Chapter 2 Introduction
2.1 What is dbt?
dbt, when in full, stands for Data build tool. dbt is a tool that data scientists and analytical engineers use to transform data in their data warehouses. For now, just think of dbt much like a recipe. In a recipe, you have the instructions to cook your favourite meal, say a roasted chicken. Sure enough, your recipe will contain details on the optimal oven temperature, heating duration and setting the table! dbt works in much the same way. We define how we want to transform or build our data. Once we hit run, the magic happens.
2.2 Encounter with dbt
How did I cross paths with dbt? Coming from the geographical sciences, my first experience with dbt, contrary to the many positive revs from online users, wasn’t so good. Perhaps it was because a lot was on my desk back then, for I was having trouble piecing together all the different components that make dbt work, and how it works. It is only after some time, and several hard knocks in between, that I was able to get a semblance of what it does.
Nevertheless, at least I got a few things. dbt could be used to create views of your tables in the data warehouse, it could perform tests and lastly, (the one I liked the most) it could be used to render your documentation!
2.3 dbt, from the professionals…
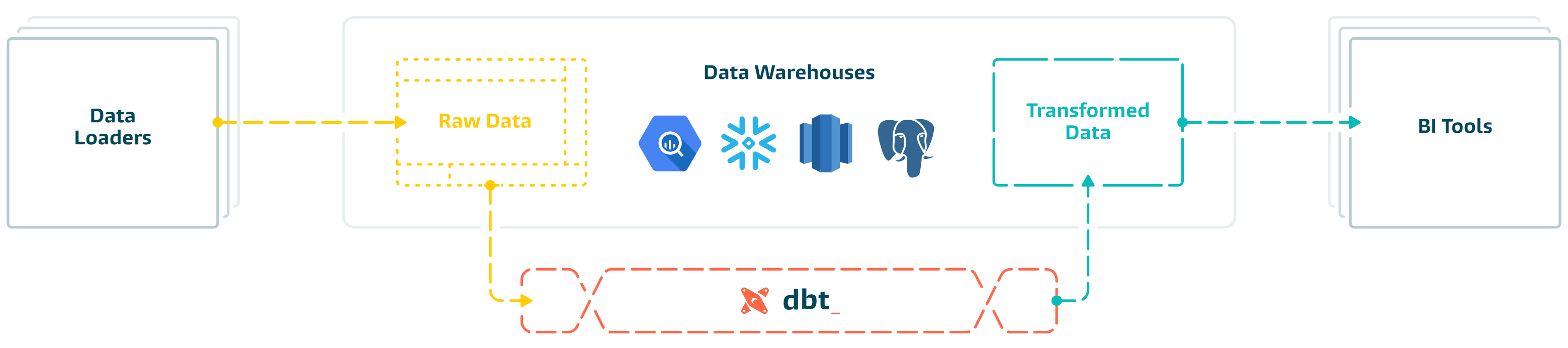
dbt, from the words of developers, is an open-source tool that analysts and data engineers use to transform data in their data warehouses. Data transformation is the process of converting data from its source format to the format required for analysis. The data transformation process is part of a three stage process known as Extract, Load and Transform (ELT). Before ELT, Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) was the king. The former involves transferring data from the source, to the destination, such as a data warehouse or data lake and performing the transformation in there. The latter, ETL, though a traditional approach, involves first identifying the data, transforming it prior to landing it to the destination, in this case a data warehouse.
Here is a better description of the Extract, Load and Transform keywords.
Extract - this is the identification and reading of data from one or more sources, such as databases, internet, comma separated value (csv) files and the like.
Load - just like you would pull up a weight into a lorry, this is the process of transferring data from the source to your data warehouse.
Transform - this is the conversion of data from its state to a format that can be used by downstream users.
You may have seen the term data warehouse coming up quite a number of times. A data warehouse is a data management system that stores current and historical data from multiple sources in a business friendly manner for easier insights and reporting. Examples of data warehouses are Google BigQuery, Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Azure Synapse Analytics, IBM Db2 Warehouse and Firebolt.
2.4 Why use dbt?
If you work with data that needs to be version controlled, that is, it can be rolled back to a previous time, you need to work in dbt. If you want to standardize the data models created across teams, dbt is the tool of choice. If you also want a central place where your data work is also documented, dbt handles this quite well. In other words, dbt should be the swiss knife when working with large datasets and where you want to maintain modularity, order and documentation of your work.
The below image summarises the role of dbt in your data processing work.
Source: Reference