Chapter 5 Multi-Layer NN Model
This chapter presents the final functional-programming model. Uses functions to define ‘neural networks’, perform forward propagation, and perform gradient descent. Section at the end details future components that could be added in.
5.1 Generate Data
For now, having 3 inputs and combining them to create y, with a random error term. Would like to tweak the setup eventually.
## create data:
m <- 1000
n_1_manual <- 3
n_L_manual <- 1
# initialize Xs
X <- data.frame(X1 = runif(n = m, min = -10, max = 10),
X2 = rnorm(n = m, mean = 0, sd = 10),
X3 = rexp(n = m, rate = 1)) %>%
as.matrix(nrow = m,
ncol = n_1_manual)
# get response
Y <- X[, 1] + 10 * sin(X[, 2])^2 + 10 * X[, 3] + rnorm(n = 1000)
# fix dims according to NN specs
X <- t(X)
Y <- t(Y)5.2 Functions
5.2.1 Link Functions
## Specify Link Functions & Derivatives
get_link <- function(type = "sigmoid") {
if (type == "identity") {
# identity
g <- function(x) {x}
} else if (type == "sigmoid") {
# sigmoid
g <- function(x) {1 / (1 + exp(-x))}
} else if (type == "relu") {
# ReLU
g <- function(x) {x * as.numeric(x > 0)}
} else (return(NULL))
return(g)
}
get_link_prime <- function(type = "sigmoid") {
if (type == "identity") {
# identity [FIX]
g_prime <- function(x) {
## there's probably a better way to do this
b <- x / x
b[is.nan(x/x)] <- 1
return(b)
}
} else if (type == "sigmoid") {
# sigmoid
g_prime <- function(x) {exp(-x) / (1 + exp(-x))^2}
} else if (type == "relu") {
# ReLU
g_prime <- function(x) {as.numeric(x > 0)}
} else (return(NULL))
return(g_prime)
}5.2.2 Loss Functions
## Specify Loss Functions & Derivatives
get_loss_function <- function(type = "squared_error") {
if (type == "squared_error") {
loss <- function(y_hat, y) {sum((y_hat - y)^2)}
} else if (type == "cross_entropy") {
loss <- function(y_hat, y) {sum(y * log(y_hat))}
} else (return(NULL))
return(loss)
}
get_loss_prime <- function(type = "squared_error") {
if (type == "squared_error") {
loss_prime <- function(y_hat, y) {sum(2 * (y_hat - y))}
} else if (type == "cross_entropy") {
loss_prime <- function(y_hat, y) {999}
} else (return(NULL))
return(loss_prime)
}5.2.3 Misc Helpers
## creates a list of n empty lists
create_lists <- function(n) {
out <- list()
for (i in 1:n) {
out[[i]] <- list()
}
return(out)
}
## friendlier diag() function
diag_D <- function(x) {
if (length(x) == 1) {
out <- x
} else {
out <- diag(as.numeric(x))
}
return(out)
}
generate_layer_sizes <- function(X,
Y,
hidden_layer_sizes) {
return(c(nrow(X), hidden_layer_sizes, nrow(Y)))
}initialize_NN <- function(layer_sizes,
activation_function = "sigmoid",
last_activation_function = "identity",
lower_bound = 0,
upper_bound = 1) {
n <- layer_sizes
## initialize parameter matrices
W <- list()
b <- list()
## could vectorize w/ mapply()
for (l in 2:length(n)) {
W[[l]] <- matrix(data = runif(n = n[l - 1] * n[l],
min = lower_bound,
max = upper_bound),
nrow = n[l],
ncol = n[l - 1])
b[[l]] <- matrix(data = runif(n = n[l],
min = lower_bound,
max = upper_bound),
nrow = n[l],
ncol = 1)
}
## return
return(list(W = W,
b = b,
activation_function = activation_function,
last_activation_function = last_activation_function))
}5.2.4 Forward Propagation
NN_output <- function(X,
NN_obj) {
L <- length(NN_obj$W)
## if X is one obs, input will be a vector so dim will be null
m <- ifelse(is.null(ncol(X)),
1,
ncol(X))
g <- get_link(NN_obj$activation_function)
g_last <- get_link(NN_obj$last_activation_function)
a <- list()
a[[1]] <- X
for (l in 2:(L - 1)) {
a[[l]] <- g(NN_obj$W[[l]] %*% a[[l - 1]] + matrix(data = rep(x = NN_obj$b[[l]],
times = m),
ncol = m))
}
a[[L]] <- g_last(NN_obj$W[[L]] %*% a[[L - 1]] + matrix(data = rep(x = NN_obj$b[[L]],
times = m),
ncol = m))
return(a[[L]])
}5.2.5 Gradient Descent Iteration
GD_iter <- function(NN_obj,
X,
Y,
rho = 1,
verbose = FALSE,
very_verbose = FALSE) {
L <- length(NN_obj$W)
## if X is one obs, input will be a vector so dim will be null
m <- ifelse(is.null(ncol(X)),
1,
ncol(X))
## get links
g <- get_link(NN_obj$activation_function)
g_prime <- get_link_prime(NN_obj$activation_function)
g_last <- get_link(NN_obj$last_activation_function)
g_last_prime <- get_link_prime(NN_obj$last_activation_function)
z <- create_lists(L)
a <- create_lists(L)
D <- create_lists(L)
delta <- create_lists(L)
del_W <- create_lists(L)
del_b <- create_lists(L)
## gradient descent
for (i in 1:m) {
## forward
a[[1]][[i]] <- X[, i]
for (l in 2:(L - 1)) {
z[[l]][[i]] <- NN_obj$W[[l]] %*% a[[l - 1]][[i]] + NN_obj$b[[l]]
a[[l]][[i]] <- g(z[[l]][[i]])
D[[l]][[i]] <- diag_D(g_prime(z[[l]][[i]]))
if (very_verbose == TRUE) {print(paste0("Forward: obs ", i, " - layer ", l))}
}
## last layer
z[[L]][[i]] <- NN_obj$W[[L]] %*% a[[L - 1]][[i]] + NN_obj$b[[L]]
a[[L]][[i]] <- g_last(z[[L]][[i]])
D[[L]][[i]] <- diag_D(g_last_prime(z[[L]][[i]]))
## backward
# eventually fix to match with loss function
delta[[L]][[i]] <- D[[L]][[i]] %*% (a[[L]][[i]] - Y[, i])
for (l in (L - 1):2) {
delta[[l]][[i]] <- D[[l]][[i]] %*% t(NN_obj$W[[l + 1]]) %*% delta[[l + 1]][[i]]
if (very_verbose == TRUE) {print(paste0("Backward: obs ", i, " - layer ", l))}
}
for (l in 2:L) {
del_W[[l]][[i]] <- delta[[l]][[i]] %*% t(a[[l - 1]][[i]])
del_b[[l]][[i]] <- delta[[l]][[i]]
if (very_verbose == TRUE) {print(paste0("del: obs ", i, " - layer ", l))}
}
if ((verbose == TRUE) & (i %% 100 == 0)) {print(paste("obs", i, "/", m))}
}
## update parameters
# get averages
## del_W is a list where each element represents a layer
## in each layer, there's a list representing the layer's result for that obs
## here we collapse the results by taking the sum of our gradients
del_W_all <- lapply(X = del_W,
FUN = Reduce,
f = "+") %>%
lapply(X = .,
FUN = function(x) x / m)
del_b_all <- lapply(X = del_b,
FUN = Reduce,
f = "+") %>%
lapply(X = .,
FUN = function(x) x / m)
# apply gradient
W_out <- mapply(FUN = function(A, del_A) {A - rho * del_A},
A = NN_obj$W,
del_A = del_W_all)
b_out <- mapply(FUN = function(A, del_A) {A - rho * del_A},
A = NN_obj$b,
del_A = del_b_all)
## return a new NN object
return(list(W = W_out,
b = b_out,
activation_function = NN_obj$activation_function,
last_activation_function = NN_obj$last_activation_function))
}5.2.6 Perform Gradient Descent
GD_perform <- function(X,
Y,
init_NN_obj,
rho = 0.01,
loss_function = "squared_error",
threshold = 1,
max_iter = 100,
print_descent = FALSE) {
## setup
done_decreasing <- FALSE
objective_function <- get_loss_function(type = loss_function)
iteration_outputs <- list()
output_objectives <- numeric()
iteration_input <- init_NN_obj
iter <- 1
initial_objective <- objective_function(y = Y,
y_hat = NN_output(X = X,
NN_obj = init_NN_obj))
if (print_descent == TRUE) {
print(paste0("iter: ", 0, "; obj: ", round(initial_objective, 1)))
}
while ((!done_decreasing) & (iter < max_iter)) {
## get input loss
in_objective <- objective_function(y = Y,
y_hat = NN_output(X = X,
NN_obj = iteration_input))
## iterate
iteration_output <- GD_iter(NN_obj = iteration_input,
X = X,
Y = Y,
rho = rho,
verbose = FALSE,
very_verbose = FALSE)
## outputs
out_objective <- objective_function(y = Y,
y_hat = NN_output(X = X,
NN_obj = iteration_output))
iteration_input <- iteration_output
iteration_outputs[[iter]] <- iteration_output
output_objectives[[iter]] <- out_objective
if (print_descent == TRUE) {
print(paste0("iter: ", iter, "; obj: ", round(out_objective, 1)))
}
iter <- iter + 1
## evaluate
if (abs(in_objective - out_objective) < threshold) {
done_decreasing <- TRUE
}
}
return(list(final_NN = iteration_output,
intermediate_NN = iteration_outputs,
output_objectives = output_objectives,
initial_objective = initial_objective,
params = list(rho = rho,
loss_function = loss_function,
initial_NN = init_NN_obj)))
}5.2.7 Summary Functions
GD_plot <- function(GD_obj) {
data.frame(x = 1:length(GD_obj$output_objectives),
y = GD_obj$output_objectives) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = x,
y = y)) +
geom_point() +
theme_bw() +
labs(x = "Iteration",
y = "Loss")
}
GD_summary <- function(GD_obj,
print_summary = TRUE) {
## num iter
num_iter <- length(GD_obj$output_objectives)
## loss improvement
initial_objective <- GD_obj$initial_objective %>% round(1)
final_objective <- last(GD_obj$output_objectives) %>% round(1)
loss_improvement_ratio <- (final_objective / initial_objective) %>% round(4)
if (print_summary == TRUE) {
## prints
cat(paste0("Gradient Descent Summary:", "\n",
" |", "\n",
" | Number of Iterations: ", num_iter, "\n",
" |", "\n",
" | Initial Objective: ", initial_objective, "\n",
" | Final Objective: ", final_objective, "\n",
" | Ratio: ", loss_improvement_ratio, "\n", "\n"))
cat(paste0("----------------------------------------", "\n",
"Initial W:", "\n", "\n"))
print(GD_obj$params$initial_NN$W[-1])
cat(paste0("----------------------------------------", "\n",
"Final W:", "\n", "\n"))
print(GD_obj$final_NN$W[-1])
cat(paste0("----------------------------------------", "\n",
"Initial b:", "\n", "\n"))
print(GD_obj$params$initial_NN$b[-1])
cat(paste0("----------------------------------------", "\n",
"Final b:", "\n", "\n"))
print(GD_obj$final_NN$b[-1])
}
return(list(num_iter = num_iter,
initial_objective = initial_objective,
final_objective = final_objective,
loss_improvement_ratio = loss_improvement_ratio))
}5.3 Test
## initialize NN
init_NN <- initialize_NN(layer_sizes = generate_layer_sizes(X = X,
Y = Y,
hidden_layer_sizes = c(3)),
activation_function = "relu",
last_activation_function = "identity",
lower_bound = 0,
upper_bound = 1)
## train NN
GD_NN <- GD_perform(X = X,
Y = Y,
init_NN_obj = init_NN,
rho = 0.001,
loss_function = "squared_error",
threshold = 100,
max_iter = 1000,
print_descent = FALSE)
final_NN <- GD_NN$final_NN
## Summaries
NN_sum <- GD_summary(GD_obj = GD_NN)## Gradient Descent Summary:
## |
## | Number of Iterations: 144
## |
## | Initial Objective: 238990.1
## | Final Objective: 16834.7
## | Ratio: 0.0704
##
## ----------------------------------------
## Initial W:
##
## [[1]]
## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] 0.3028608 0.5655690 0.95437084
## [2,] 0.5046878 0.5267906 0.02262433
## [3,] 0.2724395 0.2474305 0.40767901
##
## [[2]]
## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] 0.4370019 0.7598625 0.8453935
##
## ----------------------------------------
## Final W:
##
## [[1]]
## X1 X2 X3
## [1,] -0.001842719 0.03928530 1.9846660
## [2,] 0.695969115 0.12981398 0.7693617
## [3,] 0.187358905 -0.08034643 2.0087035
##
## [[2]]
## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] 1.699798 1.149463 2.324604
##
## ----------------------------------------
## Initial b:
##
## [[1]]
## [,1]
## [1,] 0.007521215
## [2,] 0.425427183
## [3,] 0.791751480
##
## [[2]]
## [,1]
## [1,] 0.3945866
##
## ----------------------------------------
## Final b:
##
## [[1]]
## [,1]
## [1,] 0.2857580
## [2,] 0.6093002
## [3,] 1.2551489
##
## [[2]]
## [,1]
## [1,] 0.7948542GD_plot(GD_NN)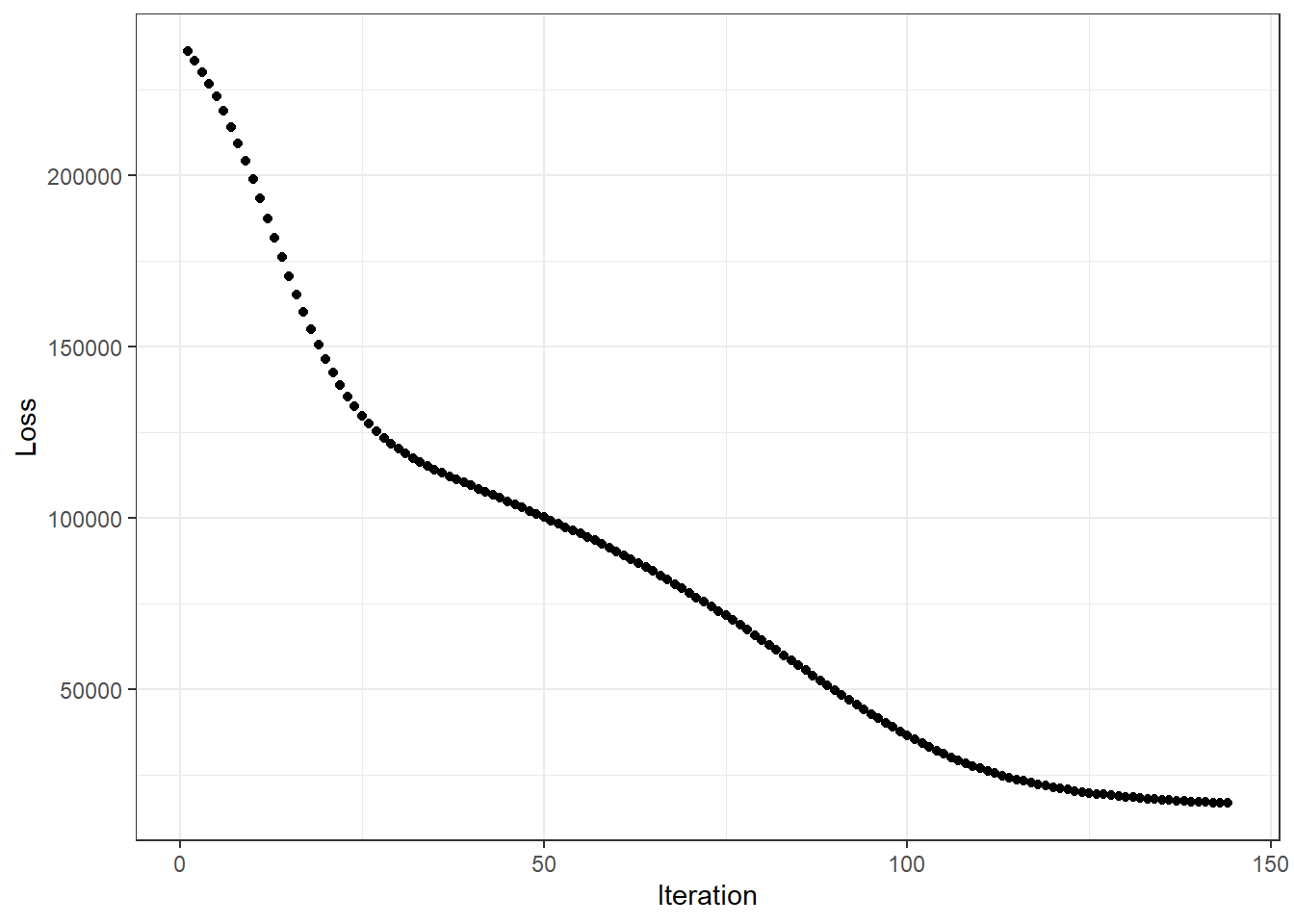
5.4 Next Steps
In the future:
- need some sort of divergence check / pick ‘best so far’ output
- vis for gradient descent — pick 2 vars and for every combo of those 2, plot the objective function
- vis for gradient descent — show the evolution of the var through gradient descent over iterations
- NN overall vis & perhaps animation
- multi-dimensional output (cat / 1-hot)
- different cost functions (softmax squared-error & cross-entropy)
- ‘from scratch’ from scratch — mmult and maybe further lol
- get ‘best-case’ / perfect objective function (if data creation process known)
- stochastic gradient descent, minibatches (what gets passed down to GD_iter from GD_perform)
- regularization methods & CV-validation