3 Selecting the unit of analysis and defining “Multi-domain”
This tab is dedicated to defining “multi-domain” terms and confirming the unit of analysis for your dataset. It encompasses the process of data cleaning for intervention and outcome codes, along with the creation of “multi-domain” categories based on EGM custom coding. Subsequent sections will guide you through cleaning EGM custom data and establishing “multi-domain” groupings.
3.1 Essential Considerations for This Application
In the process of synthesizing evidence while using this application, two critical factors determine the unit of analysis and the categorization of multi-domain interventions.
3.1.1 Unit of analysis
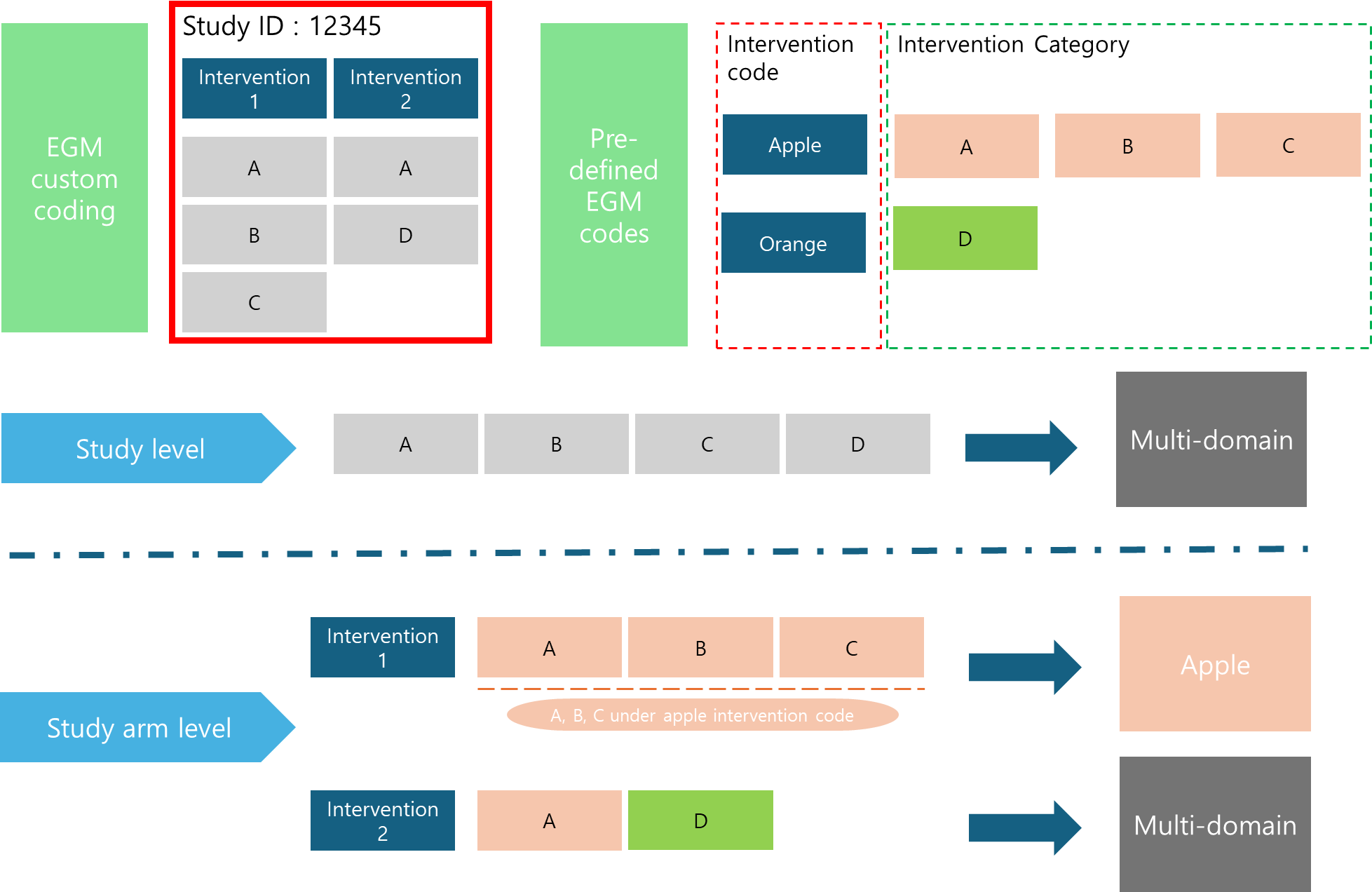
A pivotal aspect is deciding whether the synthesis will be conducted at the study level or the study arm level. At the study level, all interventions and inputs are pooled together. A study is designated as “multi-domain” if it encompasses multiple interventions, irrespective of intervention arms. This approach results in the number of interventions equating to the number of studies.
Conversely, at the study arm level, each treatment arm is treated as a distinct entity, which typically leads to a higher count of interventions compared to the number of studies. The decision-making process for categorizing each intervention is illustrated below. For example, the first intervention is categorized under the “Apple” intervention after components A, B, and C are all found to belong to subcategories within the Apple intervention group. The second intervention, combining elements A and D from different intervention groups (Apple and Orange, respectively), is coded as “Multi-domain.” This classification is made by examining the most specific codes to determine if they fall under the same overarching intervention category.
📝 Note - Order of Interventions and Their Impact
The sequence in which interventions are listed does not influence the categorization process. For instance, with intervention 2, whether listed as A, D, or D, A, does not affect the outcome.
3.1.2 “Multi-domain” in the Pre-defined EGM Coding
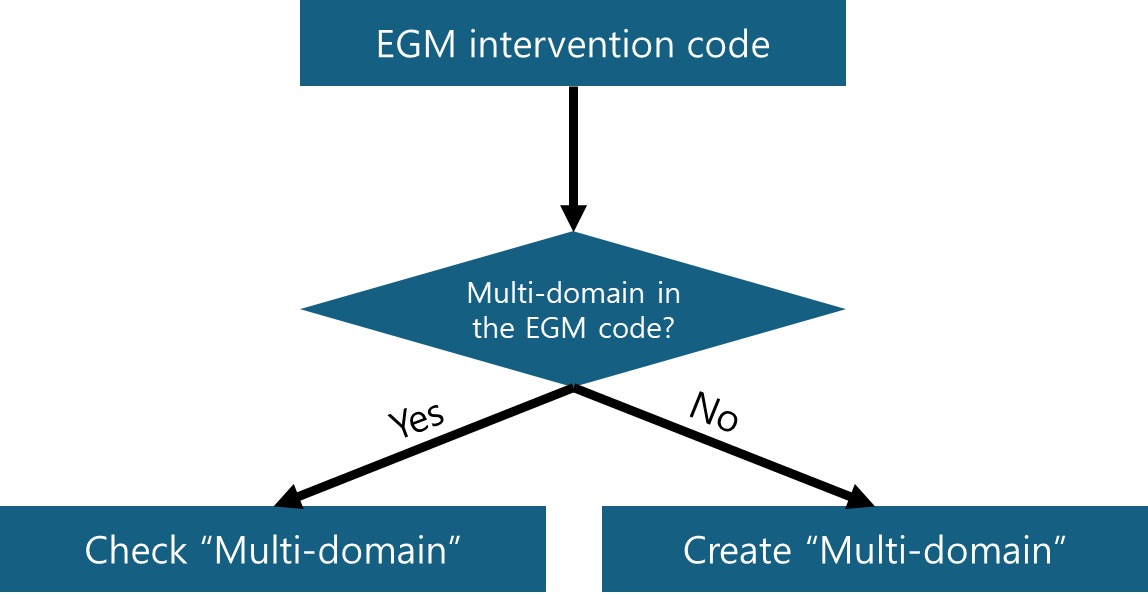
During the data cleaning process, a primary consideration is whether the pre-defined EGM codes include an option for ‘multi-domain’. If absent, ‘multi-domain’ should be incorporated into the EGM coding map (see Chapter 1 1.2 Data Quality Assessment (Part A) for details). Two scenarios often necessitate data cleaning, especially when the study arm level analysis is selected:
In the one scenario, even though ‘multi-domain’ is a selectable EGM code, there may be instances where coders list two separate interventions without opting for the ‘multi-domain’ designation. In these situations, the application proactively categorizes these entries as ‘multi-domain’. This ensures consistency in ‘multi-domain’ classification, irrespective of the initial input by coders. If this is not the case, the application employs the same rule to create a multi-component classification, as demonstrated in the above figure.
📝 Note - Definition of “Multi-domain”
When various intervention categories as part of the same intervention domain, then the overarching domain determines the final categorization.
3.2 Data cleaning process
There are two steps to refine the interventions: first, remove the repeated interventions, and second, examine each intervention category for overlapping intervention domains.
3.2.1 Remove Repeated interventions
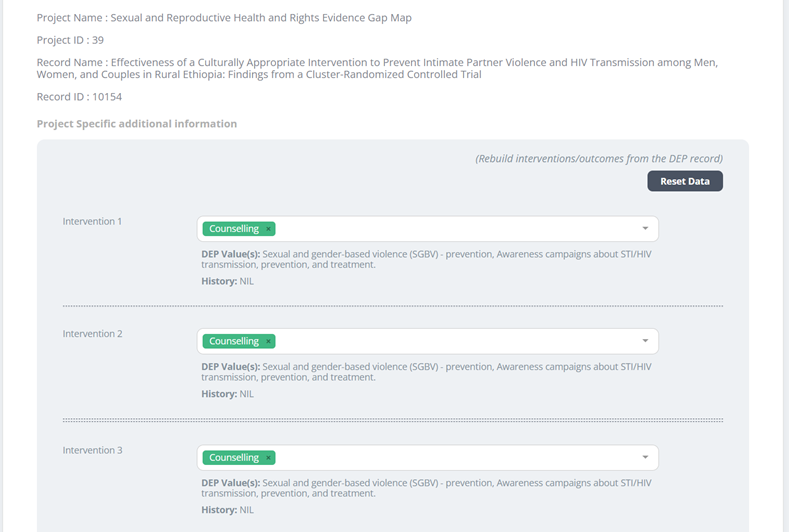
The application automatically removes any duplicated treatment arms within the data. For example, if for a particular DEP ID (10154), multiple entries of the same intervention domains are recorded, the system retains only one instance, eliminating the redundancies to streamline the dataset.
3.2.2 Remove overlapped interventions
The application consolidates interventions in study arm analyses by identifying and merging overlapping intervention domains. Despite varied combinations across arms, overlapping interventions within the same domain are unified, reducing the number of interventions for analysis.
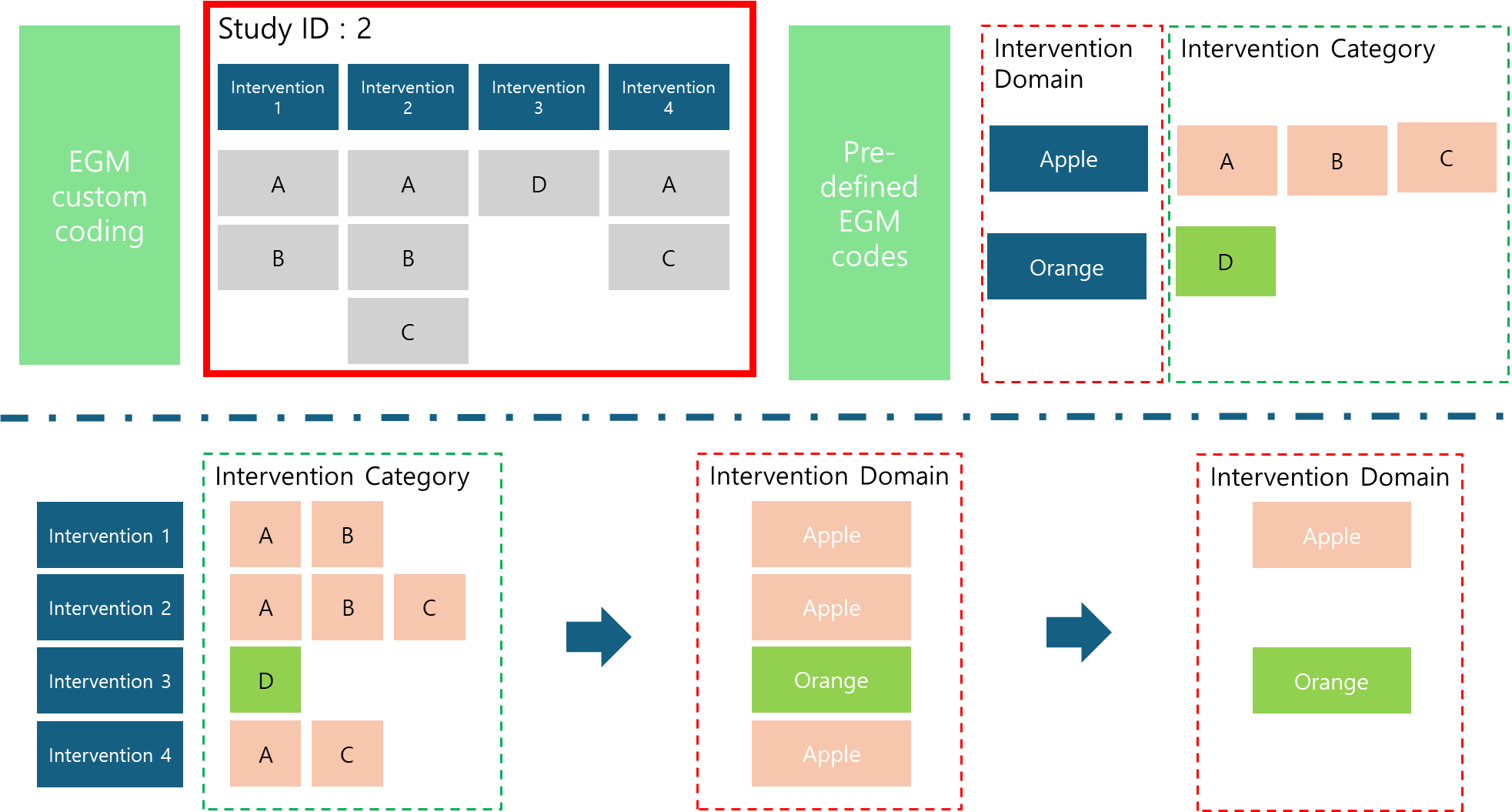
3.2.3 Multi-domain Creation
The application utilizes a standard procedure to facilitate the exporting of multi-domain classified records.
3.3 Outcome Data Cleaning Process
3.3.1 Remove the Repeated Outcome
Duplicate outcomes are removed in alignment with the cleaned intervention data. This process, including the elimination of duplicates, is detailed in the application’s right panel, which also enumerates the adjusted records.
3.4 Control Box in The Left
3.4.1 Unit of Analysis
Choose between study-level and treatment-arms-level analysis. This choice impacts all visualizations and tables due to changes in observation counts.
3.4.2 Display option
Select how to display intervention data cleaning results. Choosing ‘Intervention domain’ displays a summary by intervention level, while the alternative option presents details at the intervention category level.
3.5 Takeaways
Your choice of unit of analysis directly influences the data displayed in all graphs and tables
Multi-domains are established by eliminating duplicates and categorizing each intervention accordingly
The quality of multi-domain creation can be reviewed using the tables located on the right side of the interface.