The ‘deep’ in deep learning
- Deep learning = subfield of machine learning
- New take on learning representations from data that puts an emphasis on learning successive layers of increasingly meaningful representations
- “deep” stands for this idea of successive layers of representations
- Depth of model = how many layers contribute to a model of the data
- Modern deep learning often involves tens or even hundreds of successive layers of representations (all learned automatically from exposure to training data)
- Layered representations are (almost always) learned via models called neural networks (structured in literal layers stacked on top of each other)
- “Neural network”: Reference to neurobiology as central DL concepts inspired by inspiration from understanding brain (BUT no evidence that brain implements mechanisms used in DL!)
- Deep learning is a mathematical framework for learning representations from data
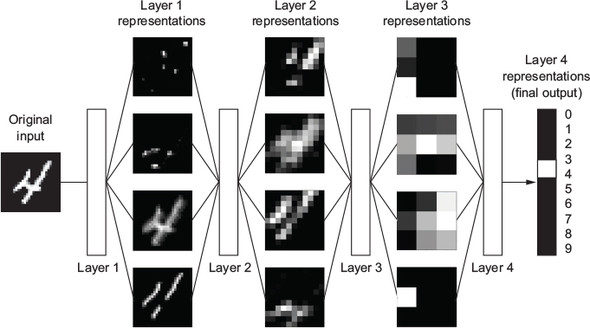
- What do the representations learned by a deep-learning algorithm look like? Let’s examine how a network several layers deep (see figure 1.5) transforms an image of a digit in order to recognize what digit it is.
- Below: Network transforms the digit image into representations that are increasingly different from the original image and increasingly informative about the final result
- Deep network = multistage information-distillation operation, where information goes through successive filters and comes out increasingly purified (that is, useful with regard to some task)
- Deep learning (technically): a multistage way to learn data representations
- Simple idea but very simple mechanisms, sufficiently scaled, can end up looking like magic