==============================================================================================
Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Model 5
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
logcost 0.78 *** 0.78 *** 0.68 ** 0.96 * 0.96 *
(0.01) (0.01) (0.22) (0.34) (0.34)
v_integrated 0.36 * 0.43 **
(0.14) (0.13)
logtax 0.16 *** 0.16 *** 0.39 *** 0.46 ** 0.46 **
(0.01) (0.01) (0.08) (0.13) (0.13)
logcost:v_integrated -0.02 -0.02 -0.02 -0.02 -0.02
(0.01) (0.01) (0.01) (0.01) (0.01)
v_integrated:logtax -0.05 * -0.05 * -0.05 ** -0.05 * -0.05 *
(0.02) (0.02) (0.02) (0.02) (0.02)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Num. obs. 755985 755985 755985 755985 755985
R^2 (full model) 0.77 0.66 0.64 0.78 0.78
R^2 (proj model) 0.71 0.64 0.10 0.01 0.01
Adj. R^2 (full model) 0.77 0.66 0.64 0.78 0.78
Adj. R^2 (proj model) 0.71 0.64 0.10 0.01 0.01
Num. groups: station 1244 1244 1244
Num. groups: town 17 17 17
Num. groups: month 59 59 59
==============================================================================================
Spec:log~log. Sample: regular gasoline. Cluster:municipality.sandbox10042024
Separate regressions
Estimating pass-through separately
Regular
Using the estimates on column 5, the %increase in the price of REGULAR gasoline after a 1% increase in the tax for a vertically integrated stations is 0.41 (.46-0.05). The mean tax is COP 139 and the mean price is COP 9050. So an increase of COP 1.39 in tax leads to an increase of .43% increase in price or COP 37.1.
Plot tax and price
Plot detrended tax and prices in log and levels
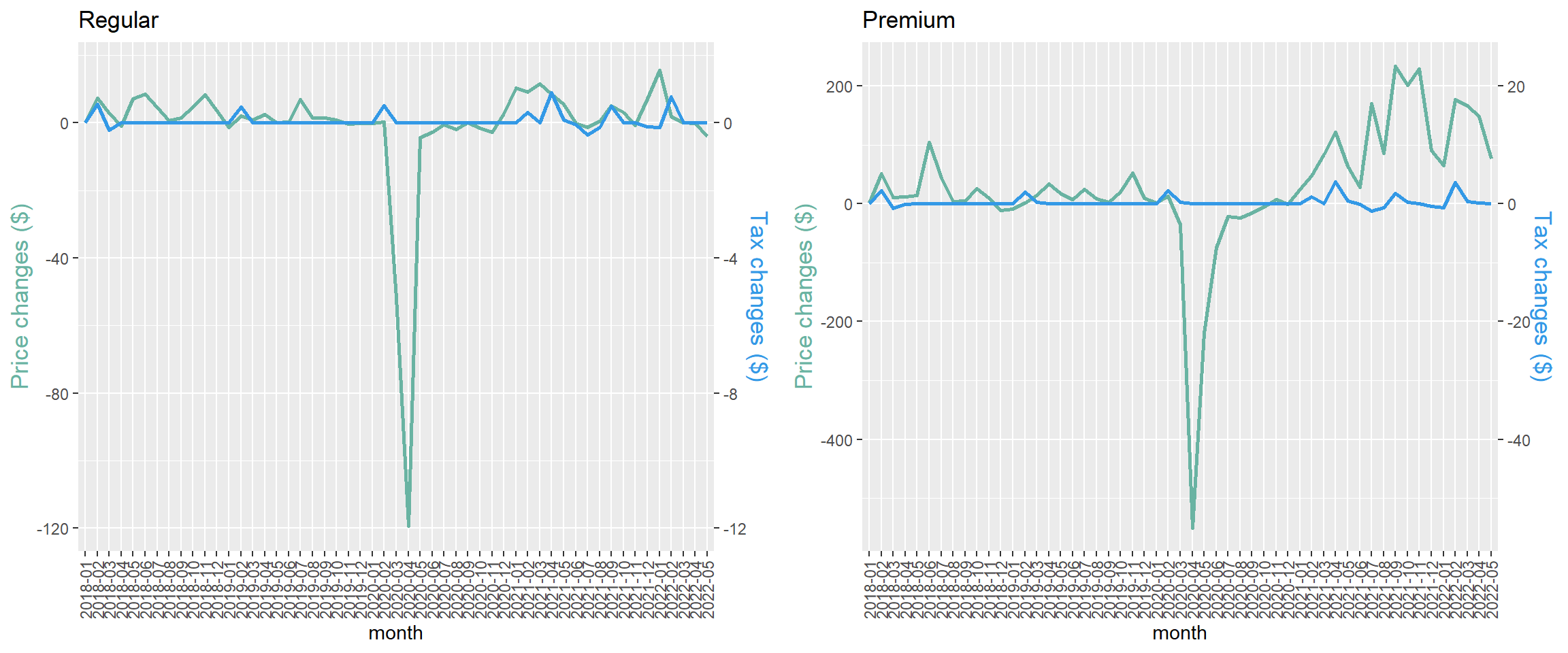
Price and tax changes ($)
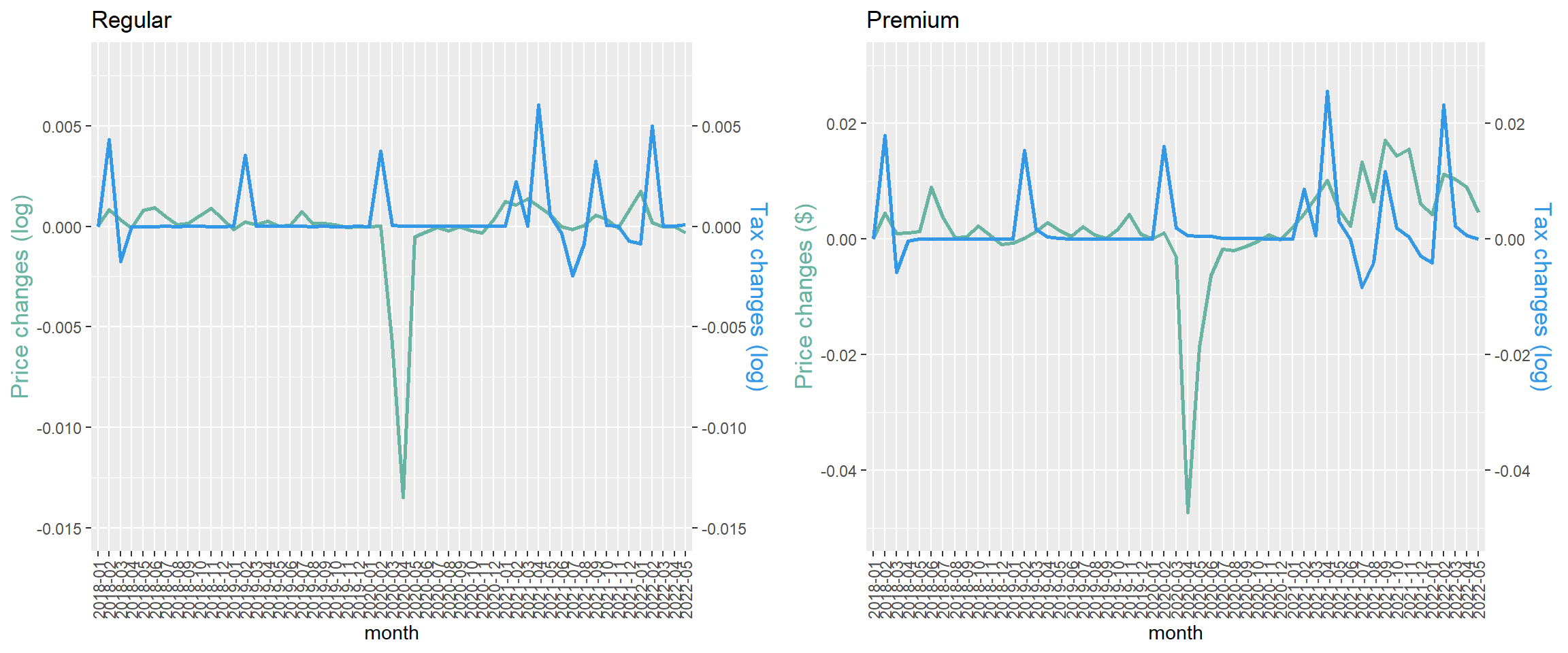
Price and tax changes (logs)
Similar plots to Bajo and Borrellas
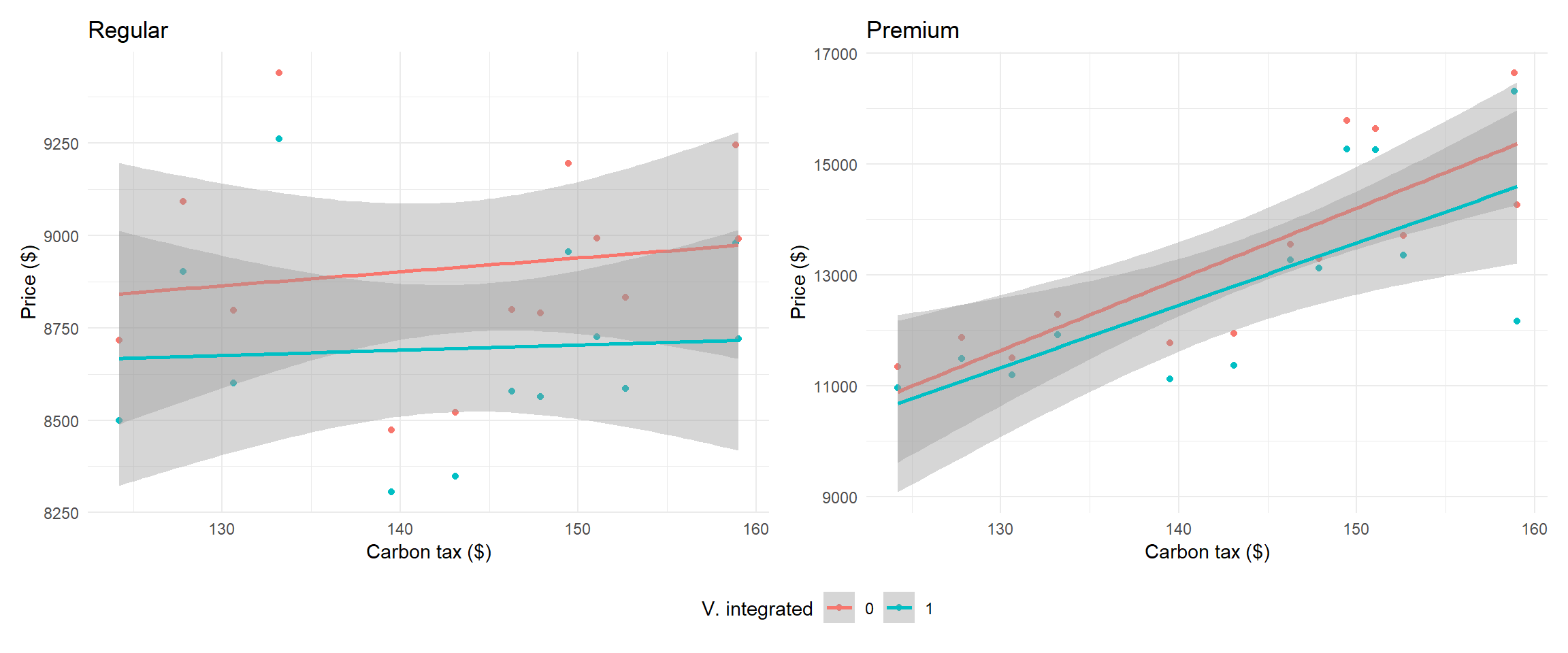
Average prices by type of fuel
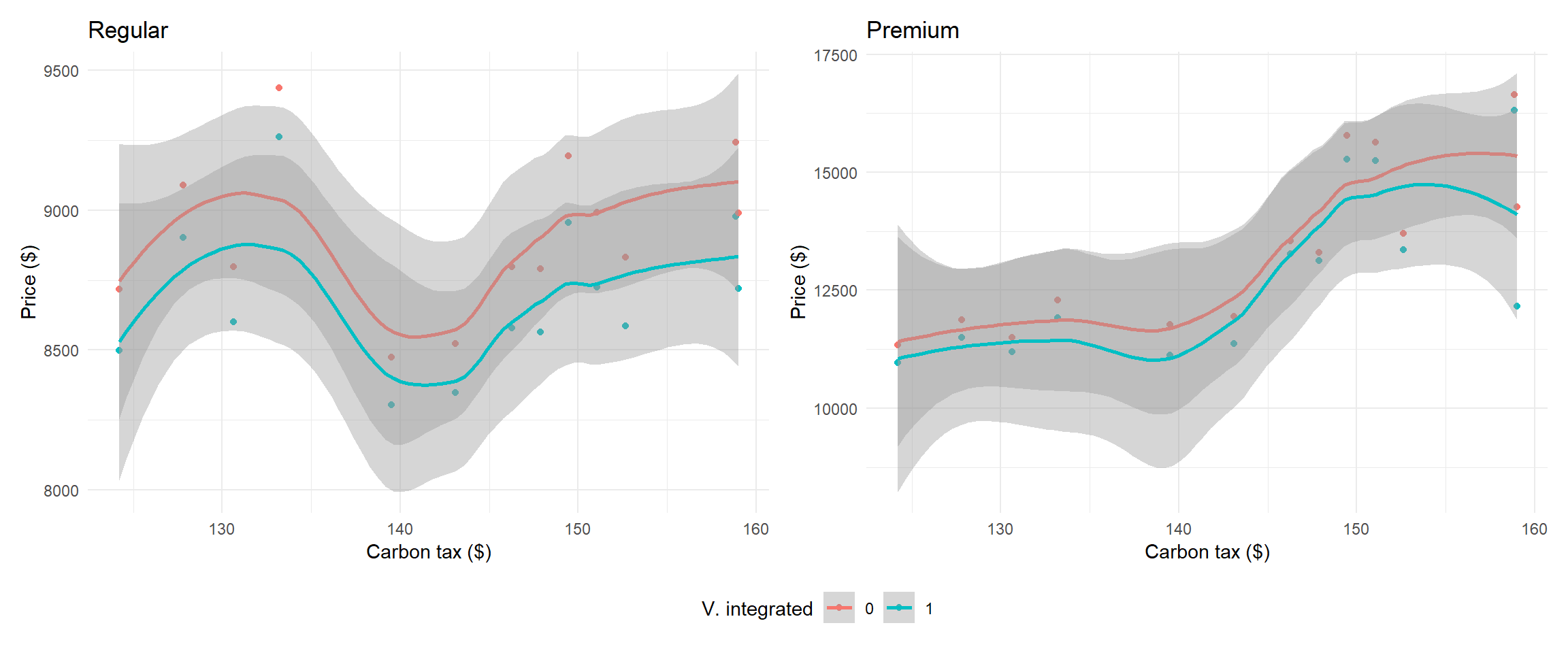
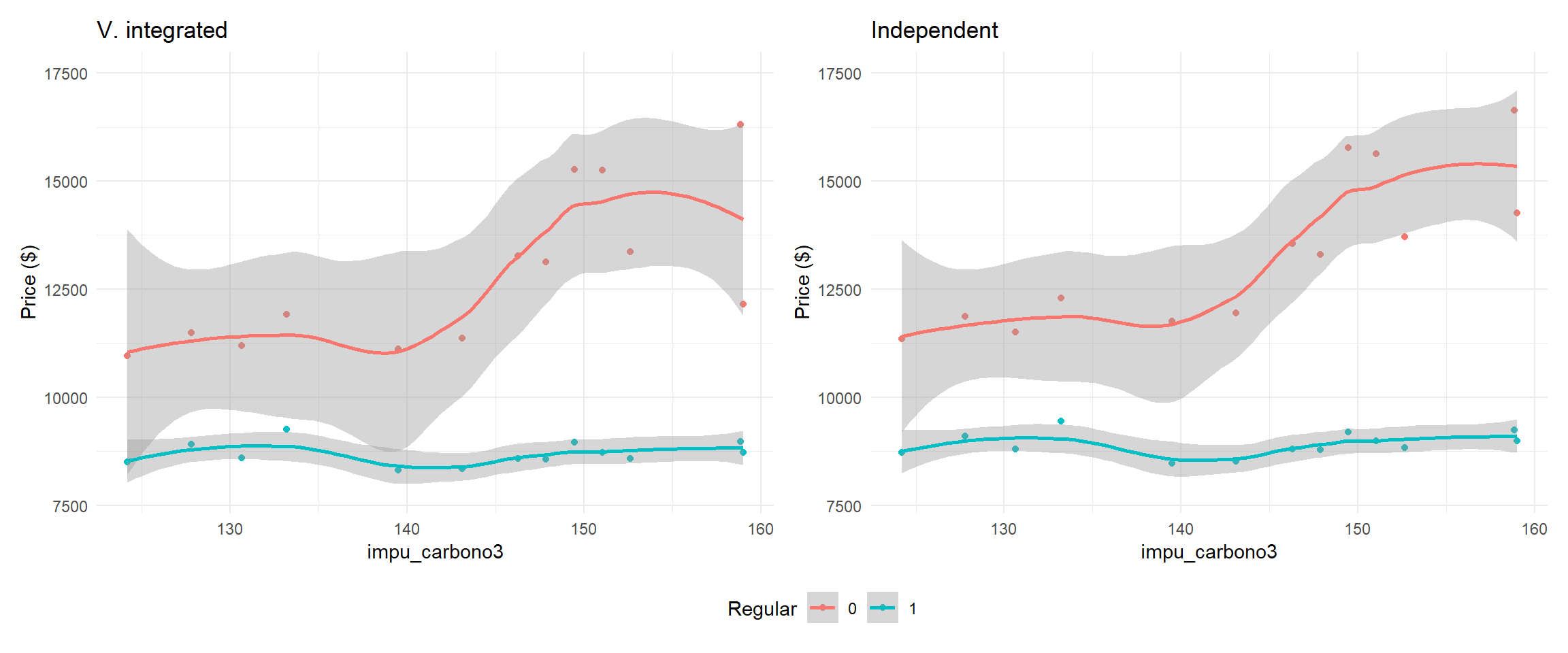
Average prices by vertical integration
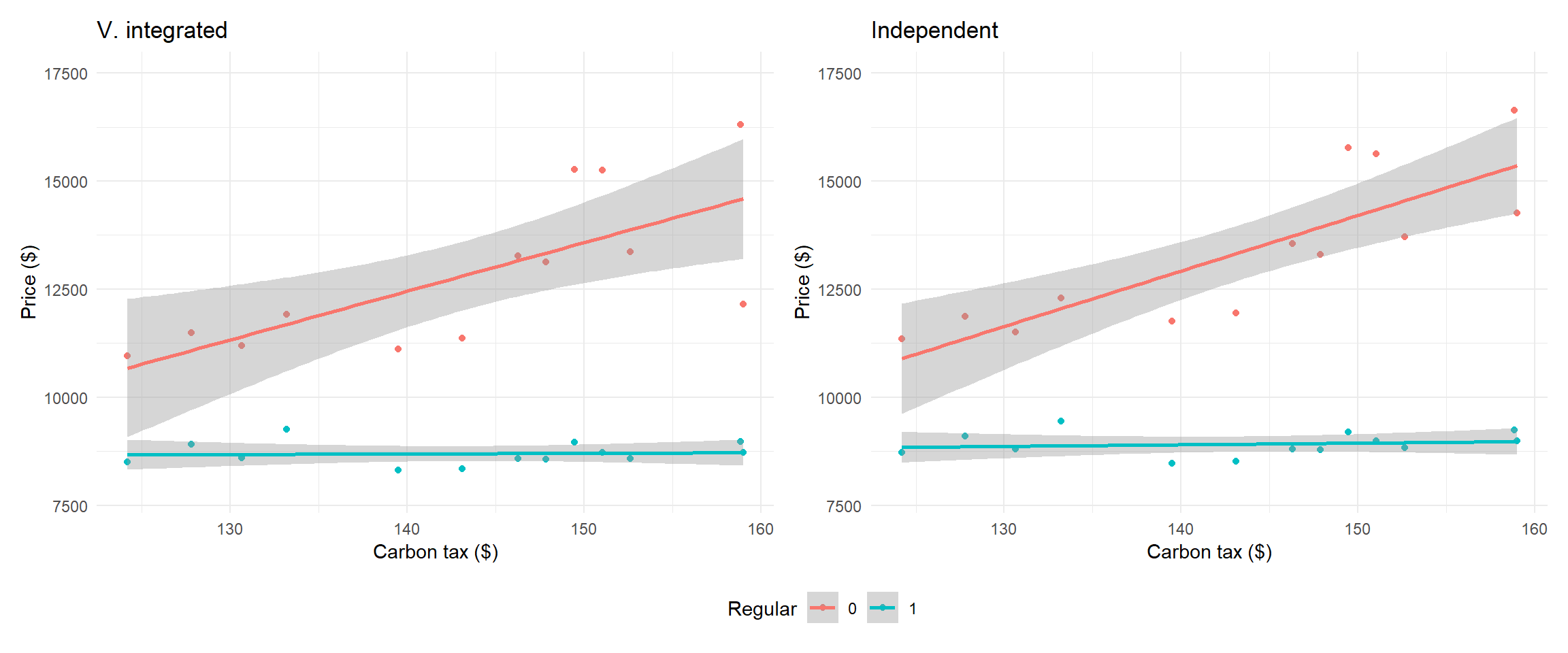
Average prices by type of fuel (linear)
Average prices by vertical integration (linear)