Chapter 9 Advanced Regression and Nonparametric Approaches
9.1 Ridge and Lasso Regression
The lm.ridge() and command, in the MASS package, can be used to fit a ridge regression model.
We first need to standardize each quantitative variable. This is done using the scale() command in R.
Train_sc <- Train %>% mutate_if(is.numeric, scale)9.1.1 Fitting a Ridge Regression Model
We can perform ridge regression using the lm.ridge() command in the MASS package.
library(MASS)M_Ridge1 <- lm.ridge(data=Train_sc, price~., lambda = 1)
head(M_Ridge1$coef)## id property_typeCondominium property_typeHouse
## 0.036320094 -0.013032610 -0.006899487
## property_typeTownhouse property_typeOther room_typePrivate room
## -0.018020782 0.058907892 -0.2880914849.1.2 Cross Validation with Ridge
We perform cross-validation to determine the optimal value of \(\lambda\). The command 10^seq(-3, 3, length = 100) defines values between 0 and 1000 for \(\lambda\), which will be tested in cross-validation.
This requires the glmnet package.
library(glmnet)control = trainControl("repeatedcv", number = 5, repeats=5)
l_vals = 10^seq(-3, 3, length = 100)
set.seed(11162020)
AirBnB_ridge <- train(price ~., data = Train_sc, method = "glmnet", trControl=control ,
tuneGrid=expand.grid(alpha=0, lambda=l_vals))Identify the optimal \(\lambda\).
AirBnB_ridge$bestTune$lambda## [1] 0.4641589Plot of RMSPE for each value of \(\lambda\).
lambda <- AirBnB_ridge$results$lambda
RMSPE <- AirBnB_ridge$results$RMSE
ggplot(data=data.frame(lambda, RMSPE), aes(x=lambda, y=RMSPE))+
geom_line() + xlim(c(0,2)) + ylim(c(0.75, 0.82)) +
ggtitle("Ridge Regression Cross Validation Results")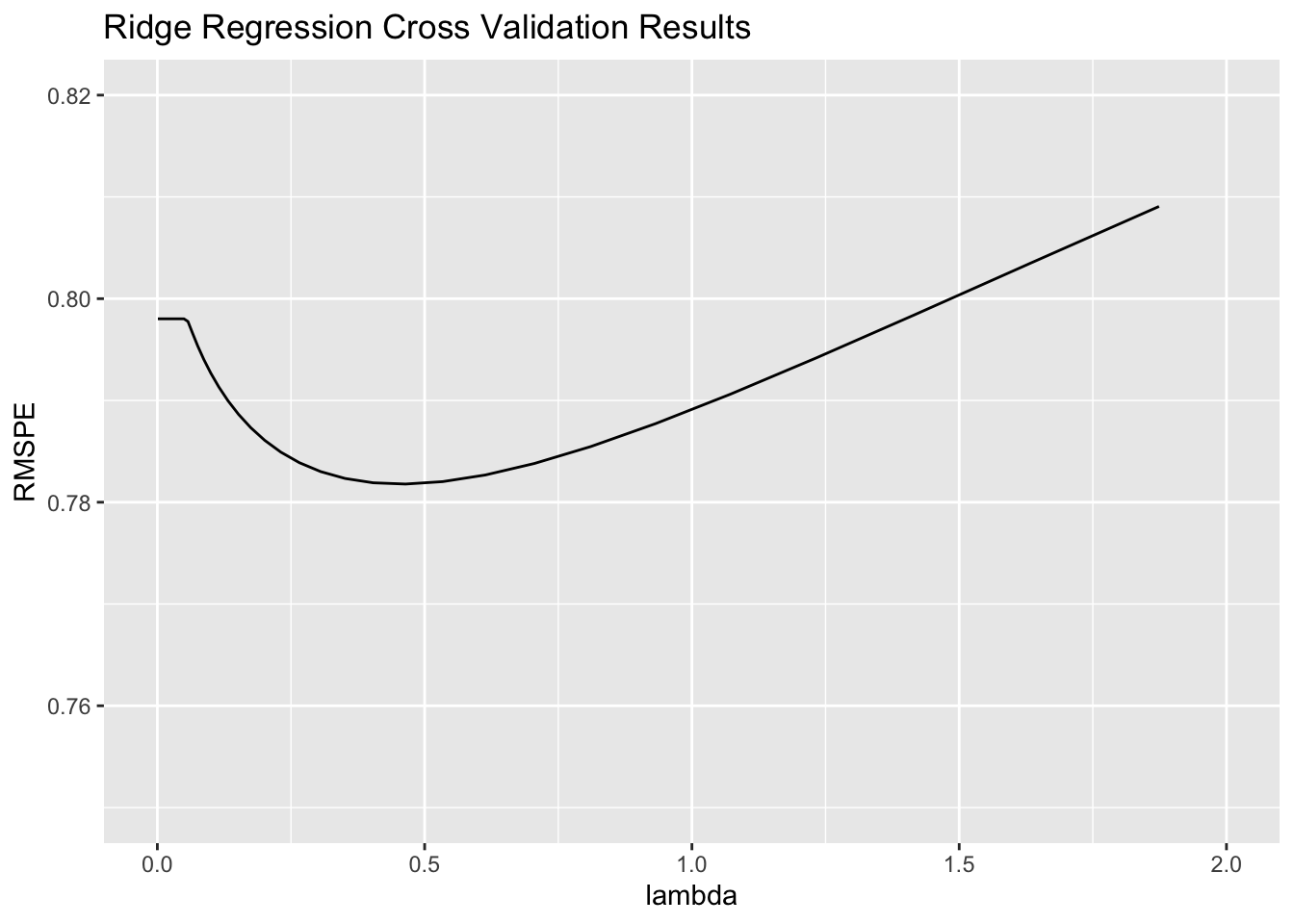
9.1.3 Cross-validation with Lasso Regression
For lasso regression, set alpha=1.
control = trainControl("repeatedcv", number = 5, repeats=5)
l_vals = 10^seq(-3, 3, length = 100)
set.seed(11162020)
AirBnB_lasso <- train(price ~., data = Train_sc, method = "glmnet", trControl=control ,
tuneGrid=expand.grid(alpha=1, lambda=l_vals))Identify the optimal \(\lambda\).
AirBnB_lasso$bestTune$lambda## [1] 0.04977024Plot of RMSPE for each value of \(\lambda\).
lambda <- AirBnB_lasso$results$lambda
RMSPE <- AirBnB_lasso$results$RMSE
ggplot(data=data.frame(lambda, RMSPE), aes(x=lambda, y=RMSPE))+geom_line() +
xlim(c(0,0.2)) + ylim(c(0.75, 0.82)) +
ggtitle("Lasso Regression Cross Validation Results")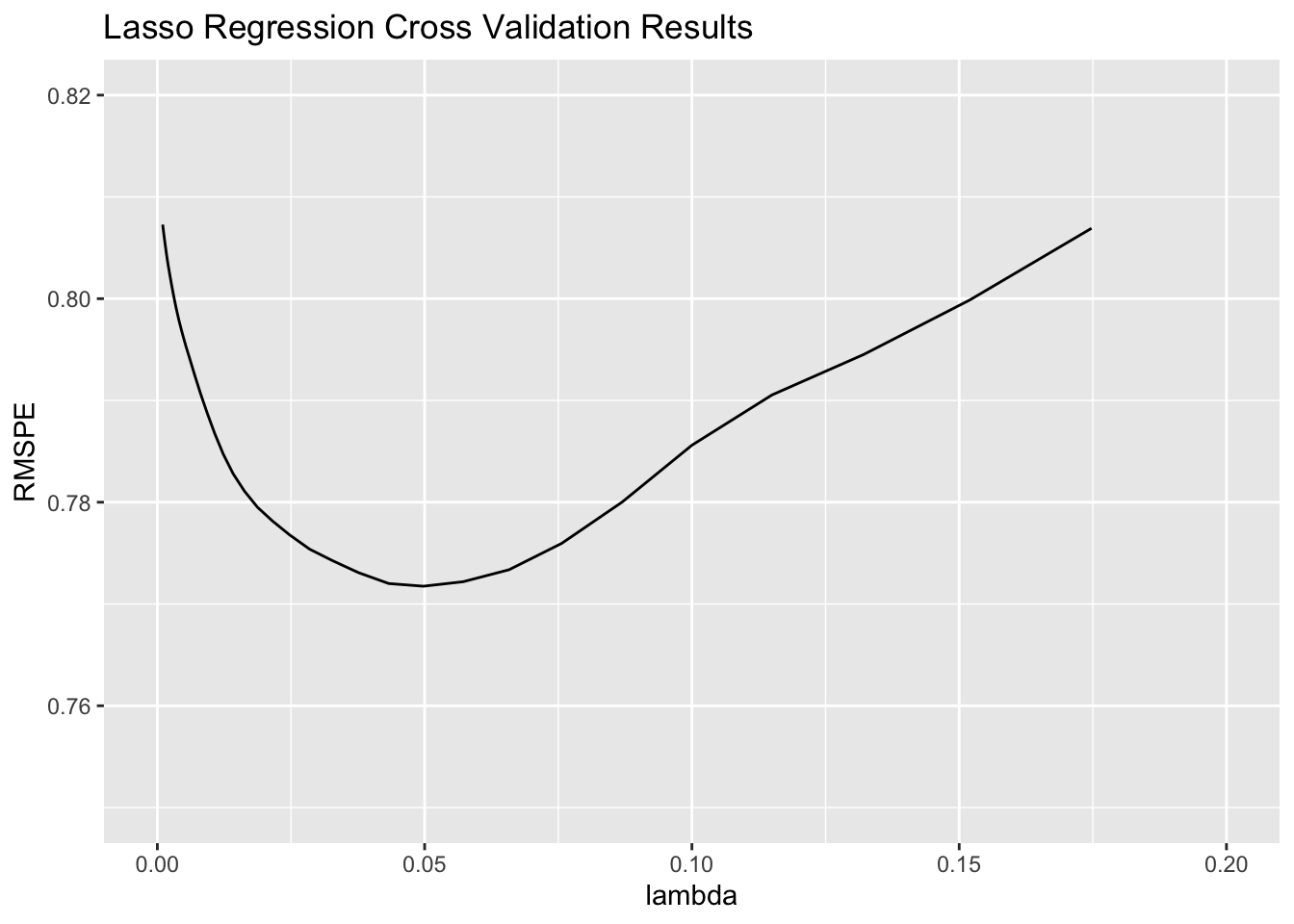
9.2 Decision Trees
We use the rpart package to grow trees, and the rpart.plot package to visualize them.
library(rpart)
library(rpart.plot)The cp parameter is a complexity parameter that determines the depth of the tree. The smaller the value of cp, the deeper the tree.
9.2.1 Decision Tree Example
tree <- rpart(price~., data=Train, cp=0.02)
rpart.plot(tree, box.palette="RdBu", shadow.col="gray", nn=TRUE, cex=1, extra=1)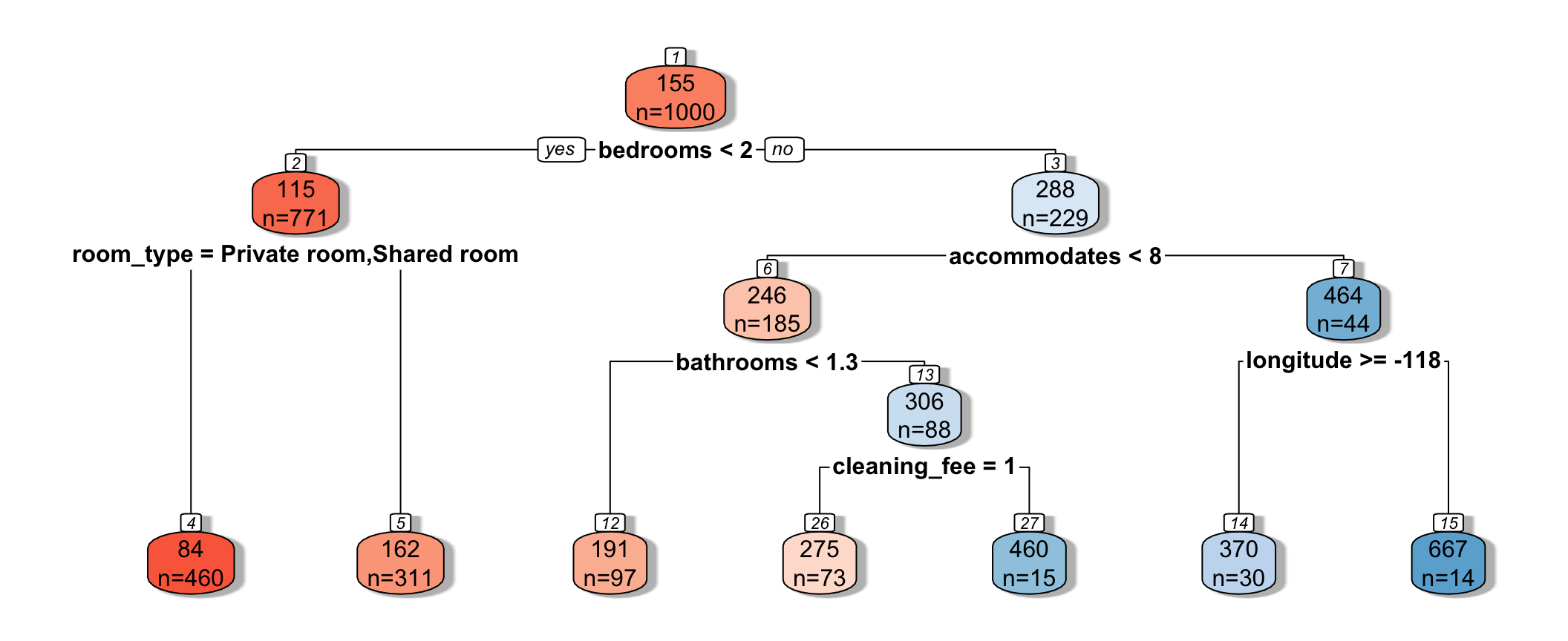
We can use cross-validation to determine the optimal value of cp.
cp_vals = 10^seq(-3, 3, length = 100)
set.seed(11162020)
AirBnB_Tree <- train(data=Train_sc, price ~ ., method="rpart", trControl=control,
tuneGrid=expand.grid(cp=cp_vals))
AirBnB_Tree$bestTune## cp
## 13 0.005336699