11.1 Medical Imaging
This is a non-invasive of internal organs, tissues, and other Biological tissues that can be done in two or three dimensions.
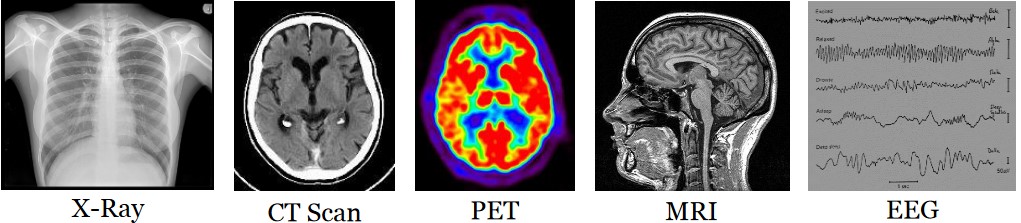
Figure 11.1: Different Kinds of Medical Images
Medical imaging is typically done in medical settings for medical interventions and visual representations of organ and tissue functions.
11.1.1 Imaging Types
There are two kinds of imaging types:
Anatomical
This can be used to assess damage to an organ.
Functional
This can be used to assess conditions (e.g., lesions, cognitions, metabolic diseases).
In an image, intensity and color can be used to capture information about the physical parameters. Intensity or color changes allow for detection, localization, and the characterization of the anatomy or the function in the image.
In a 3D display, intensities are shown in a 3D space.
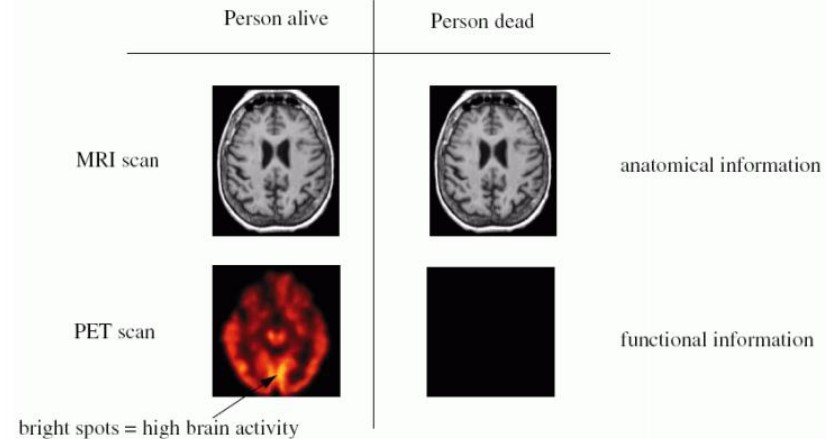
Figure 11.2: Anatomical versus Functional Imaging
In the above example, an MRI scan can indicate that somebody has a brain. A PET scan can show somebody using it.
11.1.2 Imaging Components and Terms
There are five major components:
- The patient
- Imaging system
- System operator
- The image itself
- The observer
Image quality is a combination of at least five different factors:
Contrast
This refers to different shades of gray, light intensities, and colors.
Blur
This reduces the contrast and the visibility of small objects.
Noise
This is the random variation of brightness and color information in images.
Artifact
This creates image features that don’t represent a body structure.
Distortion
This may yield inaccurate impressions of an image’s size, shape, and relative positions.
Sensitivity and Specificity
This illustrates true and false positives.
ROC Curve
This represents the relationship between sensitivity and specificity.
Principle of Resolution
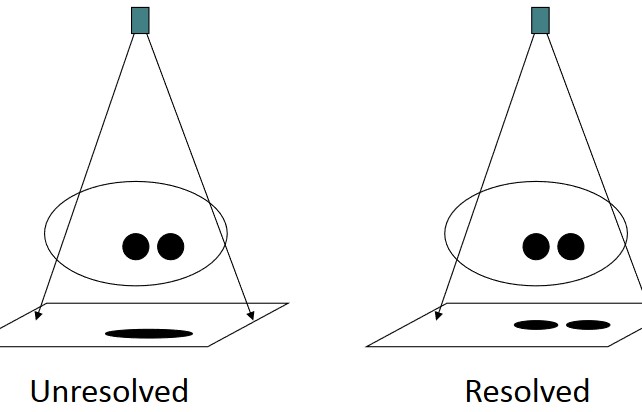
Figure 11.3: Resolution Illustrated
This is the ability to discern two points that are close to one another.
Principle of Contrast
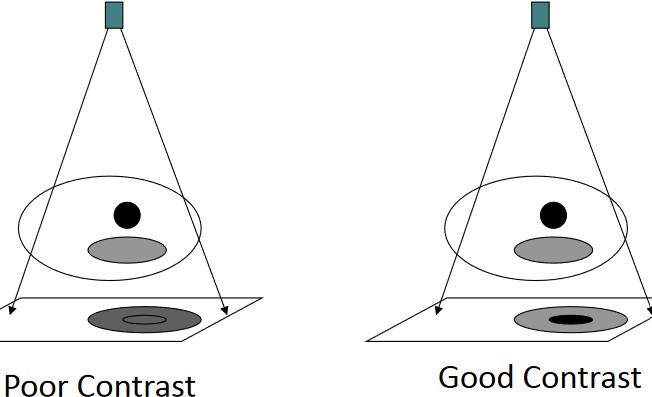
Figure 11.4: Contrast Illustrated
This is the ability to discern objects from noise or other tissues.