4.1 Sample regression line
- Let consider an hypothetical example where linear dependence between consumption and income on weekly basis is analyzed in a population of \(60\) households. Households are divided into \(10\) groups with the same level of income as presented in table 4.1.
| Income (\(X\)) | \(E(Y\)|\(X)\) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 65 | ||
| 100 | 65 | 70 | 74 | 80 | 85 | 88 | 77 | |
| 120 | 79 | 84 | 90 | 94 | 98 | 89 | ||
| 140 | 80 | 93 | 95 | 103 | 108 | 113 | 115 | 101 |
| 160 | 102 | 107 | 110 | 116 | 118 | 125 | 113 | |
| 180 | 110 | 115 | 120 | 130 | 135 | 140 | 125 | |
| 200 | 120 | 136 | 140 | 144 | 145 | 137 | ||
| 220 | 135 | 137 | 140 | 152 | 157 | 160 | 162 | 149 |
| 240 | 137 | 145 | 155 | 165 | 175 | 189 | 161 | |
| 260 | 150 | 152 | 175 | 178 | 180 | 185 | 191 | 173 |
- An average weekly consumption is given by the income level, i.e. the conditional mean (we often say conditional expectation) is a linear function of variable \(X\)
\[\begin{equation} E(Y|X)=\beta_0+\beta_1X \tag{4.2} \end{equation}\]
\[\begin{align} 65&=\beta_0+\beta_1 80 \\ 77&=\beta_0+\beta_1 100 \\ ~~~~~~~\vdots \\ 173&=\beta_0+\beta_1 260 \\ \tag{4.3} \end{align}\]
- From any two equations of the system (4.3) it’s easy to find two population parameters
\[\begin{equation} \beta_0=17~~~~~~~~\beta_1=0.6 \end{equation}\]
- Conditional expectations are therefore easily computed for each level of income when population parameters are known
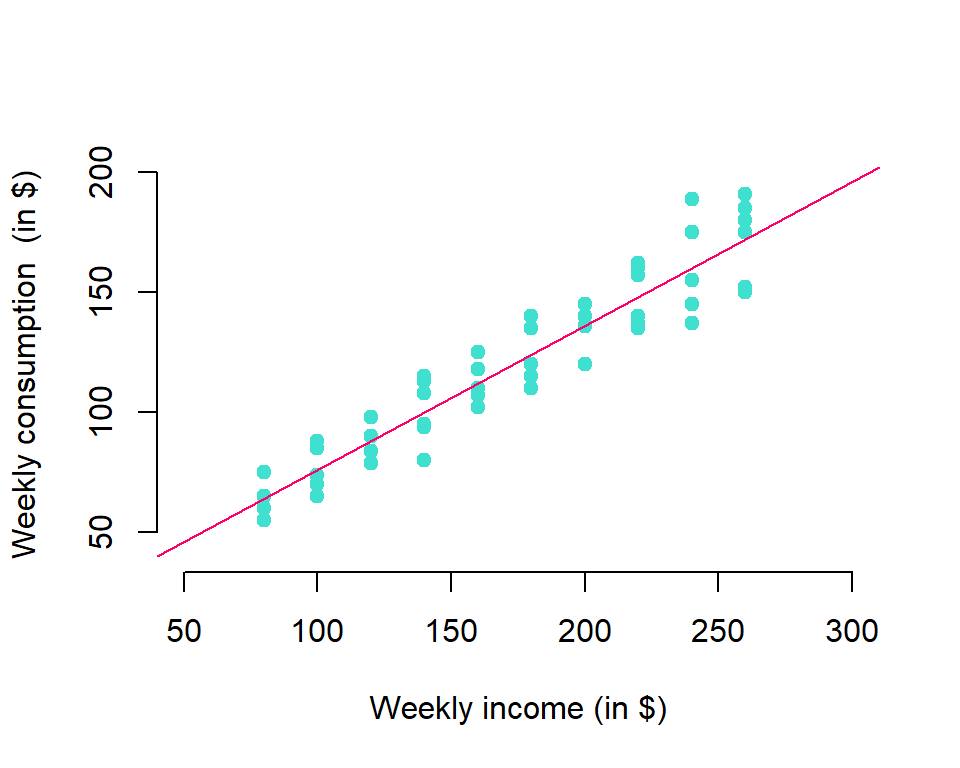
FIGURE 4.1: Population regression line
Regression line passes through the conditional expectations of variable \(Y\) for every level of income \(X\)
However, weekly consumption for every household individually \(y_i\) differs from the conditional expectation
\[\begin{equation} y_i-E(Y|x_i)=u_i \tag{4.4} \end{equation}\]
- Finally, population regression line is
\[\begin{equation} y_i=\underbrace{\beta_0+\beta_1x_i}_{E(Y|x_i)}+u_i \tag{4.5} \end{equation}\]
- Disturbances \(u_i\) are error terms which represent random variables with zero conditional mean for every level of income
\[\begin{equation} E(u|x_i)=0 \tag{4.6} \end{equation}\]
Condition (4.6) indicates that variable \(X\) does not give us any information about error term \(u\), i.e. variables \(X\) and \(u\) are independent
Population is often finite but unknown or infinite, so the error terms \(u_i\) are also uknown as well as parameters \(\beta_0\) and \(\beta_1\)
Parameters and error terms can be estimated from the sample and thus a sample regression line is
\[\begin{equation} y_i=\underbrace{\hat{\beta}_0+\hat{\beta}_1 x_i}_{\hat{y}_i}+\hat{u}_i \tag{4.7} \end{equation}\]
- Different random samples can be chosen when selecting one household from each group of income level
|
|
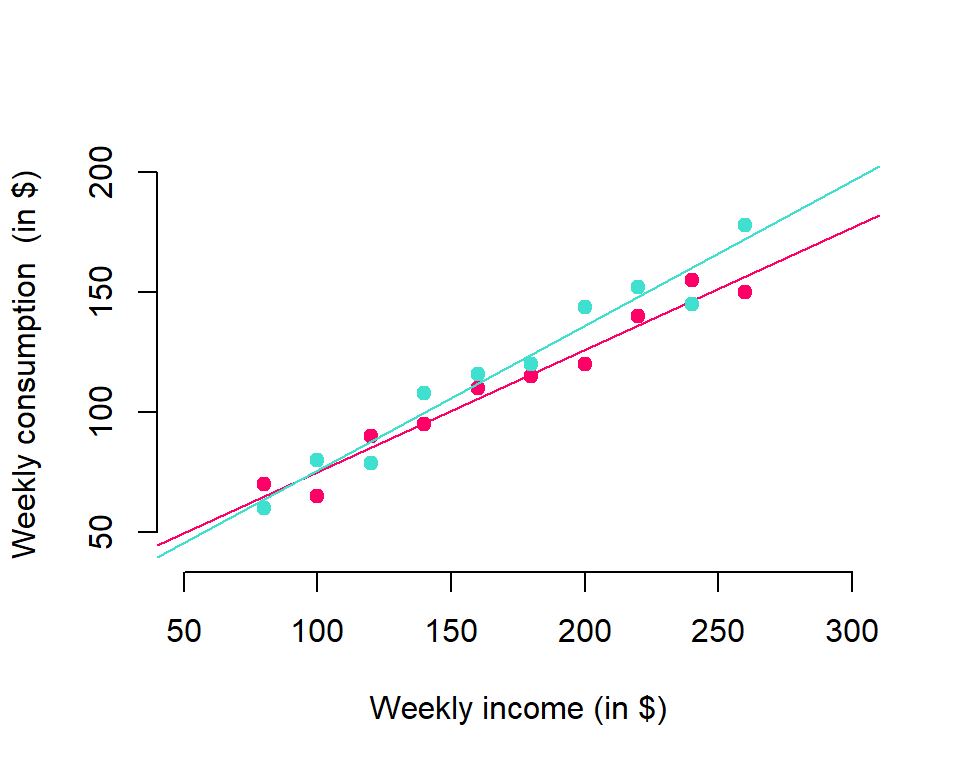
FIGURE 4.2: Two sample regression lines
Selection of simple random sample requires that error terms are identically distributed (with zero mean and constant variance) and independently distributed (zero covariances)
Estimated error terms are called residuals and usually denoted as \(\hat{u}_i\)
One residual is the difference between the actual value \(y_i\) observed from the sample and the fitted or estimated value \(\hat{y}_i\) on regression line