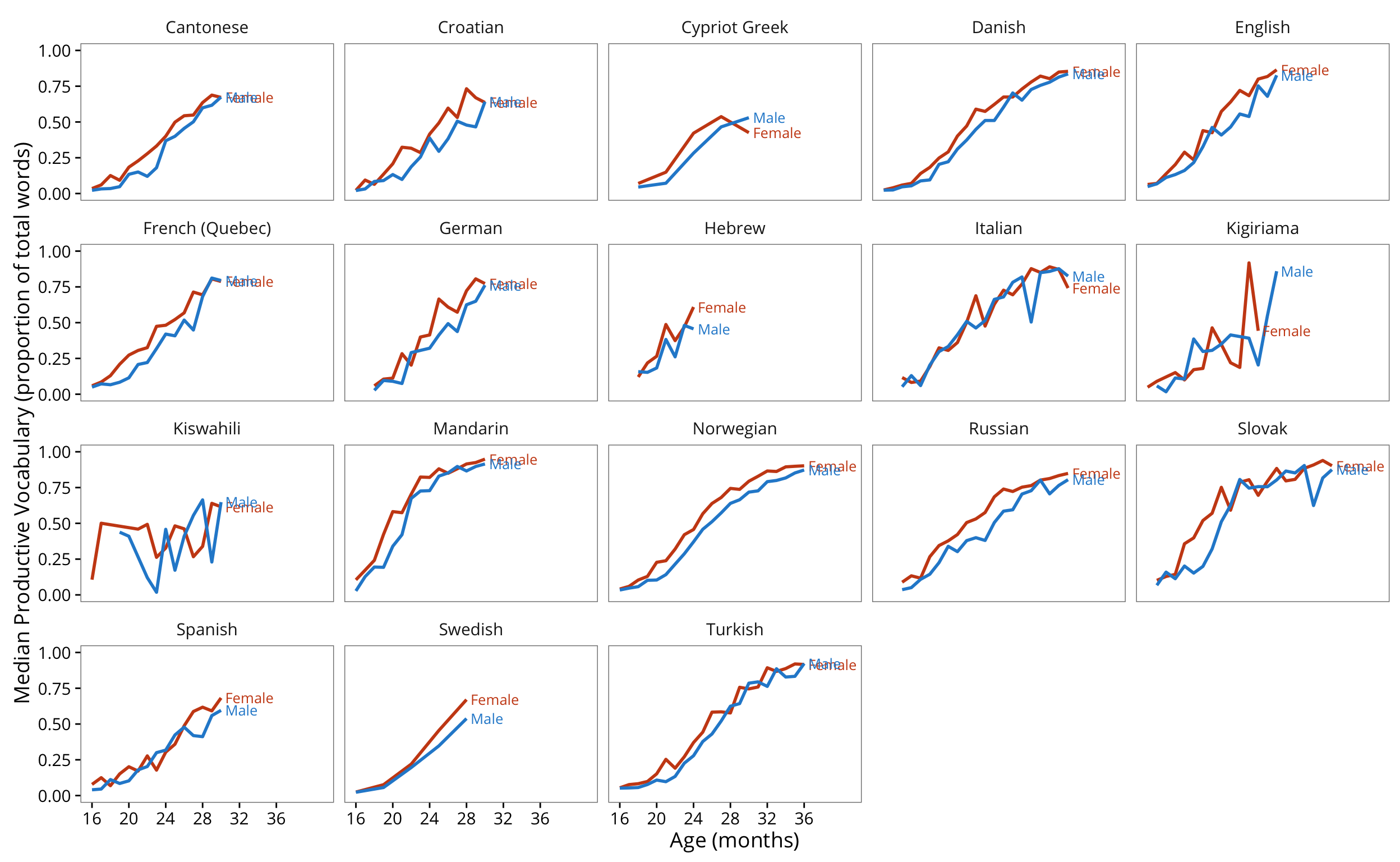
3.2 Gender
This analysis examines how vocabulary development differs by children’s reported gender, replicating and extending the results of:
Eriksson, M., Marschik, P. B., Tulviste, T., Almgren, M., Pérez Pereira, M., Wehberg, S., … Gallego, C. (2012). Differences between girls and boys in emerging language skills: Evidence from 10 language communities. British Journal of Developmental Psychology 30, 326–343.
Get administration data and filter to administrations of Words & Sentences that have sex/gender coded.
vocab_admins <- get_administration_data() %>%
select(data_id, language, form, age, sex, production) %>%
filter(form == "WS", !is.na(sex))Get item information to find the number of items on each language’s form.
num_words <- get_item_data() %>%
filter(form == "WS", type == "word") %>%
group_by(language) %>%
summarise(n = n())Normalize productive vocabulary size as a proportion of items and calculate median vocabulary size for each language, sex/gender, and age.
vocab_data <- vocab_admins %>%
left_join(num_words) %>%
mutate(production = as.numeric(production) / n) %>%
group_by(language, sex, age) %>%
summarise(median = median(production))Plot vocabulary size over age by gender.
min_age <- min(vocab_data$age)
max_age <- max(vocab_data$age)
ggplot(filter(vocab_data),
aes(x = age, y = median, colour = sex, label = sex)) +
facet_wrap(~language) +
geom_line(size = 1) +
scale_colour_solarized(guide = FALSE) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = seq(min_age, max_age, 4),
limits = c(min_age, max_age + 5),
name = "Age (months)") +
ylab("Median Productive Vocabulary (proportion of total words)") +
ylim(c(0, 1)) +
geom_dl(method = list(dl.trans(x = x + 0.1), "last.points",
fontfamily = font, cex = 0.8))