Chapter 8 Conditional manatees
8.1 Building an interaction
\(R\) = ruggedness, \(G\) = GDP, \(C\) = continent, \(U\) = unobserved variables.
library(dagitty)
library(rethinking)
dag_8.1 <- dagitty("dag{
R -> G
C -> G
U -> G
U -> R
}")
coordinates(dag_8.1) <- list(y = c(R = 0, G = 0, C = 0, U = 1),
x = c(R = 0, G = 1, U = 1, C = 2))
drawdag(dag_8.1)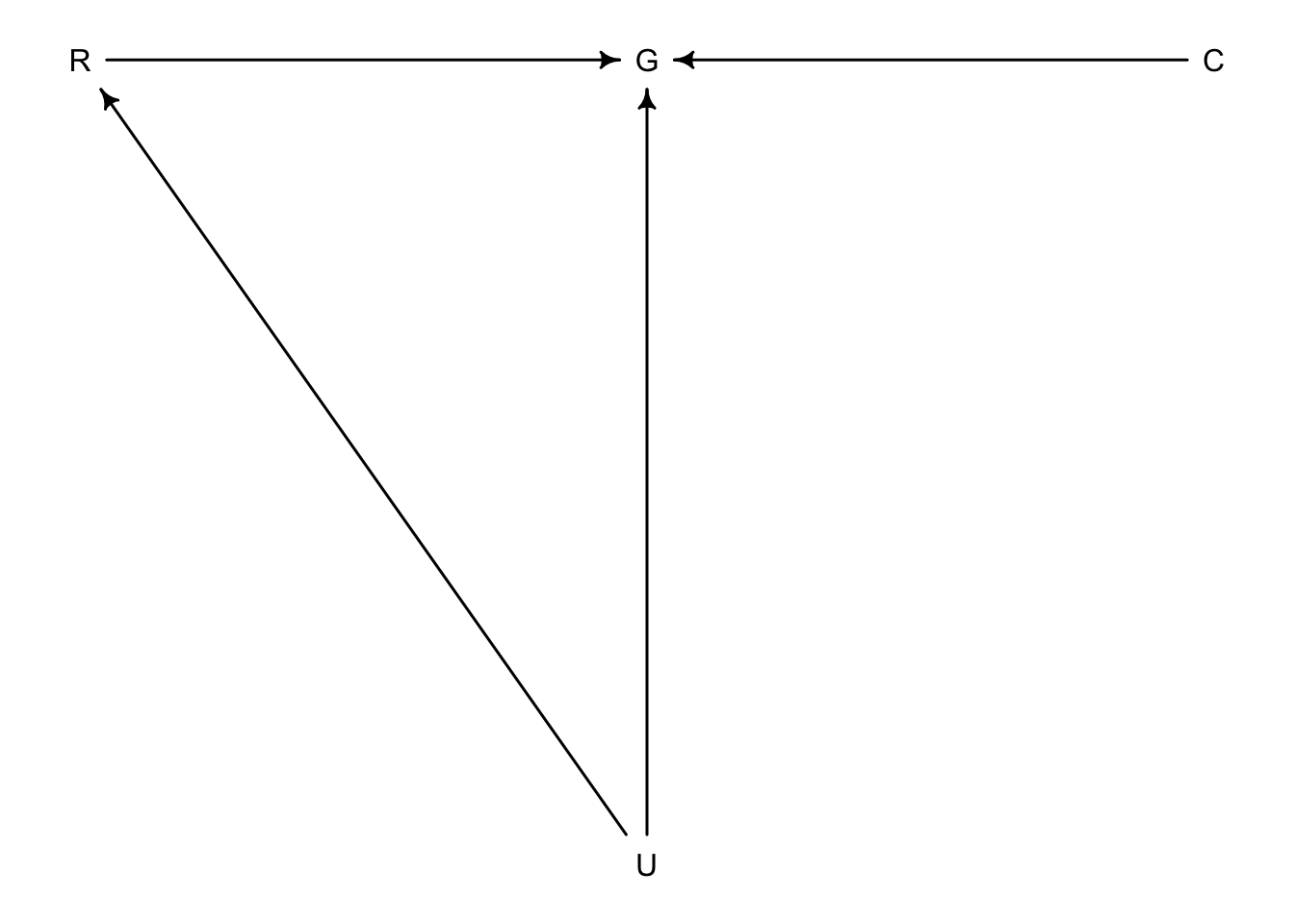
\(G = f(R,C)\)
8.1.1 Making a rugged model
library(rethinking)
data(rugged)
d <- rugged
#log transform GDP
d$log_gdp <- log(d$rgdppc_2000)
#only include countries with GDP data
dd <- d[complete.cases(d$rgdppc_2000),]
#rescale variables
dd$log_gdp_std <- (dd$log_gdp) / mean(dd$log_gdp) # values of 1 is average
dd$rugged_std <- (dd$rugged) / max(dd$rugged) # values range from 0 to max ruggedness (1)Basic model \[\text{log}(y_{i}) \sim \text{Normal}(\mu_{i}, \sigma)\\ \mu_{i} = \alpha + \beta(r_{i} - \overline{r})\\ \alpha \sim \text{Normal}|(1,1)\\ \beta \sim \text{Normal}(0, 1)\\ \sigma \sim \text{Exponential}(1)\]
In R:
m8.1 <- quap(
alist(
log_gdp_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <- a + b*(rugged_std - 0.215),
a ~ dnorm(1, 1),
b ~ dnorm(0, 1),
sigma ~ dexp(1)
), data = dd
)Sample priors:
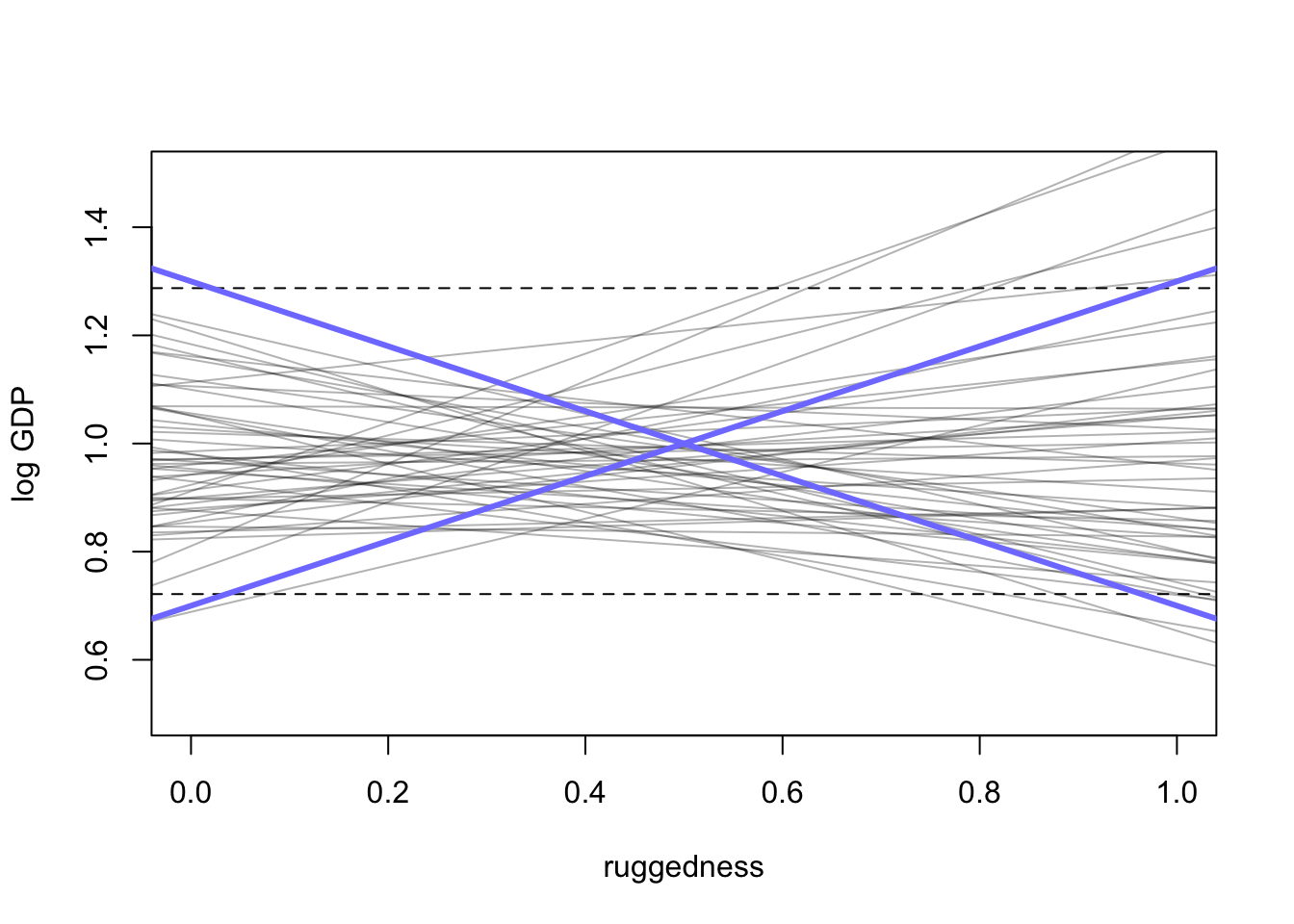
set.seed(11)
prior <- extract.prior(m8.1)
#set plot
plot(NULL, xlim=c(0,1), ylim=c(0.5, 1.5), xlab = "ruggedness", ylab = "log GDP")
abline(h=min(dd$log_gdp_std), lty = 2)
abline(h=max(dd$log_gdp_std), lty = 2)
#draw lines from prior
rugged_seq <- seq(from = -0.1, to = 1.1, length.out=30)
mu <- link(m8.1, post = prior, data = data.frame(rugged_std=rugged_seq))
for(i in 1:50){
lines(rugged_seq, mu[i,], col=col.alpha('black',0.3))
}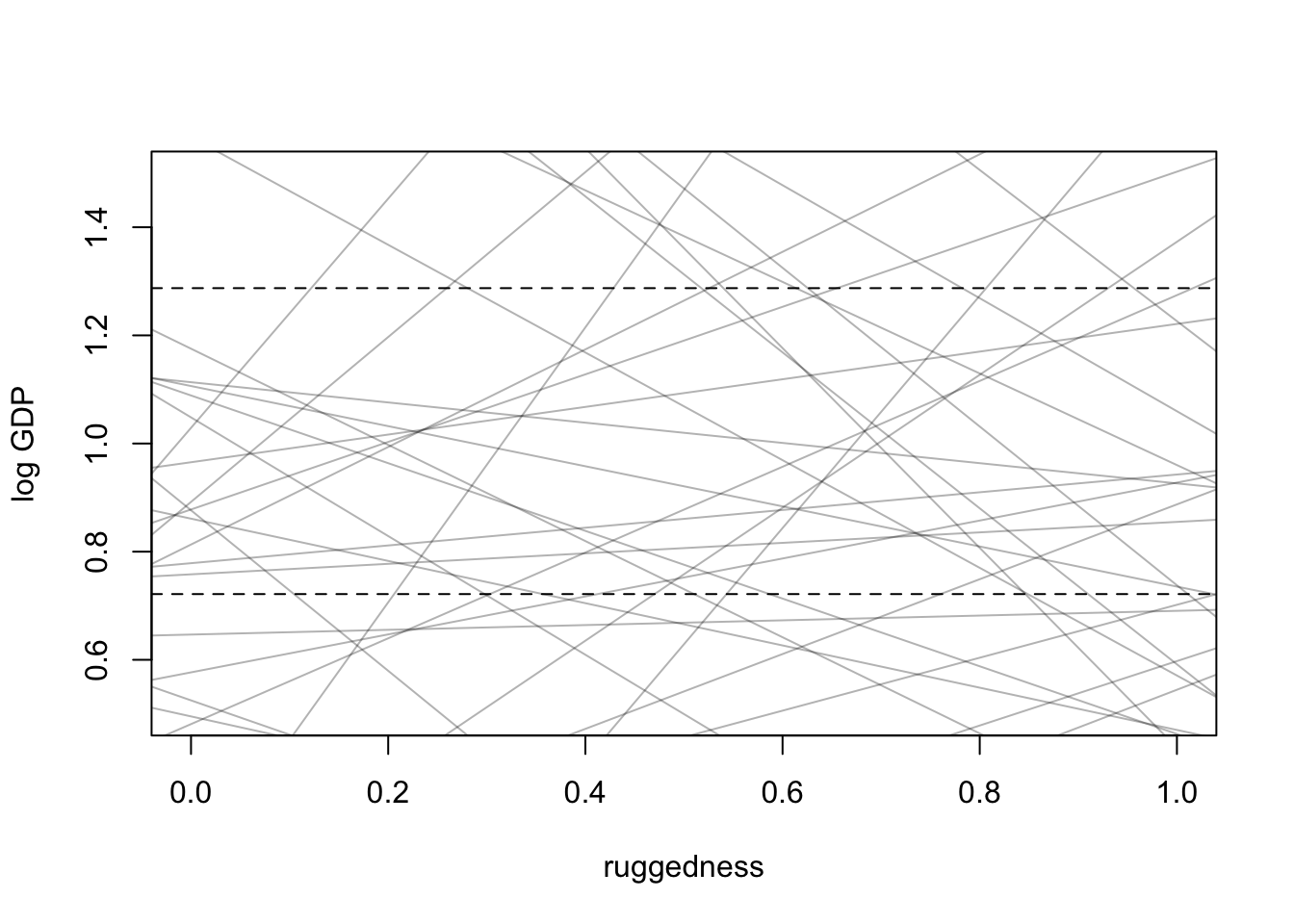
\(\alpha\) is too wild. intercept should be somewhere around where the mean of ruggedness hits 1 on the log GDP scale so adjust to Normal(1, 0.1).
\(\beta\) is also out of control. we need something (positive or negative) that spans the difference between the dashed lines
Slope should be \(\pm 0.6\) which is the differece between the maximum and minimum values of GDP
max(dd$log_gdp_std) - min(dd$log_gdp_std)## [1] 0.5658058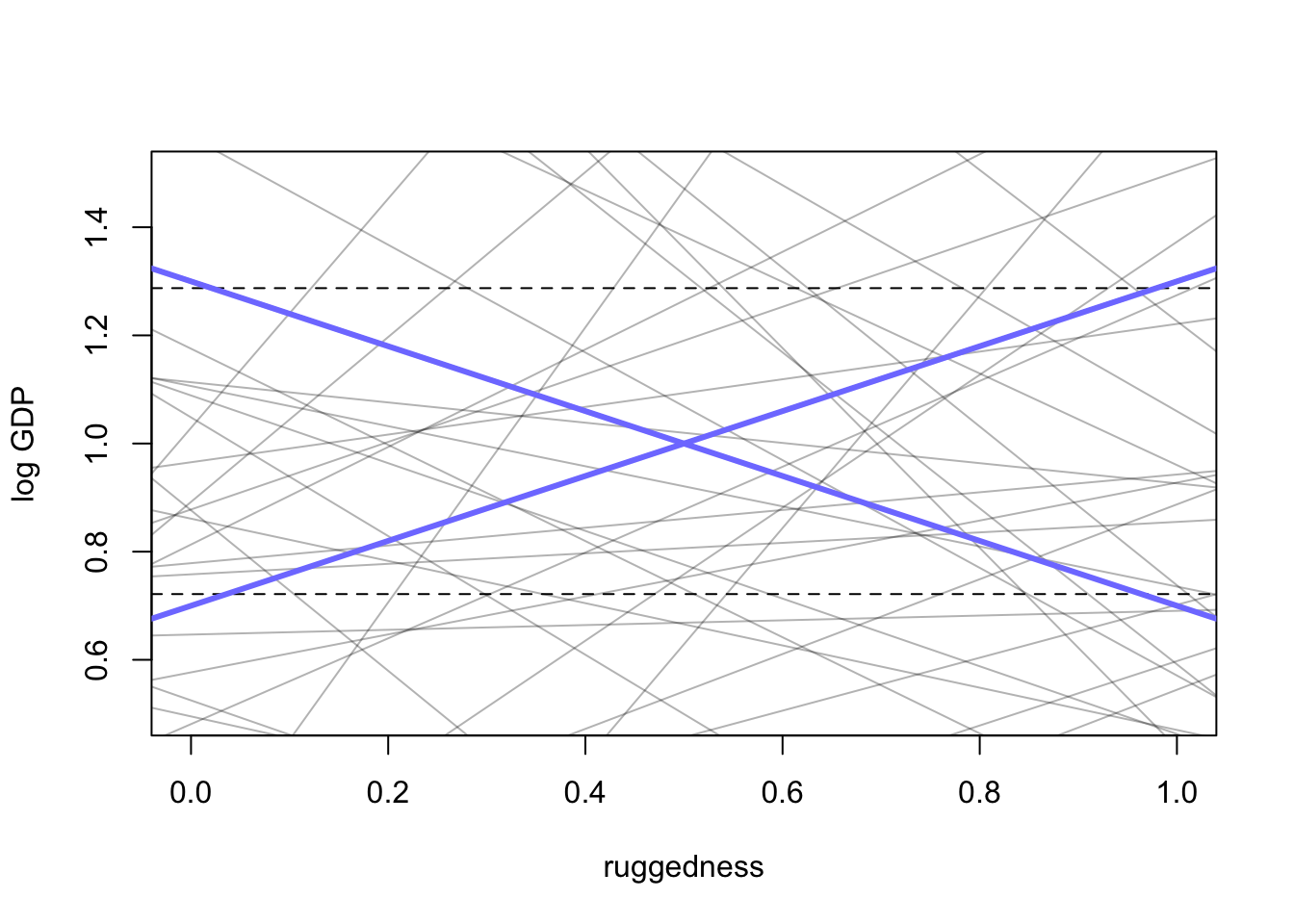
#proportion of slopes greater than 0.6
sum(abs(prior$b) > 0.6) / length(prior$b)## [1] 0.54Let’s fix the model
m8.1 <- quap(
alist(
log_gdp_std ~dnorm(mu,sigma),
mu <-a+b*(rugged_std-0.215),
a ~dnorm(1,0.1),
b ~dnorm(0,0.3),
sigma ~dexp(1)
), data = dd
)
precis(m8.1)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a 0.999998578 0.010412457 0.98335746 1.01663970
## b 0.001994904 0.054795958 -0.08557962 0.08956943
## sigma 0.136503830 0.007397023 0.12468196 0.14832570No association seen yet
8.1.2 Adding an indicator isn’t enough
Update \(\mu\)
\[\mu_{i} = \alpha_{CID[i]} + \beta(r_{i} - \overline{r})\]
#make an index variable for Africa (1) and other continents (2)
dd$cid <- ifelse(dd$cont_africa == 1, 1, 2)Now update the model
m8.2 <- quap(
alist(
log_gdp_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <-a[cid] + b * (rugged_std - 0.215),
a[cid] ~ dnorm(1, 0.1),
b ~ dnorm(0, 0.3),
sigma ~dexp(1)
), data = dd
)compare(m8.1, m8.2)## WAIC SE dWAIC dSE pWAIC weight
## m8.2 -252.1508 15.25508 0.00000 NA 4.291725 1.000000e+00
## m8.1 -188.9664 13.28913 63.18439 15.11018 2.574284 1.904075e-14precis(m8.2, depth = 2)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a[1] 0.88040848 0.015938408 0.8549358 0.90588113
## a[2] 1.04916209 0.010186473 1.0328821 1.06544204
## b -0.04651791 0.045690786 -0.1195406 0.02650479
## sigma 0.11239762 0.006092464 0.1026607 0.12213455post <- extract.samples(m8.2)
diff_a1_a2 <- post$a[,1] - post$a[,2]
PI(diff_a1_a2)## 5% 94%
## -0.1988472 -0.1384092rugged.seq <- seq(from = -0.1, to = 1.1, length.out = 30)
mu.NotAfrica <- link(m8.2, data = data.frame(cid=2, rugged_std=rugged.seq))
mu.Africa <- link(m8.2, data = data.frame(cid = 1, rugged_std = rugged.seq))
mu.NotAfrica_mu <- apply(mu.NotAfrica, 2, mean)
mu.NotAfrica_ci <- apply(mu.NotAfrica, 2, PI, prob = 0.97)
mu.Africa_mu <- apply(mu.Africa, 2, mean)
mu.Africa_ci <- apply(mu.Africa, 2, PI)
plot(NULL, xlim=c(0,1), ylim=c(0.5, 1.5), xlab = "ruggedness", ylab = "log GDP")
points(dd$rugged_std, dd$log_gdp_std, col = dd$cid, pch = 16)
lines(rugged.seq, mu.Africa_mu, lwd = 2, col = 1)
shade(mu.Africa_ci, rugged.seq)
lines(rugged.seq, mu.NotAfrica_mu, lwd = 2, col = 2)
shade(mu.NotAfrica_ci, rugged.seq, col = col.alpha(2, 0.3))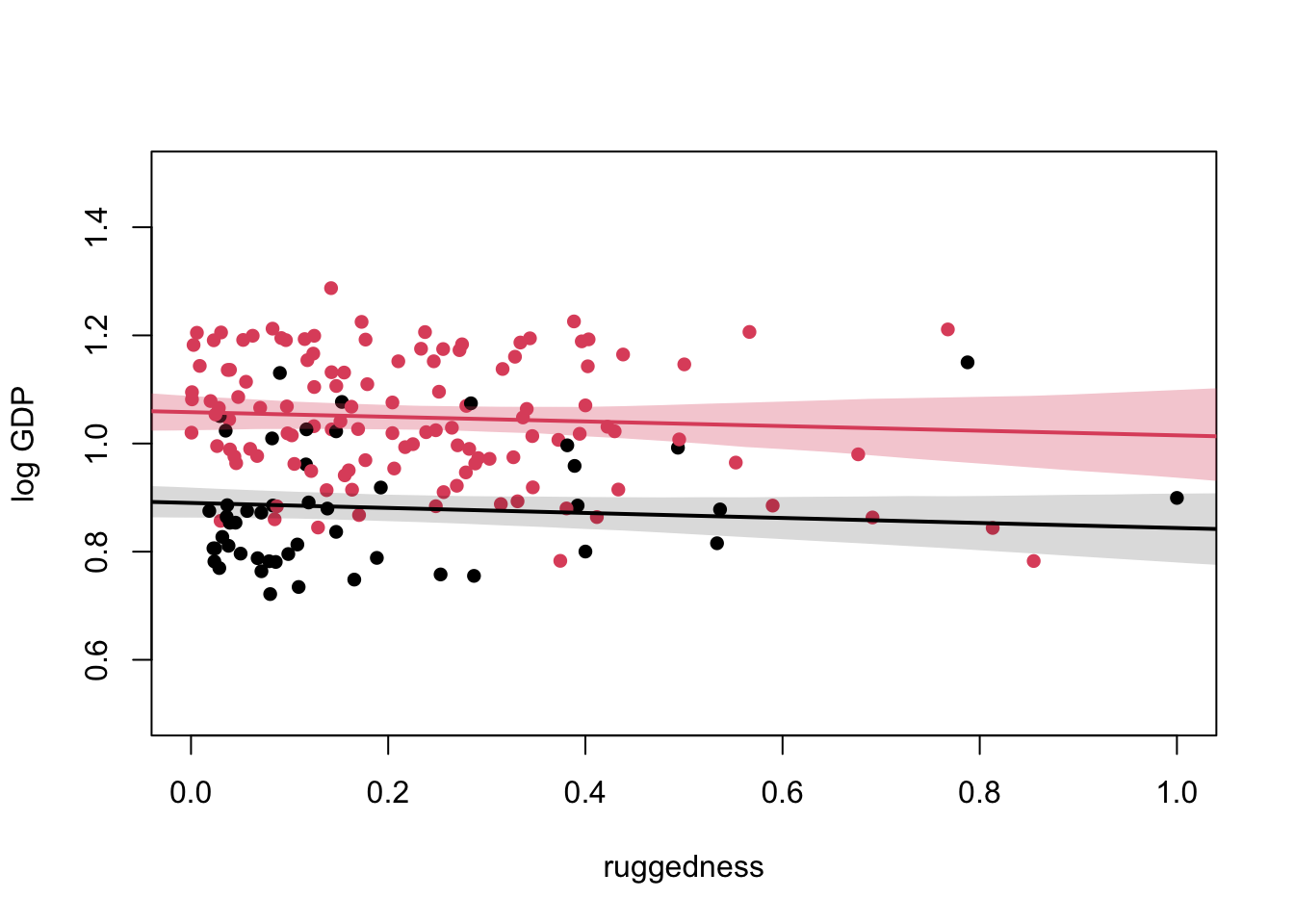
8.1.3 Adding an interaction does work
\[\mu_{i} = \alpha_{CID[i]} + \beta_{CID[i]}(r_{i} - \overline{r})\]
m8.3 <- quap(
alist(
log_gdp_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <-a[cid] + b[cid] * (rugged_std - 0.215),
a[cid] ~ dnorm(1, 0.1),
b[cid] ~ dnorm(0, 0.3),
sigma ~dexp(1)
), data = dd
)
precis(m8.3, depth = 2)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a[1] 0.8865632 0.015675727 0.86151037 0.91161605
## a[2] 1.0505709 0.009936627 1.03469025 1.06645155
## b[1] 0.1325019 0.074204597 0.01390861 0.25109517
## b[2] -0.1425818 0.054749512 -0.23008206 -0.05508147
## sigma 0.1094944 0.005935331 0.10000855 0.11898016compare(m8.1, m8.2, m8.3, func=PSIS)## Some Pareto k values are high (>0.5). Set pointwise=TRUE to inspect individual points.## PSIS SE dPSIS dSE pPSIS weight
## m8.3 -258.8749 15.35435 0.000000 NA 5.314384 9.688047e-01
## m8.2 -252.0033 15.30167 6.871589 6.936621 4.354277 3.119533e-02
## m8.1 -188.4136 13.40307 70.461243 15.674795 2.856543 4.850334e-16plot(PSIS(m8.3, pointwise = TRUE)$k)## Some Pareto k values are high (>0.5). Set pointwise=TRUE to inspect individual points.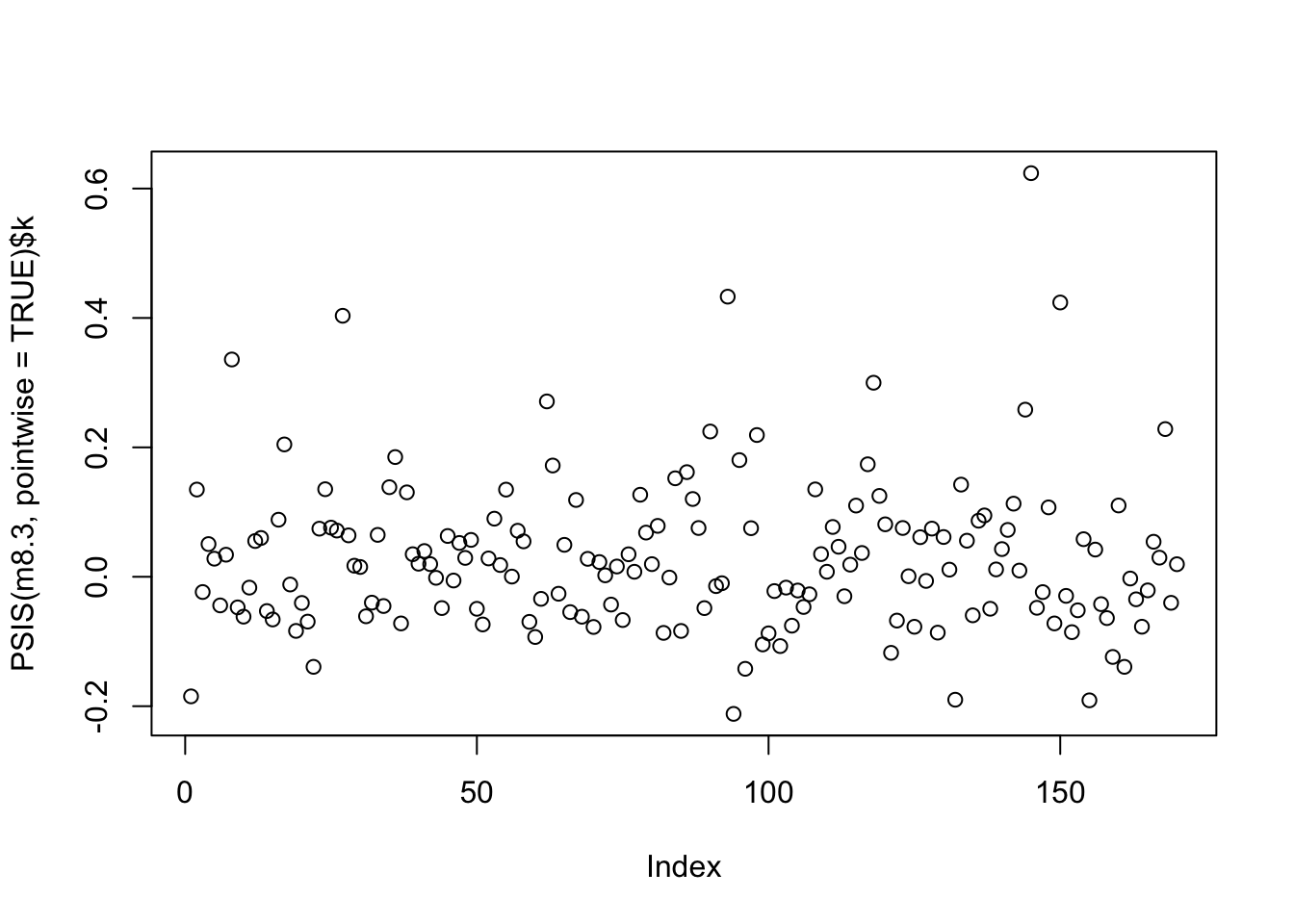
8.1.4 Plotting the interaction
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
# plot Africa - cid = 1
d.A1 <-dd[dd$cid == 1,]
plot(d.A1$rugged_std, d.A1$log_gdp_std, pch=16, col=rangi2,
xlab="ruggedness (standardized)",ylab="log GDP (as proportion of mean)",
xlim=c(0,1) )
mu <-link(m8.3,data=data.frame(cid=1,rugged_std=rugged_seq))
mu_mean <-apply(mu,2,mean)
mu_ci <-apply(mu,2,PI,prob=0.97)
lines( rugged_seq,mu_mean,lwd=2)
shade( mu_ci,rugged_seq,col=col.alpha(rangi2,0.3))
mtext("African nations")
# plotnon-Africa-cid=2
d.A0 <-dd[dd$cid==2,]
plot( d.A0$rugged_std,d.A0$log_gdp_std,pch=1,col="black",
xlab="ruggedness (standardized)",ylab="logGDP(asproportionofmean)",
xlim=c(0,1) )
mu <-link(m8.3,data=data.frame(cid=2,rugged_std=rugged_seq))
mu_mean <-apply(mu,2,mean)
mu_ci <-apply(mu,2,PI,prob=0.97)
lines( rugged_seq,mu_mean,lwd=2)
shade( mu_ci,rugged_seq)
mtext("Non-African nations")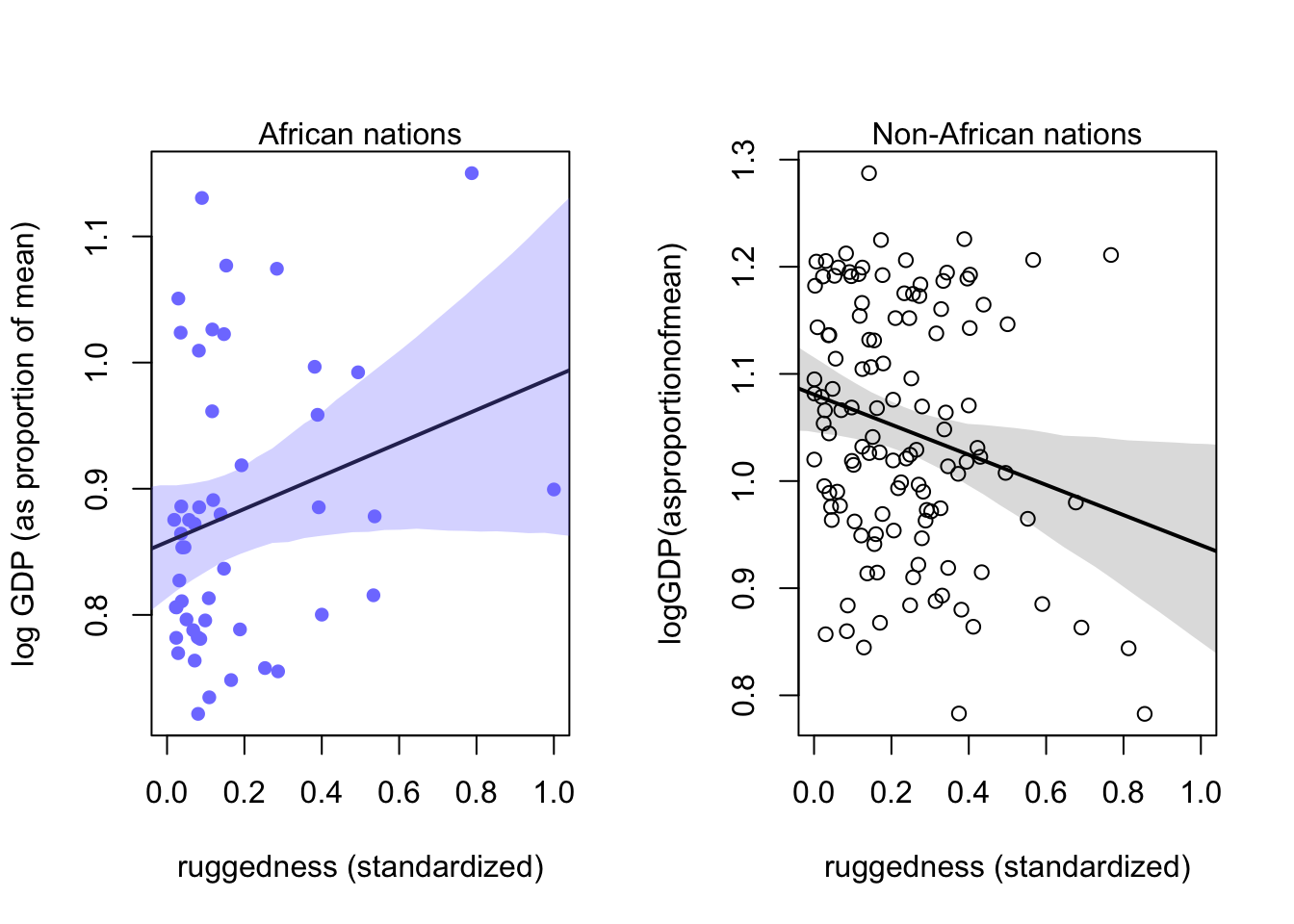
8.2 Symmetry of interactions
You can break an interaction into 2 identical phrasings
1. GDP ~ ruggedness depending on Africa
2. Africa ~ GDP depending on rugedness
\[\mu_{i} = (2 - CID_{i})(\alpha_{1} + \beta_{1}(r_{i} - \overline{r})) + (CID_{i} - 1)(\alpha_{2} + \beta_{2}(r_{i} - \overline{r}))\]
rugged_seq <- seq(from = -0.2, to = 1.2, length.out = 30)
muA <- link(m8.3, data=data.frame(cid=1, rugged_std=rugged_seq))
muN <- link(m8.3, data=data.frame(cid=2, rugged_std=rugged_seq))
delta <- muA - muN
mu.delta <- apply(delta, 2, mean)
PI.delta <- apply(delta, 2, PI)
plot(x=rugged_seq, type = 'n', xlim = c(0,1), ylim = c(-0.3, 0.2),
xlab = 'ruggedness (std)', ylab = 'expected difference log GDP')
shade(PI.delta, rugged_seq, col='grey')
abline(h = 0, lty = 2)
text(x = 0.2, y = 0, label = "Africa higher GDP\nAfrica lower GDP")
lines(rugged_seq, mu.delta)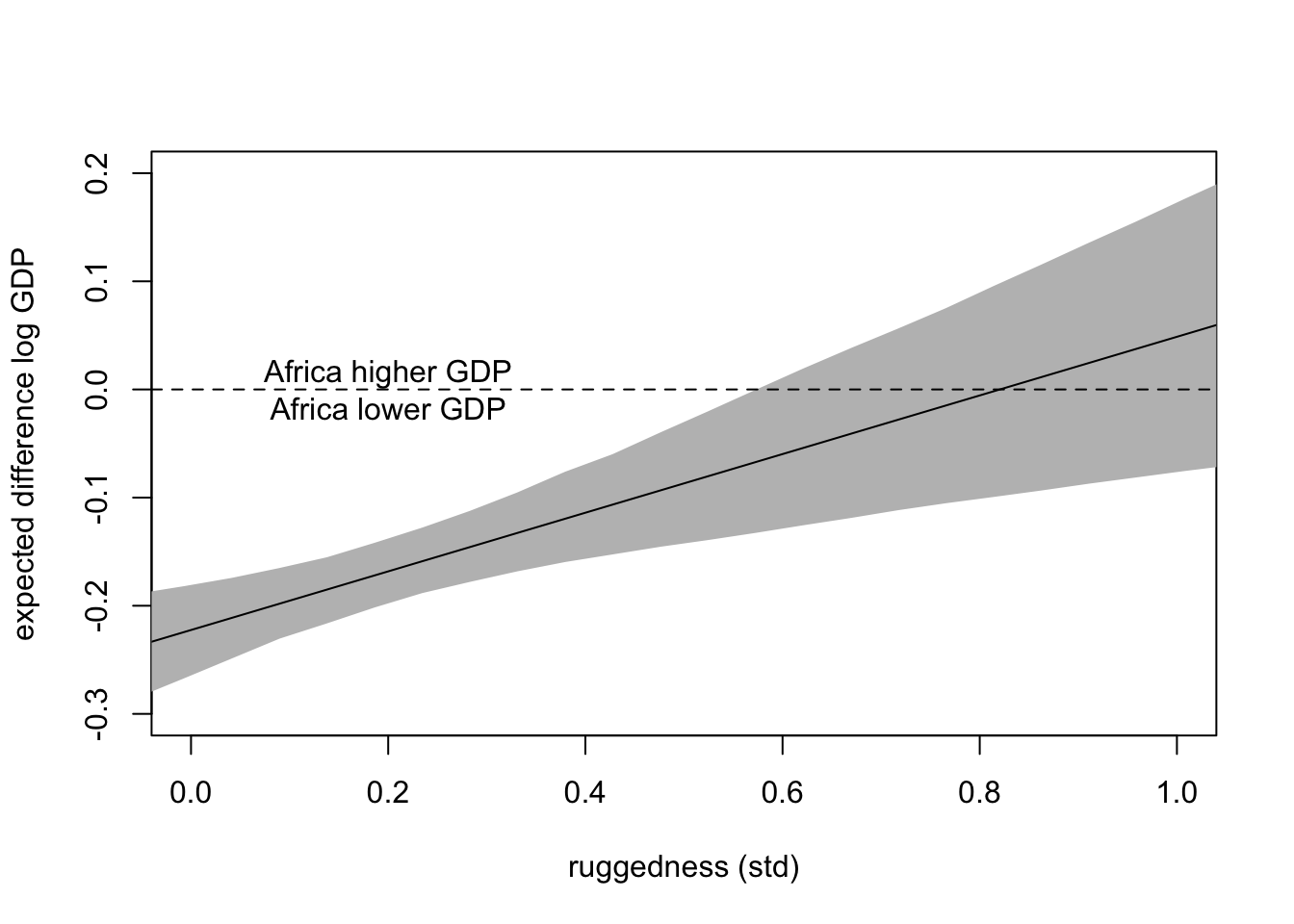
At high ruggedness, being in Africa gives higher than expected GDP.
8.3 Continuous interactions
8.3.1 A winter flower
data(tulips)
d <- tulips
str(d)## 'data.frame': 27 obs. of 4 variables:
## $ bed : Factor w/ 3 levels "a","b","c": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 ...
## $ water : int 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 1 ...
## $ shade : int 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 ...
## $ blooms: num 0 0 111 183.5 59.2 ...8.3.2 the models
Water and Shade work together to create Blooms; \(W \rightarrow B \leftarrow S ; B = f(W,S)\)
- water
\[\beta_{i} \sim \text{Normal}(\mu_{i}, \sigma)\\ \mu_{i} = \alpha + \beta_{W}(W_{i} - \overline{W})\\ \alpha \sim \text{Normal}(0.5,1)\\ \beta_{W} \sim \text{Normal}(0,1)\\ \sigma \sim \text{Exponential}(1)\] - shade
\[\beta_{i} \sim \text{Normal}(\mu_{i}, \sigma)\\ \mu_{i} = \alpha + \beta_{S}(S_{i} - \overline{S})\\ \alpha \sim \text{Normal}(0.5,1)\\ \beta_{S} \sim \text{Normal}(0,1)\\ \sigma \sim \text{Exponential}(1)\] - water + shade
\[\beta_{i} \sim \text{Normal}(\mu_{i}, \sigma)\\ \mu_{i} = \alpha + \beta_{W}(W_{i} - \overline{W}) + \beta_{S}(S_{i} - \overline{S})\\ \alpha \sim \text{Normal}(0.5,1)\\ \beta_{W} \sim \text{Normal}(0,1)\\ \beta_{S} \sim \text{Normal}(0,1)\\ \sigma \sim \text{Exponential}(1)\] - water * shade
$$$$
#center predictors and scale outcome
d$blooms_std <- d$blooms / max(d$blooms)
d$water_cent <- d$water - mean(d$water)
d$shade_cent <- d$shade - mean(d$shade)The \(\alpha\) prior is likely too broad. We need it to be between 0 and 1. How much is outside that?
a <- rnorm(1e4, 0.5, 1); sum(a < 0 | a > 1) / length(a)## [1] 0.623Let’s tighten it
a <- rnorm(1e4, 0.5, 0.25); sum(a < 0 | a > 1) / length(a)## [1] 0.047range of water and shade are each 2 units. range of blooms is one unit. max slopes = 2/1 (0.5) so we can set the prior to 0 with 0.25 sd to get values ranging from -0.5 to 0.5.
#water
m8.4a <- quap(
alist(
blooms_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <- a + bw*water_cent,
a ~ dnorm(0.5,0.25),
bw ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
sigma ~ dexp(1)
), data = d
)
#shade
m8.4b <- quap(
alist(
blooms_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <- a + bs*shade_cent,
a ~ dnorm(0.5,0.25),
bs ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
sigma ~ dexp(1)
), data = d
)
# water + shade
m8.4c <- quap(
alist(
blooms_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <- a + bw*water_cent + bs*shade_cent,
a ~ dnorm(0.5,0.25),
bw ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
bs ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
sigma ~ dexp(1)
), data = d
)
#water * shade
m8.4d <- quap(
alist(
blooms_std ~ dnorm(mu, sigma),
mu <- a + bw*water_cent + bs*shade_cent + bws*water_cent*shade_cent,
a ~ dnorm(0.5,0.25),
bw ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
bs ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
bws ~ dnorm(0, 0.25),
sigma ~ dexp(1)
), data = d
)prior simulations
set.seed(11)
prior_a <- extract.prior(m8.4a) #water
prior_b <- extract.prior(m8.4b) #shade
prior_c <- extract.prior(m8.4c) #water + shade
prior_d <- extract.prior(m8.4d) #water * shade
#set plot
plot(NULL, xlim=c(0,2), ylim=c(0, 1.25), xlab = "Water / shade", ylab = "blooms")
abline(h=min(d$blooms_std), lty = 2)
abline(h=max(d$blooms_std), lty = 2)
#draw lines from prior
water_seq <- seq(from = -1.1, to = 1.1, length.out=30)
shade_seq <- seq(from = -1.1, to = 1.1, length.out=30)
mu_a <- link(m8.4a, post = prior_a, data = data.frame(water_cent=water_seq))
mu_b <- link(m8.4b, post = prior_b, data = data.frame(shade_cent=shade_seq))
mu_c <- link(m8.4c, post = prior_c, data = data.frame(water_cent=water_seq, shade_cent=shade_seq))
mu_d <- link(m8.4d, post = prior_d, data = data.frame(water_cent=water_seq, shade_cent=shade_seq))
#set plot
plot(NULL, xlim=c(-1,1), ylim=c(0, 1.25), xlab = "Water / shade (centered)", ylab = "blooms (std)")
abline(h=min(d$blooms_std), lty = 2)
abline(h=max(d$blooms_std), lty = 2)
for(i in 1:50){
lines(water_seq, mu_a[i,], col=col.alpha('blue',0.3))
}
for(i in 1:50){
lines(water_seq, mu_b[i,], col=col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
for(i in 1:50){
lines(water_seq, mu_c[i,], col=col.alpha('green',0.3))
}
for(i in 1:50){
lines(water_seq, mu_d[i,], col=col.alpha('red',0.3))
}
text(x = -0.75, y = 1.2, label = "Water", col = "blue")
text(x = -0.45, y = 1.2, label = "Shade", col = "black")
text(x = 0, y = 1.2, label = "Water + Shade", col = "green")
text(x = 0.5, y = 1.2, label = "Water * Shade", col = 'red')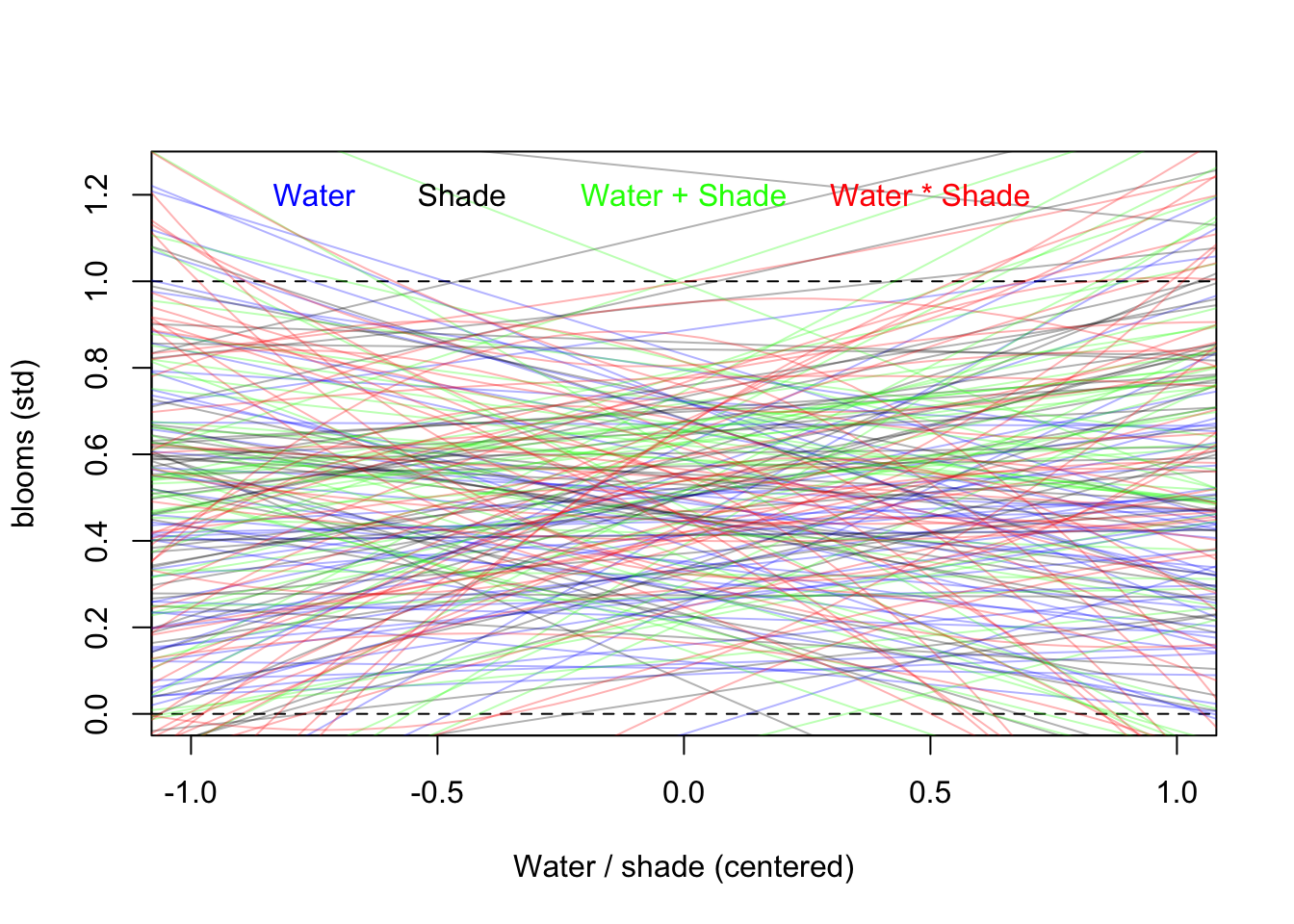
precis(m8.4a)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a 0.3594883 0.03502089 0.3035181 0.4154584
## bw 0.2034854 0.04270338 0.1352371 0.2717336
## sigma 0.1837433 0.02489828 0.1439510 0.2235355precis(m8.4b)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a 0.3611171 0.04403635 0.2907385 0.43149566
## bs -0.1097643 0.05351857 -0.1952973 -0.02423127
## sigma 0.2323701 0.03143809 0.1821260 0.28261427precis(m8.4c)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a 0.3587452 0.03022116 0.3104459 0.40704441
## bw 0.2050352 0.03689240 0.1460741 0.26399641
## bs -0.1125324 0.03687853 -0.1714714 -0.05359337
## sigma 0.1581668 0.02144796 0.1238888 0.19244481precis(m8.4d)## mean sd 5.5% 94.5%
## a 0.3579980 0.02391747 0.31977332 0.39622278
## bw 0.2067288 0.02923282 0.16000910 0.25344849
## bs -0.1134595 0.02922579 -0.16016795 -0.06675103
## bws -0.1431791 0.03567746 -0.20019860 -0.08615967
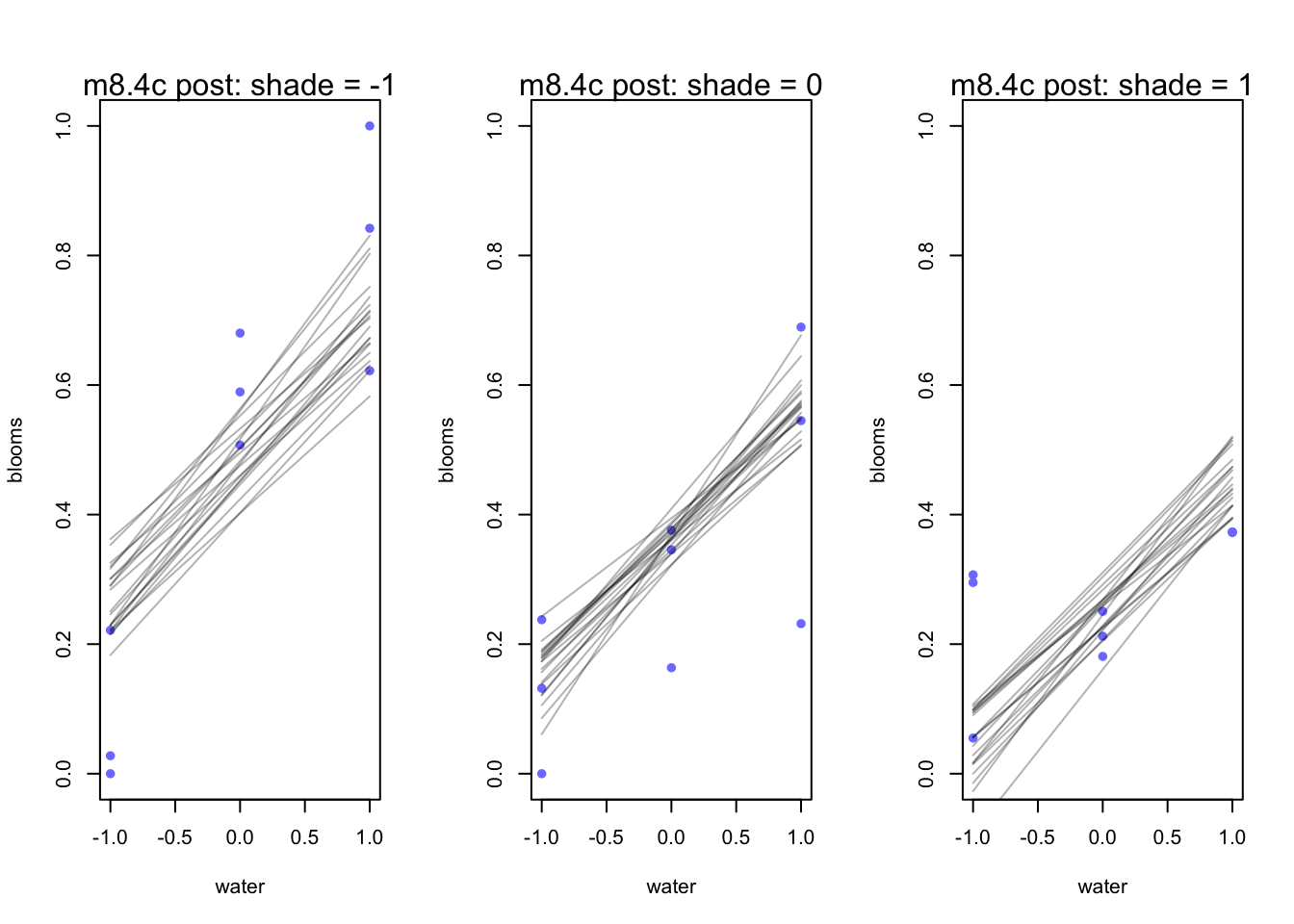
## sigma 0.1248375 0.01693790 0.09776742 0.151907508.3.3 Plotting posterior predictions
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$shade_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$water_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(0,1),
xlab = "water", ylab = "blooms", pch = 16, col = rangi2)
mu <- link(m8.4c, data = data.frame(shade_cent=s, water_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: shade = ", s))
}
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$shade_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$water_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(0,1),
xlab = "water", ylab = "blooms", pch = 16, col = rangi2)
mu <- link(m8.4d, data = data.frame(shade_cent=s, water_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
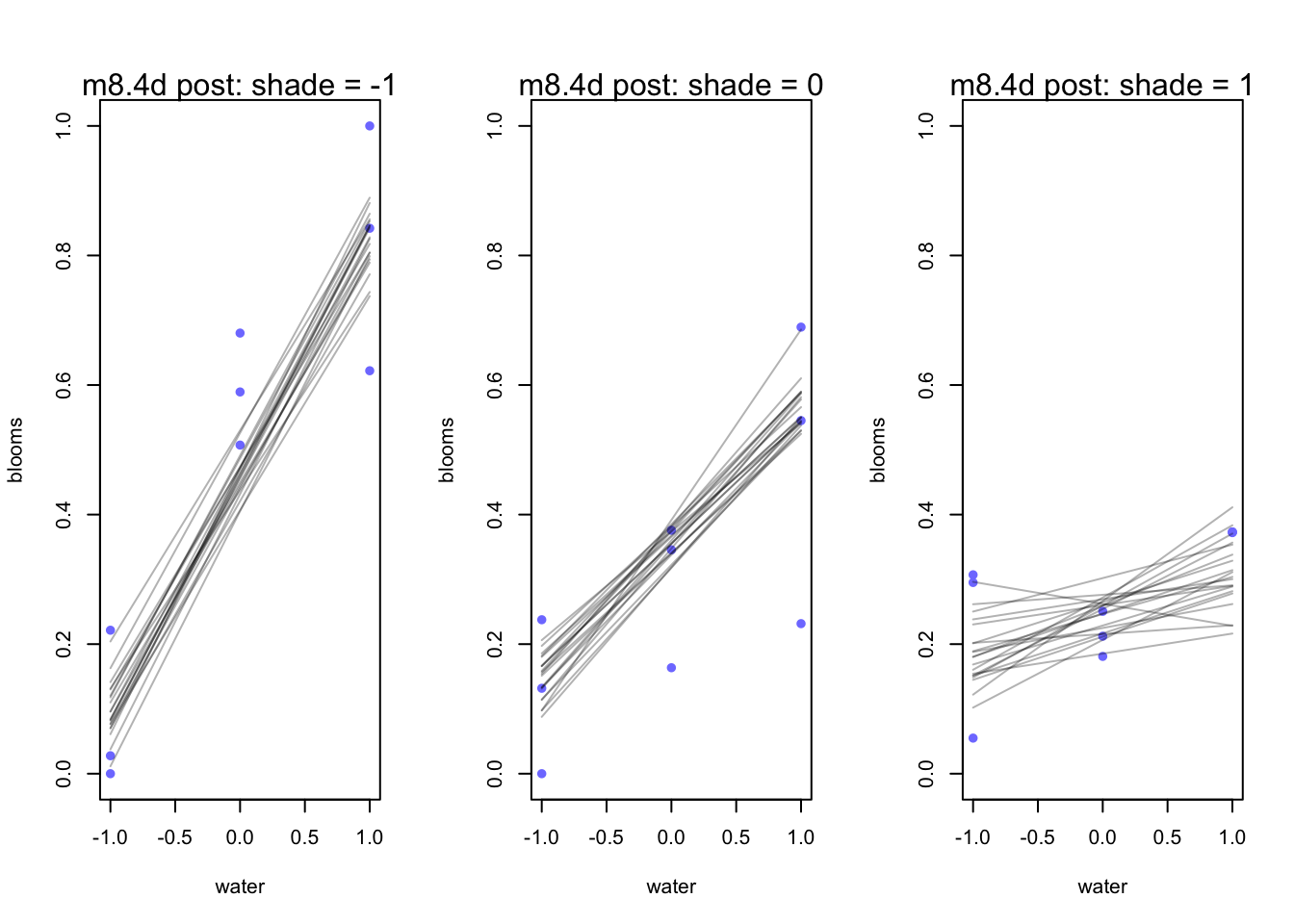
mtext(concat("m8.4d post: shade = ", s))
}
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$water_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$shade_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(0,1),
xlab = "shade", ylab = "blooms", pch = 16, col = rangi2)
mu <- link(m8.4c, data = data.frame(water_cent=s, shade_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
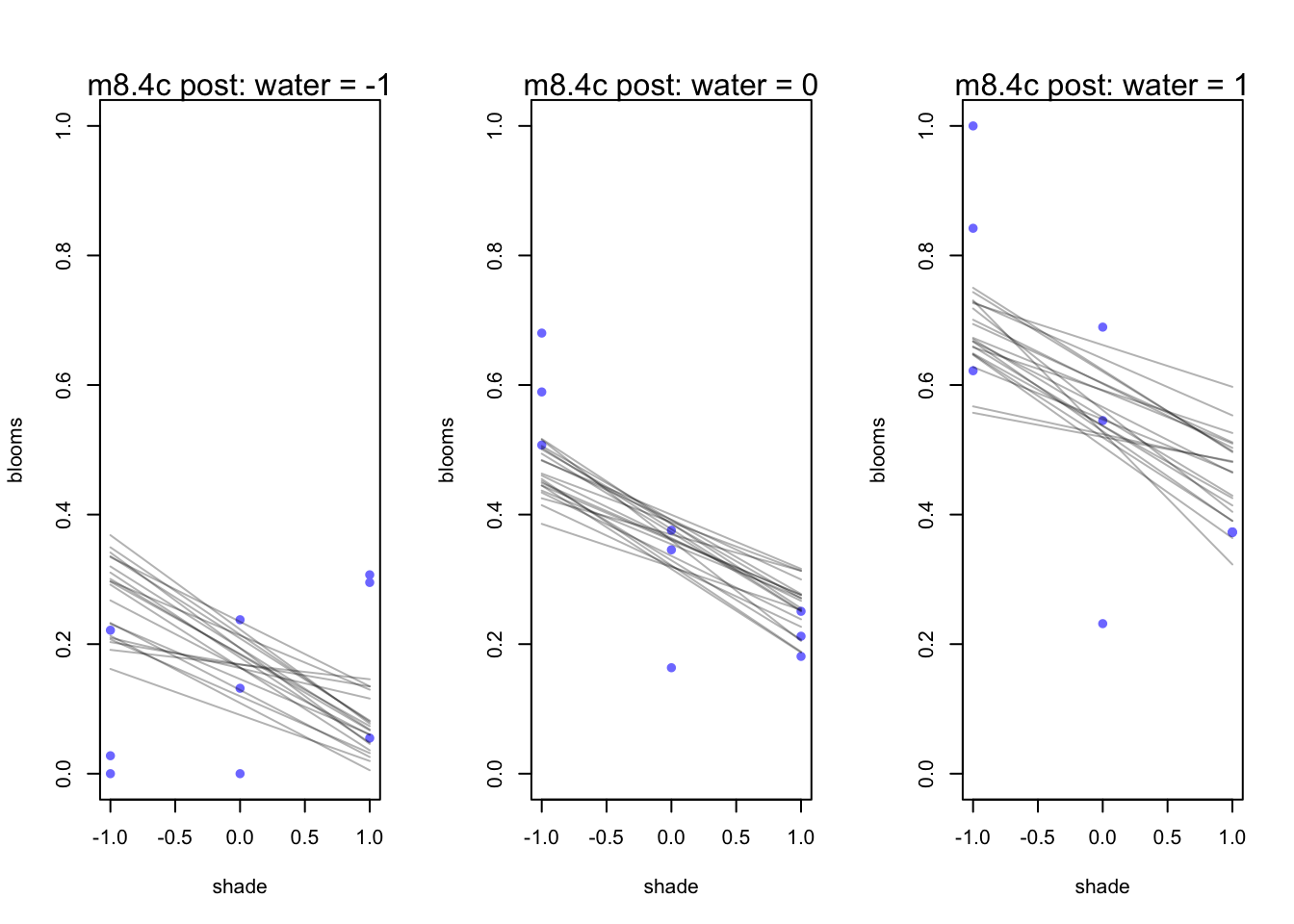
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: water = ", s))
}
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$water_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$shade_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(0,1),
xlab = "shade", ylab = "blooms", pch = 16, col = rangi2)
mu <- link(m8.4d, data = data.frame(water_cent=s, shade_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
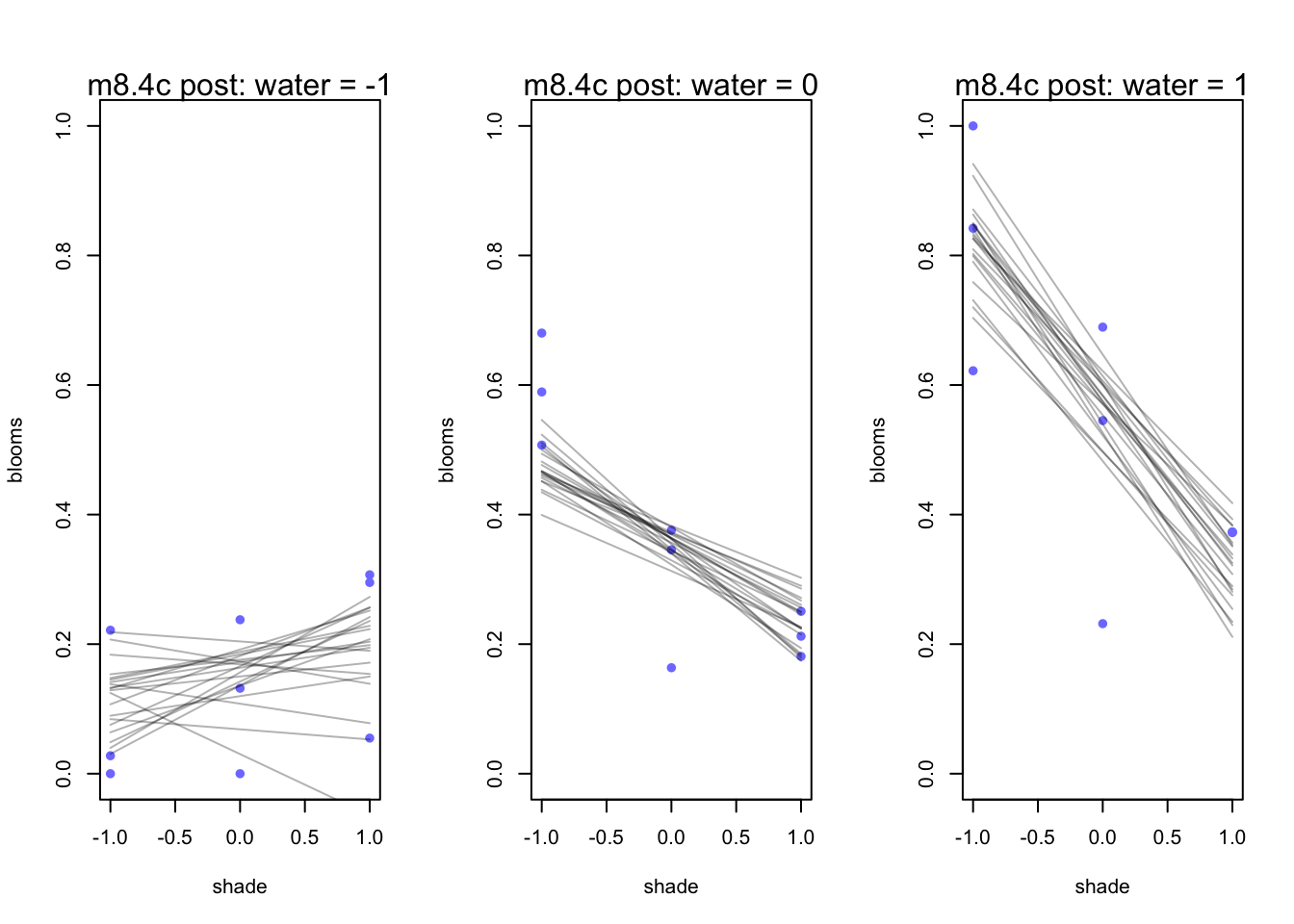
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: water = ", s))
}
8.3.4 Plotting prior predictions
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$shade_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$water_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, type = 'n', xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(-0.5,1.5),
xlab = "water", ylab = "blooms")
mu <- link(m8.4c, post = prior_c, data = data.frame(shade_cent=s, water_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
lines(-1:1, mu[11,], lwd = 2, col = rangi2)
abline(h = 0, lty = 2)
abline(h = 1, lty = 2)
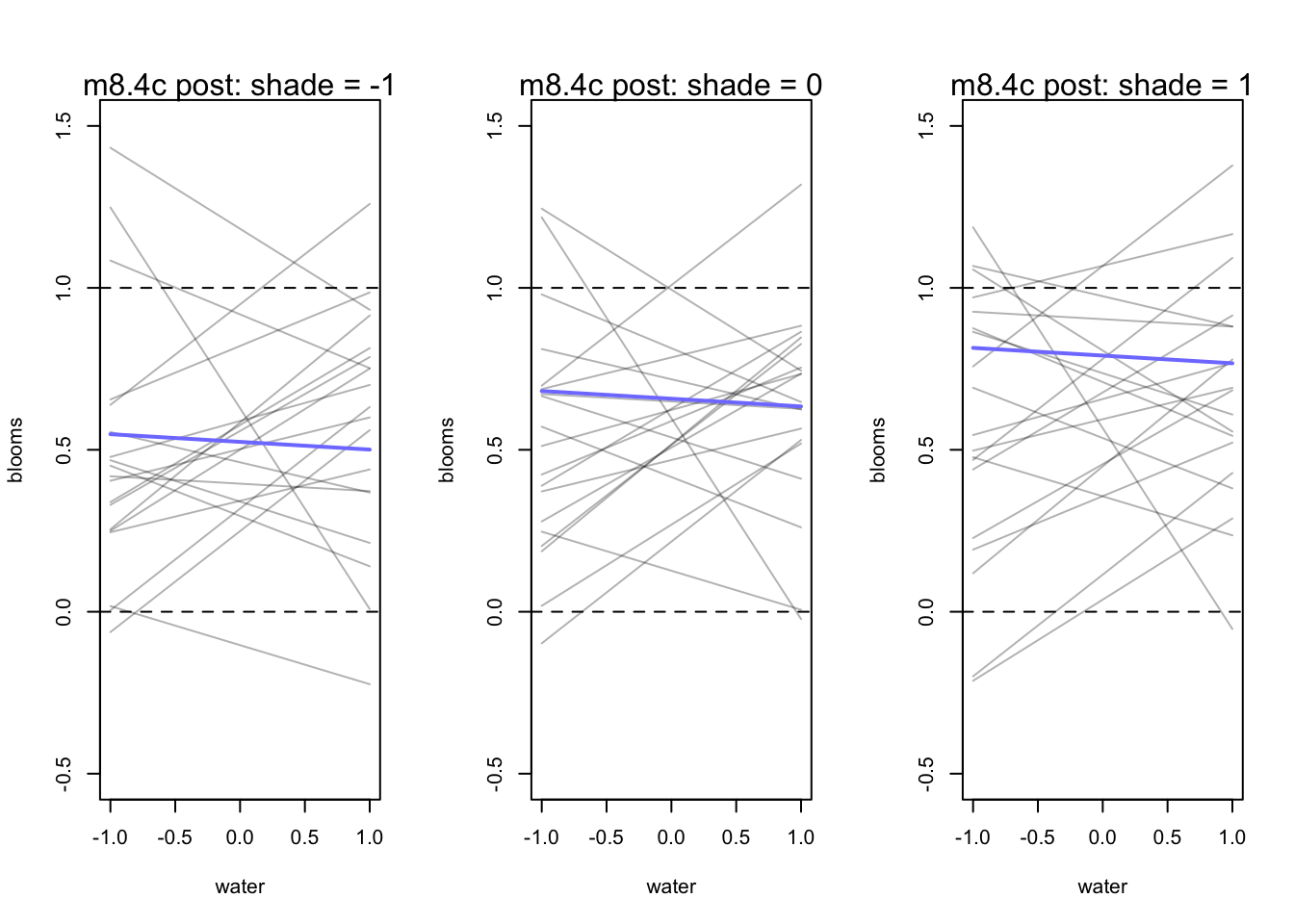
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: shade = ", s))
}
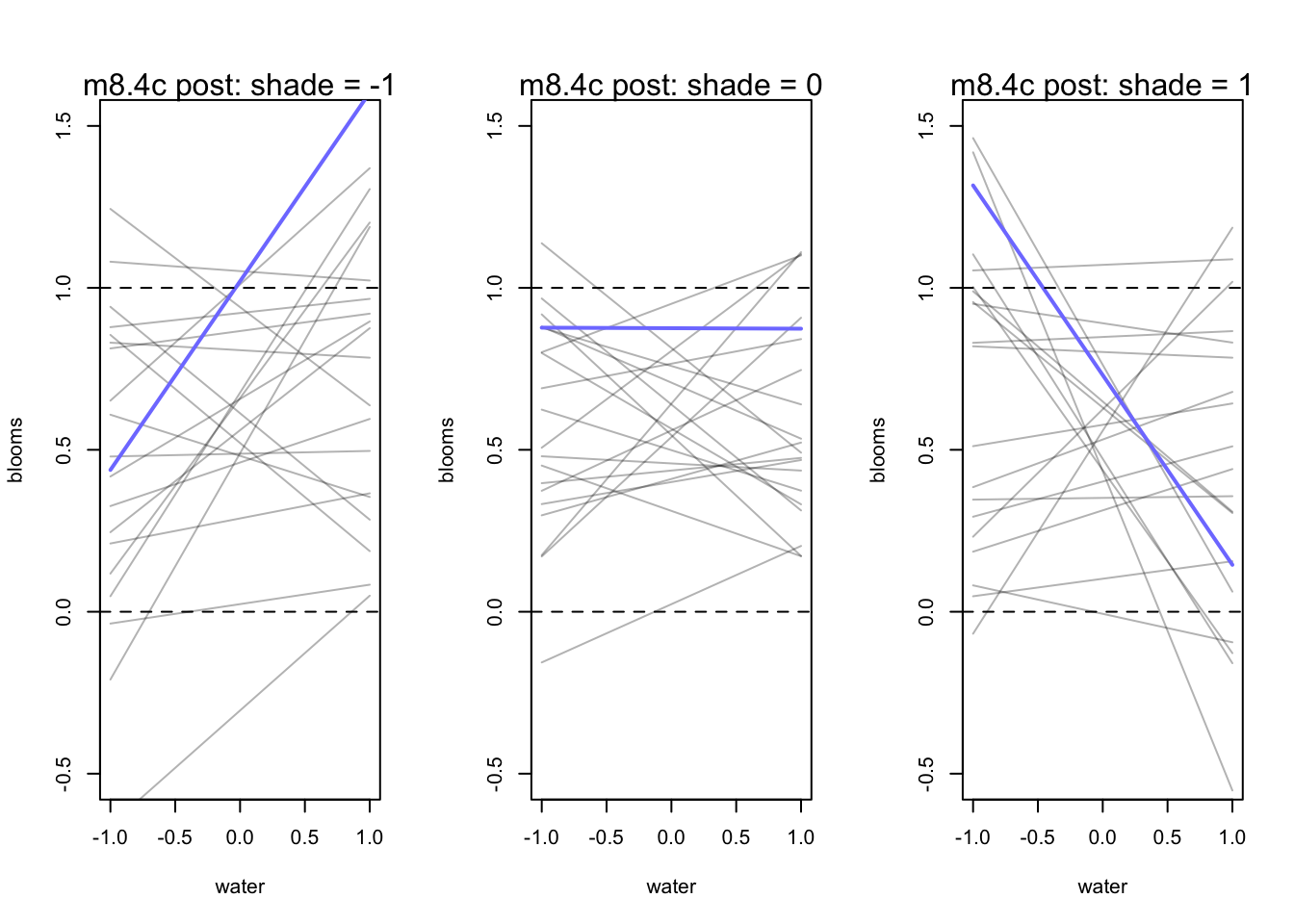
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$shade_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$water_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, type = 'n', xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(-0.5,1.5),
xlab = "water", ylab = "blooms")
mu <- link(m8.4d, post = prior_d, data = data.frame(shade_cent=s, water_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
lines(-1:1, mu[11,], lwd = 2, col = rangi2)
abline(h = 0, lty = 2)
abline(h = 1, lty = 2)
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: shade = ", s))
}
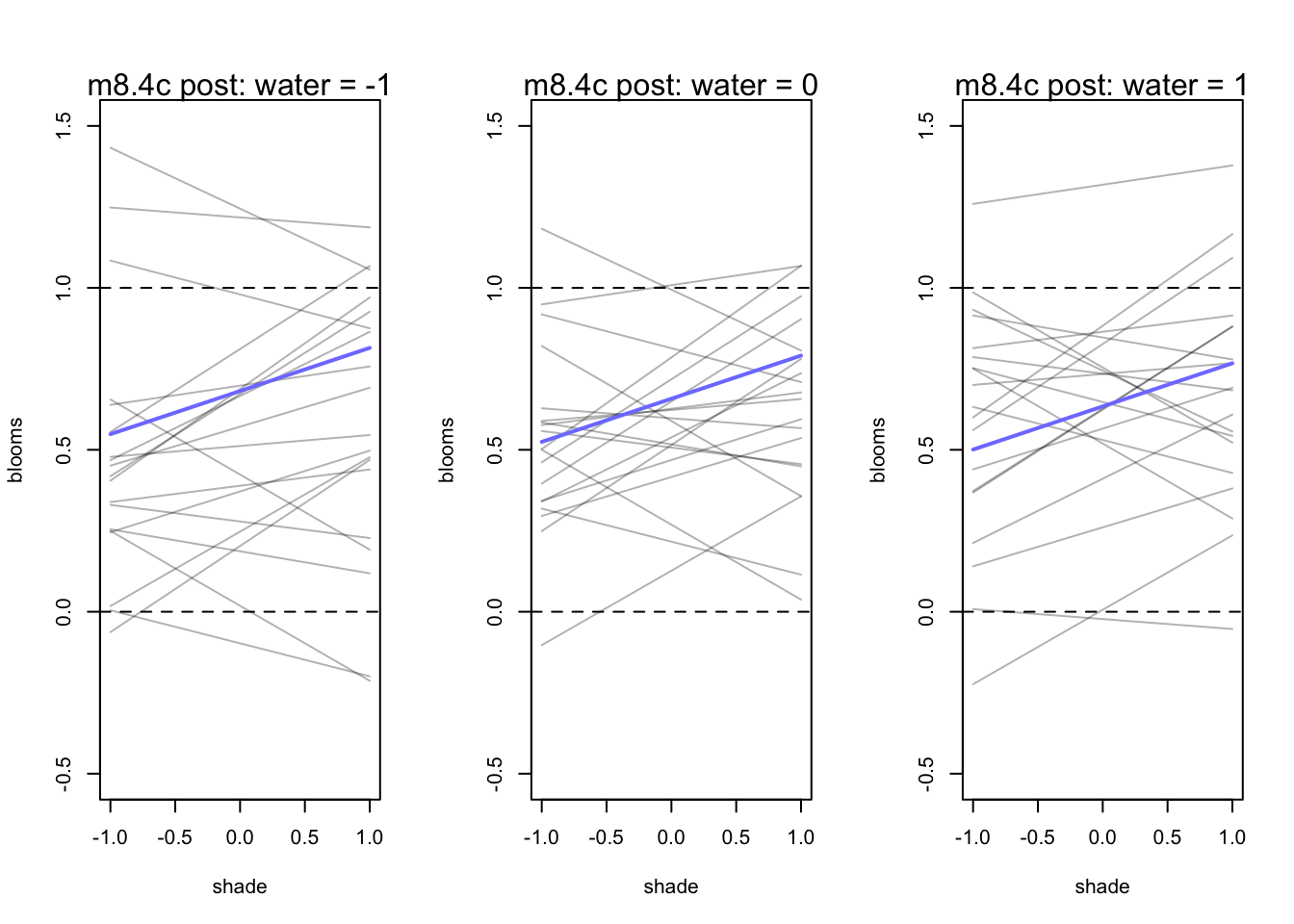
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$water_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$shade_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, type = 'n', xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(-0.5,1.5),
xlab = "shade", ylab = "blooms")
mu <- link(m8.4c, post = prior_c, data = data.frame(water_cent=s, shade_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
lines(-1:1, mu[11,], lwd = 2, col = rangi2)
abline(h = 0, lty = 2)
abline(h = 1, lty = 2)
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: water = ", s))
}
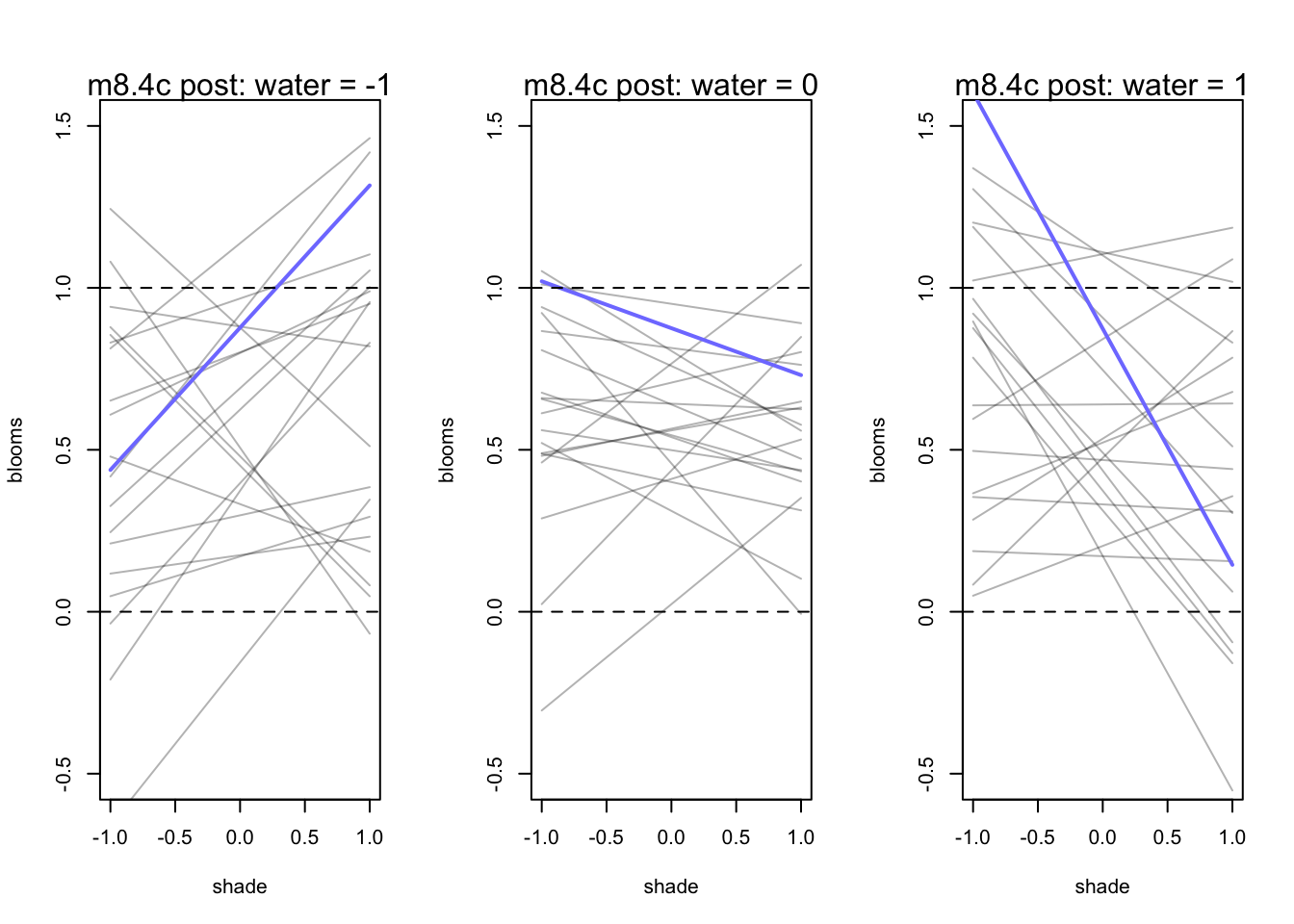
par(mfrow = c(1,3))
for (s in -1:1){
idx <- d[d$water_cent == s,]
plot(x = idx$shade_cent, y = idx$blooms_std, type = 'n', xlim = c(-1,1), ylim = c(-0.5,1.5),
xlab = "shade", ylab = "blooms")
mu <- link(m8.4d, post = prior_d, data = data.frame(water_cent=s, shade_cent = -1:1))
for(i in 1:20){
lines(-1:1, mu[i,], col = col.alpha('black',0.3))
}
lines(-1:1, mu[11,], lwd = 2, col = rangi2)
abline(h = 0, lty = 2)
abline(h = 1, lty = 2)
mtext(concat("m8.4c post: water = ", s))
}