Chapter 6 Signal Transduction Pathways
General signal transduction
Content from Environmental Physiology of Animals: Willmer et al. lab copy here.
Four types of receptor proteins:
1. Intracellular receptors
2. Enzyme-linked receptors: mostly linked to a protein kinase and the ligand-binding site is outside the cell and the catalytic side on the inside of the cell.
3. Ion channel-linked receptors: perform function of both channels and receptors; rapid signaling; the signal molecule causes a transient opening or closing of a channel through the protein structure
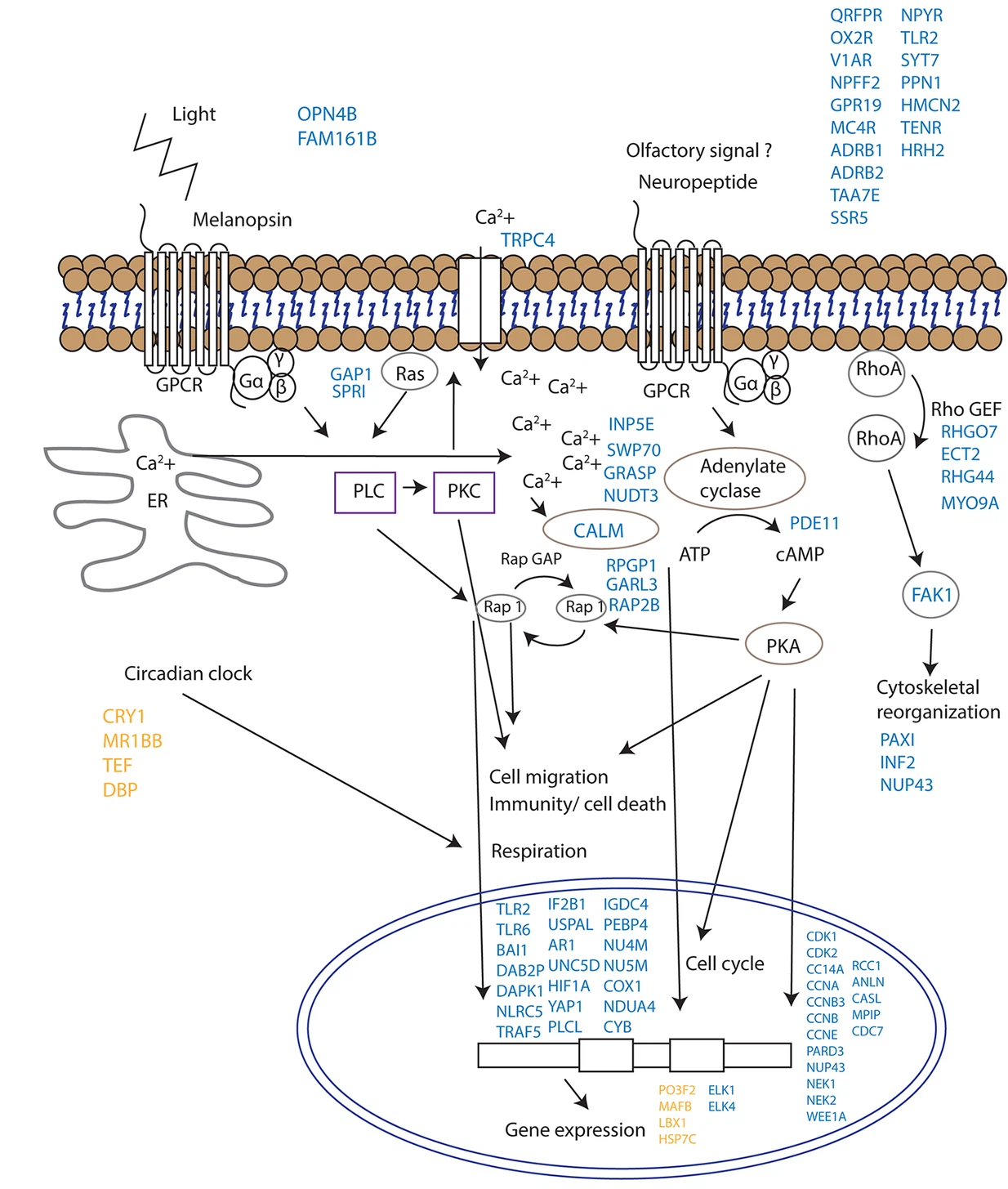
4. G-protein-linked-receptor: GTP-binding regulatory protein; sit in membranes adjacent to a receptor protein and another target protein (could be either #2 or #3 as well).

gprotein

path
Intracellular mediators and second messengers:
- messengers are small enough to move through gap junctions b/w adjacent cells so that signaling can be shared amongst cell communities. Extracellular signaling is therefore amplified and integrated together.
cAMP:
- synthesized from ATP from a membrane-bound enzyme adenyl cyclase
- rapidly destroyed by cAMP phosphodiesterase enzymes
- can increase five-fold in a few seconds (that’s insane..)
- works through cAMP-dependent protein kinase (kinase A), being linked to receptor via one or two G-proteins (see diagram above) that are stimulatory or inhibitory
- Eventual product of cAMP-induced phosphorylations may bind to a cAMP-response element, adjacent to the transcribed gene, to produce the final response.
Ionic calcium: can act as messenger by opening Ca2+ channels and producing an automatic inward flux w/ rise of cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration.
- When G-protein is activated by an appropriate signal, it in turn activates a membrane-bound enzyme, phospholipase C.
- which hydrolyzes a specific phospholipid in the cell membrane to produe a soluble intermediate: inositol triphosphate (IP3).
- IP3 travels through cytoplasm and releases calcium via IP3-gated Ca2+ channels from internal membrane stores.
- Ca2+ can activate targets by directly binding enzymes as an allosteric ligand or active indirectly via binding to calmodulin (CaM). As more Ca2+ binds to CaM, it then binds to enzymes or indirectly through a CaM-dependent multifunctional kinase (PKII or CaM-kinase II).

ca
Heat shock pathway:

heat
Thermostranduction
Neurobiology of TRP Channels in invertebrates book chapter 4 (cross reference with what is in corals):
- Mechanosensory neurons have to detect mechanical stimuli and thermosensory neurons have to detect temperatures warmer and cooler than the preferred.
- Transient receptor potential (TRP) genes encode cation channels with key roles in fxn of sensory neurons. TRP channel subunits detect mechanical and thermal stimuli.
Calcium dependent protein kinase 2 is upregulated in heat stress and plays a role in signal transduction pathways that involve calcium as a second messenger (Bellantuono et al 2018).
Pre-conditioning-based improvements in thermal tolerance in P. acuta are accompanied by host increases in glutathione reductase (GR) activity and expression. This supports reducing intracellular environment that facilitates ROS scavenging and prevents DNA damage. Bax-inhibitor 1 (BI-1) could regulate GR expression in corals through Nrf2/ARE pathway (Majerova and Drury 2021).
Transient receptor potential multigene superfamily encodes integral membrane proteins that function as ion channels (Nilius nad Owsianik 2011).
- Most are non selective cation channels, only a few are Ca2+ selective
- Gating mechanims include: ligand binding, voltage, and changes in temperature, covalent modifications of nucleophilic residues
- Activated TRP channels cause depolarization of the cellular membrane, which in turn activates voltage-dependent ion channels and a change of intracellular Ca2+ concentration.
Thermosensing
Chapter 3 of biochemical adaptation (Somero et al):
TRP proteins = cation (positive charge) channels that when are thermosensors they are called thermoTRPs. TRP proteins can have differing fxns based on what cell they are in.
- D. melanogaster genome encodes for 16 TRPs and the human genome encodes for 28 TRPs.
Different types of channels:
channels

ion-channel
Thermal response of thermoTRP variants depends on:
1. Temperature at which an ortholog is activated, at which the ion channel opens and therefore neurofiring to occur. Activation temps of TRP channels can reflect differential thermal phenotypes.
2. thermoTRPs differ in fxn for increases or decreases in temps.
3. Responses of different paralogs of thermoTRPs to increases in temp differ with respecto severity of thermal stress. thermoTRPs are tuned to respond to either 1.) not harmful/moderate temps just beyond optimal range or 2.) potentially damaging temps that are well outside thermal range.
thermoTRPs fxn in conjunction with other temperature-sensing ion channel systems:
- An alternative relies on cGMP as a regulatory signal: [cGMP] varies with temperature, so do activities of cGMP-gated ion channels thta modulate activities of thermosensing neurons.
In thermosensing neurons, ion flux rates through temp-sensing ion channels are very responsive to slight changes in temp.
dTRPA1 responds to mild heating
TRP PYREXIA: activated at more extreme temperatures
TRP PAINLESS: even more extreme temperatures
TRPs can also be involved in phototransduction.
TRPM3 (found in mammals) is conserved in Hydra vulgaris: nociceptor calcium channel involved in detection of noxious heat. heat shock protein and TRPM3 (i.e. pregnenolone sulfate) induces modulation of heat shock protein 70 and nitric oxide synthase (NOS). TRPM3 agonist and heat shock induce expression of nuclear txn enrythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Malafoglia et al 2016).
Glauser and Goodman 2016 figure below:

thermo