3 Experimental Design of BOLD fMRI
實驗設計的目標:操弄受試者的經驗或行為,使其產生特定功能的神經血管反應(functionally specific neurovascular response)。
我們可以操弄什麼?
所呈現的刺激的性質。
所呈現的刺激的時點。
給受試者的指導語。
3.1 實驗設計的類型
3.1.1 Simple Subtraction
- 例如讓受試者看手抓握和手放鬆的影片,並要求受試者照著影片的動作進行。比較 motion block 與 control block 的差別。
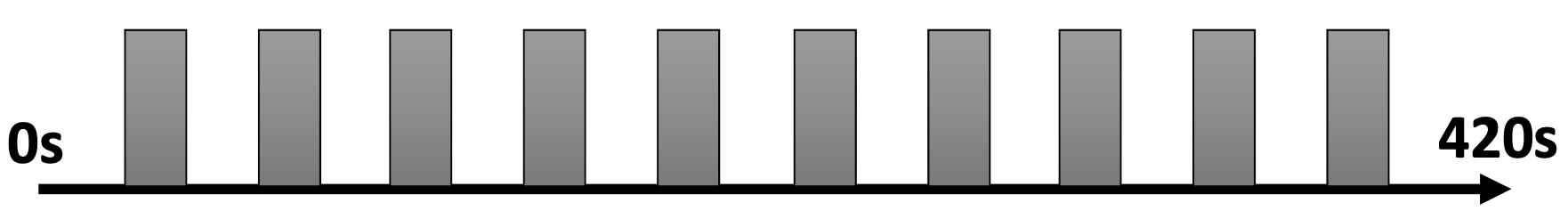
Figure 3.1: Block design. 10 個 task blocks,各 20 秒,其間與前後有 rest interval 20 秒,共 420 秒。
3.1.2 Categorical Design
- 目標:在各種刺激類型之間比較大腦的活動。
- Example.
刺激為視覺呈現 12 個名詞;作業內容為判斷何者是生命體,何者不是。
但要注意的是,此實驗設計建立在一個很強的假設,即 pure insertion 下。必須滿足這個假設,我們才能使用 cognitive subtraction 來進行因果推論。此假設描述的是在複雜的心理歷程的腦機制只是較簡單的心理歷程的腦機制再加上另一些機制,如圖 3.2。2
- Aim.
了解單一歷程(如認臉)之下的神經結構。
- Procedure.
有 \(Y\) 的作業 \(-\) 沒有 \(Y\) 的作業(控制組)\(=Y\)。
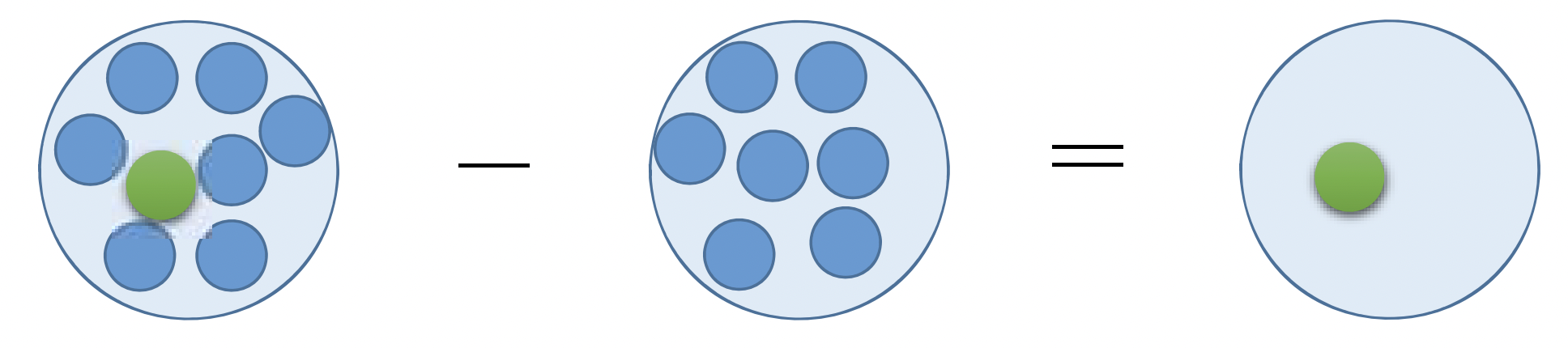
Figure 3.2: Categorical design 的概念。
另一個例子。如果圖 3.3 是 target face,那圖 3.4 哪一個是適合的控制刺激(control stimulus)?
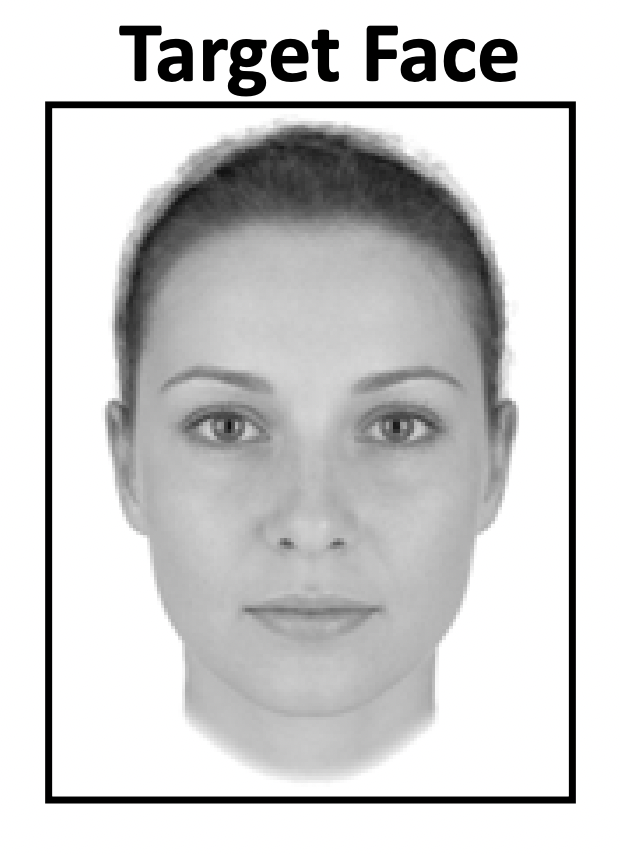

Figure 3.3: Target face.
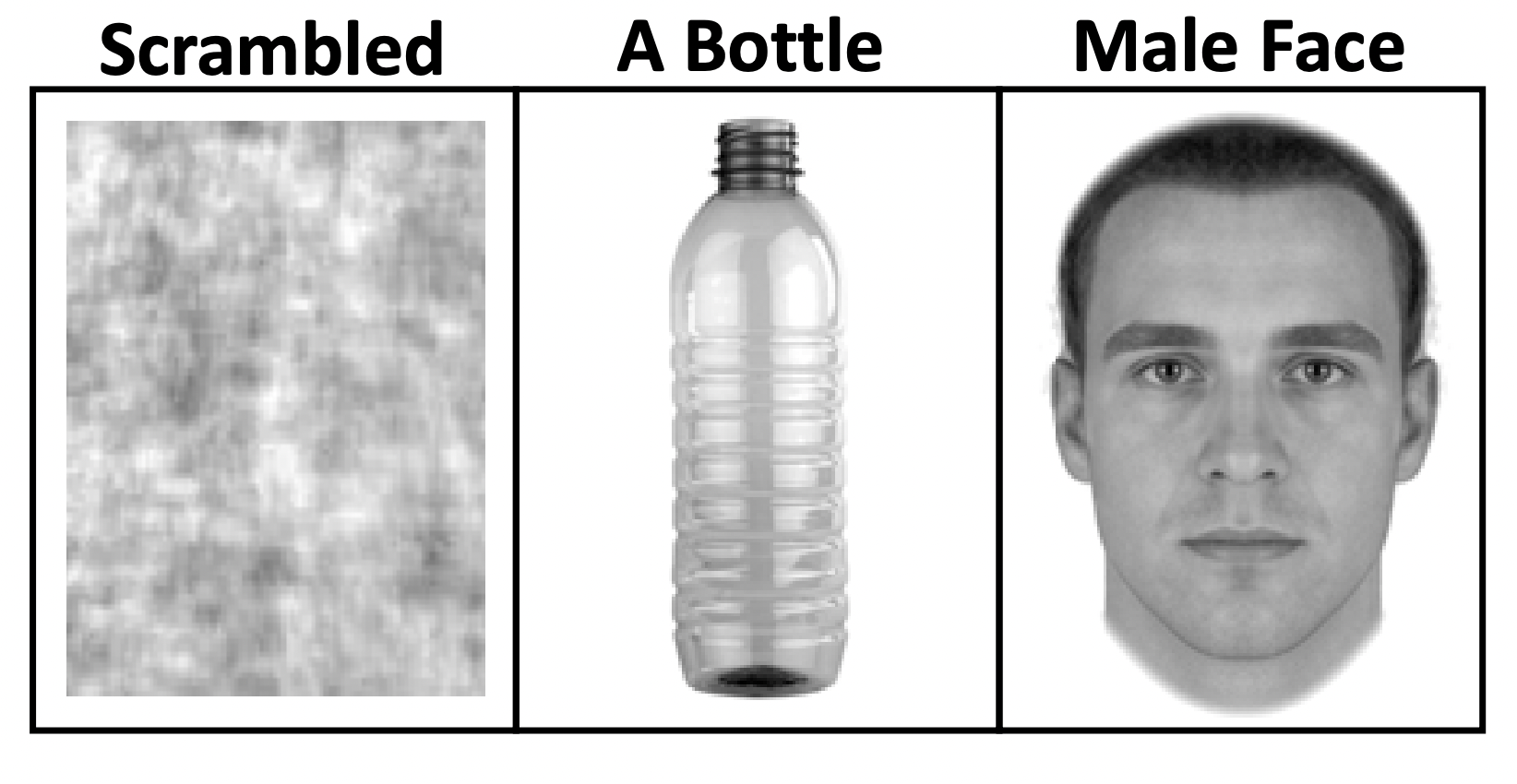
Figure 3.4: 哪一個是適合的控制刺激?
圖 3.4 中,左一的組成成分長得與人臉太不一樣了,只是一團混沌;但右一又太像了,只有性別不同。事實上,在此例中,水瓶才是最適合的。
3.1.3 Factorial Design
Factorial Design 即在一個作業中,結合兩個或以上的因素,然後觀察一項因素對另一個因素的反應,如表 3.1。此設計也不需要 pure insertion 的假設。
| Viewing | Naming | |
| Gray-level | (Gray-level, Viewing) | (Gray-level, Naming) |
| Color | (Color, Viewing) | (Color, Naming) |
那麼,此作業的 main effect 呢?
Main effect of task: \(\rm [(G, V)+ (C, V)] – [(G, N) + (C, N)]\)
Main effect of stimuli: \(\rm [(G, V) + (G, N)] – [(C,V) + C, N]\)
3.1.4 Parametric Design
Parametric Design 比較像 categorical design,而不像較複雜的 factorial design。其與 categorical design 的差異之處在後者所測量的是類別的連續變數,前者是連續的。如圖 3.5,我們可以計算腦活動與反應時間之間的相關性。
Figure 3.5: Parametric design. 三種不同認知負擔的作業,受試者的反應時間將會不同。
3.2 刺激時點設計
刺激時點設計(stimulus timing design)有兩種,分別是:
Block design:結合一連串的 trials 的 BOLD responses。
Event‐related (ER) design:透過單一的事件得到 BOLD response。
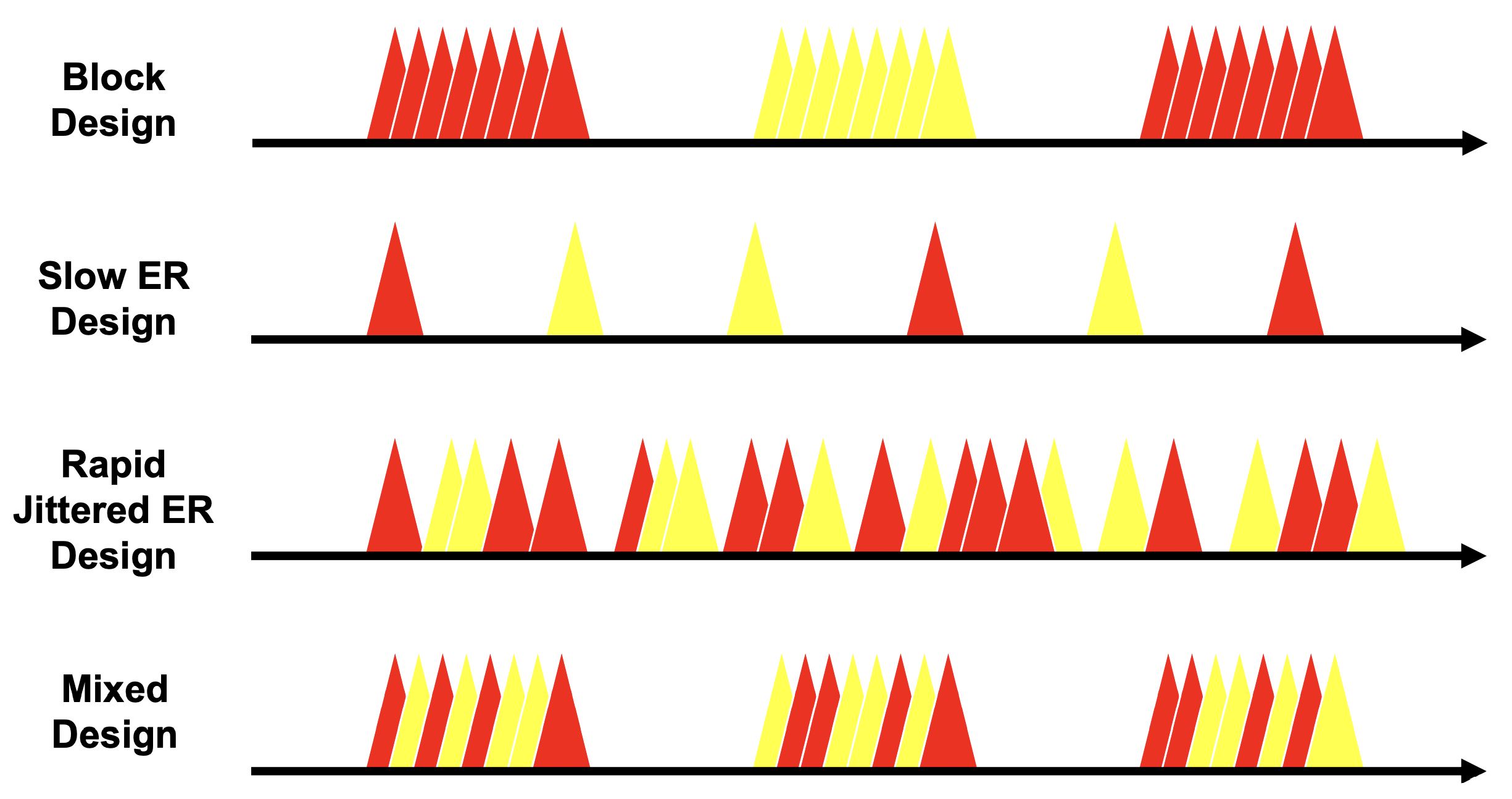
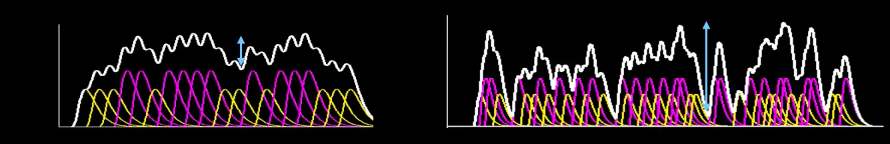
Figure 3.6: 不同時點的實驗設計,其中紅色代表一種 trial,黃色代表另一種。
3.2.1 Block Design
在 block design 中,分成 task blocks(呈現約 15–30 秒),其中有 rest blocks。掃描的次數在所有條件(例如左手、右手)下都要相當。每個 block 的時間不能太長,否則會造成 BOLD signal 與 low-frequency noise 相關,一般都是設計成 20 秒左右。但如果太短也不行,還沒回到 baseline 就接下一個 block 的話也會產生偏誤。
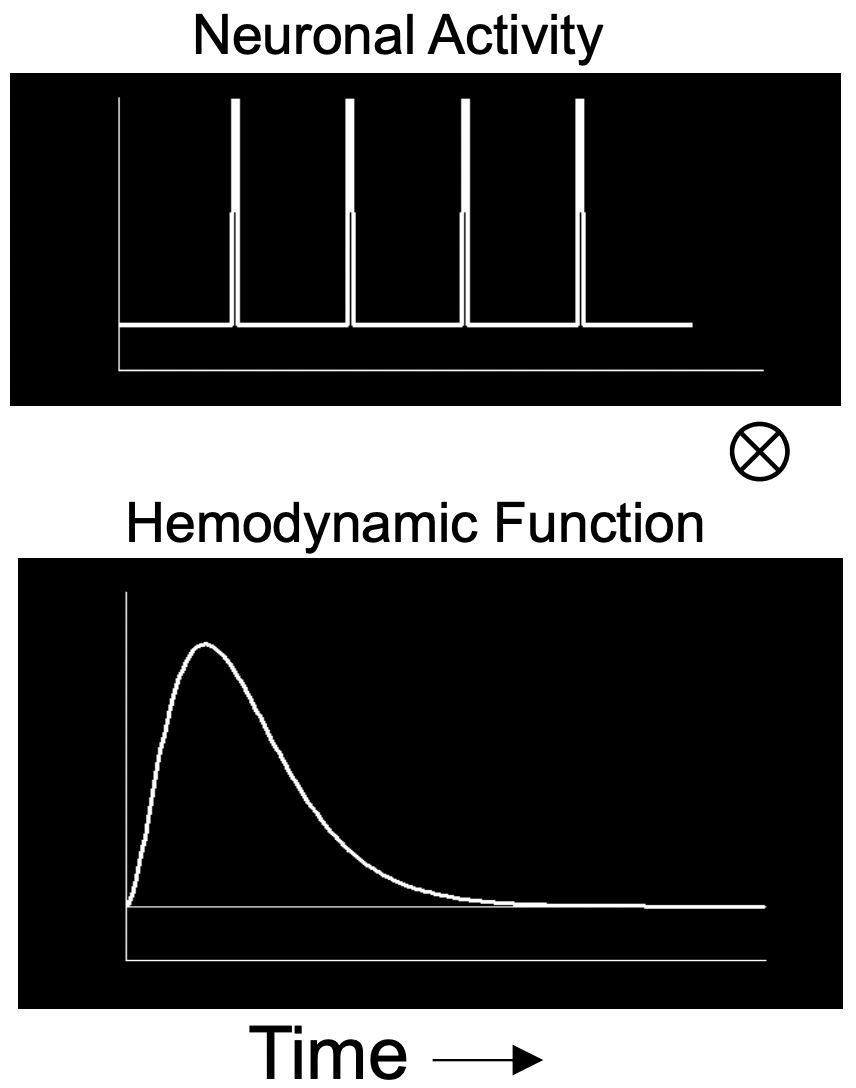
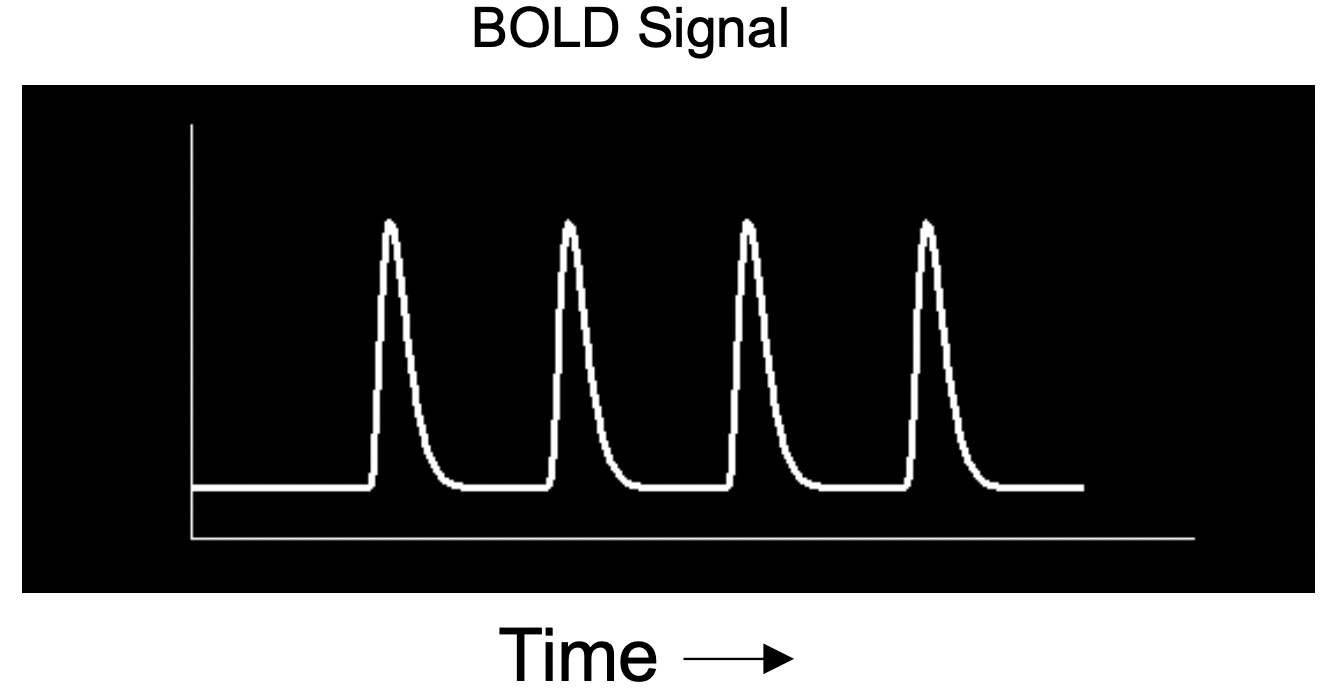
在 block design 中,會有所謂 box-car function,即在 no-task 時是 0,而在 task 時是 1,如圖 3.7A。但其實真實的 hemodynamic (BOLD) changes 不像這樣活動,事實上是像 3.7B,所以我們要以 HRF 與 box-car function convolve。
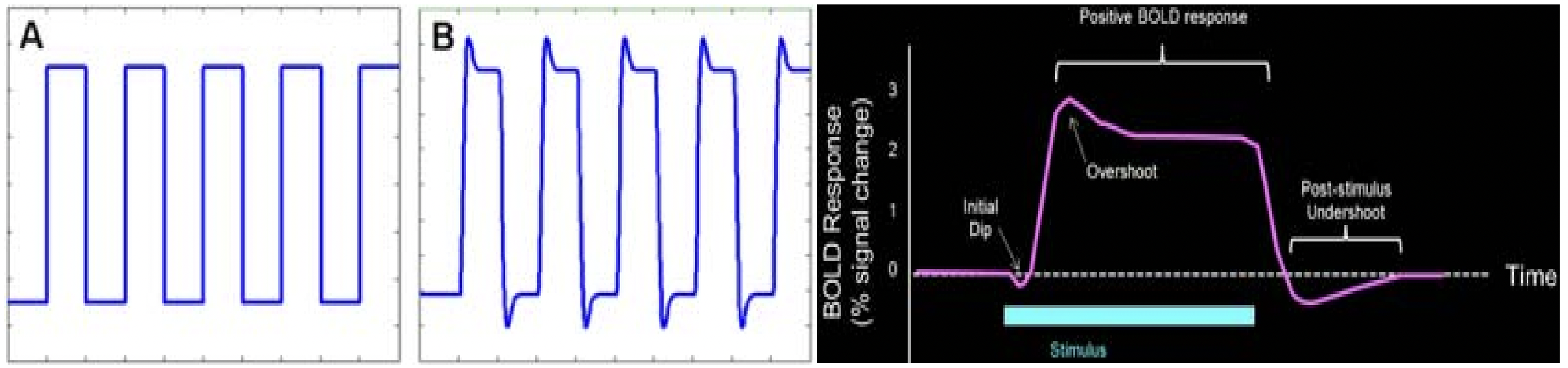
Figure 3.7: Block design. 圖源:Matthijs Vink, Preprocessing and analysis of functional MRI data, 2007.
Block desgin 的優點
high detection power of activated voxel/region.
在 fMRI 研究中為最廣泛使用的途徑。
accurate estimation of hemodynamic response function is not as critical as with event‐related designs.
Block desgin 的缺點
poor estimation power to differentiate the time courses in response to different conditions.
- 因為我們會把各個 block 加起來,所以如果各個時點有不同條件就不適用了。
太容易被受試者預測
- 會導致腦部活動較不活躍。
can’t look at effects of single events.
becomes unmanageable with too many conditions (e.g., more than 4 conditions + baseline).
- 因為如果每個條件都要 3–5 個 blocks,那掃描時間會變得很長。
3.3 總結:Rules of thumb
Blocked Designs.
- Powerful for detecting activation
- Useful for examining state change
Event‐Related Designs.
- Powerful for estimating time course of activity
- Allows determination of baseline activity
- Best for post hoc trial sorting
Mixed Designs.
- Best combination of detection and estimation
- Much more complicated analyses
呈現刺激的方法
要在 fMRI 實驗中呈現實驗刺激切記要使用 MRI compatible 的硬體設備,以下的硬體都會為 fMRI 特別設計:
In‐room viewing monitor/projector.3
Goggles with integrated EyeTracking cameras.
Audio system.
Response pads/grips/buttons.
Trigger/synchronization box (MR scanner \(\Leftrightarrow\) stimulus presentation software).
此外,也有一些專門設計來呈現刺激的軟體,例如 E‐prime (BIOPAC Systems) 或 Presentation (Neurobehavioral Systems)。
BOLD 與 HRF 的特性
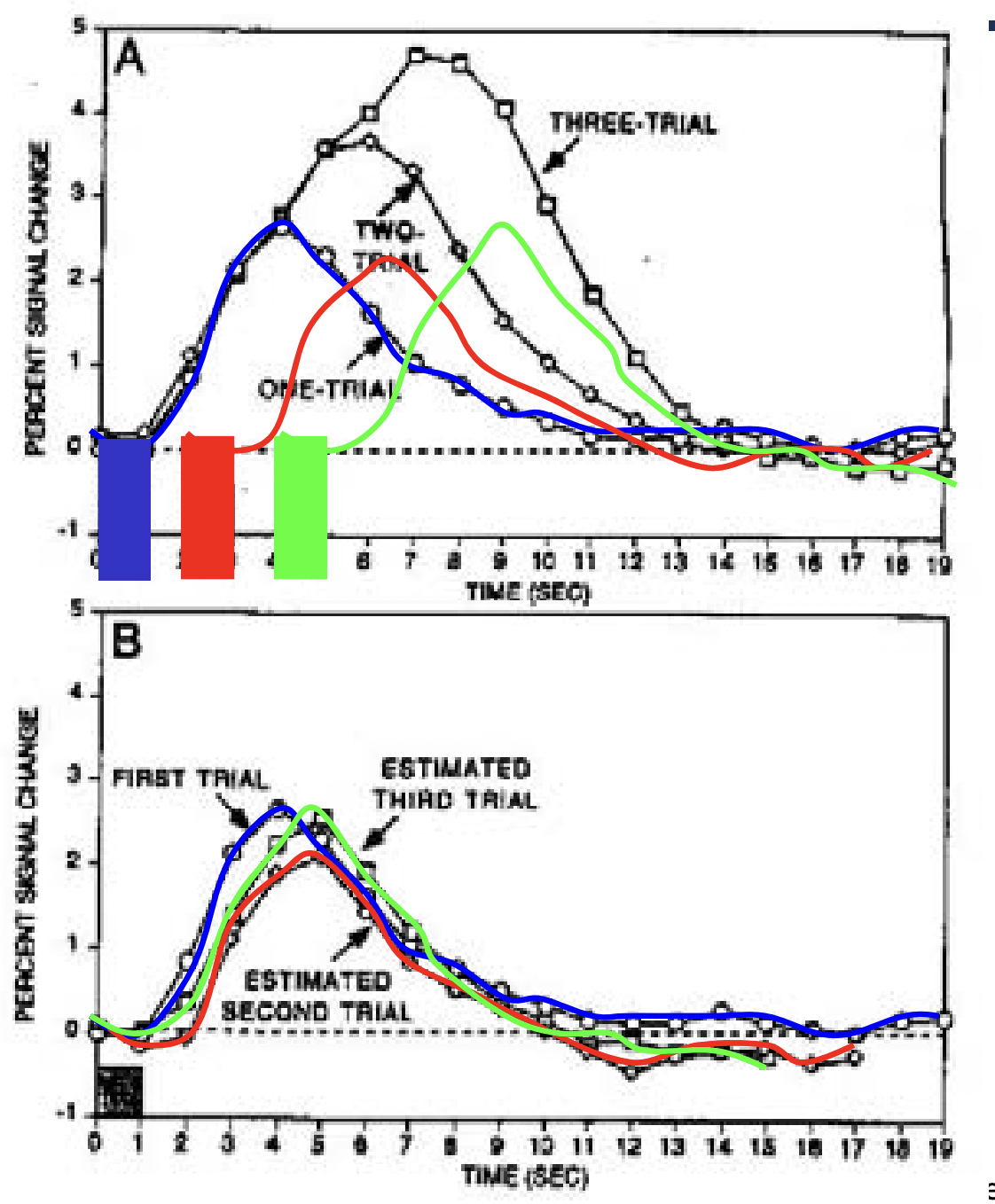
動作電位觸發與產生突觸後電位電位時間相當短。但因為平滑肌的反應需時間,所以神經活動與 BOLD signal 的產生之間有延遲。在 initial dip 大約延遲 1 秒鐘,大約 4–6 秒以後會到 peak,而回到 baseline 則大約要 20 秒。
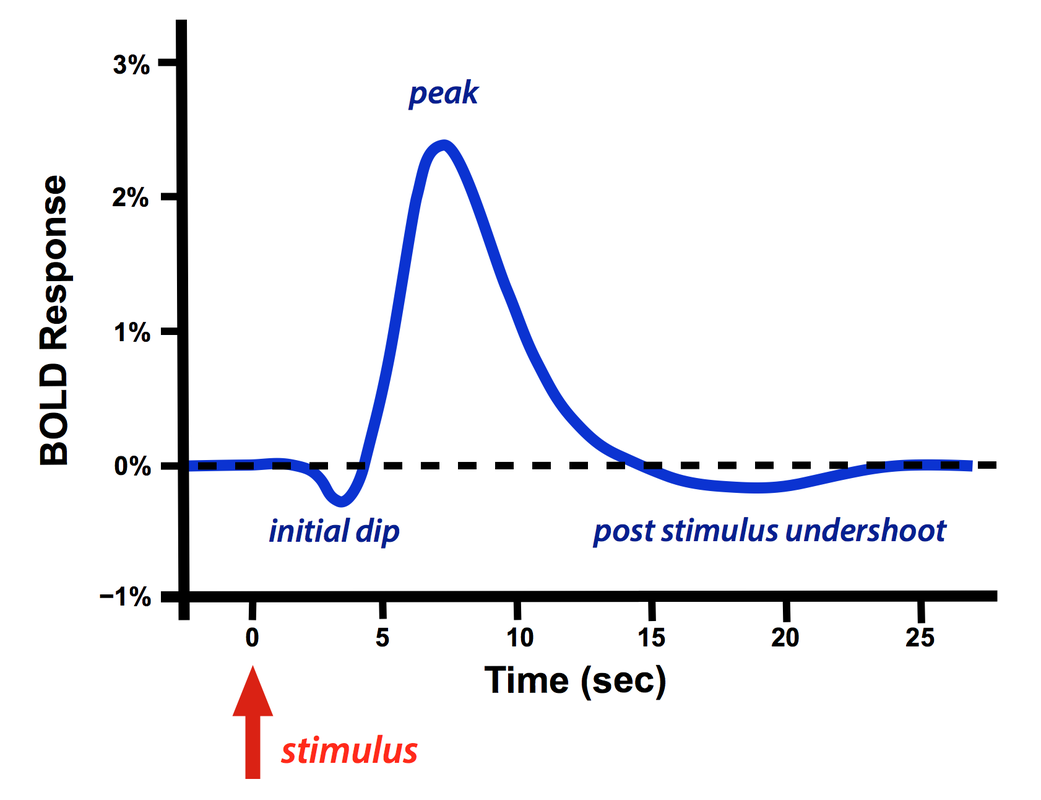
Figure 3.13: BOLD HRF 在短暫的刺激之後。圖源:http://mriquestions.com/does-boldbrain-activity.html。
要注意的是,hemodynamic response function (HRF) 的特性有 inter-region difference 與 inter-subject difference。前者即在不同腦區的差別,後者則是在不同受試者的差別。
The adaption of HRF in
The onset time (temporal derivative)
Dispersion/width of curve (dispersion derivative)
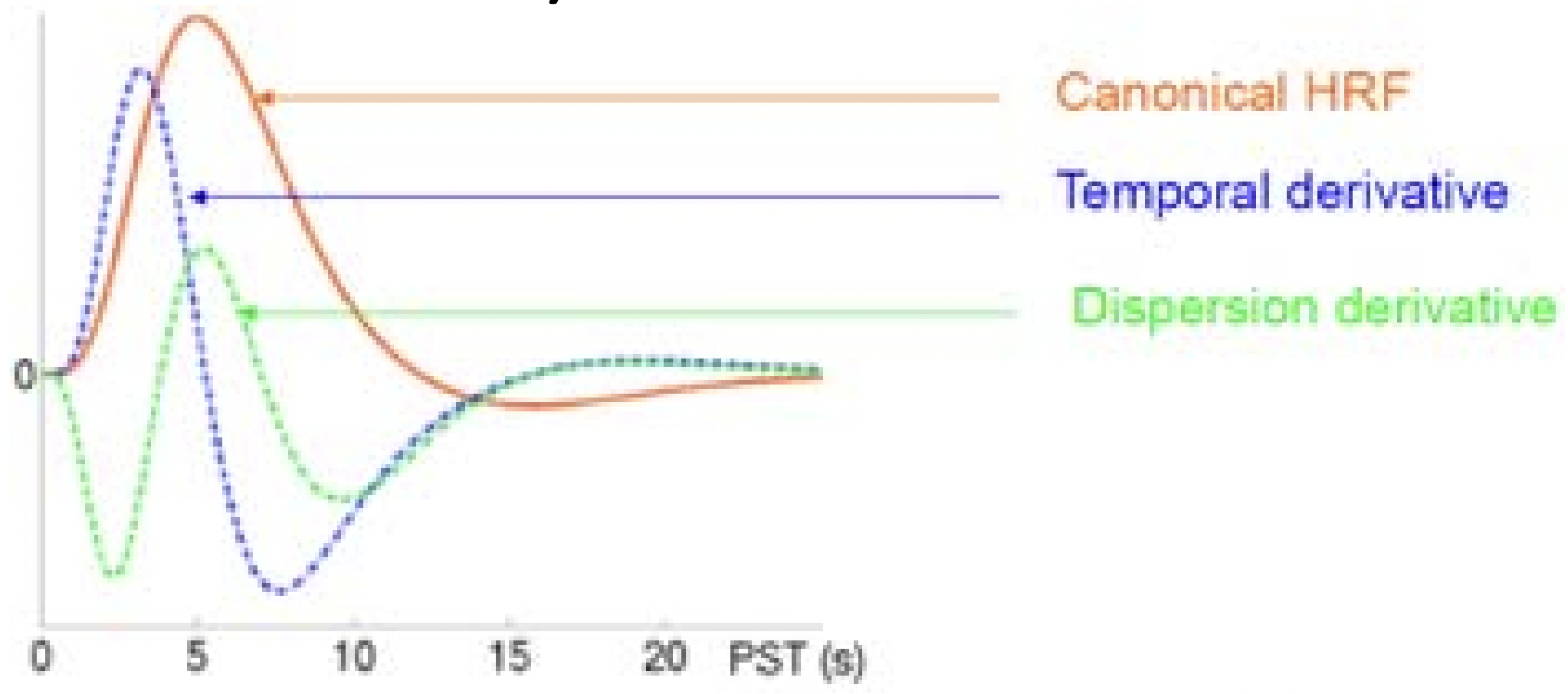
Figure 3.14: The adaption of HRF.