1 What is an option?
1.1 Understand Option by Insurance
We can start learning option by anaology using the instrument we are more familiar with in daily life: insurance. Option is a contingent insurance.
| insurance | insurance_examples | option | option_examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| insured asset | house | underlying asset | BAC stock trading at $27.86 |
| insured period | 12 months | time to expiration | 3 months |
| value insured | $300,000 | strike price | $25 put |
| deductible | $3,000 | out-of-money | 2.86/27 |
| insurance premiums | $1,500 | option preimums | $1 |
| loss ratio | 10% | probability of profit | 60% |
| claims | yes,then pay out claim no keep the preimum | expired | seller obligations and buyer rights |
| reinsurance | buy insurance from another company to protect from carastrophic losses such as flood, thunderstorm | hedge | buy far OTM to protect against large market losses 1987 black monday |
1.2 Understand Option by Real Estate
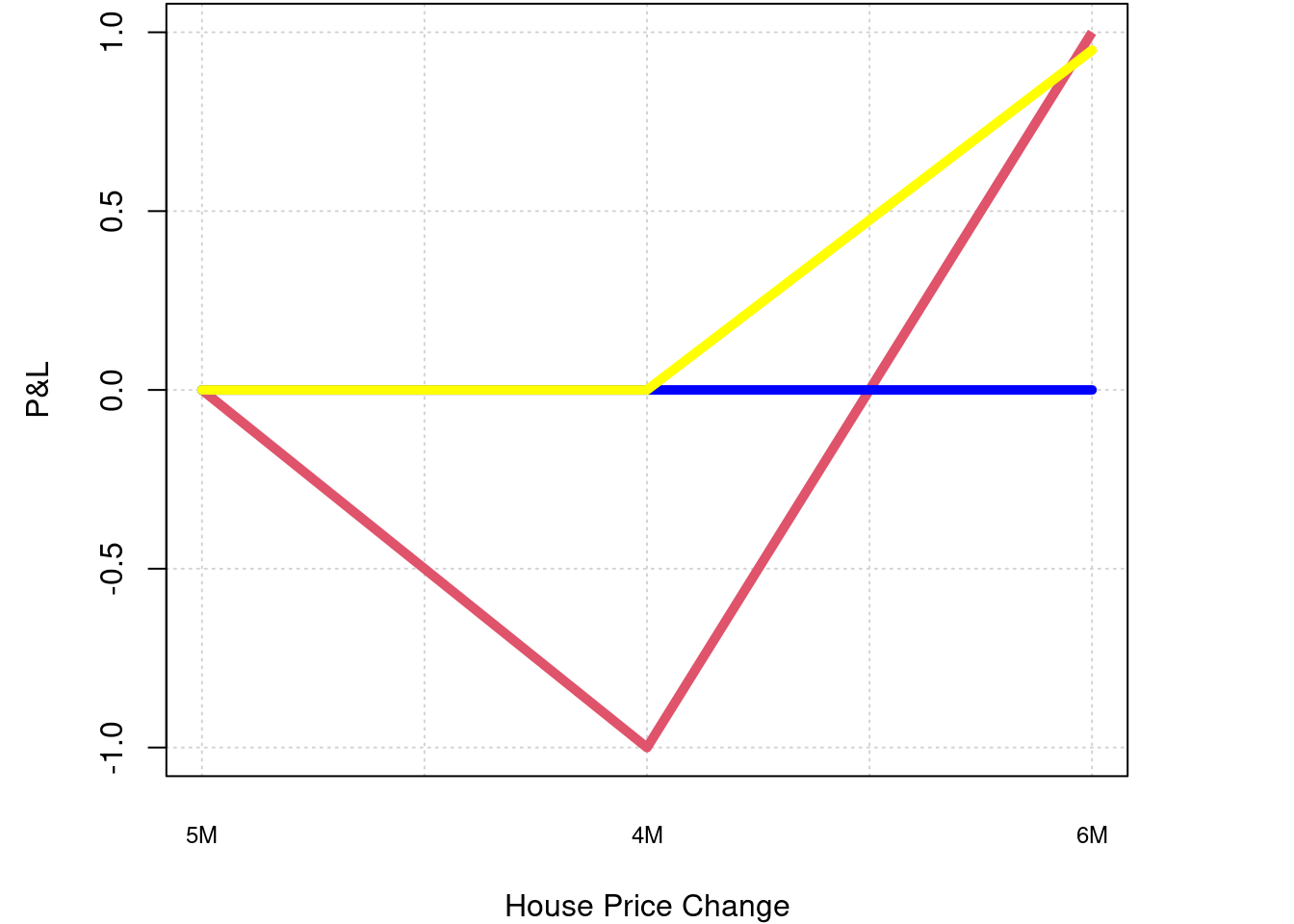
Imagine you want to buy a 5 million house, there are three ways:
- you pay all by cash(red).
- you buy will 10X leverage paying 500k as down payment(blue).
- you buy off-the-plan property paying a deposit of 50k accomplished by the right of being able to buy it in the price of 500k(yellow).
Now if the housing price decrease to 400k and increase to 600k on the market after your decision. Below is your P&L chart under those three circumstances, the last one is an option trading.
1.3 Understand Option by Bond
If bond price is a discount of future cash flow, then option price is a discount of future volatility.