Chapter 5 R Data and information visualization
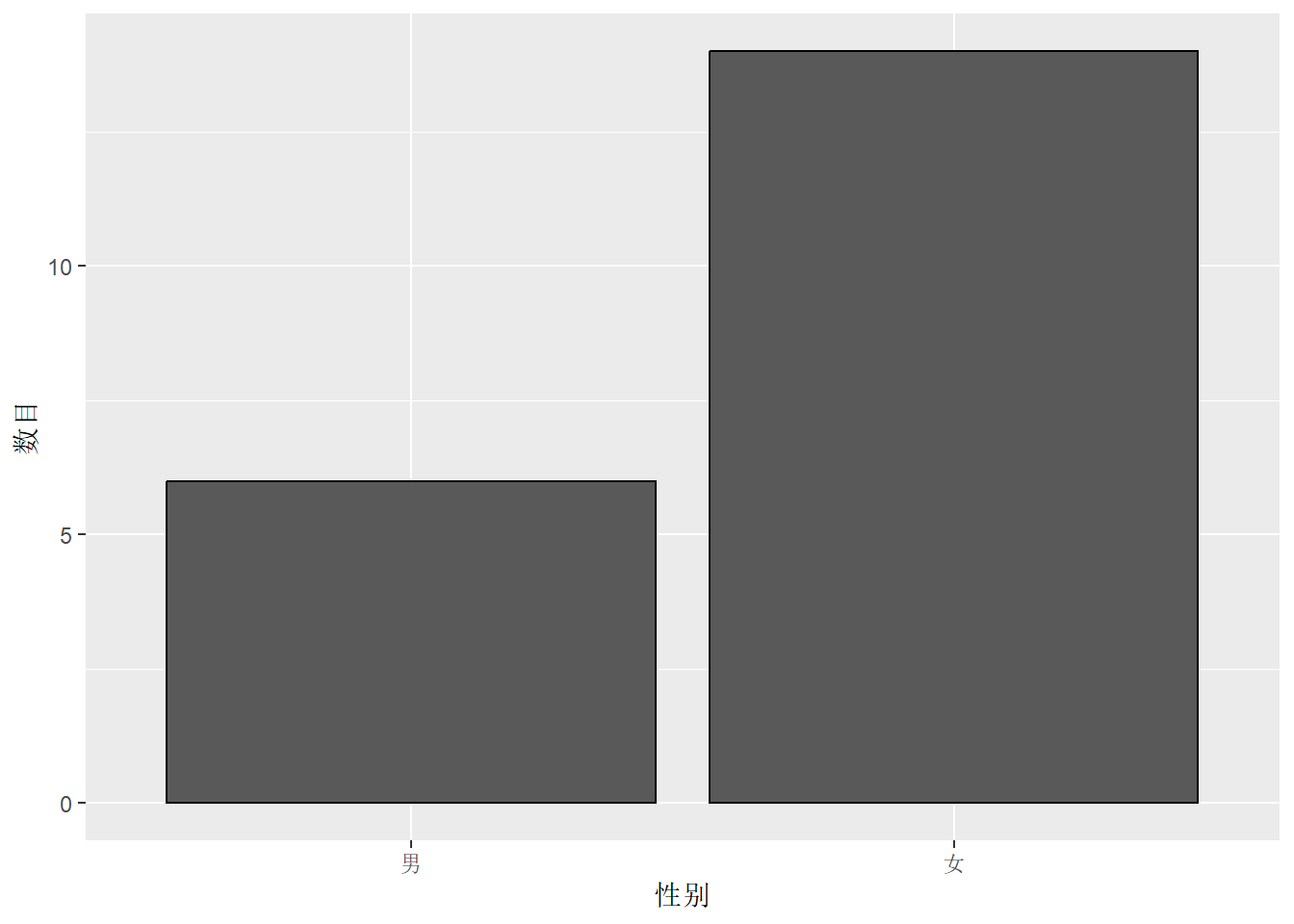
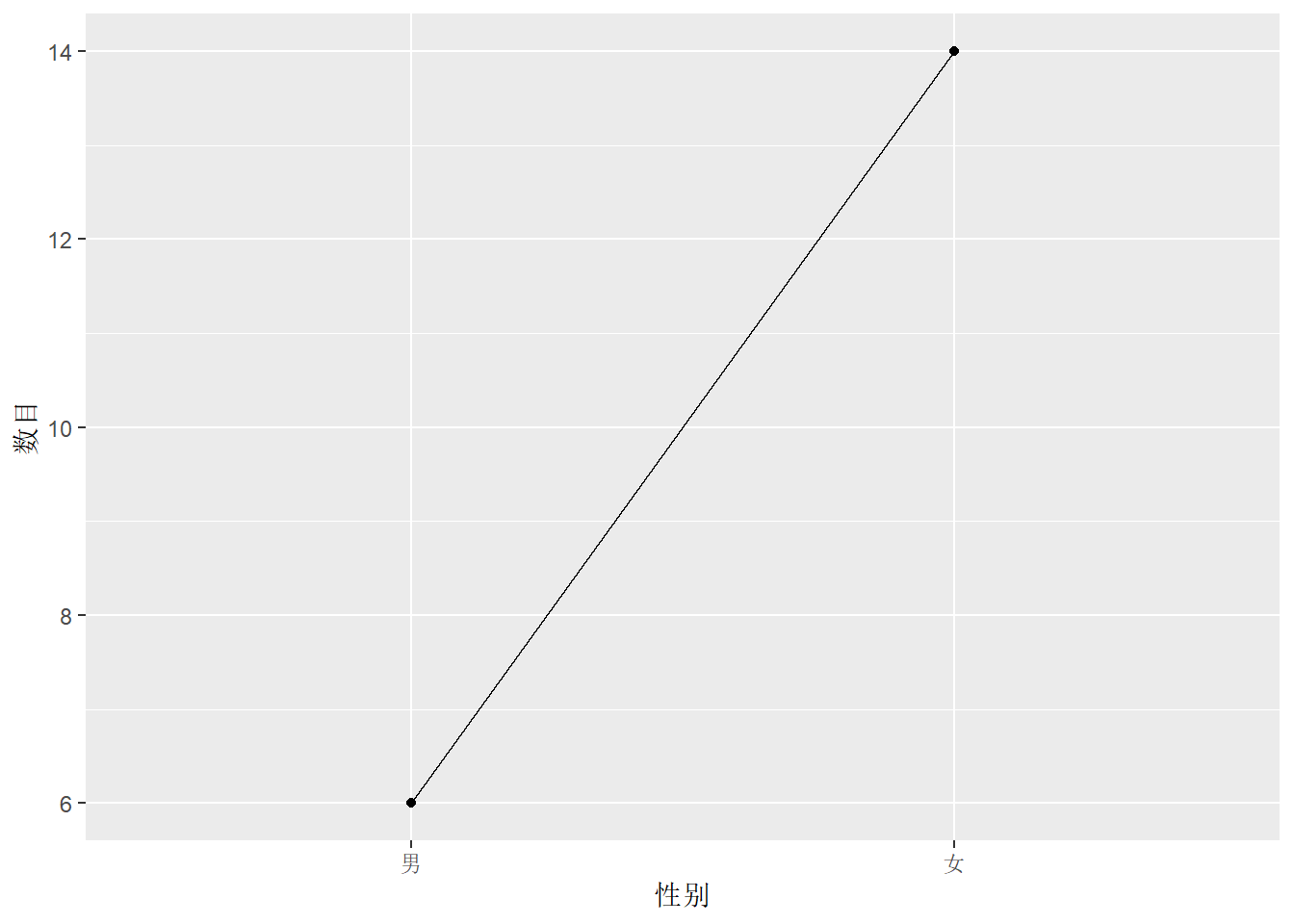
变量类型:分类变量、离散数值变量、连续数值变量
library(ggplot2)
library(ggridges)
library(RColorBrewer)
library(viridis)5.1 一个分类变量:条形图、折线图
5.2 两个数值变量:散点图
# 查看学生英语和数学成绩分布
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 语文, y = 数学)) +
geom_point()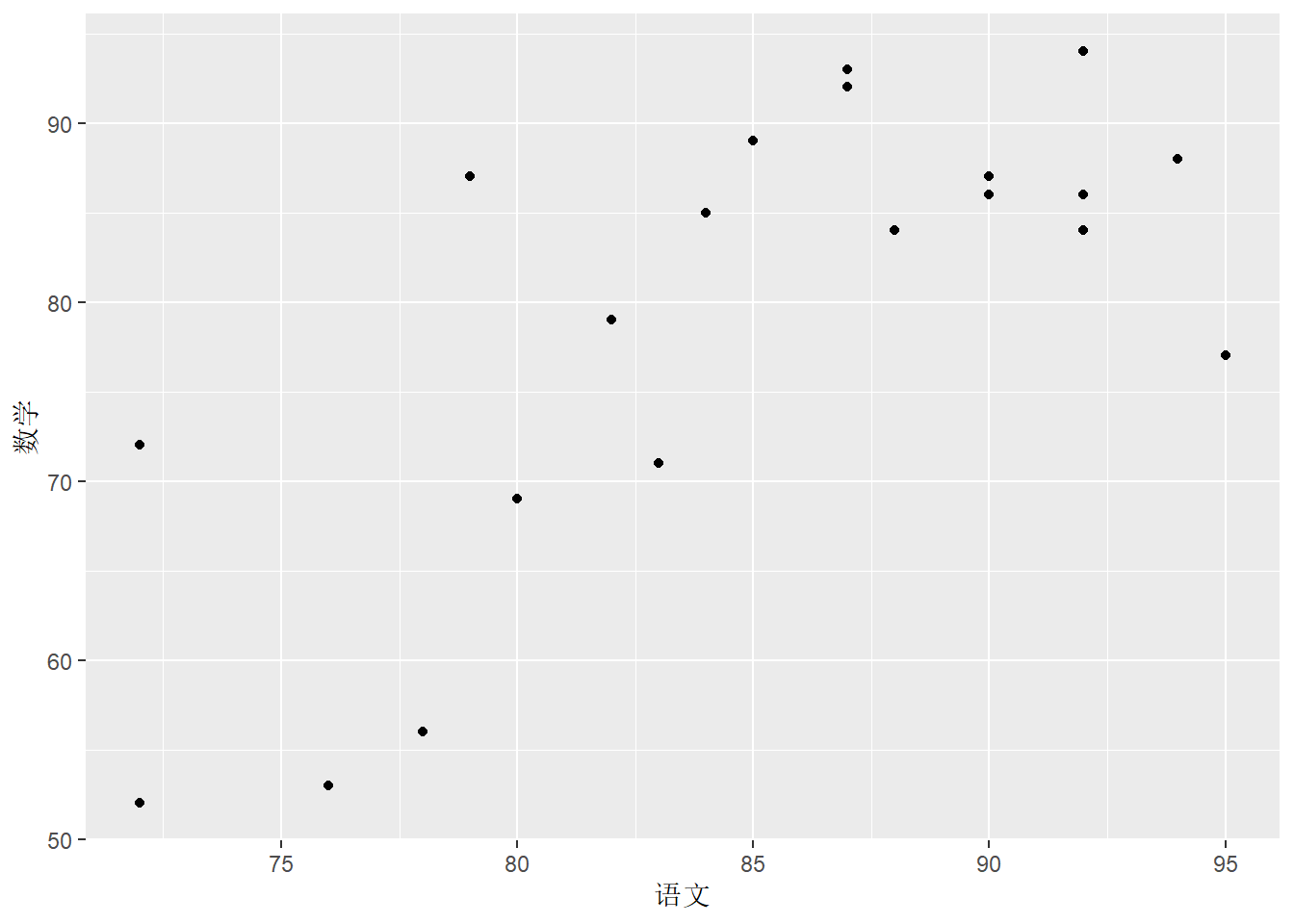
# 按语文成绩从低到高查看学生英语和数学成绩分布
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = reorder(语文, 数学), y = 数学)) +
geom_point()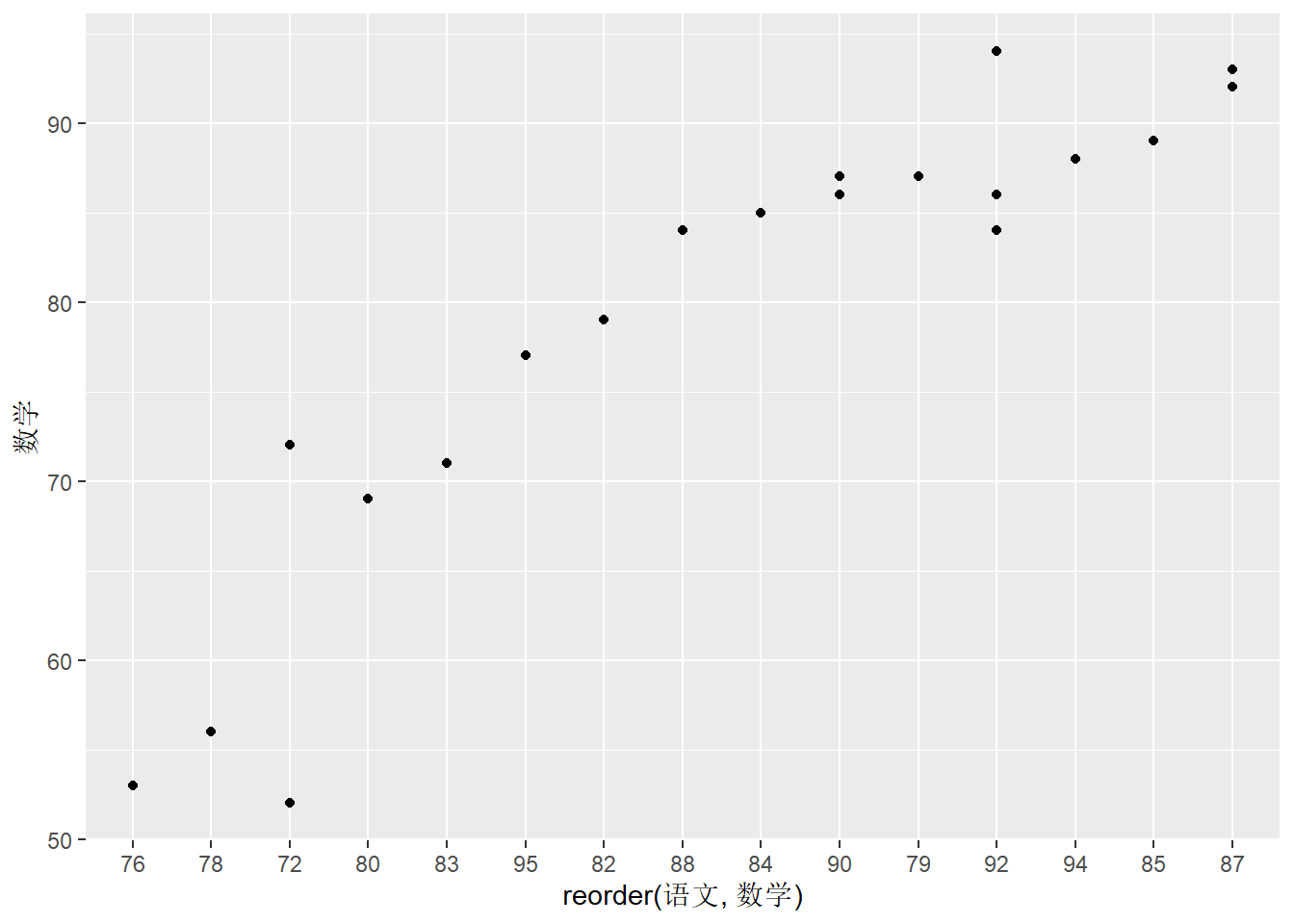
# 按照班级查看学生英语和数学成绩分布
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = reorder(语文, 数学), y = 数学)) +
geom_point() +
facet_grid(.~班级, scale="free", space="free_x") 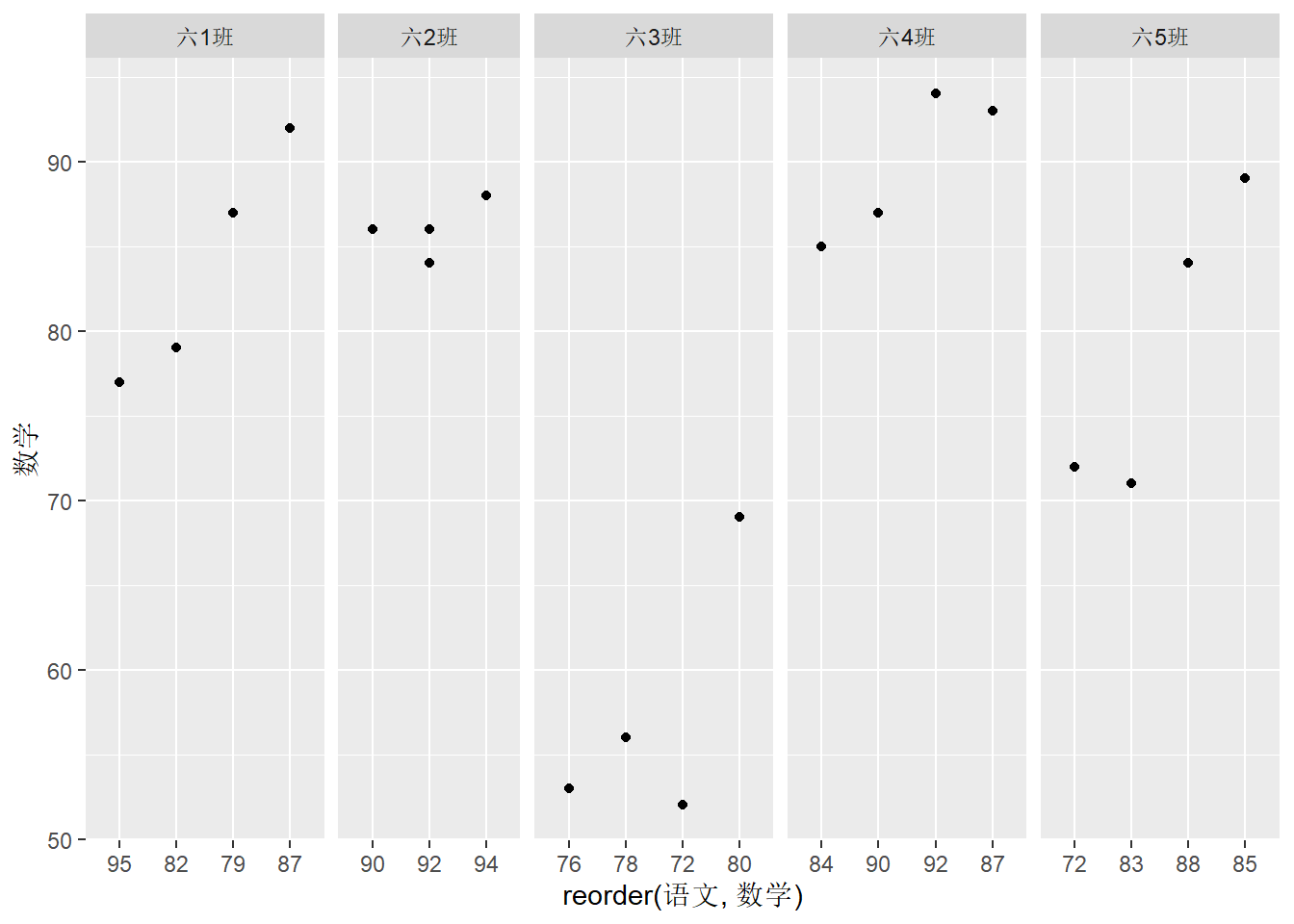
5.3 一个分类变量,一个数值变量:箱型图、小提琴图、山脊图
5.3.1 箱型图
# 箱型图绘制班级平均成绩
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 班级, y = 平均值)) +
geom_boxplot()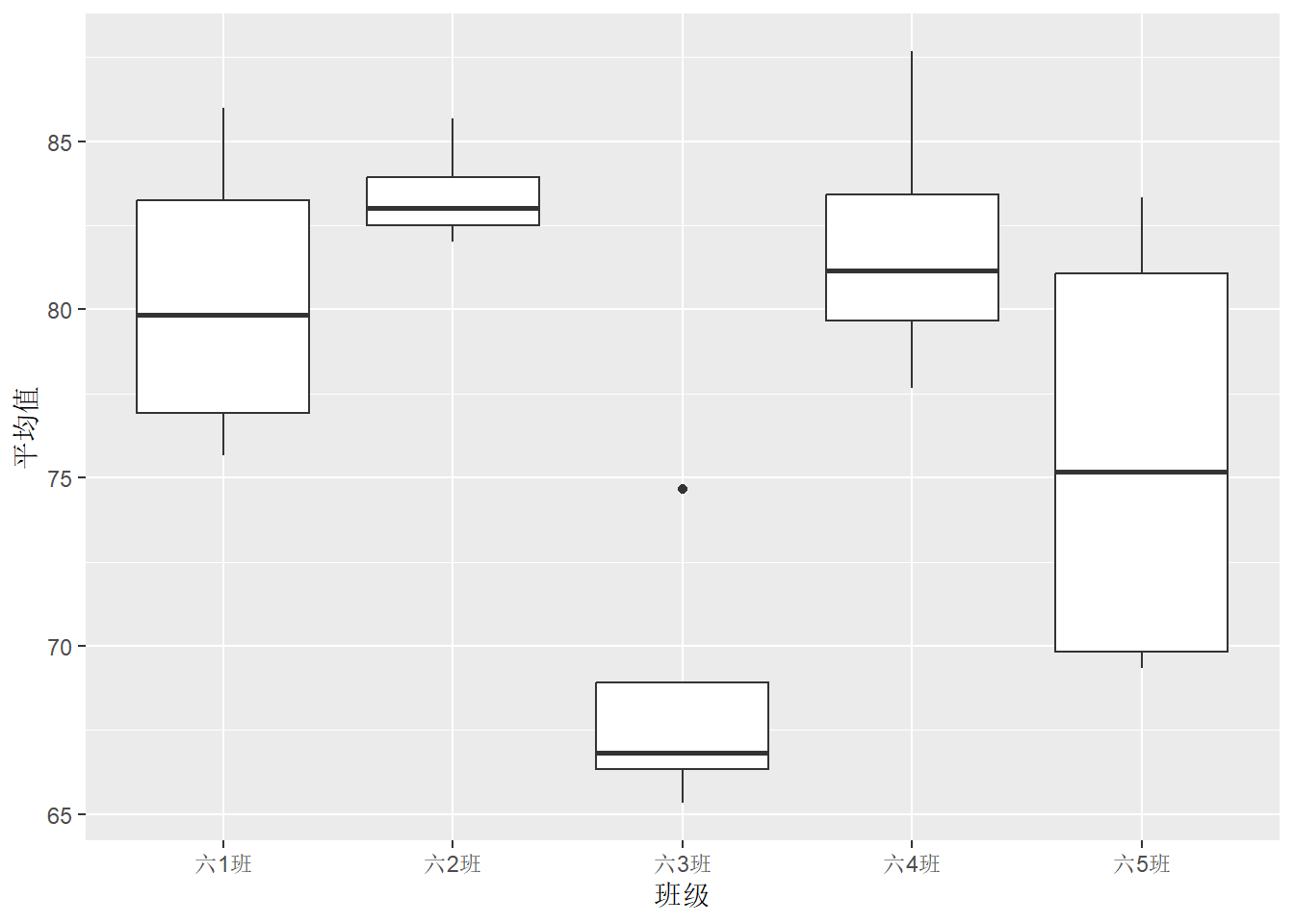
# 以班级和性别分类学生平均成绩
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 性别, y = 平均值, fill = 性别)) +
geom_boxplot()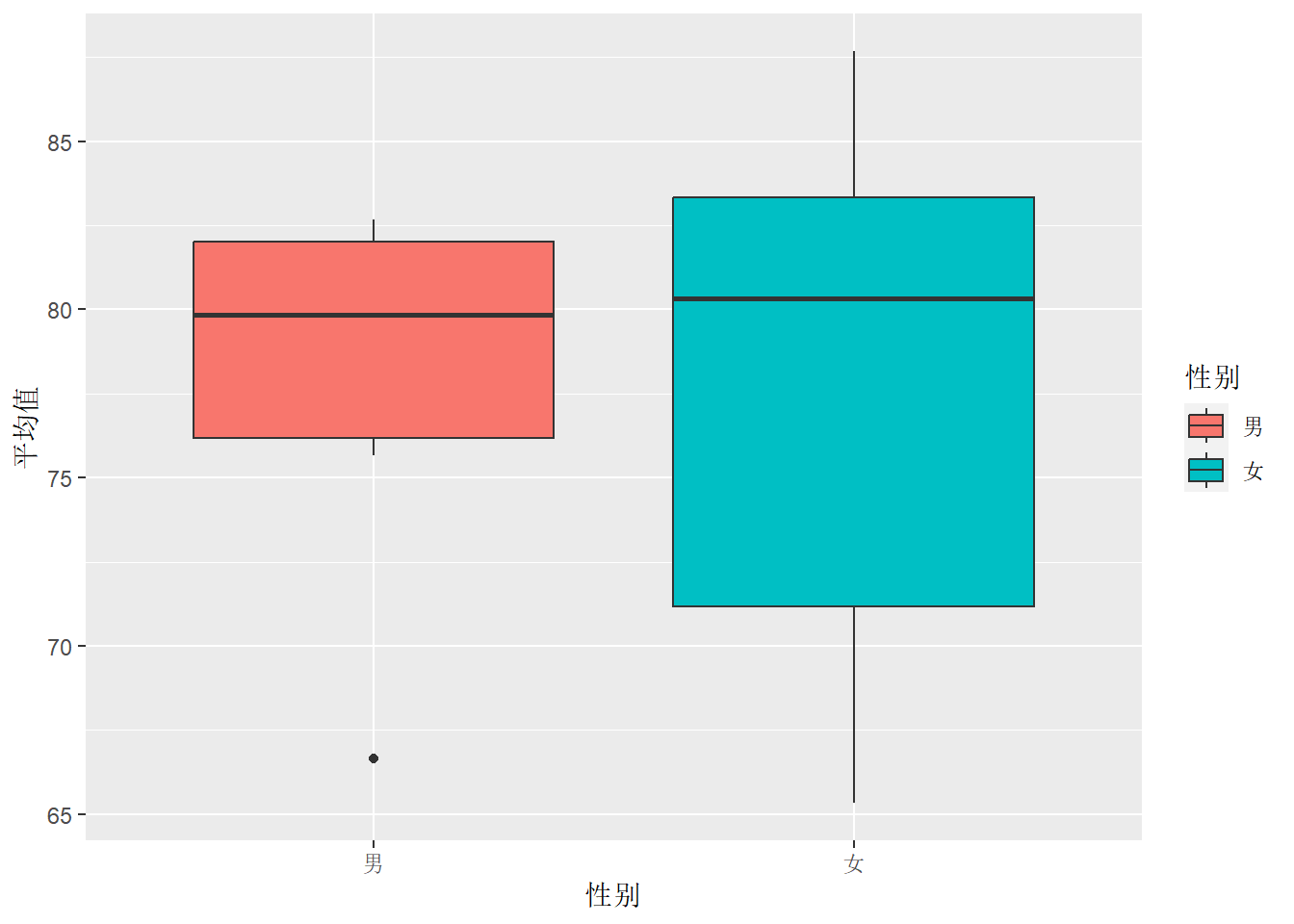
df.out %>%
mutate(性别 = factor(性别)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 性别, y = 平均值, fill = 性别)) +
geom_boxplot() +
geom_jitter() 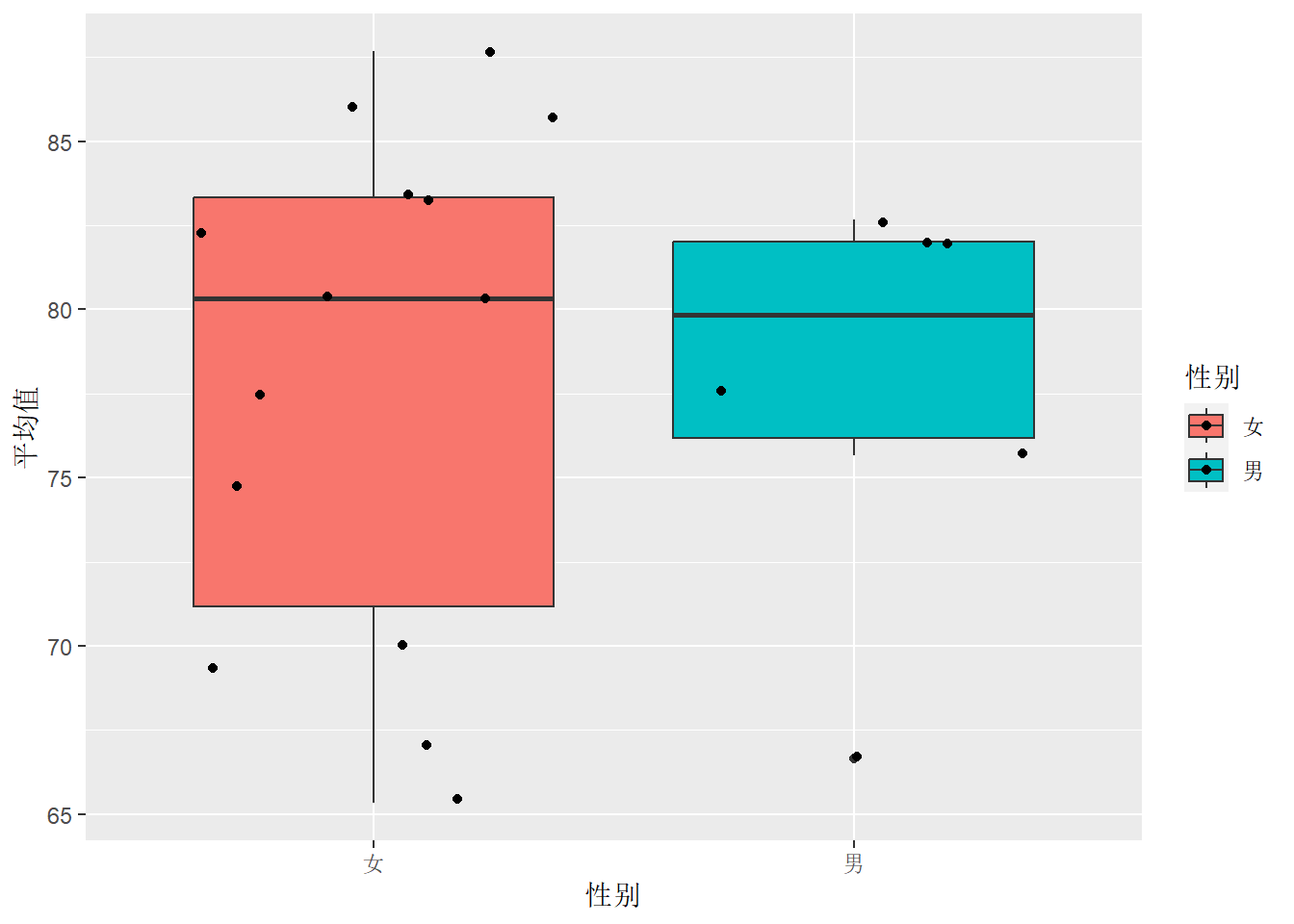
5.3.2 小提琴图
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 性别, y = 平均值)) +
geom_violin()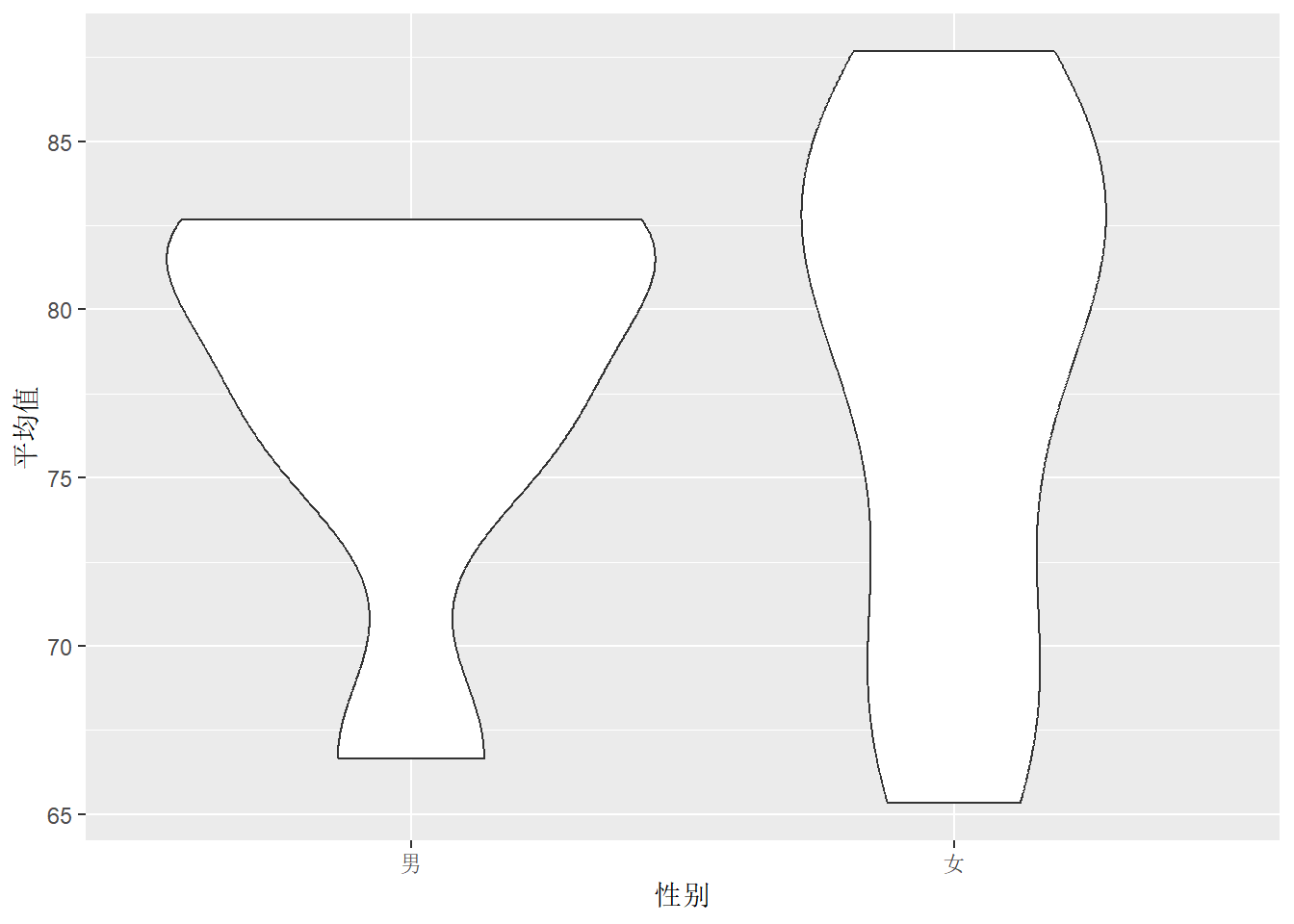
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 性别, y = 平均值, fill = 性别)) +
geom_violin() +
geom_jitter() 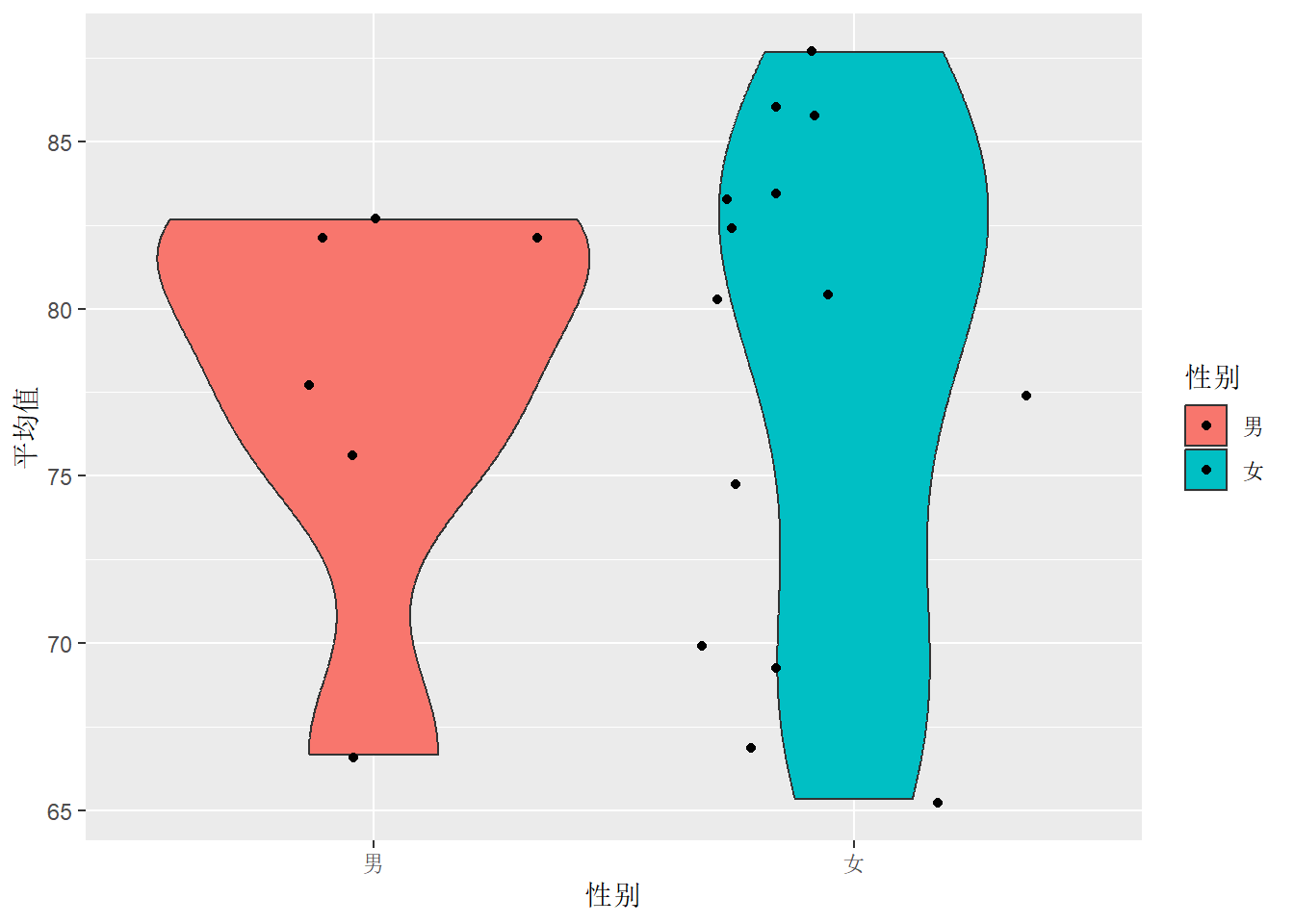
5.3.3 山脊图
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 平均值, y = 班级)) +
geom_density_ridges()## Picking joint bandwidth of 2.41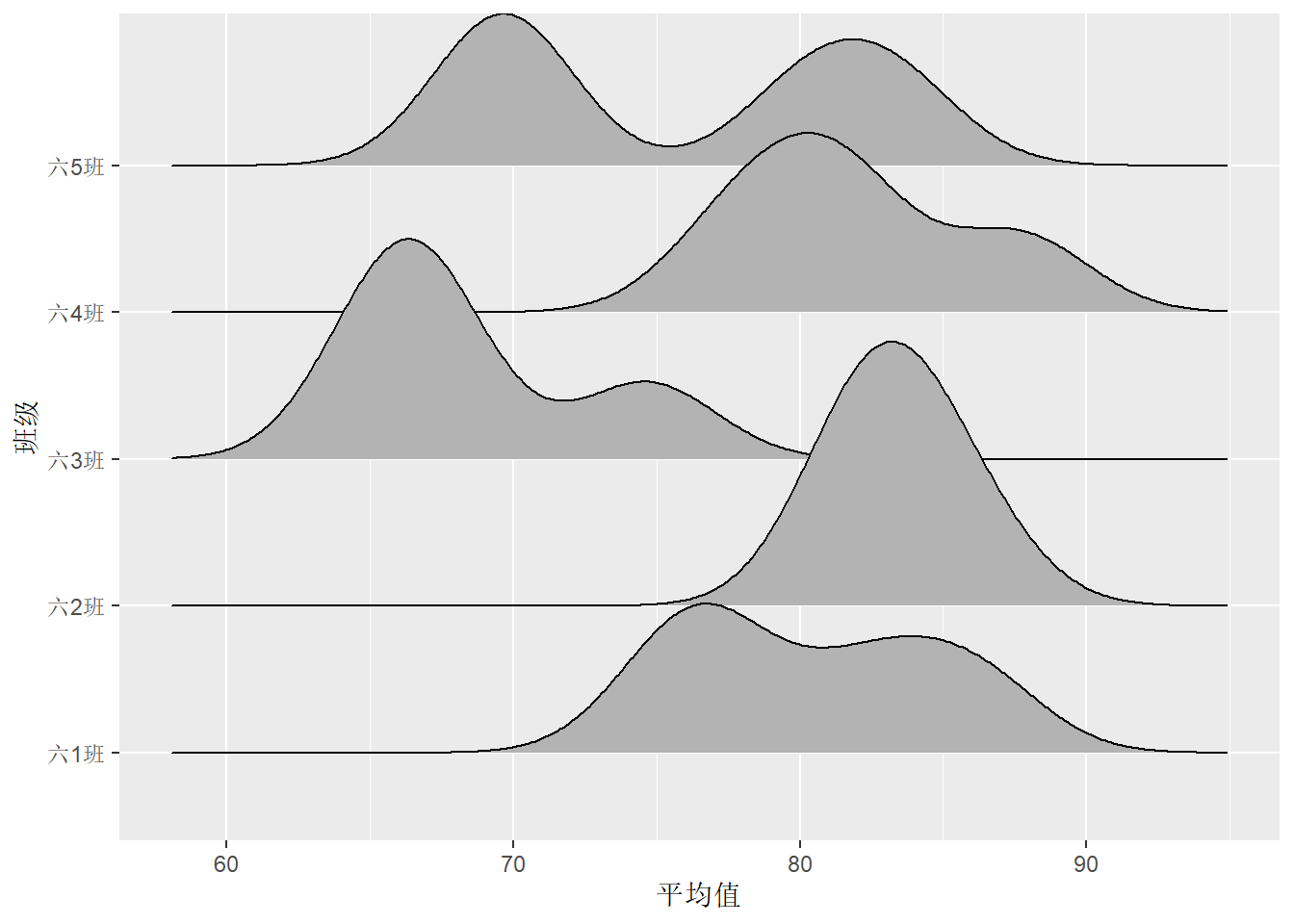
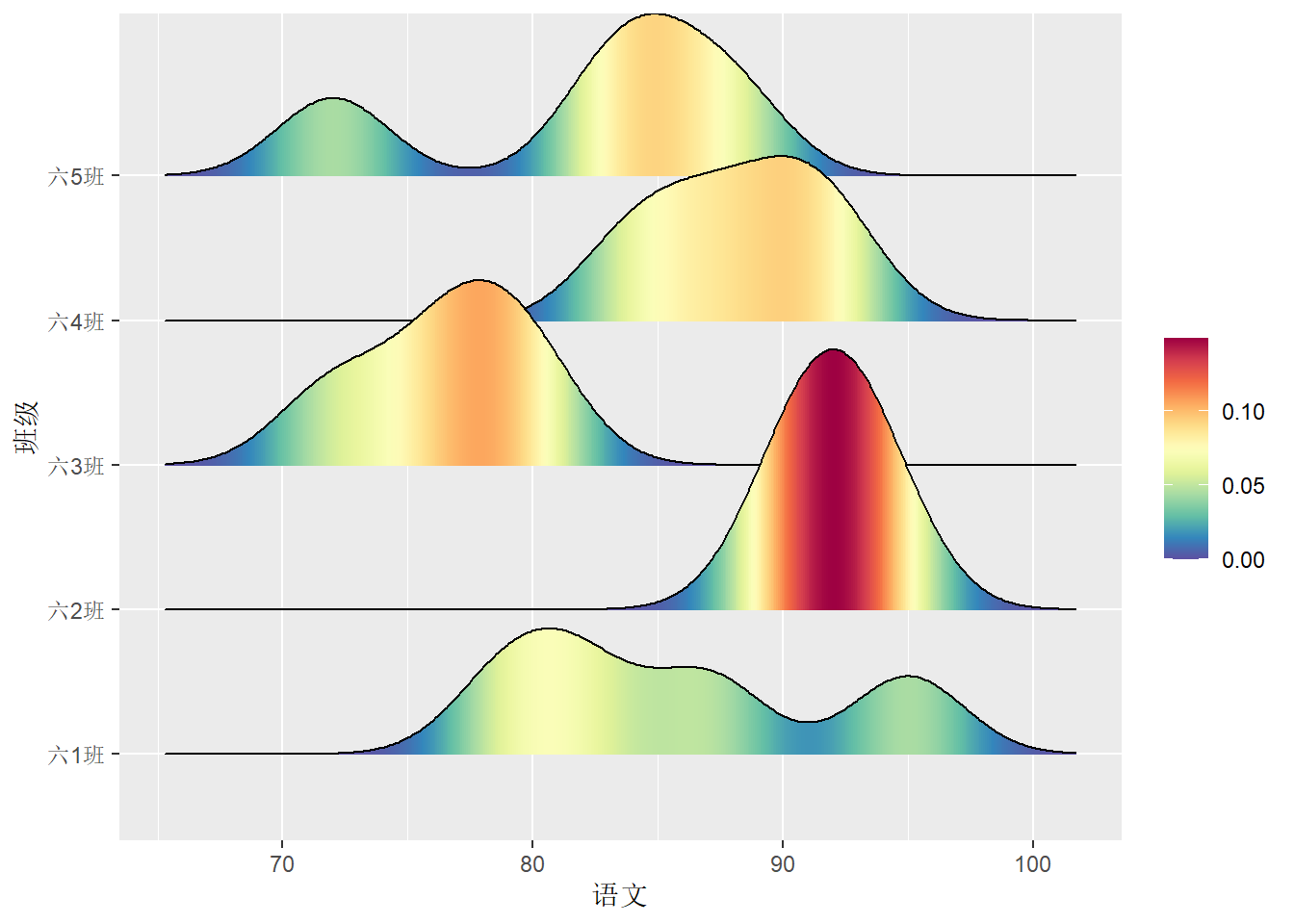
# 以颜色区分语文成绩
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 语文, y = 班级)) +
geom_density_ridges_gradient(aes(fill=stat(x))) +
scale_fill_gradientn(name = "",
colours = colorRampPalette(rev(brewer.pal(11,'Spectral')))(32)) ## Picking joint bandwidth of 2.24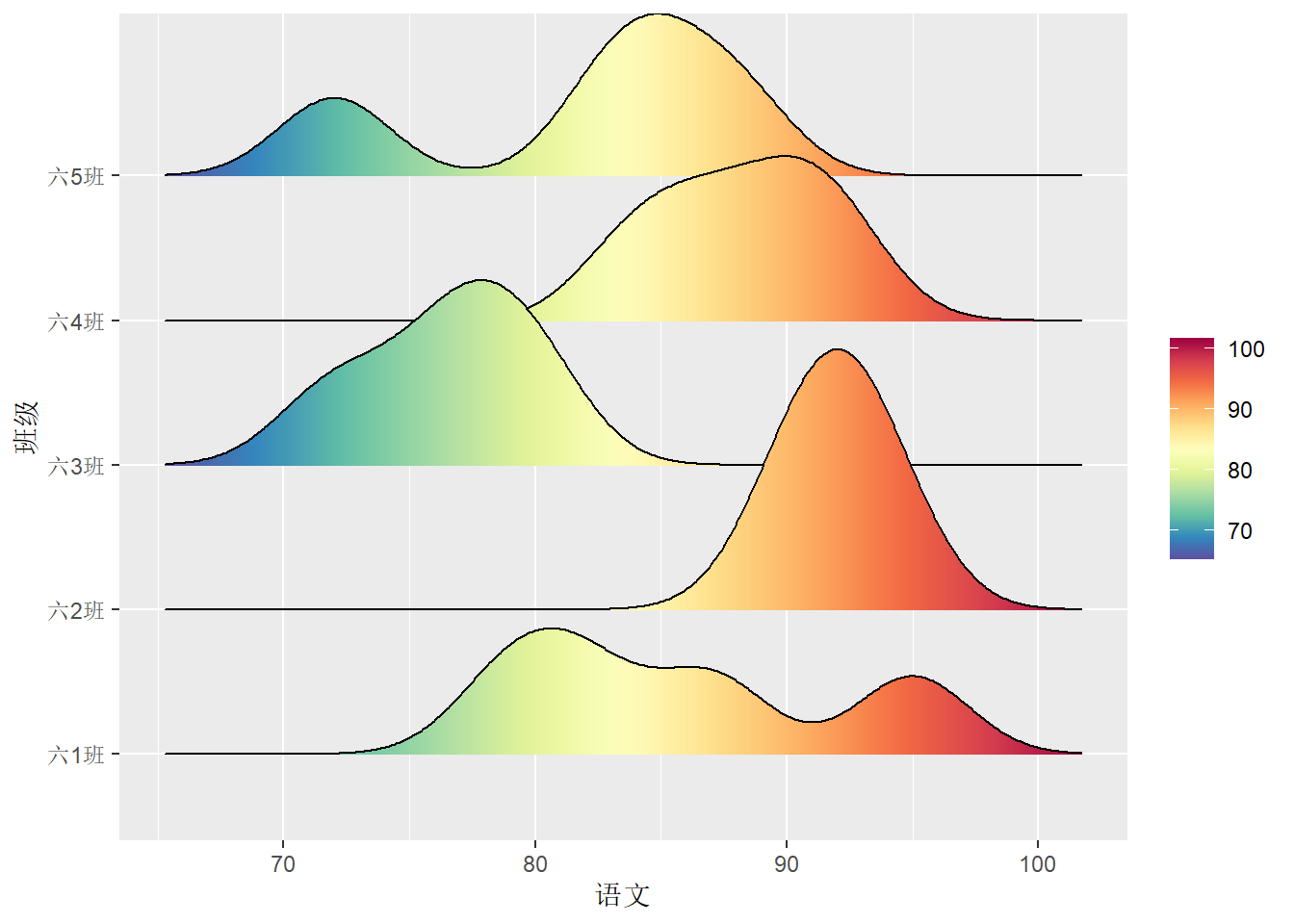
# 以颜色区分区间内该分数学生占比
df.out %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 语文, y = 班级)) +
geom_density_ridges_gradient(aes(fill = ..density..)) +
scale_fill_gradientn(name = "",
colours = colorRampPalette(rev(brewer.pal(11,'Spectral')))(32)) ## Picking joint bandwidth of 2.24