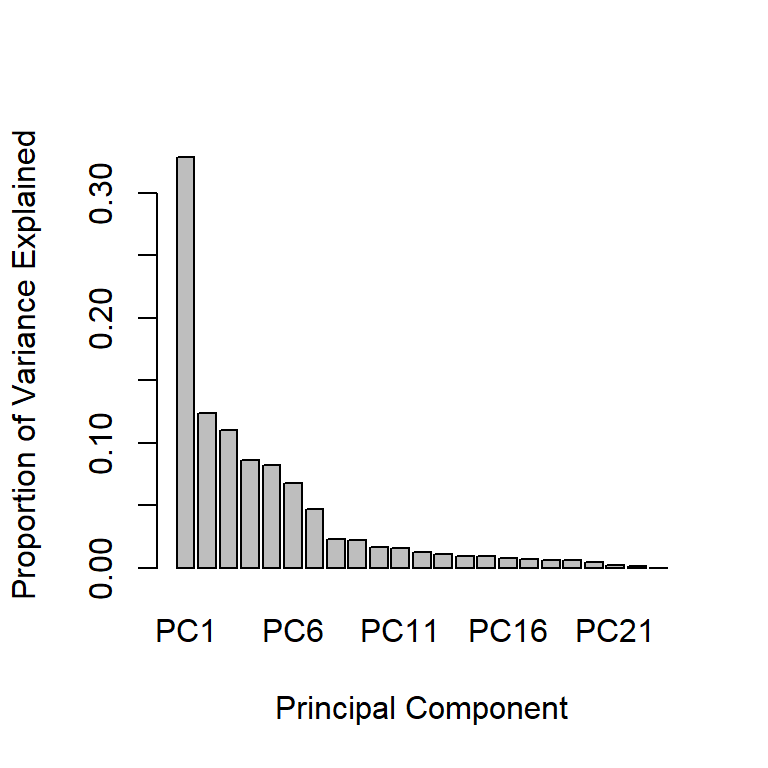 - In addition to the individual variance explained plots, also the cumulative variance explained is frequently looked at.
- In addition to the individual variance explained plots, also the cumulative variance explained is frequently looked at.