Chapter 14 Analyses
In dbt, analyses are those kind of queries that might not exactly be very much needed as a model but can be used for data exploration and visualization. Typically, any SQL model that is for analytical rather than modeling purposes is stored within the analyses directory. Thereafter, running the code dbt compile will create the compiled SQL file inside the target/compiled/{project name}/analyses/sql_file_name.sql directory. The code inside this directory can be pasted in a data visualization tool but it will not appear in the data warehouse. You read that well: it will not.
14.1 Creating an analysis
As mentioned earlier, analyses queries are stored within the analysis folder. To begin with, we shall create a SQL query that performs a join. The below query will join the rows in nyc_bikes_nyc_bikes2014.2014-tripdata with those in nyc_bikes.citi_trips_round based on station id. The aforementioned contents are found within the start_join_bikes SQL within the analyses folder.
WITH `2014-tripdata` AS (
SELECT * FROM {{ source('nyc_bikes_nyc_bikes2014', '2014-tripdata') }}
),
WITH citi_trips_round AS (
SELECT * FROM {{ source('nyc_bikes', 'citi_trips_round') }}
)
SELECT cs.`start station id`, cs.`start station name`,
ct.bikeid, ct.start_station_id, ct.trip_min_round
FROM `2014-tripdata` cs
JOIN citi_trips_round ct
ON cs.`start station id` = ct.start_station_id
WHERE ct.trip_min_round > 50000
Thereafter type and hit dbt compile on the terminal. The results will appear in the dbt_book/target/compiled/dbt_book/analyses directory. The query is actually the same, as you can see below. The only exception is that the references within the source file have been expanded to contain the full table path.
WITH `2014-tripdata` AS (
SELECT * FROM `dbt-project-437116`.`nyc_bikes_nyc_bikes2014`.`2014-tripdata`
),
WITH citi_trips_round AS (
SELECT * FROM `dbt-project-437116`.`nyc_bikes`.`citi_trips_round`
)
SELECT cs.`start station id`, cs.`start station name`,
ct.bikeid, ct.start_station_id, ct.trip_min_round
FROM `2014-tripdata` cs
JOIN citi_trips_round ct
ON cs.`start station id` = ct.start_station_id
WHERE ct.trip_min_round > 50000However, pasting this on BigQuery results in the below error.
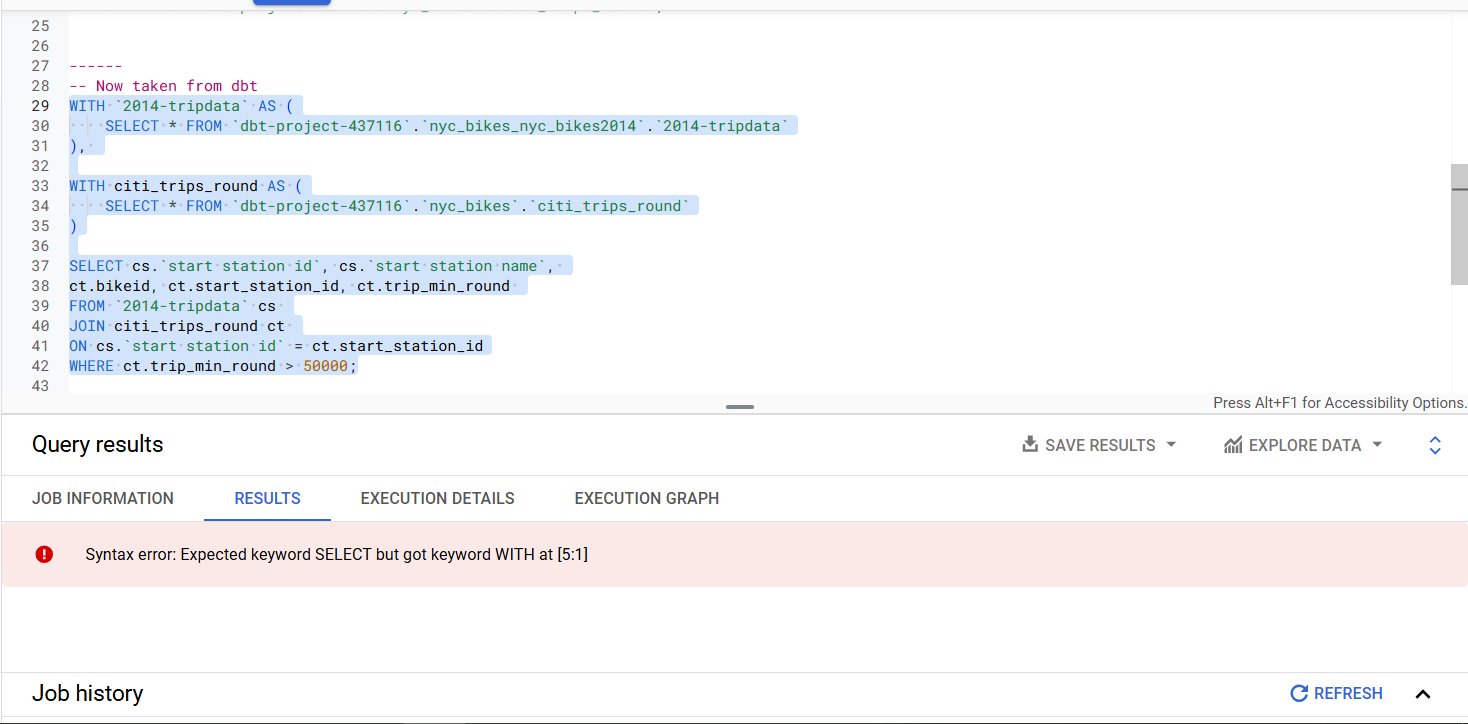
Therefore, we created a second model which does the same work but without the WITH statement. These are the contents of station_join_bikes_snd.sql.
SELECT cs.`start station id`, cs.`start station name`,
ct.bikeid, ct.start_station_id, ct.trip_min_round
FROM {{ source('nyc_bikes_nyc_bikes2014', '2014-tripdata') }} cs
JOIN {{ source('nyc_bikes', 'citi_trips_round') }} ct
ON cs.`start station id` = ct.start_station_id
WHERE ct.trip_min_round > 50000;
The contents of the SQL file inside the dbt_book/target/compiled/dbt_book/analyses directory are as follows:
SELECT cs.`start station id`, cs.`start station name`,
ct.bikeid, ct.start_station_id, ct.trip_min_round
FROM `dbt-project-437116`.`nyc_bikes_nyc_bikes2014`.`2014-tripdata` cs
JOIN `dbt-project-437116`.`nyc_bikes`.`citi_trips_round` ct
ON cs.`start station id` = ct.start_station_id
WHERE ct.trip_min_round > 50000;The full table path was expanded and pasting this query into BigQuery produces the results without a fuss.