Code
# install.packages('meta')JW Tsai
May 17, 2023
dataset01.csvdataset02.csvdataset03.csvdataset04.csvdataset05.csvdataset06.csvChapter 2: 02-continuous.Rmeta packagemeta package!!! 安裝 meta 套件,需要花一點時間,請先執行這一行! (後面才有辦法執行)
Loading 'meta' package (version 6.5-0).
Type 'help(meta)' for a brief overview.
Readers of 'Meta-Analysis with R (Use R!)' should install
older version of 'meta' package: https://tinyurl.com/dt4y5drs── Attaching core tidyverse packages ──────────────────────── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.4
✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.1
✔ ggplot2 3.4.4 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
✔ lubridate 1.9.3 ✔ tidyr 1.3.0
✔ purrr 1.0.2 ── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors author year Ne Me Se Nc Mc Sc
1 Boner 1988 13 13.54 13.85 13 20.77 21.46
2 Boner 1989 20 15.70 13.10 20 22.70 16.47
3 Chudry 1987 12 21.30 13.10 12 39.70 12.90
4 Comis 1993 12 14.50 12.20 12 31.30 15.10
5 DeBenedictis 1994a 17 14.40 11.10 17 27.40 17.30
6 DeBenedictis 1994b 8 14.80 18.60 8 31.40 20.60
7 DeBenedictis 1995 13 15.70 16.80 13 29.60 18.90
8 Debelic 1986 12 29.83 15.95 12 48.08 15.08
9 Henriksen 1988 12 17.50 13.10 12 47.20 16.47
10 Konig 1987 12 12.00 14.60 12 26.20 12.30
11 Morton 1992 16 15.83 13.43 16 38.36 18.01
12 Novembre 1994f 24 15.42 8.35 24 28.46 13.84
13 Novembre 1994s 19 11.00 12.40 19 26.10 14.90
14 Oseid 1995 20 14.10 9.50 20 28.90 18.00
15 Roberts 1985 9 18.90 17.70 9 38.90 18.90
16 Shaw 1985 8 10.27 7.02 8 34.43 10.96
17 Todaro 1993 13 10.10 8.90 13 23.50 4.00# 2. Calculate mean difference and its standard error for
# study 1 (Boner 1988) of dataset data1:
MD <- with(data1[1, ], Me - Mc)
seMD <- with(data1[1, ], sqrt(Se^2 / Ne + Sc^2 / Nc))
# 3. Print mean difference and limits of 95% confidence
# interval using round function to show only two digits:
round(c(MD, MD + c(-1, 1) * qnorm(1 - (0.05 / 2)) * seMD), 2)[1] -7.23 -21.11 6.65[1] -1.0206 0.3074metacont 的結果兩種寫法是一樣的
Number of observations: o = 26
MD 95%-CI z p-value
-7.23 [-21.11; 6.65] -1.02 0.3074Number of observations: o = 26
MD 95%-CI z p-value
1 -7.23 [-21.11; 6.65] -1.02 0.3074 md se_md ci_lower ci_upper z_score p_value
1 -7.23 7.083861 -21.11411 6.654112 -1.02063 0.3074298 author Ne Me Se Nc Mc Sc
1 Blashki(75%150) 13 6.40 5.40 18 11.40 9.60
2 Hormazabal(86) 17 11.00 8.20 16 19.00 8.20
3 Jacobson(75-100) 10 17.50 8.80 6 23.00 8.80
4 Jenkins(75) 7 12.30 9.90 7 20.00 10.50
5 Lecrubier(100) 73 15.70 10.60 73 18.70 10.60
6 Murphy(100) 26 8.50 11.00 28 14.50 11.00
7 Nandi(97) 17 25.50 24.00 10 53.20 11.20
8 Petracca(100) 11 6.20 7.60 10 10.00 7.60
9 Philipp(100) 105 -8.10 3.90 46 -8.50 5.20
10 Rampello(100) 22 13.40 2.30 19 19.70 1.30
11 Reifler(83) 13 12.50 7.60 15 12.50 7.60
12 Rickels(70) 29 1.99 0.77 39 2.54 0.77
13 Robertson(75) 13 11.00 8.20 13 15.00 8.20
14 Rouillon(98) 78 15.80 6.80 71 17.10 7.20
15 Tan(70) 23 -8.50 8.60 23 -8.30 6.00
16 Tetreault(50-100) 11 51.90 18.50 11 74.30 18.50
17 Thompson(75) 11 8.00 8.10 18 10.00 9.70 Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
14.00 26.00 31.00 53.06 54.00 151.00 # 1. Calculate standardised mean difference (SMD) and
# its standard error (seSMD) for study 1 (Blashki) of
# dataset data2:
N <- with(data2[1, ], Ne + Nc)
SMD <- with(
data2[1, ],
(1 - 3 / (4 * N - 9)) * (Me - Mc) /
sqrt(((Ne - 1) * Se^2 + (Nc - 1) * Sc^2) / (N - 2))
)
seSMD <- with(
data2[1, ],
sqrt(N / (Ne * Nc) + SMD^2 / (2 * (N - 3.94)))
)
# 2. Print standardised mean difference and limits of 95% CI
# interval using round function to show only two digits:
round(c(SMD, SMD + c(-1, 1) * qnorm(1 - (0.05 / 2)) * seSMD), 2)[1] -0.60 -1.33 0.13data2 |>
slice(1) |>
summarise(
n = Ne + Nc,
smd = (1 - 3 / (4 * N - 9)) * (Me - Mc) /
sqrt(((Ne - 1) * Se^2 + (Nc - 1) * Sc^2) / (N - 2)),
se_smd = sqrt(N / (Ne * Nc) + SMD^2 / (2 * (N - 3.94))),
ci_lower = smd - qnorm(1 - (0.05 / 2)) * se_smd,
ci_upper = smd + qnorm(1 - (0.05 / 2)) * se_smd,
z_score = smd/se_smd,
p_value = 2*pnorm(abs(z_score), lower.tail=FALSE)
) n smd se_smd ci_lower ci_upper z_score p_value
1 31 -0.5989891 0.372972 -1.330001 0.1320226 -1.605989 0.1082762Number of observations: o = 31
SMD 95%-CI z p-value
-0.5990 [-1.3299; 0.1319] -1.61 0.1082
Details:
- Hedges' g (bias corrected standardised mean difference; using exact formulae)The fixed effect model is
\[\hat \theta_k = \theta + \sigma_k \epsilon_k,\\ \epsilon_k \overset{\mathrm{iid}}{\sim} N(0,1) \]
The fixed effect estimate \(\hat \theta_F\) and its variance can be calculated using the following quantities:
(考慮一開始的 fixed effect model)
Or in SMD,
[1] -15.514[1] 1.4126[1] -15.5140 1.4126 MD 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
Boner 1988 -7.2300 [-21.1141; 6.6541] 2.8 3.1
Boner 1989 -7.0000 [-16.2230; 2.2230] 6.4 6.6
Chudry 1987 -18.4000 [-28.8023; -7.9977] 5.0 5.3
Comis 1993 -16.8000 [-27.7835; -5.8165] 4.5 4.8
DeBenedictis 1994a -13.0000 [-22.7710; -3.2290] 5.7 5.9
DeBenedictis 1994b -16.6000 [-35.8326; 2.6326] 1.5 1.6
DeBenedictis 1995 -13.9000 [-27.6461; -0.1539] 2.9 3.1
Debelic 1986 -18.2500 [-30.6692; -5.8308] 3.5 3.8
Henriksen 1988 -29.7000 [-41.6068; -17.7932] 3.8 4.1
Konig 1987 -14.2000 [-25.0013; -3.3987] 4.7 4.9
Morton 1992 -22.5300 [-33.5382; -11.5218] 4.5 4.8
Novembre 1994f -13.0400 [-19.5067; -6.5733] 13.0 12.1
Novembre 1994s -15.1000 [-23.8163; -6.3837] 7.1 7.3
Oseid 1995 -14.8000 [-23.7200; -5.8800] 6.8 7.0
Roberts 1985 -20.0000 [-36.9171; -3.0829] 1.9 2.1
Shaw 1985 -24.1600 [-33.1791; -15.1409] 6.7 6.9
Todaro 1993 -13.4000 [-18.7042; -8.0958] 19.3 16.6
Number of studies: k = 17
Number of observations: o = 480
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -15.5140 [-17.8435; -13.1845] -13.05 < 0.0001
Random effects model -15.6436 [-18.1369; -13.1502] -12.30 < 0.0001
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 2.4374 [0.0000; 40.8996]; tau = 1.5612 [0.0000; 6.3953]
I^2 = 8.9% [0.0%; 45.3%]; H = 1.05 [1.00; 1.35]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
17.57 16 0.3496
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tau[1] 0.01992783[1] 0.7079028[1] 2.82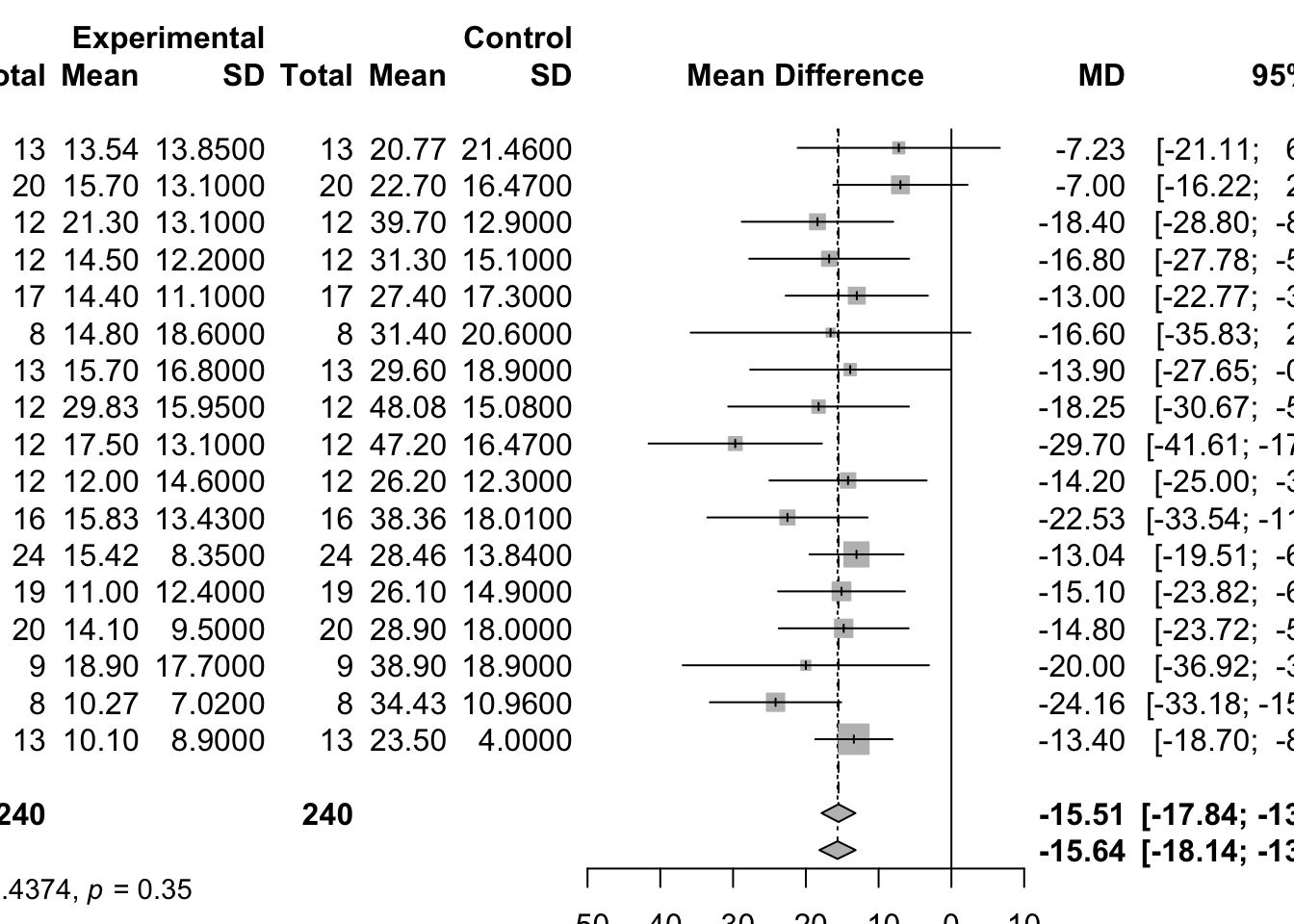
[1] -15.51403 -15.64357[1] -15.51403 -15.64702# 1. Calculate standardised mean difference,
# variance and weights
N <- with(data2, Ne + Nc)
SMD <- with(
data2,
(1 - 3 / (4 * N - 9)) * (Me - Mc) /
sqrt(((Ne - 1) * Se^2 + (Nc - 1) * Sc^2) / (N - 2))
)
varSMD <- with(
data2,
N / (Ne * Nc) + SMD^2 / (2 * (N - 3.94))
)
weight <- 1 / varSMD
# 2. Calculate the inverse variance estimator
round(weighted.mean(SMD, weight), 4)[1] -0.3915[1] 0.0049[1] -0.3918 0.0049 SMD 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
1 -0.5990 [-1.3299; 0.1319] 3.5 5.7
2 -0.9518 [-1.6767; -0.2268] 3.6 5.7
3 -0.5908 [-1.6296; 0.4480] 1.7 4.1
4 -0.7062 [-1.7975; 0.3850] 1.6 3.9
5 -0.2815 [-0.6076; 0.0445] 17.6 8.1
6 -0.5375 [-1.0816; 0.0065] 6.3 6.8
7 -1.3204 [-2.1888; -0.4520] 2.5 4.9
8 -0.4800 [-1.3512; 0.3913] 2.5 4.9
9 0.0918 [-0.2549; 0.4385] 15.6 8.0
10 -3.2433 [-4.2020; -2.2846] 2.0 4.5
11 0.0000 [-0.7427; 0.7427] 3.4 5.6
12 -0.7061 [-1.2020; -0.2103] 7.6 7.1
13 -0.4724 [-1.2536; 0.3088] 3.1 5.4
14 -0.1849 [-0.5071; 0.1372] 18.0 8.2
15 -0.0265 [-0.6045; 0.5515] 5.6 6.6
16 -1.1647 [-2.0819; -0.2476] 2.2 4.7
17 -0.2127 [-0.9651; 0.5397] 3.3 5.6
Number of studies: k = 17
Number of observations: o = 902
SMD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -0.3918 [-0.5286; -0.2551] -5.62 < 0.0001
Random effects model -0.5861 [-0.8709; -0.3014] -4.03 < 0.0001
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.2315 [0.1379; 0.9822]; tau = 0.4812 [0.3714; 0.9911]
I^2 = 72.6% [55.5%; 83.1%]; H = 1.91 [1.50; 2.43]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
58.38 16 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tau
- Hedges' g (bias corrected standardised mean difference; using exact formulae)The random effect model is
\[\hat \theta_k = \theta + \mu_k + \sigma_k \epsilon_k,\\ \epsilon_k \overset{\mathrm{iid}}{\sim} N(0,1), \\ u_k \overset{\mathrm{iid}}{\sim} N(0,\tau^2)\]
ANd the random effects estimate and its variance are given by
The following methods to estimate the between-study variance \(\tau^2\) are available in the metagen and other functions of R package meta (argument method.tau):
method.tau="DL") (課本 2014 年當時 default)method.tau="PM")method.tau="REML") (現在 meta 6.2-1 default)method.tau="ML")method.tau="HS")method.tau="SJ")method.tau="HE")method.tau="EB") SMD 95%-CI %W(random)
1 -0.5990 [-1.3299; 0.1319] 5.7
2 -0.9518 [-1.6767; -0.2268] 5.7
3 -0.5908 [-1.6296; 0.4480] 4.1
4 -0.7062 [-1.7975; 0.3850] 3.9
5 -0.2815 [-0.6076; 0.0445] 8.1
6 -0.5375 [-1.0816; 0.0065] 6.8
7 -1.3204 [-2.1888; -0.4520] 4.9
8 -0.4800 [-1.3512; 0.3913] 4.9
9 0.0918 [-0.2549; 0.4385] 8.0
10 -3.2433 [-4.2020; -2.2846] 4.5
11 0.0000 [-0.7427; 0.7427] 5.6
12 -0.7061 [-1.2020; -0.2103] 7.1
13 -0.4724 [-1.2536; 0.3088] 5.4
14 -0.1849 [-0.5071; 0.1372] 8.2
15 -0.0265 [-0.6045; 0.5515] 6.6
16 -1.1647 [-2.0819; -0.2476] 4.7
17 -0.2127 [-0.9651; 0.5397] 5.6
Number of studies: k = 17
Number of observations: o = 902
SMD 95%-CI t p-value
Random effects model -0.5861 [-0.9514; -0.2209] -3.40 0.0036
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.2315; tau = 0.4812; I^2 = 72.6% [55.5%; 83.1%]; H = 1.91 [1.50; 2.43]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
58.38 16 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Hartung-Knapp adjustment for random effects model (df = 16)
- Hedges' g (bias corrected standardised mean difference; using exact formulae) 95%-CI %W(random)
1 -0.5990 [-1.3299; 0.1319] 5.7
2 -0.9518 [-1.6767; -0.2268] 5.7
3 -0.5908 [-1.6296; 0.4480] 4.1
4 -0.7062 [-1.7975; 0.3850] 3.9
5 -0.2815 [-0.6076; 0.0445] 8.1
6 -0.5375 [-1.0816; 0.0065] 6.8
7 -1.3204 [-2.1888; -0.4520] 4.9
8 -0.4800 [-1.3512; 0.3913] 4.9
9 0.0918 [-0.2549; 0.4385] 8.0
10 -3.2433 [-4.2020; -2.2846] 4.5
11 0.0000 [-0.7427; 0.7427] 5.6
12 -0.7061 [-1.2020; -0.2103] 7.1
13 -0.4724 [-1.2536; 0.3088] 5.4
14 -0.1849 [-0.5071; 0.1372] 8.2
15 -0.0265 [-0.6045; 0.5515] 6.6
16 -1.1647 [-2.0819; -0.2476] 4.7
17 -0.2127 [-0.9651; 0.5397] 5.6
Number of studies: k = 17
95%-CI t p-value
Random effects model (HK) -0.5861 [-0.9514; -0.2209] -3.40 0.0036
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.2315; tau = 0.4812; I^2 = 72.6% [55.5%; 83.1%]; H = 1.91 [1.50; 2.43]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
58.38 16 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Hartung-Knapp adjustment for random effects model (df = 16) MD 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
Boner 1988 -7.2300 [-21.1141; 6.6541] 2.8 3.1
Boner 1989 -7.0000 [-16.2230; 2.2230] 6.4 6.6
Chudry 1987 -18.4000 [-28.8023; -7.9977] 5.0 5.3
Comis 1993 -16.8000 [-27.7835; -5.8165] 4.5 4.8
DeBenedictis 1994a -13.0000 [-22.7710; -3.2290] 5.7 5.9
DeBenedictis 1994b -16.6000 [-35.8326; 2.6326] 1.5 1.6
DeBenedictis 1995 -13.9000 [-27.6461; -0.1539] 2.9 3.1
Debelic 1986 -18.2500 [-30.6692; -5.8308] 3.5 3.8
Henriksen 1988 -29.7000 [-41.6068; -17.7932] 3.8 4.1
Konig 1987 -14.2000 [-25.0013; -3.3987] 4.7 4.9
Morton 1992 -22.5300 [-33.5382; -11.5218] 4.5 4.8
Novembre 1994f -13.0400 [-19.5067; -6.5733] 13.0 12.1
Novembre 1994s -15.1000 [-23.8163; -6.3837] 7.1 7.3
Oseid 1995 -14.8000 [-23.7200; -5.8800] 6.8 7.0
Roberts 1985 -20.0000 [-36.9171; -3.0829] 1.9 2.1
Shaw 1985 -24.1600 [-33.1791; -15.1409] 6.7 6.9
Todaro 1993 -13.4000 [-18.7042; -8.0958] 19.3 16.6
Number of studies: k = 17
Number of observations: o = 480
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -15.5140 [-17.8435; -13.1845] -13.05 < 0.0001
Random effects model -15.6436 [-18.1369; -13.1502] -12.30 < 0.0001
Prediction interval [-19.9360; -11.3511]
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 2.4374 [0.0000; 40.8996]; tau = 1.5612 [0.0000; 6.3953]
I^2 = 8.9% [0.0%; 45.3%]; H = 1.05 [1.00; 1.35]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
17.57 16 0.3496
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tau
- Prediction interval based on t-distribution (df = 15) author year Ne Me Se Nc Mc Sc duration
1 Bontognali 1991 30 0.70 3.76 30 1.27 4.58 <= 3 months
2 Castiglioni 1986 311 0.10 0.21 302 0.20 0.29 <= 3 months
3 Cremonini 1986 21 0.25 0.23 20 0.71 0.29 <= 3 months
4 Grassi 1994 42 0.16 0.29 41 0.45 0.43 <= 3 months
5 Jackson 1984 61 0.11 0.00 60 0.13 0.00 <= 3 months
6 Allegra 1996 223 0.07 0.11 218 0.11 0.14 > 3 months
7 Babolini 1980 254 0.13 0.18 241 0.33 0.27 > 3 months
8 Boman 1983 98 0.20 0.27 105 0.32 0.30 > 3 months
9 Borgia 1981 10 0.05 0.08 9 0.15 0.17 > 3 months
10 Decramer 2005 256 0.10 0.11 267 0.11 0.16 > 3 months
11 Grassi 1976 35 0.14 0.15 34 0.27 0.21 > 3 months
12 Grillage 1985 54 0.10 0.00 55 0.12 0.00 > 3 months
13 Hansen 1994 59 0.11 0.15 70 0.16 0.19 > 3 months
14 Malerba 2004 115 0.06 0.08 119 0.07 0.08 > 3 months
15 McGavin 1985 72 0.42 0.34 76 0.52 0.35 > 3 months
16 Meister 1986 90 0.15 0.15 91 0.20 0.19 > 3 months
17 Meister 1999 122 0.06 0.15 124 0.10 0.15 > 3 months
18 Moretti 2004 63 0.12 0.14 61 0.17 0.17 > 3 months
19 Nowak 1999 147 0.03 0.06 148 0.06 0.12 > 3 months
20 Olivieri 1987 110 0.18 0.31 104 0.33 0.41 > 3 months
21 Parr 1987 243 0.18 0.21 210 0.21 0.21 > 3 months
22 Pela 1999 83 0.17 0.18 80 0.29 0.32 > 3 months
23 Rasmussen 1988 44 0.13 0.21 47 0.14 0.19 > 3 monthsWarning in metacont(Ne, Me, Se, Nc, Mc, Sc, data = data3, studlab =
paste(author, : Note, studies with non-positive values for sd.e or sd.c get no
weight in meta-analysis. MD 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
Bontognali 1991 -0.5700 [-2.6904; 1.5504] 0.0 0.0
Castiglioni 1986 -0.1000 [-0.1402; -0.0598] 4.9 6.2
Cremonini 1986 -0.4600 [-0.6207; -0.2993] 0.3 2.1
Grassi 1994 -0.2900 [-0.4482; -0.1318] 0.3 2.1
Jackson 1984 -0.0200 0.0 0.0
Allegra 1996 -0.0400 [-0.0635; -0.0165] 14.2 6.7
Babolini 1980 -0.2000 [-0.2406; -0.1594] 4.8 6.1
Boman 1983 -0.1200 [-0.1984; -0.0416] 1.3 4.5
Borgia 1981 -0.1000 [-0.2216; 0.0216] 0.5 3.0
Decramer 2005 -0.0100 [-0.0334; 0.0134] 14.3 6.7
Grassi 1976 -0.1300 [-0.2163; -0.0437] 1.1 4.2
Grillage 1985 -0.0200 0.0 0.0
Hansen 1994 -0.0500 [-0.1087; 0.0087] 2.3 5.4
Malerba 2004 -0.0100 [-0.0305; 0.0105] 18.7 6.8
McGavin 1985 -0.1000 [-0.2112; 0.0112] 0.6 3.3
Meister 1986 -0.0500 [-0.0998; -0.0002] 3.2 5.7
Meister 1999 -0.0400 [-0.0775; -0.0025] 5.6 6.3
Moretti 2004 -0.0500 [-0.1049; 0.0049] 2.6 5.5
Nowak 1999 -0.0300 [-0.0516; -0.0084] 16.8 6.8
Olivieri 1987 -0.1500 [-0.2478; -0.0522] 0.8 3.7
Parr 1987 -0.0300 [-0.0688; 0.0088] 5.2 6.2
Pela 1999 -0.1200 [-0.2001; -0.0399] 1.2 4.4
Rasmussen 1988 -0.0100 [-0.0925; 0.0725] 1.2 4.3
Number of studies: k = 21
Number of observations: o = 5055
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -0.0455 [-0.0544; -0.0367] -10.06 < 0.0001
Random effects model -0.0812 [-0.1085; -0.0538] -5.82 < 0.0001
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.0027 [0.0000; 0.0123]; tau = 0.0524 [0.0000; 0.1111]
I^2 = 85.5% [79.1%; 89.9%]; H = 2.63 [2.19; 3.15]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
138.08 20 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tauWarning in metacont(Ne, Me, Se, Nc, Mc, Sc, data = data3, studlab =
paste(author, : Note, studies with non-positive values for sd.e or sd.c get no
weight in meta-analysis.Warning in metacont(x$n.e[sel], x$mean.e[sel], x$sd.e[sel], x$n.c[sel], : Note,
studies with non-positive values for sd.e or sd.c get no weight in
meta-analysis.
Warning in metacont(x$n.e[sel], x$mean.e[sel], x$sd.e[sel], x$n.c[sel], : Note,
studies with non-positive values for sd.e or sd.c get no weight in
meta-analysis. MD 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random) duration
Bontognali 1991 -0.5700 [-2.6904; 1.5504] 0.0 0.0 <= 3 months
Castiglioni 1986 -0.1000 [-0.1402; -0.0598] 4.9 6.2 <= 3 months
Cremonini 1986 -0.4600 [-0.6207; -0.2993] 0.3 2.1 <= 3 months
Grassi 1994 -0.2900 [-0.4482; -0.1318] 0.3 2.1 <= 3 months
Jackson 1984 -0.0200 0.0 0.0 <= 3 months
Allegra 1996 -0.0400 [-0.0635; -0.0165] 14.2 6.7 > 3 months
Babolini 1980 -0.2000 [-0.2406; -0.1594] 4.8 6.1 > 3 months
Boman 1983 -0.1200 [-0.1984; -0.0416] 1.3 4.5 > 3 months
Borgia 1981 -0.1000 [-0.2216; 0.0216] 0.5 3.0 > 3 months
Decramer 2005 -0.0100 [-0.0334; 0.0134] 14.3 6.7 > 3 months
Grassi 1976 -0.1300 [-0.2163; -0.0437] 1.1 4.2 > 3 months
Grillage 1985 -0.0200 0.0 0.0 > 3 months
Hansen 1994 -0.0500 [-0.1087; 0.0087] 2.3 5.4 > 3 months
Malerba 2004 -0.0100 [-0.0305; 0.0105] 18.7 6.8 > 3 months
McGavin 1985 -0.1000 [-0.2112; 0.0112] 0.6 3.3 > 3 months
Meister 1986 -0.0500 [-0.0998; -0.0002] 3.2 5.7 > 3 months
Meister 1999 -0.0400 [-0.0775; -0.0025] 5.6 6.3 > 3 months
Moretti 2004 -0.0500 [-0.1049; 0.0049] 2.6 5.5 > 3 months
Nowak 1999 -0.0300 [-0.0516; -0.0084] 16.8 6.8 > 3 months
Olivieri 1987 -0.1500 [-0.2478; -0.0522] 0.8 3.7 > 3 months
Parr 1987 -0.0300 [-0.0688; 0.0088] 5.2 6.2 > 3 months
Pela 1999 -0.1200 [-0.2001; -0.0399] 1.2 4.4 > 3 months
Rasmussen 1988 -0.0100 [-0.0925; 0.0725] 1.2 4.3 > 3 months
Number of studies: k = 21
Number of observations: o = 5055
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -0.0455 [-0.0544; -0.0367] -10.06 < 0.0001
Random effects model -0.0812 [-0.1085; -0.0538] -5.82 < 0.0001
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.0027 [0.0000; 0.0123]; tau = 0.0524 [0.0000; 0.1111]
I^2 = 85.5% [79.1%; 89.9%]; H = 2.63 [2.19; 3.15]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
138.08 20 < 0.0001
Results for subgroups (common effect model):
k MD 95%-CI Q I^2
<= 3 months 4 -0.1310 [-0.1688; -0.0931] 22.43 86.6%
> 3 months 17 -0.0406 [-0.0497; -0.0314] 94.92 83.1%
Test for subgroup differences (common effect model):
Q d.f. p-value
Between groups 20.73 1 < 0.0001
Within groups 117.35 19 < 0.0001
Results for subgroups (random effects model):
k MD 95%-CI tau^2 tau
<= 3 months 4 -0.2763 [-0.4995; -0.0531] 0.0350 0.1871
> 3 months 17 -0.0646 [-0.0900; -0.0391] 0.0020 0.0443
Test for subgroup differences (random effects model):
Q d.f. p-value
Between groups 3.41 1 0.0647
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tau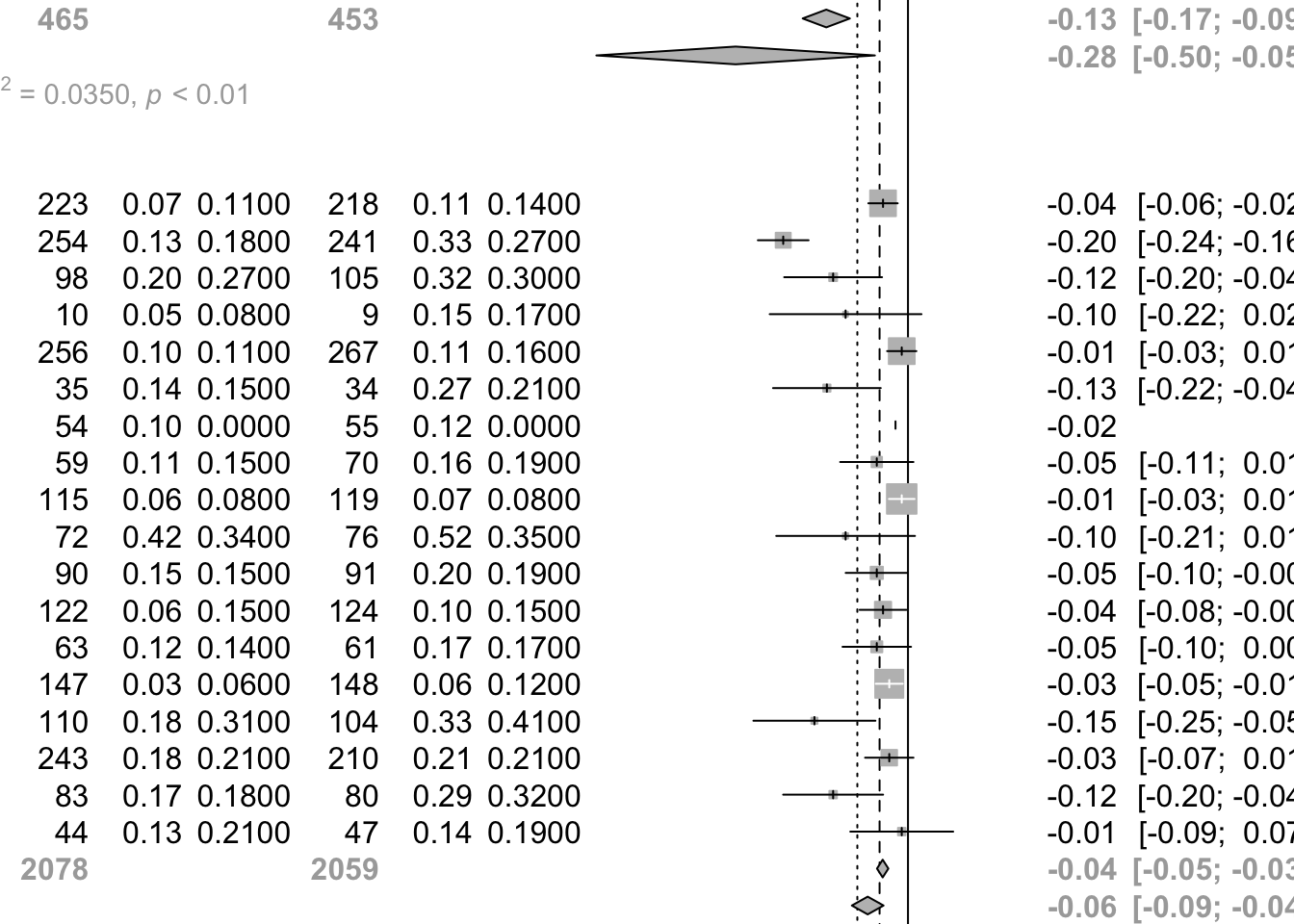
Warning in metacont(Ne, Me, Se, Nc, Mc, Sc, data = data3, subset = duration ==
: Note, studies with non-positive values for sd.e or sd.c get no weight in
meta-analysis.Number of studies: k = 4
Number of observations: o = 918
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -0.1310 [-0.1688; -0.0931] -6.78 < 0.0001
Random effects model -0.2763 [-0.4995; -0.0531] -2.43 0.0153
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.0350 [0.0000; 0.7472]; tau = 0.1871 [0.0000; 0.8644]
I^2 = 86.6% [67.6%; 94.5%]; H = 2.73 [1.76; 4.25]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
22.43 3 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tauNumber of studies: k = 4
Number of observations: o = 918
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -0.1310 [-0.1688; -0.0931] -6.78 < 0.0001
Random effects model -0.2763 [-0.4995; -0.0531] -2.43 0.0153
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.0350 [0.0000; 0.7472]; tau = 0.1871 [0.0000; 0.8644]
I^2 = 86.6% [67.6%; 94.5%]; H = 2.73 [1.76; 4.25]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
22.43 3 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and taumetacor function for meta-analysis of correlations,metainc function for meta-analysis of incidence rate ratios,metaprop function for meta-analysis of single proportions. author year Ne Nc logHR selogHR
1 FCG on CLL 1996 53 52 -0.5920 0.3450
2 Leporrier 2001 341 597 -0.0791 0.0787
3 Rai 2000 195 200 -0.2370 0.1440
4 Robak 2000 133 117 0.1630 0.3120 HR 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
FCG on CLL 1996 0.5532 [0.2813; 1.0878] 3.7 5.8
Leporrier 2001 0.9239 [0.7919; 1.0780] 70.7 59.8
Rai 2000 0.7890 [0.5950; 1.0463] 21.1 27.3
Robak 2000 1.1770 [0.6386; 2.1695] 4.5 7.1
Number of studies: k = 4
HR 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model 0.8865 [0.7787; 1.0093] -1.82 0.0688
Random effects model 0.8736 [0.7388; 1.0331] -1.58 0.1142
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.0061 [0.0000; 0.8546]; tau = 0.0778 [0.0000; 0.9245]
I^2 = 17.2% [0.0%; 87.3%]; H = 1.10 [1.00; 2.81]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
3.62 3 0.3049
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tau author year N mean SE corr
1 Skrabal et al. 1981a 20 -4.5 2.1 0.49
2 Skrabal et al. 1981b 20 -0.5 1.7 0.54
3 MacGregor et al. 1982 23 -4.0 1.9 0.41
4 Khaw and Thom 1982 20 -2.4 1.1 0.83
5 Richards et al. 1984 12 -1.0 3.4 0.50
6 Smith et al. 1985 20 0.0 1.9 0.50
7 Kaplan et al. 1985 16 -5.8 1.6 0.65
8 Zoccali et al. 1985 23 -3.0 3.0 0.50
9 Matlou et al. 1986 36 -3.0 1.5 0.61
10 Barden et al. 1986 44 -1.5 1.4 0.44
11 Poulter and Sever 1986 19 2.0 2.2 0.36
12 Grobbee et al. 1987 40 -0.3 1.5 0.61
13 Krishna et al. 1989 10 -8.0 2.2 0.48
14 Mullen and O'Connor 1990a 24 3.0 2.0 0.50
15 Mullen and O'Connor 1990b 24 1.4 2.0 0.50
16 Patki et al. 1990 37 -13.1 0.7 0.53
17 Valdes et al. 1991 24 -3.0 2.0 0.50
18 Barden et al. 1991 39 -0.6 0.6 0.88
19 Overlack et al. 1991 12 3.0 2.0 0.50
20 Smith et al. 1992 22 -1.7 2.5 0.29
21 Fotherby and Potter 1992 18 -6.0 2.5 0.81 MD 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
Skrabal et al. 1981a -4.5000 [ -8.6159; -0.3841] 2.2 4.7
Skrabal et al. 1981b -0.5000 [ -3.8319; 2.8319] 3.3 4.9
MacGregor et al. 1982 -4.0000 [ -7.7239; -0.2761] 2.6 4.8
Khaw and Thom 1982 -2.4000 [ -4.5560; -0.2440] 7.9 5.2
Richards et al. 1984 -1.0000 [ -7.6639; 5.6639] 0.8 3.8
Smith et al. 1985 0.0000 [ -3.7239; 3.7239] 2.6 4.8
Kaplan et al. 1985 -5.8000 [ -8.9359; -2.6641] 3.7 5.0
Zoccali et al. 1985 -3.0000 [ -8.8799; 2.8799] 1.1 4.1
Matlou et al. 1986 -3.0000 [ -5.9399; -0.0601] 4.2 5.0
Barden et al. 1986 -1.5000 [ -4.2439; 1.2439] 4.9 5.1
Poulter and Sever 1986 2.0000 [ -2.3119; 6.3119] 2.0 4.6
Grobbee et al. 1987 -0.3000 [ -3.2399; 2.6399] 4.2 5.0
Krishna et al. 1989 -8.0000 [-12.3119; -3.6881] 2.0 4.6
Mullen and O'Connor 1990a 3.0000 [ -0.9199; 6.9199] 2.4 4.7
Mullen and O'Connor 1990b 1.4000 [ -2.5199; 5.3199] 2.4 4.7
Patki et al. 1990 -13.1000 [-14.4720; -11.7280] 19.5 5.3
Valdes et al. 1991 -3.0000 [ -6.9199; 0.9199] 2.4 4.7
Barden et al. 1991 -0.6000 [ -1.7760; 0.5760] 26.5 5.4
Overlack et al. 1991 3.0000 [ -0.9199; 6.9199] 2.4 4.7
Smith et al. 1992 -1.7000 [ -6.5999; 3.1999] 1.5 4.4
Fotherby and Potter 1992 -6.0000 [-10.8999; -1.1001] 1.5 4.4
Number of studies: k = 21
MD 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model -3.7146 [-4.3197; -3.1096] -12.03 < 0.0001
Random effects model -2.3808 [-4.7560; -0.0055] -1.96 0.0495
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 27.0262 [8.5264; 41.2225]; tau = 5.1987 [2.9200; 6.4205]
I^2 = 92.5% [89.9%; 94.5%]; H = 3.66 [3.14; 4.25]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
267.24 20 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and tau author year b SE
1 Hiatt and Bawol 1984 0.004340 0.00247
2 Hiatt et al. 1988 0.010900 0.00410
3 Willett t al. 1987 0.028400 0.00564
4 Schatzkin et al. 1987 0.118000 0.04760
5 Harvey et al. 1987 0.012100 0.00429
6 Rosenberg et al. 1982 0.087000 0.02320
7 Webster et al. 1983 0.003110 0.00373
8 Paganini-Hill and Ross 1983 0.000000 0.00940
9 Byers and Funch 1982 0.005970 0.00658
10 Rohan and McMichael 1988 0.047900 0.02050
11 Talamini et al. 1984 0.038900 0.00768
12 O'Connell et al. 1987 0.203000 0.09460
13 Harris and Wynder 1988 -0.006730 0.00419
14 Le et al. 1984 0.011100 0.00481
15 La Vecchia et al. 1985 0.014800 0.00635
16 Begg et al. 1983 -0.000787 0.00867 logRR 95%-CI %W(common) %W(random)
Hiatt and Bawol 1984 0.0043 [-0.0005; 0.0092] 28.5 9.6
Hiatt et al. 1988 0.0109 [ 0.0029; 0.0189] 10.3 8.8
Willett t al. 1987 0.0284 [ 0.0173; 0.0395] 5.5 8.0
Schatzkin et al. 1987 0.1180 [ 0.0247; 0.2113] 0.1 0.5
Harvey et al. 1987 0.0121 [ 0.0037; 0.0205] 9.4 8.7
Rosenberg et al. 1982 0.0870 [ 0.0415; 0.1325] 0.3 1.9
Webster et al. 1983 0.0031 [-0.0042; 0.0104] 12.5 9.0
Paganini-Hill and Ross 1983 0.0000 [-0.0184; 0.0184] 2.0 5.8
Byers and Funch 1982 0.0060 [-0.0069; 0.0189] 4.0 7.4
Rohan and McMichael 1988 0.0479 [ 0.0077; 0.0881] 0.4 2.3
Talamini et al. 1984 0.0389 [ 0.0238; 0.0540] 2.9 6.8
O'Connell et al. 1987 0.2030 [ 0.0176; 0.3884] 0.0 0.1
Harris and Wynder 1988 -0.0067 [-0.0149; 0.0015] 9.9 8.8
Le et al. 1984 0.0111 [ 0.0017; 0.0205] 7.5 8.5
La Vecchia et al. 1985 0.0148 [ 0.0024; 0.0272] 4.3 7.6
Begg et al. 1983 -0.0008 [-0.0178; 0.0162] 2.3 6.2
Number of studies: k = 16
logRR 95%-CI z p-value
Common effect model 0.0082 [0.0056; 0.0108] 6.24 < 0.0001
Random effects model 0.0131 [0.0062; 0.0199] 3.73 0.0002
Quantifying heterogeneity:
tau^2 = 0.0001 [0.0002; 0.0013]; tau = 0.0110 [0.0135; 0.0364]
I^2 = 80.1% [68.5%; 87.4%]; H = 2.24 [1.78; 2.82]
Test of heterogeneity:
Q d.f. p-value
75.31 15 < 0.0001
Details on meta-analytical method:
- Inverse variance method
- DerSimonian-Laird estimator for tau^2
- Jackson method for confidence interval of tau^2 and taumeta 目前版本是 version 6.2-1,如果閱讀 Meta-Analysis with R (Use R!) 遇到問題,可能要安裝舊版本。 https://tinyurl.com/dt4y5drsinstall.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("guido-s/meta", ref = "R-book-first-edition")read.csv() 可以讀取網址,所以read.csv('https://www.uniklinik-freiburg.de/fileadmin/mediapool/08_institute/biometrie-statistik/Dateien/Englisch/Studies_and_Teaching/Educational_Books/Meta-Analysis_with_R/Datasets/dataset01.csv')可以讀取 dataset01.csv ,依此類推。
R version 4.3.1 (2023-06-16)
Platform: aarch64-apple-darwin20 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Sonoma 14.2.1
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.3-arm64/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.3-arm64/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib; LAPACK version 3.11.0
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
time zone: Asia/Taipei
tzcode source: internal
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] repr_1.1.6 lubridate_1.9.3 forcats_1.0.0 stringr_1.5.1
[5] dplyr_1.1.4 purrr_1.0.2 readr_2.1.4 tidyr_1.3.0
[9] tibble_3.2.1 ggplot2_3.4.4 tidyverse_2.0.0 meta_6.5-0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] utf8_1.2.4 generics_0.1.3 xml2_1.3.5
[4] stringi_1.8.3 lattice_0.21-8 hms_1.1.3
[7] lme4_1.1-34 digest_0.6.33 magrittr_2.0.3
[10] timechange_0.2.0 evaluate_0.23 grid_4.3.1
[13] CompQuadForm_1.4.3 fastmap_1.1.1 jsonlite_1.8.8
[16] Matrix_1.6-1.1 fansi_1.0.6 scales_1.3.0
[19] numDeriv_2016.8-1.1 cli_3.6.2 rlang_1.1.2
[22] munsell_0.5.0 splines_4.3.1 base64enc_0.1-3
[25] withr_2.5.2 yaml_2.3.8 tools_4.3.1
[28] tzdb_0.4.0 nloptr_2.0.3 minqa_1.2.6
[31] metafor_4.4-0 colorspace_2.1-0 mathjaxr_1.6-0
[34] boot_1.3-28.1 vctrs_0.6.5 R6_2.5.1
[37] lifecycle_1.0.4 htmlwidgets_1.6.4 MASS_7.3-60
[40] pkgconfig_2.0.3 pillar_1.9.0 gtable_0.3.4
[43] glue_1.6.2 Rcpp_1.0.11 xfun_0.41
[46] tidyselect_1.2.0 rstudioapi_0.15.0 knitr_1.45
[49] htmltools_0.5.7 nlme_3.1-162 rmarkdown_2.25
[52] compiler_4.3.1 metadat_1.2-0