Chapter 11 flexdashboard
The first lesson to build your own webpage is to choose your page layout(頁面切割佈局). The challenge of it comes from building a view port responsive design. R package flexdashboard is to help you achieve that.
11.2 安裝
install.packages("flexdashboard")11.3 使用

11.4 頁面佈局(layout)
在頁面上切割的每個格子都像是個box:
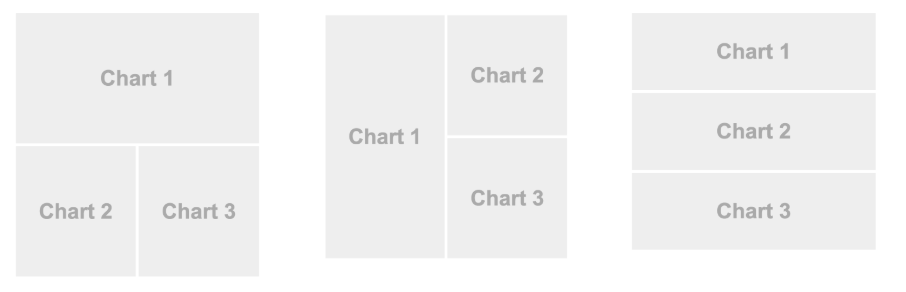
頁面上的3個box,它們放上去的順序是如何決定?
11.5 頁面部局設定
參考資料:HTML layout
By column or by row:
by column: 頁面切成好幾個columns由左往右,裡頭的box由上往下擺。
by row: 頁面切成好幾個rows由上到下,裡頭的box由左往右擺。
11.5.1 by column
設定:
Frontmatter
output: flexdashboard::flex_dashboardStart a new column
Column
-------------------------------------Insert a chart
### Chart11.5.1.1 by column 可否超出頁面
內定不行
允許超出頁面
output:
flexdashboard::flex_dashboard:
vertical_layout: scroll11.5.2 by row
Frontmatter
output:
flexdashboard::flex_dashboard:
orientation: rowsStart a new row
Row
-------------------------------------Insert a chart
### Chartby row 不可自行換行
在網頁語法上可以(在flex container設定flex-wrap: wrap;,但flexdashboard並不提供(因為不適合儀表板的要求)
11.5.3 使用標籤(tabset)節省空間
在Start a new row/column在Row/Column旁加上{.tabset}
請從plot.ly任意下載幾個圖製作你的第一個dashboard。
11.5.4 Markdown語法補充
heading/header (段落標頭):有level 1-6
header level 1-2有兩種表示法
Level 1
# 標題
標題
===============
Level 2
## 標題
標題
---------------
11.5.5 Plot.ly 圖件
自plot.ly下載回來的圖件會有設定htmlwidgets的寬高,在引入flexdashboard時要取消其設定否則圖形不會自動縮放。
library(plotly)
api_download_plot("128","caluchko") -> .plotly
.plotly[["x"]][["layout"]][["autosize"]]<-T #允許autoresize
.plotly[["x"]][["layout"]][["height"]]<-c() # 取消限高
.plotly[["x"]][["layout"]][["width"]]<-c() # 取消限寛
.plotly-> goodPlotly如果常用就寫成一個函數, 如:
flex_plotly<-function(.plotly){
.plotly[["x"]][["layout"]][["autosize"]]<-T
.plotly[["x"]][["layout"]][["height"]]<-c()
.plotly[["x"]][["layout"]][["width"]]<-c()
.plotly
}以後只需:
api_download_plot("290","PatrickMerlot") %>%
flex_plotly -> plotly211.5.6 其他
frontmatter設定切割by row或by column。
使用markdown level 2 header增加新row/column。
使用markdown level 3 header增加新chart。
- header的標題可以自行命名。
11.6 Size
11.6.1 相對限制
在header level 2/3 標題旁可加上
控制「相對」高
{data-height=xxx}或
控制「相對」寬
{data-width=xxx}來改變同level區塊各別所佔相對視窗大小。由於是相對所以,xxx可以用習慣的總數去分,如100,分成20、80;或10分成2、8。
要小心的是,由於responsive design,假設在大視窗時我們設:
column 1: A(80),B(20)
column 2: C(300),D(500)
若小視窗會只有一個column,則會變成:
- column: A(80),B(20),C(300),D(500)
這時A和B會變很小。
11.6.2 Chart高度
若 vertical_layout: fill (內定):
- 在
###透過{data-height=xxx}控制
若 vertical_layout: scroll:
- 在
{r fig.height=xxx}控制xxx是inch
11.7 dashboard元素
https://rmarkdown.rstudio.com/flexdashboard/using.html#components
HTML widgets(可互動的圖件)
R graphics(靜態圖件,如ggplot2)
Tabular Data(互動表格)
Value Boxes(數值箱)
Gauges(儀表板)
Navigation bar(導航欄)
Text annotation:只能放在
第一個Row/Colum之「前」;或
沒有圖的
###section裡;或做圖的Title/Note。
### All Lung Deaths
```{r}
dygraph(ldeaths)
```
> Monthly deaths from lung disease in the UK, 1974–1979
11.8 風格設定與使用
11.8.1 CSS來源設定
CSS設定由兩個部份掌控。
- frontmatter: 對應html external css source設定
output:
flexdashboard::flex_dashboard:
css: styles.css- body: 使用css code chunk,對應html internal css style,如:
```{css, echo=FALSE}
.bad-code { background-color: salmon; }
```
11.8.2 CSS使用
11.8.2.1 在heading
直接在heading標題後加上{.css_classname}, 如:
#### 第4章{.bad-code}
第4章{.bad-code}
--------------------
若有多個class,「無需」用逗點分開:
#### 第4章{.bad-code .alert}
第4章{.bad-code .alert}
--------------------
11.8.2.2 在code chunk
```{r, class.source="bad-code"}
11.8.3 CSS優先順序
11.9 Flexbox
DOM structure
library(DiagrammeR)
mermaid("
graph LR
A[flex-container]-->B[All 'direct' children become flex,<br>aka flex items]
"
)11.9.1 Default of flex items
Items display in a row (the flex-direction property’s default is row).
The items start from the start edge of the main axis (即左到右).
The items do not stretch on the main dimension, but can shrink (不會水平填滿flex container).
The items will stretch to fill the size of the cross axis (但會垂直填滿flex container).
The flex-basis property is set to auto (flex item有設大小時以其為主,否則以flex item的’內容’決定所需大小).
The flex-wrap property is set to nowrap (水平填滿時會自動縮小).