Sec 2 About Time Series
2.1 What is time series?
- Observations (obs.) could be
- univariate or multiivariate
- discrete (count) or continuous (measurement)
- Set of obs. recorded sequentially (has a natural order)
- time
- spatial ordering, eg. \(1^{st}\) plaint in a row, \(2^{nd}\) plaint in a row
- depth, eg. soil (土壤) PH: 1m down, 2m down
- Recording interval could be
- regular, eg. hourly, daily, monthly
- irregular, eg. earthquake, observe stock price at transaction times
- take average or median to change it into regular
2.2 Plot of time series data
plot data vs time to look:
- trend: upward or downward (整體趨勢)
- repetitive pattern is unknown or unknown:
- periodicity: in regular pattern, eg. 1.3 years
- seasonality: known period, eg. 1 year, 12 month for mothly data
- heteroskadesticity \(\sigma^2_t\): changing variance
- dependence: positive or negative
- successive obs. (\(x_t, x_{t+1}\)) are similar or dissimilar
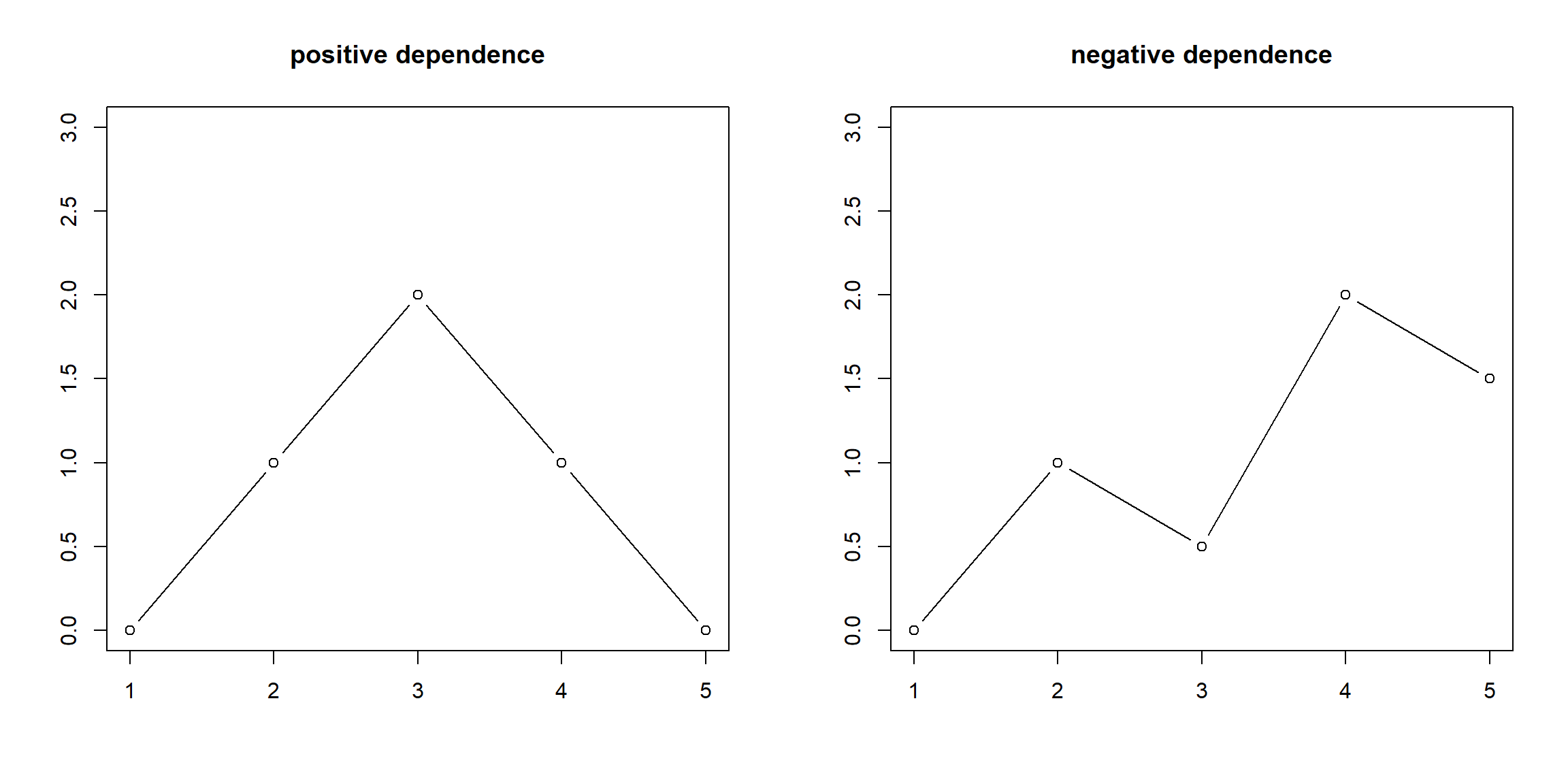
- successive obs. (\(x_t, x_{t+1}\)) are similar or dissimilar
- missing, outliers
2.3 Why use time series
- difference between Regression (reg.) and Time Series (TS)
- Reg.: need (X, Y)
X之間獨立 (independent, indep.), X和Y之間不獨立 (dependent, dep.) - TS: only need X (times)
X之間 dep.
- Reg.: need (X, Y)
- Often in time series data:
- trend 不好使用 global regression function 來 fitted
- 如下圖,就需要2個 reg.
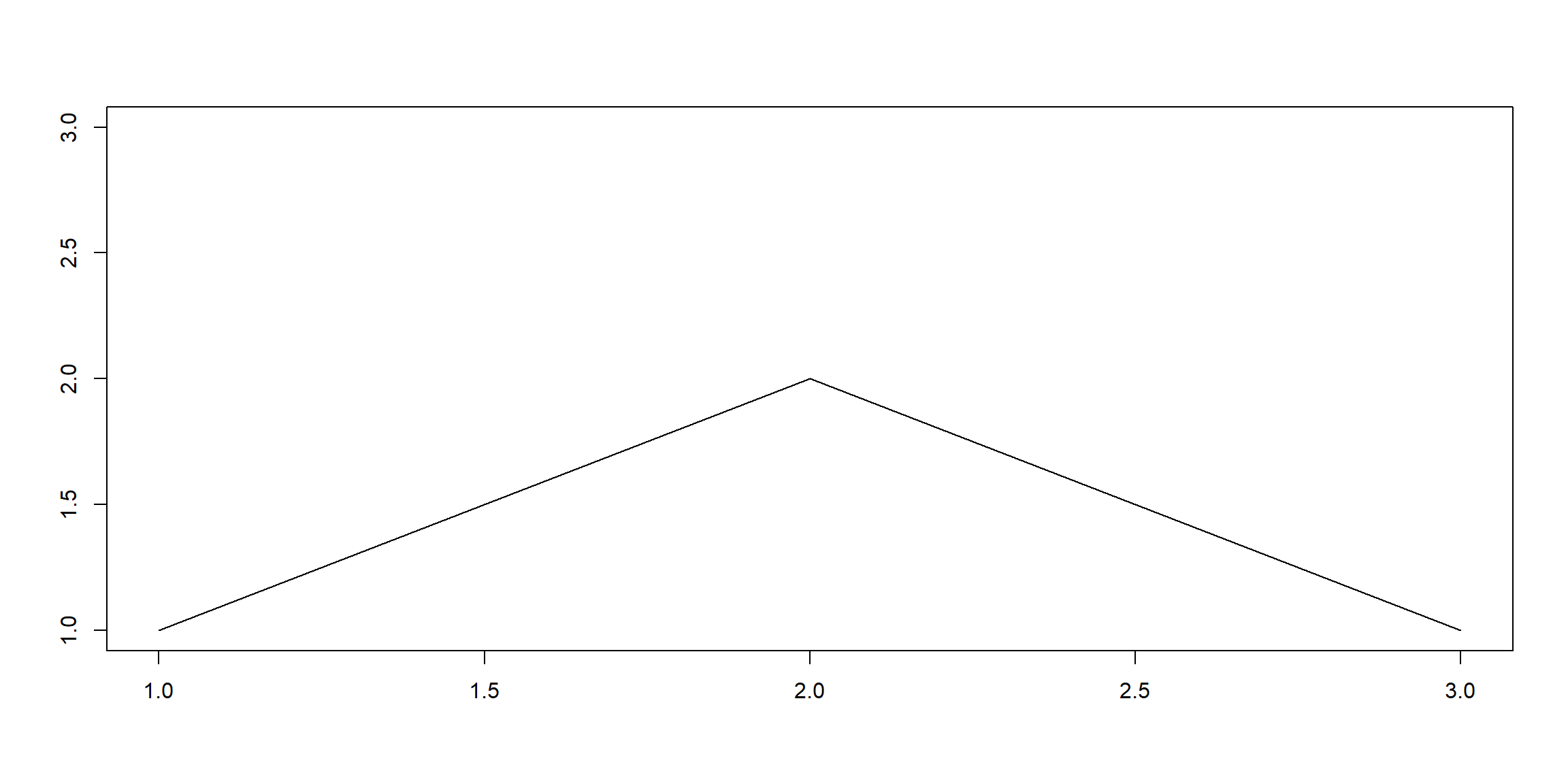
- 如下圖,就需要2個 reg.
- display time-varying local behavior
- often have seasonality
- Ignore dependence often lead to:
- inefficient estimates of reg. parameters
- poor prediction
- standard errors (std.): unrealistically small
- confidence interval (CI.): unrealistically narrow
- hypothesis testing: improper inferences
2.4 Objective of time series analysis
- provide an interpretable model of data
- often involve multivariate series
- test if the variable is significance (sig.) influence
- predict future values of series
- predictive model often do not try to explain
2.5 Modeling strategy
\[\hat{y}_{t+1}=trend+dependence\] \[trend \leftarrow reg., \:dependence \leftarrow TS\]
- difficulties
- random variables (r.v.) not identically distributed
- r.v. not independent
- different means due to trend or seasonality
- different variance
- try to make it easier
- to focus on modeling dependence
- eliminate trend and seasonality
- eliminate changing variance
- model remainder as dependent but identically distributed