Chapter 3 SPC-based QA: A Presentation
3.1 Paradigm
Statistical Process Control as the cornerstone of QA/QI, Peer Review, and clinical performance evaluations: focus on process management
3.1.1 What is Statistical Process Control?
“SPC stands for statistical process control. Statistical Process Control is a scientific visual method used to monitor, control and improve processes by eliminating special cause variation from manufacturing, service and financial processes.”
“Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control which employs statistical methods to monitor and control a process. This helps to ensure that the process operates efficiently, producing more specification-conforming products with less waste”
“Statistical process control (SPC) is defined as the use of statistical techniques to control a process or production method. SPC tools and procedures can help you monitor process behavior, discover issues in internal systems, and find solutions for production issues.”
3.1.2 How It Works
A control chart helps one record data and lets you see when an unusual event, such as a very high or low observation compared with “typical” process performance, occurs.
Control charts attempt to distinguish between two types of process variation:
- Common cause variation, which is intrinsic to the process and will always be present
- Special cause variation, which stems from external sources and indicates that the process is out of statistical control
- Various tests can help determine when an out-of-control event has occurred.
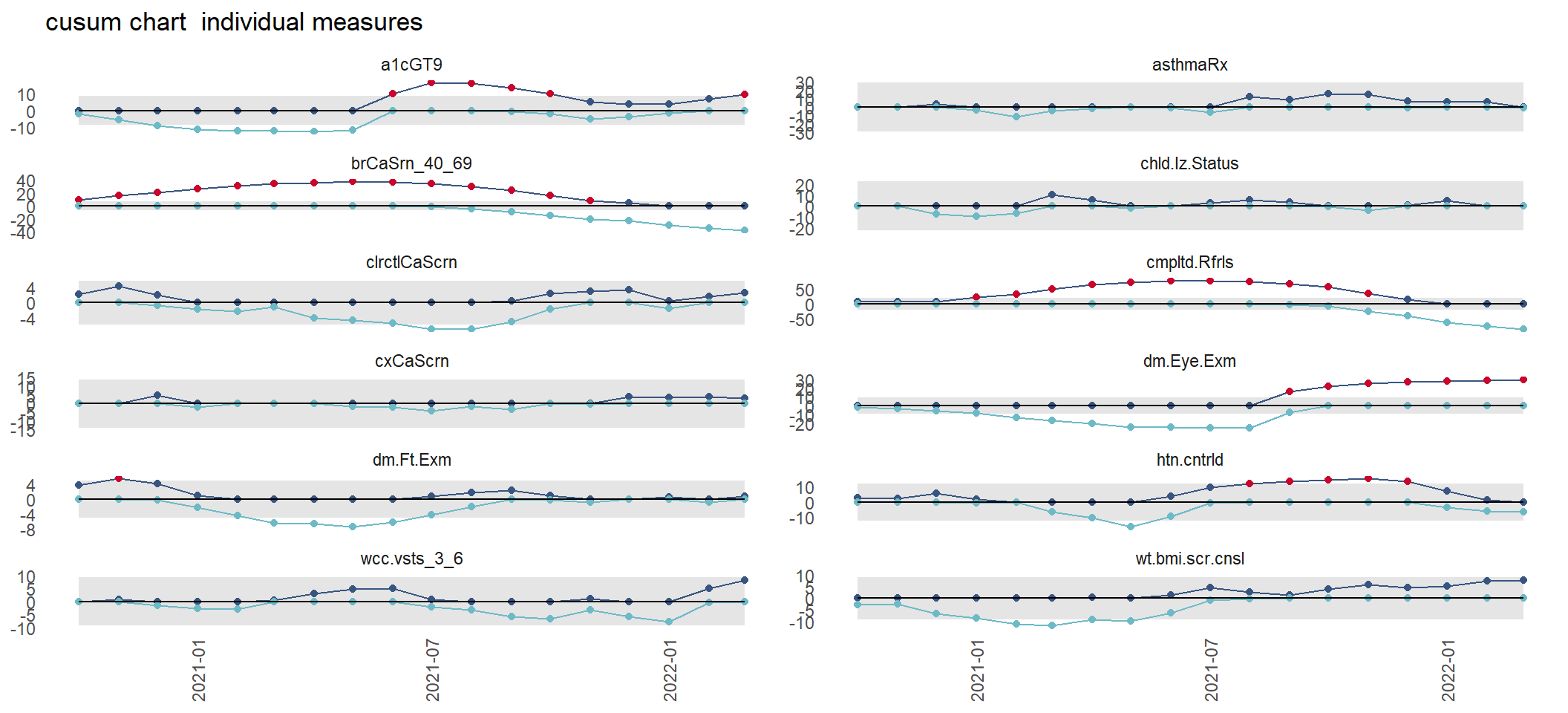
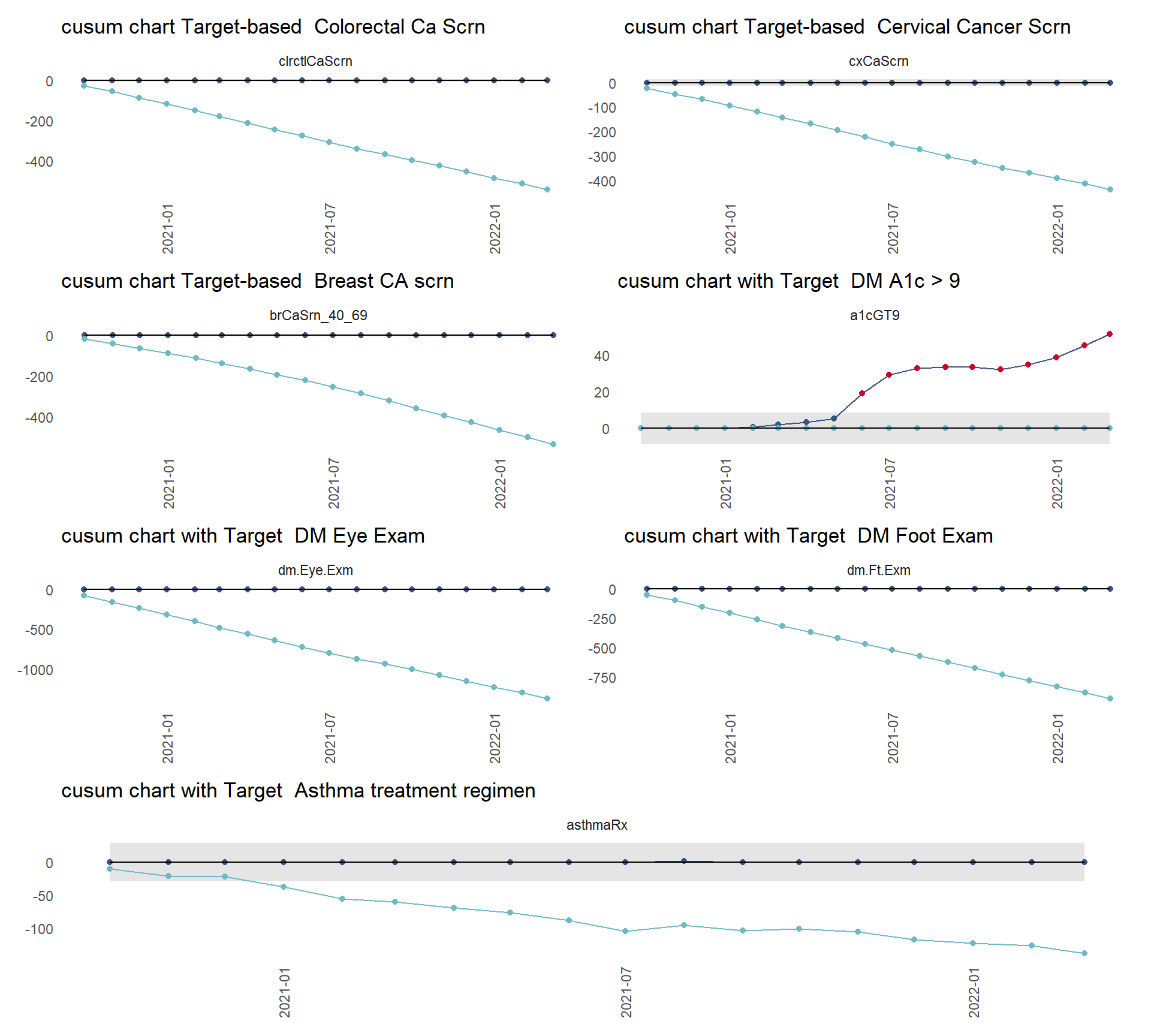
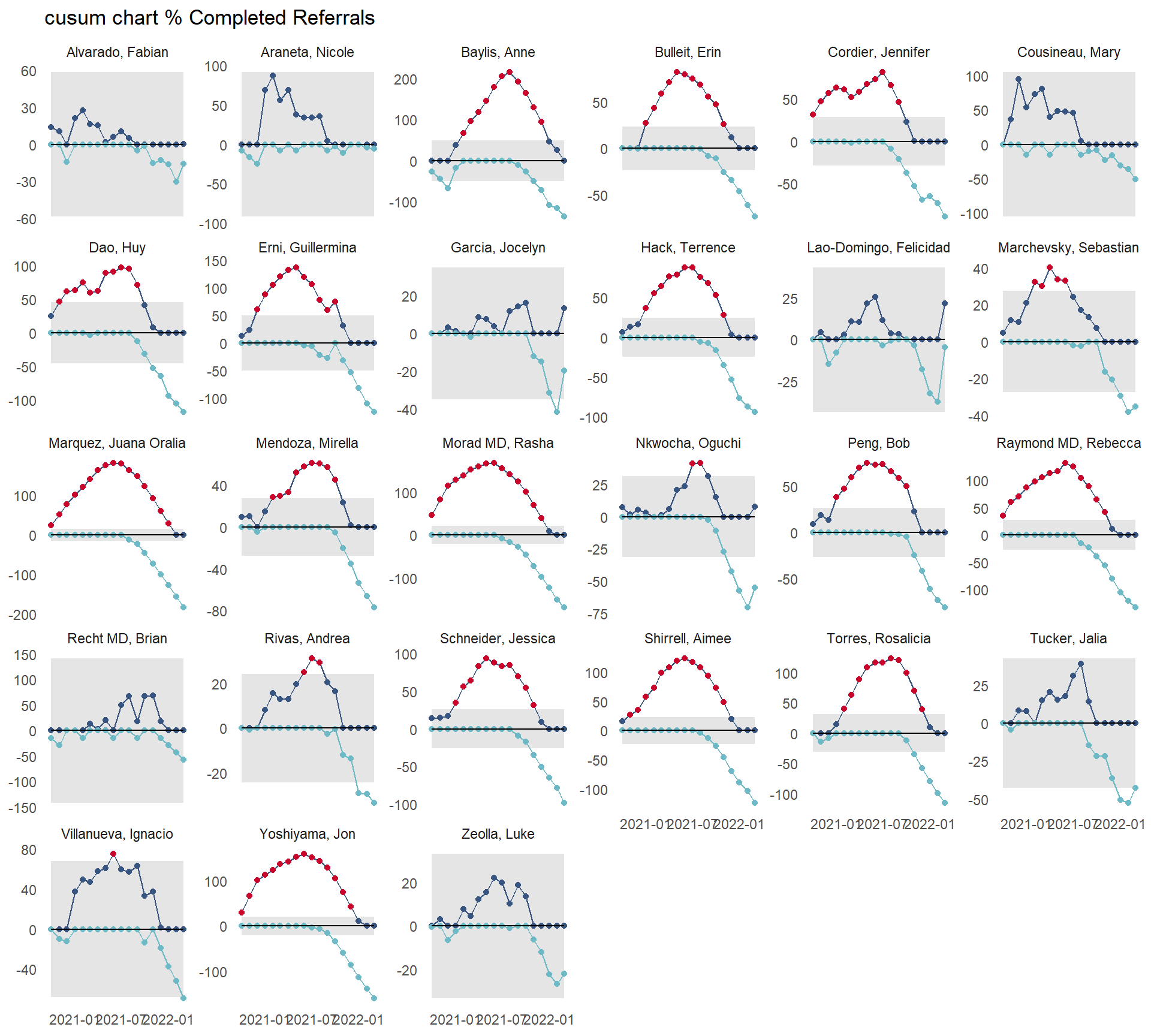
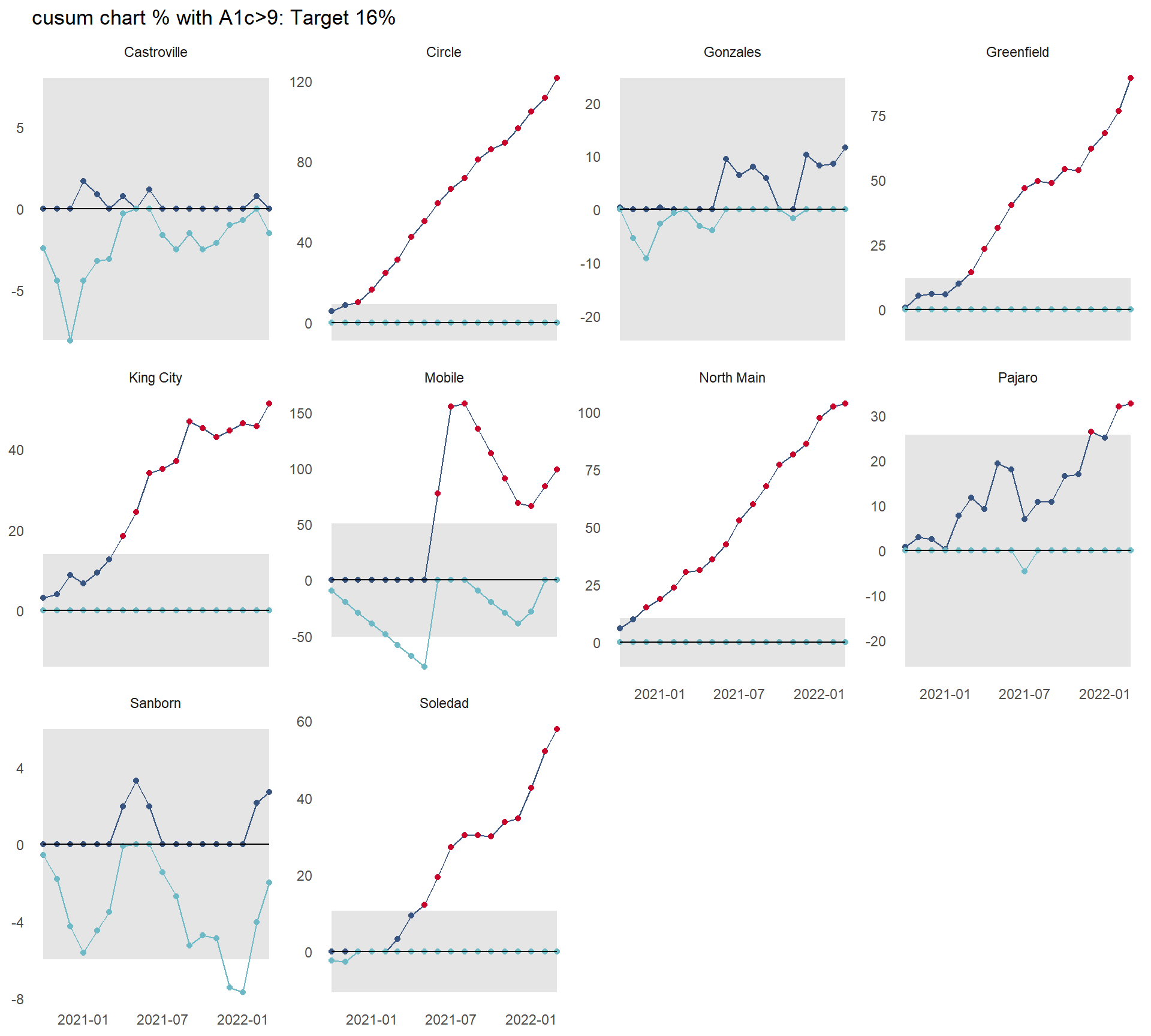
3.1.3 SPC focus on CUSUM Charts
CUSUM charts pick up on small shifts of less than 1 standard deviation from the mean / target (whereas SPC (standard) control limits are set at 3 sigma).
they are good at highlighting that change is underway.
need early warning? Then CUSUMS are your friend
may use a supplied target, or the mean or median of the data.
3.4 Components of SPC QA
3.5 DATA
3.5.1 UDS Medical Measures (12):
3.7 SUMMARY
Focus on PROCESS control
Detect small output deviations (indicating faulty process) using CUSUM charts
Use profiles for comparison
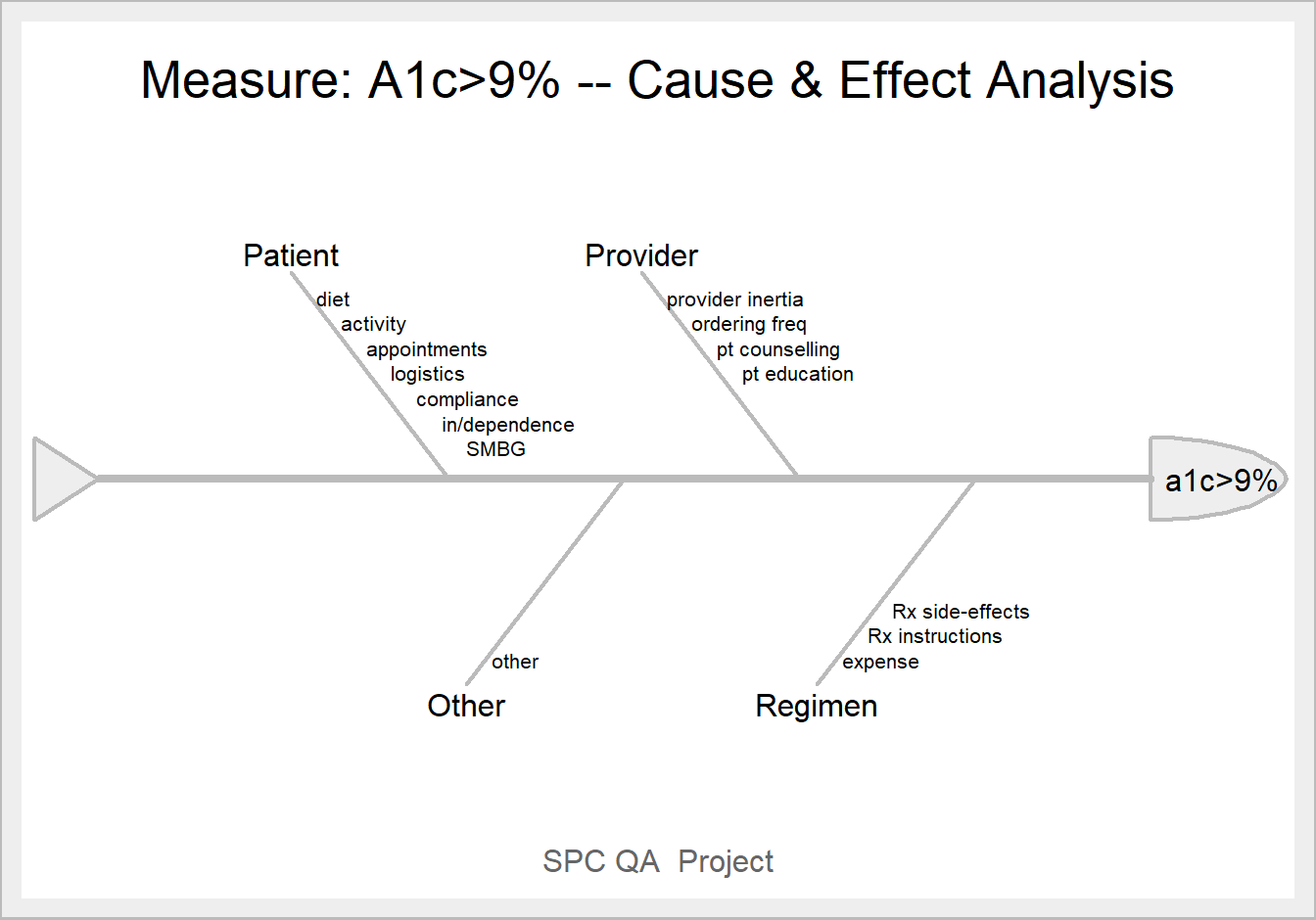
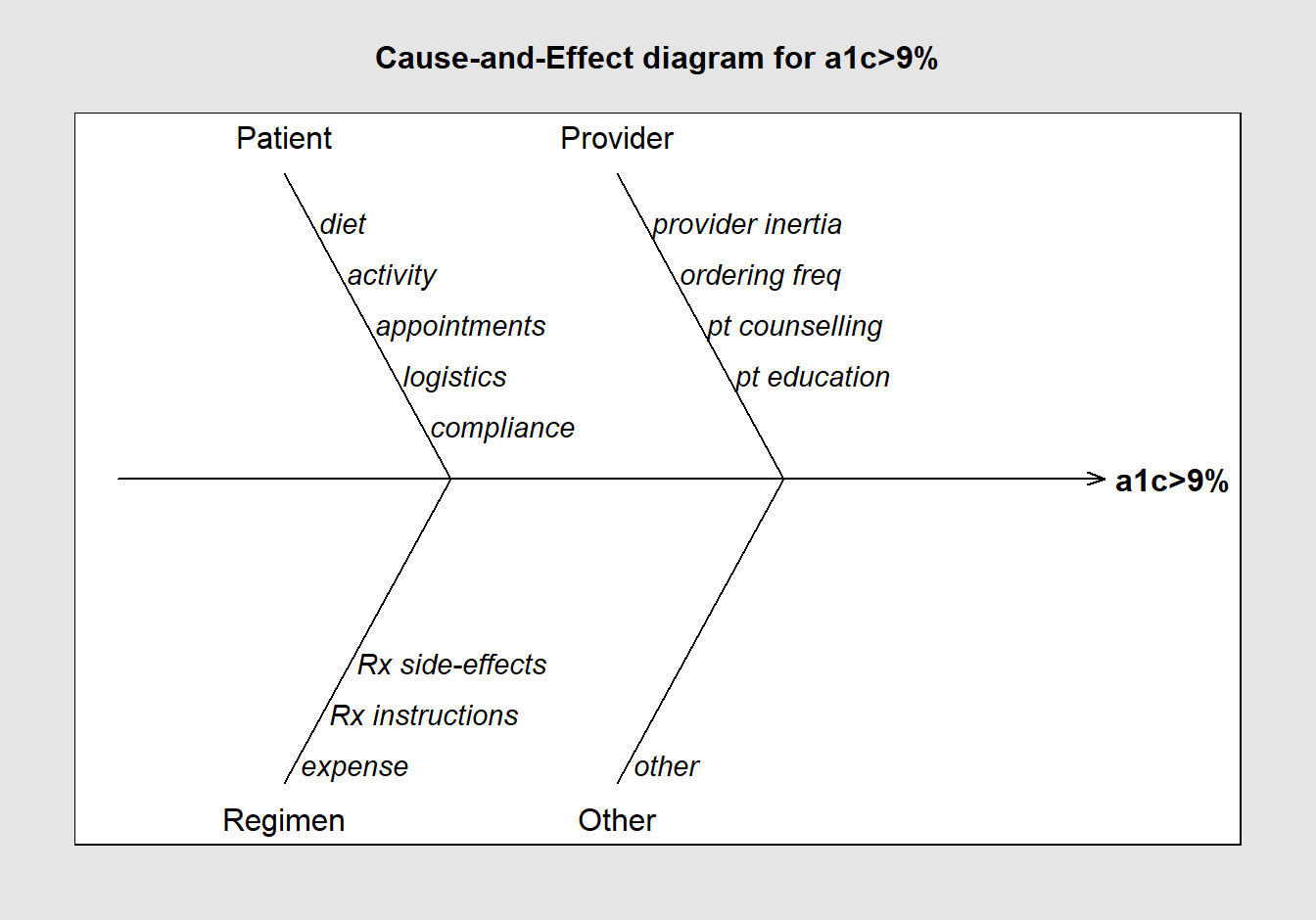
Analyze & determine cause - effect using FISHBONE diagram.
need early warning? Then CUSUMS are your friend
Make appropriate changes to the process
Monitor with CUSUM charts